Found 301 results
Open Access
Review
03 September 2025Defect Engineering in Carbon-Based Metal-Free Catalysts: Active Sites, Reduction Mechanisms, and 3D Architectures for Sustainable 4-Nitrophenol Reduction
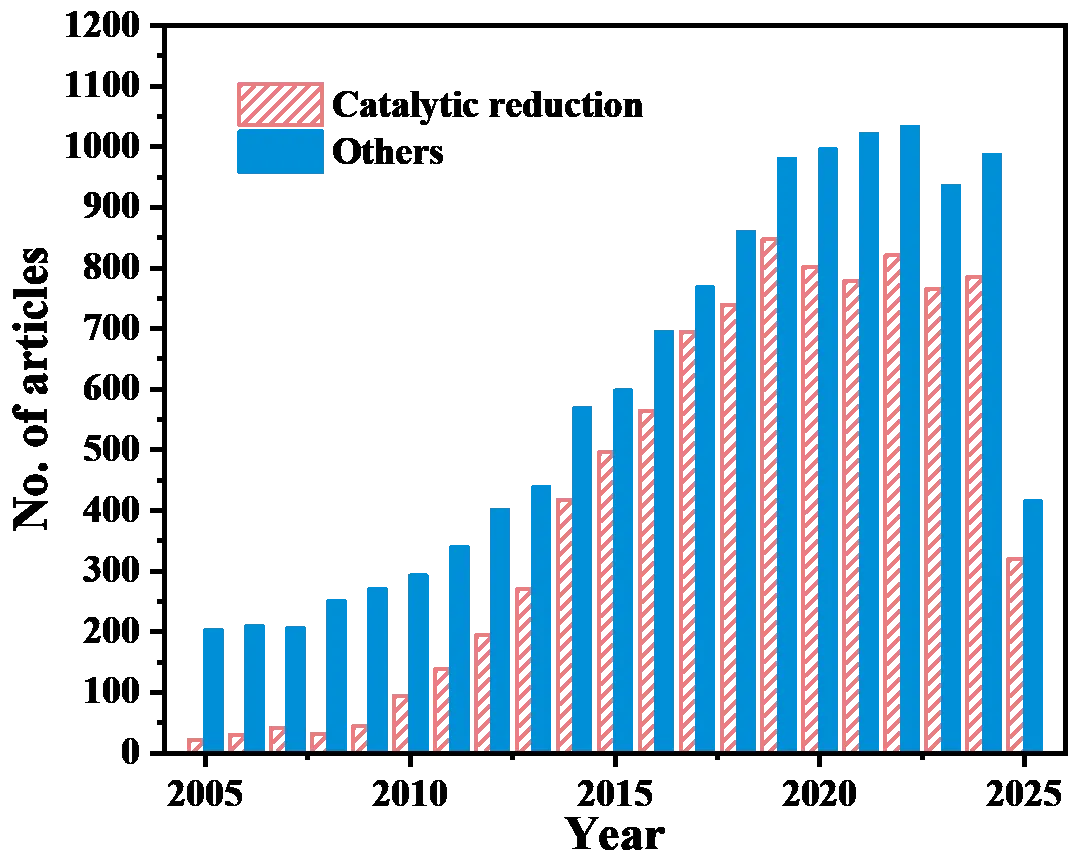
Nitrophenols (NPs), classified as priority pollutants due to their significant toxicity, persistence, and bioaccumulation potential, pose severe threats to ecosystems and human health. Catalytic reduction, particularly the conversion of NPs like 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) to less toxic aminophenols using sodium borohydride (NaBH4), represents a promising remediation strategy. While conventional metal-based catalysts face limitations including high cost, poor durability, and potential metal leaching, carbon-based metal-free catalysts (C-MFCs) have emerged as highly efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective alternatives. However, the precise reaction mechanisms governing NP reduction over C-MFCs remain ambiguous, and significant debate surrounds the nature of the active sites and the structure-activity relationships dictating performance. This review systematically elucidates the catalytic sites and associated reduction mechanisms in C-MFCs. We comprehensively summarize design principles centered on defect engineering strategies, encompassing single-atom (N, S, B, P, O), dual-atom (B,N; N,S; N,P), and tri-atom (B,N,F; N,P,F) doping, alongside non-doping defects such as edge and pore defects. The critical structure-performance relationships linking these engineered active sites to catalytic activity (e.g., turnover frequency, TOF) are analyzed, integrating experimental evidence and theoretical insights. Furthermore, strategies for constructing three-dimensional architectures to enhance active site accessibility and catalyst stability are highlighted. This work provides fundamental insights to guide the rational design of next-generation high-performance C-MFCs for sustainable nitrophenol pollution control.
Open Access
Article
02 September 2025The Crystallography of Diverse Intermetallic Phases in Binary La-Ni Alloy Obtained by Melting and Its Structural Evolution under High Temperature Sintering
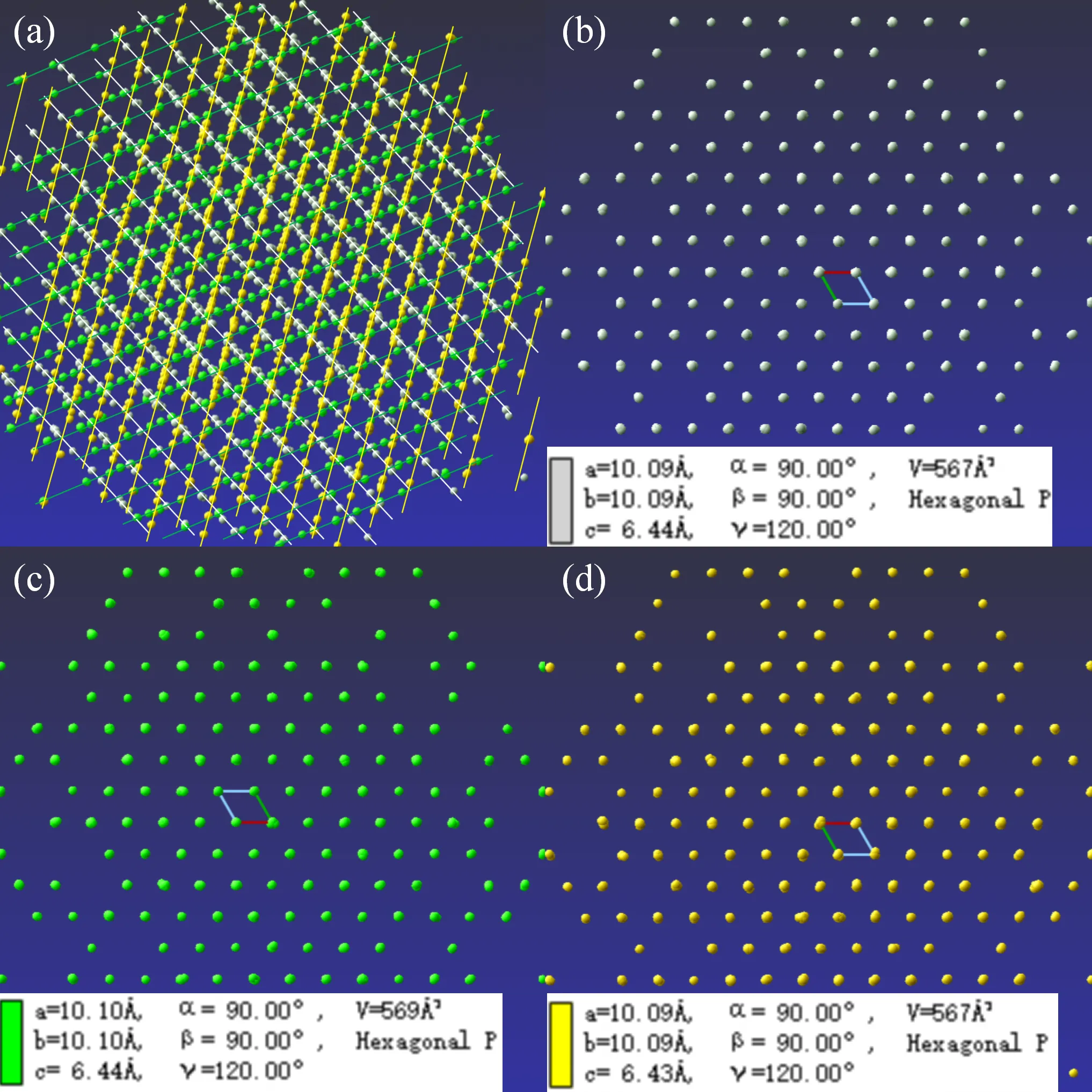
In this study, we have investigated the structural evolution of binary La-Ni alloy under different heat treatments by combing single crystal X-ray diffraction (SXRD) as well as scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). It has been found that LaNi and La7Ni3 can be successfully synthesized through the arc melting method. Then it was found that LaNi5 appears in the binary La-Ni mixture wrapped by a Tantalum sheet, followed by high-temperature sintering. Next, some pilot experiments have been carried out on the La-Ni mixture by sealing tube technique with some residual oxygen. Serendipitously, oxidation has not been found while La3Ni3Si2 and La2NiSi besides LaNi phase show up. Meanwhile, the detailed crystal structure information and their topological features of the aforementioned phases as well as their high-resolution TEM images, have been obtained. Furthermore, the orientation relationships of the Si-contaminated mixed phases have been thoroughly investigated by advanced precession images of SXRD patterns.
Open Access
Article
29 August 2025Vocabulary of Chinese Origin in the Language of Russian Residents of Harbin in the First Half of the 20th Century
The purpose of the article is to study the functioning of lexical units of Chinese origin in the speech of representatives of the Far Eastern emigration. The language of everyday communication is the first to respond to socio-cultural, ethnocultural, ethno-religious processes occurring in society. At present, when the culture of Far Eastern emigration in its close interaction with Chinese culture has become a fact of history, the reconstruction of the processes of intercultural communication between Russians and Chinese in Harbin causes great difficulties. This explains the relevance of studying the Chinese influence on the language of Russian emigrants who found refuge in Harbin in the first half of the 20th century. The novelty of the work is due to the lack of comprehensive studies dealing with Chinese borrowings in the everyday language of ordinary Harbin residents. An appeal to the memories and oral histories of Harbin residents allows us to trace how lexemes borrowed from the Chinese language and continuing to live in the linguistic consciousness of people who grew up in Harbin. The methodology of this article is based on historical-cultural, functional, linguocultural, and lexical-semantic approaches, as well as interviewing. The work uses materials from the authors’ field research among Harbin residents. Based on the results of the study, the authors conclude that although most Russians living in Harbin in the first half of the 20th century did not speak Chinese, Chinese borrowings were a constant part of their lives. This is especially true for various lacunae related to everyday realities, cooking, traditional culture, etc. Harbin residents organically assimilated such lexical units and preserved them in their speech for decades—even outside China. Of course, this testifies to close ethnocultural contacts between Russians and Chinese in Manchuria.

Open Access
Opinion
22 August 2025Are Probiotics a Panacea for All Diseases? A Scientific Opinion
Probiotics have gained widespread attention for their potential health benefits, particularly in promoting gut health and modulating the immune system. This article critically examines whether probiotics can be a universal remedy for all diseases, as often claimed in scientific literature and popular media. The objective is to evaluate the current scientific evidence regarding the efficacy of probiotics in preventing and treating various medical conditions, including gastrointestinal disorders, metabolic syndromes, allergies, and mental health issues. While some studies suggest promising outcomes in specific contexts, the evidence remains inconsistent and often limited to specific strains and conditions. Importantly, this review highlights that probiotics are not a one-size-fits-all solution and their effects can vary widely depending on individual physiology, dosage, and microbial composition. The article also addresses safety concerns, regulatory challenges, and the need for more rigorous, large-scale clinical trials. By analyzing existing data and expert opinions, this work aims to separate fact from hype and provide a balanced perspective on probiotics’ true potential and limitations in modern medicine.

Open Access
Case Report
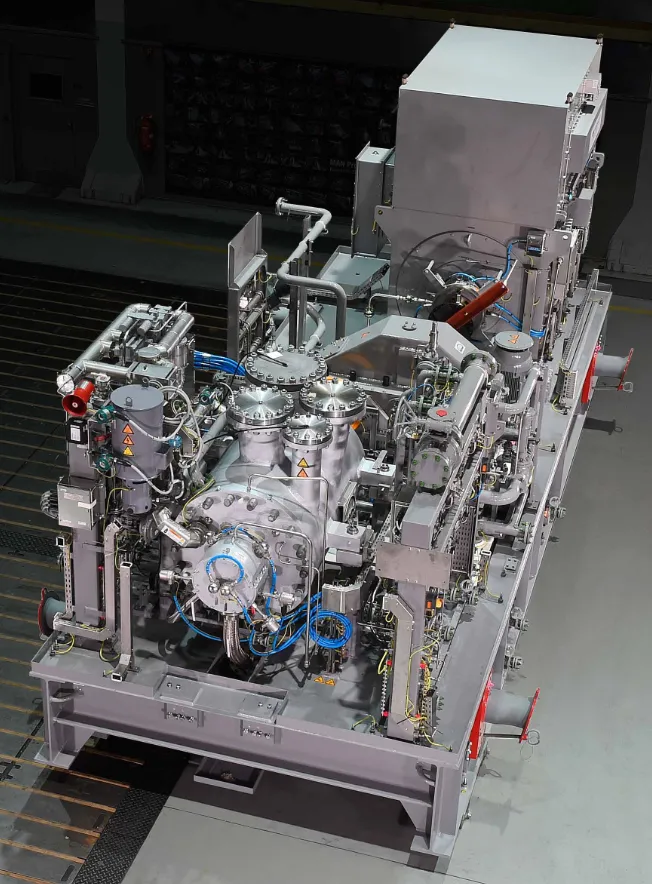
22 August 2025Root Cause Identification of Vibration and Wear Due to Strainer Obstruction in Hydrocarbon Processing Compressors
This study examines the root causes of vibration and wear in centrifugal compressors, particularly emphasising strainer obstruction in hydrocarbon processing environments. Strainer fouling is primarily driven by deposits from inlet gas compositions and deviations in operating conditions, which restrict flow, increase vibration, and accelerate component degradation. A combined methodology was applied to investigate these issues, including baroscopic inspection of compressor internals, chemical analysis of deposited materials, and evaluation of operational records against design specifications. Maintenance histories and strainer cleaning frequencies were also reviewed to establish links between performance decline and operating practices. The findings show that chemical cleaning is the most effective and cost-efficient solution, outperforming high-pressure water jet cleaning and full compressor overhauls by minimising downtime, restoring flow dynamics, and improving mechanical stability. Successful implementation across multiple compressors confirmed its scalability and reliability. This research validates chemical cleaning as a preferred maintenance strategy, delivering significant operational and economic benefits while extending compressor service life.
Open Access
Review
20 August 2025On the Utility of Nailfold Capillaroscopy in Detecting the Effects of Fibrinaloid Microclots in Diseases Involving Blood Stasis
A variety of chronic, inflammatory vascular and autoimmune diseases are accompanied by fibrinaloid microclots. Such diseases reflect endothelial dysfunction and may be detected using a ‘structural’ assay in the form of the fluorescence microscopic or flow ‘clotometry’ analysis of suitably stained platelet-poor plasma. Their amyloid nature and the presence of anti-fibrinolytic molecules therein make the fibrinaloid microclots comparatively resistant to the normal processes of clot degradation. By inhibiting the free flow of blood, the many effects of fibrinaloid microclots include those causing hypoxia, oxidative stress, and ‘blood stasis’ in the microcirculation. Nailfold capillaroscopy is an established observational technique (with both ‘structural’ and ‘functional’ elements) for assessing the microcirculation, and it is thus of interest to establish whether it too demonstrates changes when these syndromes are diagnosed. All diseases in which both methods have been applied show both the presence of fibrinaloid microclots and changes in capillary properties, indicating the complementary value of the structural and functional assays. This also suggests the potential value of nailfold capillaroscopy in a variety of other diseases involving coagulopathies or a deficient microcirculation, which has been little studied to date.
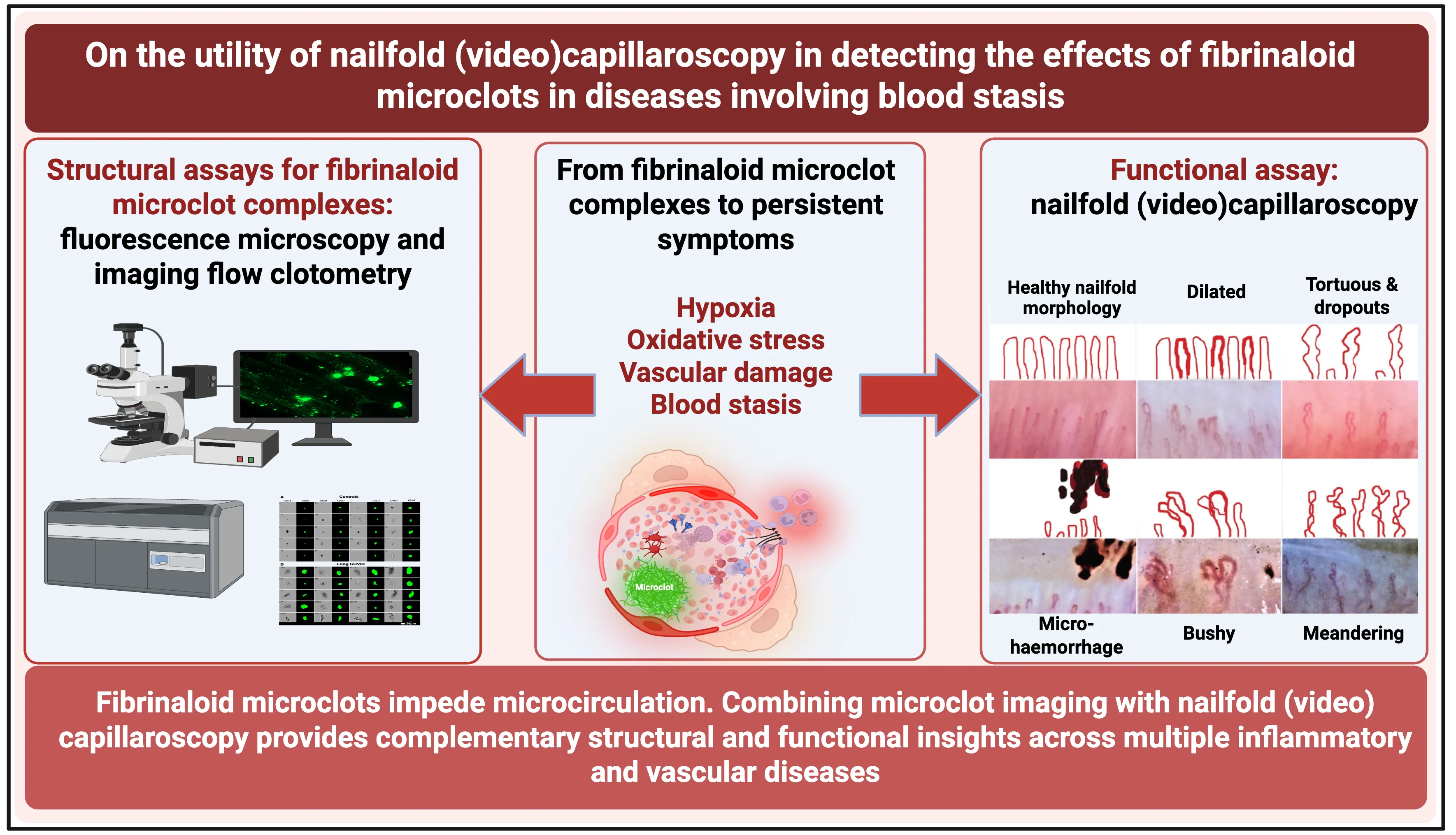
Open Access
Article
18 August 2025From Police Academy Training to Criminal Investigation: Strengthening Forensic Science in Policing
Forensic science is a critical element of policing. In the past three decades, it has become one of the most important investigative tools in criminal investigations. The importance of forensic science is operationalized by linking suspects to crime scenes, exoneration of the wrongly convicted, novel forensic technologies in cold case clearances, and many other aspects. Although modern policing is equipped with forensic resources, it faces some challenges, including investigative flaws that are heavily impacted by the neglect and misuse of forensic science. With the development of forensic science, it is necessary to take advantage of technology in investigations to the maximum extent. From police academy training to criminal investigation, there are many procedures in the process that require forensic and related professionalism. In this respect, the need to strengthen forensic education, training, and practice to improve policing is urgent. This article addresses the current situation and problems of forensic science in general procedures and proposes strategies for improving forensic science in policing.

Open Access
Article
18 August 2025Ethanothermal Synthesis of Dual Emissive Supramolecular Carbon Dots from Naphthalenediol and Quinones with Aggregate Tuned Fluorescence
Carbon dots (CDs) have attracted considerable interest due to their unique photoluminescence and broad potential in sensing, bioimaging, and optoelectronics. However, precise control of their emission properties through molecular design and understanding of supramolecular aggregation remain challenging. Here, nitrogen-doped carbon dots (H-CDs) with green fluorescence are synthesized via an ethanol-mediated solvothermal method using 1,3-dihydroxynaphthalene as a rigid π-conjugated carbon source and 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-p-benzoquinone (DDQ) as both oxidant and nitrogen donor. The synthesis involves complex molecular transformations yielding amorphous supramolecular carbon dots stabilized mainly by noncovalent interactions. Characterization confirmed abundant oxygen- and nitrogen-containing functional groups and an amorphous structure devoid of crystalline residues. Hierarchical H-type aggregation driven by π-π stacking and hydrogen bonding governs the photophysical behavior of the H-CDs, inducing a concentration-dependent evolution from blue-emitting monomers to green-emitting supra-CDs, accompanied by particle growth, red-shifts in the emission spectrum, and a pronounced elongation of the fluorescence lifetime. Temperature- and salt-dependent studies reveal that emission intensity increases with rising temperature and low ionic strength, due to distorted H′-aggregates with weak excitonic coupling and electrostatic screening of surface charges. These insights deepen the understanding of structure-property relationships in carbon dots and offer guidance for tailoring their photophysical properties for advanced optoelectronic applications.
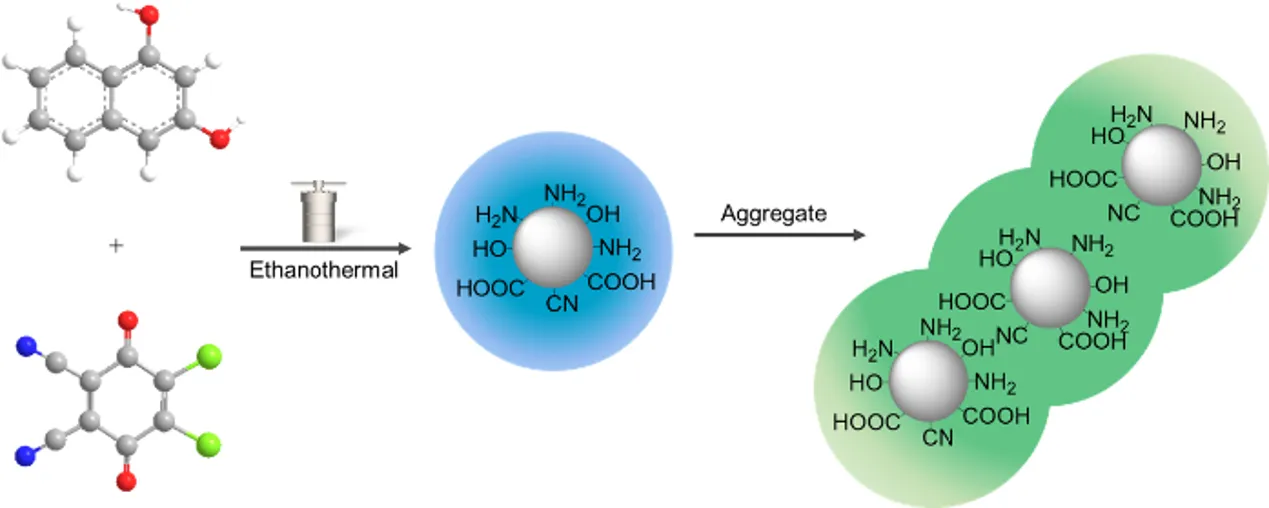
Open Access
Article
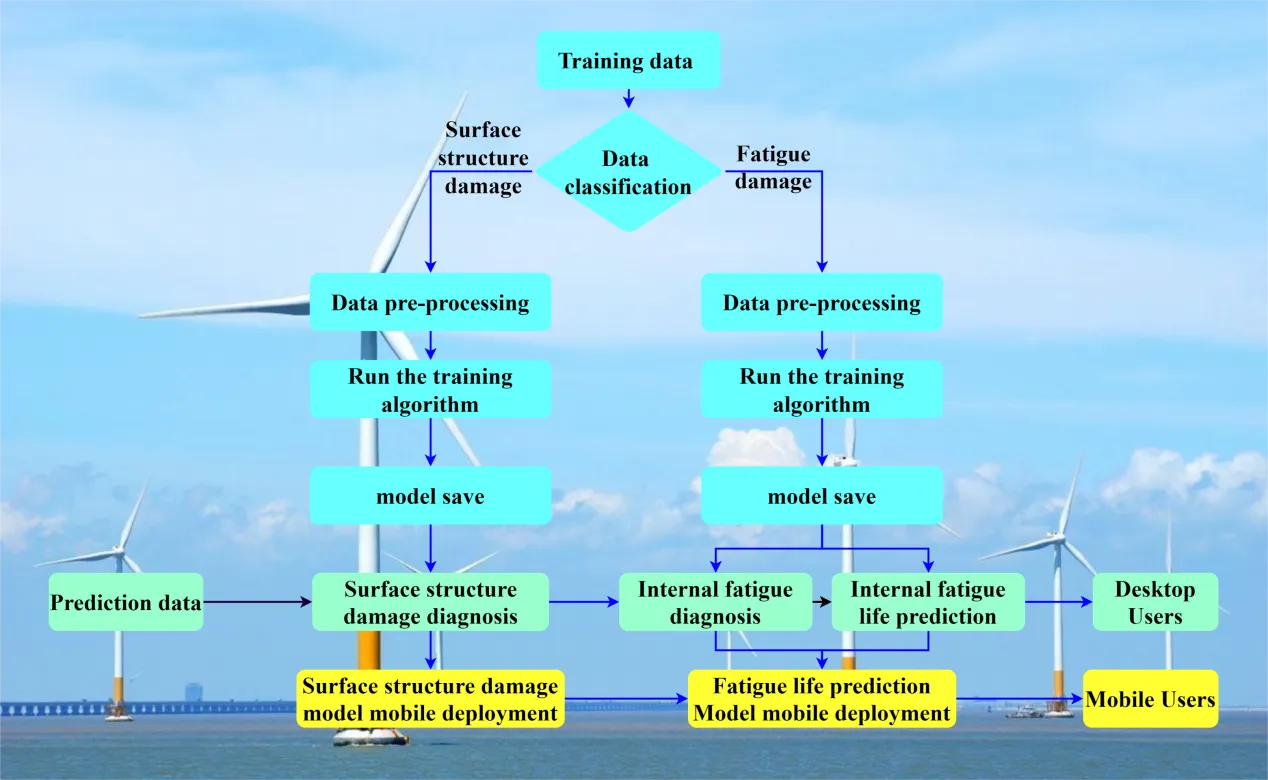
14 August 2025Advanced Study on Structural Health Diagnosis and Maintenance for Floating Wind Turbines Using Computer Vision
Global offshore wind capacity has now surpassed 50 GW and is projected to reach 264 GW by 2050, highlighting the pivotal role of floating wind in the future of clean energy. Given the complexity of marine environments, intelligent diagnostics for floating turbines are crucial for improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring robust and sustainable energy production. This paper presents a structural damage detection framework for floating wind turbines, integrating computer vision with advanced artificial intelligence technologies. First, a dataset is constructed through industry collaboration and open-source collection. Then, to optimise the YOLOv7 algorithm, SE attention mechanisms and WISE-IoU loss functions are incorporated, which significantly enhance the accuracy of surface damage detection. Experimental results indicate that the mAP (mean Average Precision) increases from 82.44% to 86.24% compared to the original YOLOv7. Finally, a deployment approach and an example are provided to use the diagnostic framework as a portable application. This enables real–time on–site analysis, enhances detection timeliness, and reduces maintenance costs. It allows for immediate issue identification and adaptation to diverse environments.