Found 301 results
Open Access
Article
23 September 2025Techno-Economic Evaluation of Vegetated Swales for Urban Stormwater Management in South Australia
Urban stormwater runoff continues to challenge cities worldwide due to increasing impervious surfaces and intensified rainfall from climate change. Swales—vegetated conveyance channels designed to manage runoff volume and quality—offer a nature-based solution that integrates hydrological function, ecological enhancement, and cost-effectiveness. This study investigates the performance and lifecycle economics of swale systems using a case study in South Australia. A MUSICX model simulation was conducted to quantify pollutant removal and flow reduction, and lifecycle costing was performed to evaluate construction and annual maintenance requirements. Results indicate exceptionally high treatment efficiencies, with over 99% removal of total suspended solids, nitrogen, phosphorus, and gross pollutants, and a 99.09% reduction in runoff volume. The total capital cost of the swale network was estimated at $19,726.50, with annual maintenance at $6157.49. Economic benefits from pollutant removal and avoided downstream treatment were valued at $14,874 per year, demonstrating a favorable benefit-cost profile. The findings underscore the potential of well-designed swales to function as cost-effective, modular components of decentralized stormwater management systems. These results contribute evidence supporting the broader integration of swales into urban planning, particularly in water-sensitive design frameworks seeking to achieve sustainability, climate adaptation, and SDG-aligned outcomes.
Open Access
Article
23 September 2025Marine Photovoltaic Module Salt Detection via Semantic-Driven Feature Optimization in Mask R-CNN
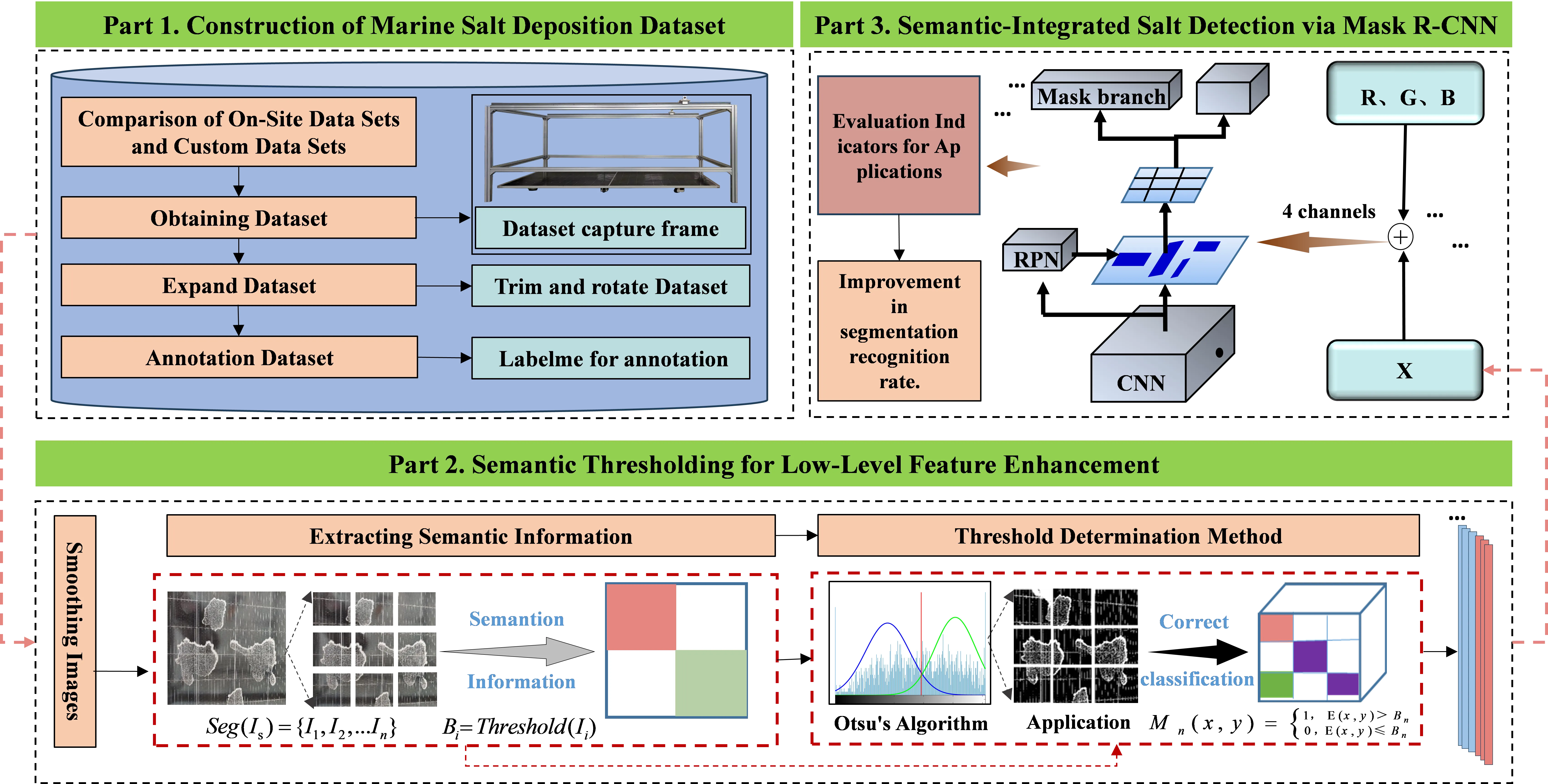
Offshore floating photovoltaic systems are highly susceptible to salt crystallization on the surfaces of photovoltaic modules, highlighting the need for intelligent inspection and cleaning technologies to improve operational efficiency and overcome the limitations of conventional manual maintenance methods. However, the presence of surface gridlines on the photovoltaic modules introduces significant visual interference, which complicates the accurate identification of salt deposition regions. To address this challenge, a semantic information-guided detection framework is proposed to enable precise segmentation of salt-affected areas. The key innovation lies in the effective classification of gridlines as background features by extracting semantic priors through low-level thresholding, which are then fused with the original red-green-blue image to construct a four-channel input. This fusion enhances the model’s ability to extract and discriminate features related to salt crystallization. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves a 4.6% improvement in segmentation accuracy and a 3.7% increase in recognition accuracy compared to conventional models, based on evaluation metrics such as mean average precision and F1-score. The proposed framework offers a robust technical foundation for developing intelligent maintenance systems tailored to offshore floating photovoltaic applications.
Open Access
Article
19 September 2025The Relationship between Resilience and Disruptive Behaviour among In-School Adolescents in Lagos State
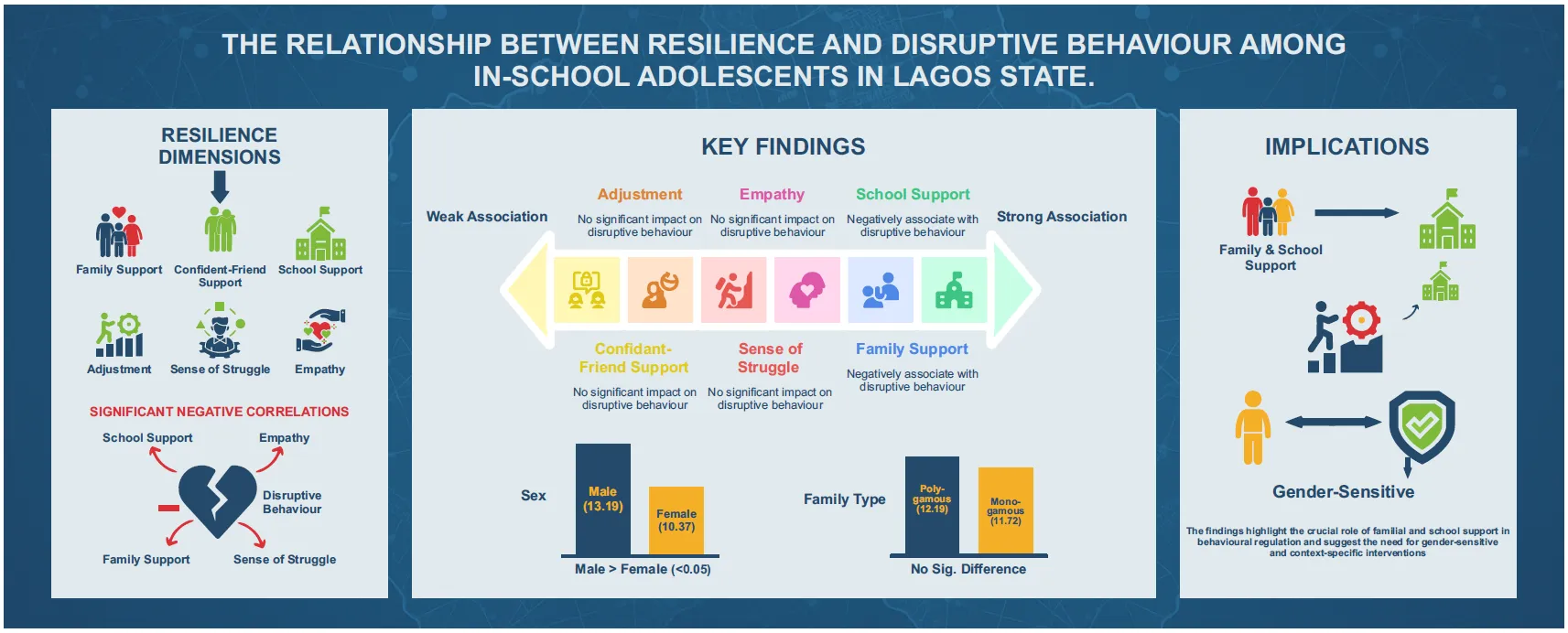
This study investigated the relationship between resilience and disruptive behaviour among in-school adolescents in Lagos State, Nigeria. The objectives were to examine: the association between six resilience dimensions (family support, confidant-friend support, school support, adjustment, sense of struggle, and empathy) and disruptive behaviour; the differences between sex and family type on disruptive behaviour. A cross-sectional design was employed, sampling 897 adolescents (M = 14.8 years; 50.8% male) from selected secondary schools using a multi-stage sampling technique. Data were collected using validated psychological resilience and disruptive behaviour scales. Results revealed a significant negative correlation between disruptive behaviour and four resilience dimensions: family support, school support, sense of struggle, and empathy. Regression analysis showed that these resilience dimensions jointly accounted for 6.6% of the variance in disruptive behaviour, with only family and school support emerging as significant predictors. Male adolescents exhibited significantly higher disruptive behaviour than females, while no significant differences were found based on family type. The findings highlight the crucial role of familial and school support in behavioural regulation and suggest the need for gender-sensitive and context-specific interventions.
Open Access
Article
17 September 2025An Approach to Simulation & Navigation of Autonomous Unmanned Aerial Vehicle in 3D
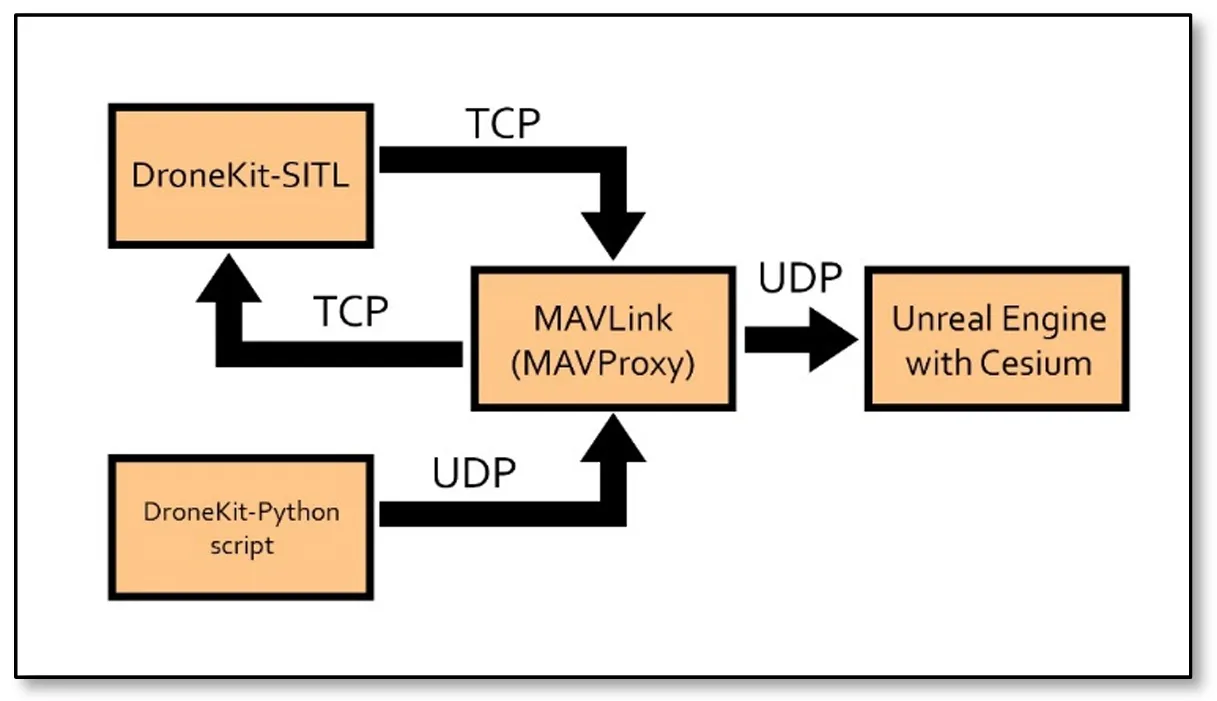
Drone simulation refers to the emulation of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in a virtual environment, replicating real-world conditions to study and test the behavior, performance, and functionalities of drones. This paper explores the simulation of UAVs in the Unreal Engine environment using MAVProxy (Micro Air Vehicle Proxy) and the Python library DroneKit. By leveraging the computational capabilities of computers, this approach enables precise visualization and control of UAV flight dynamics in three dimensions. The use of Blueprints in Unreal Engine facilitates a cost-effective and accessible simulation process, allowing engineers and scientists to refine their UAV designs before real-world deployment. Results show the applicability of this approach vs. different environments, where an alternative approach also emerges as a viable option for visualizing textured buildings. This approach shows the power of open-source collaboration in advancing innovative solutions in the dynamic field of science and technology.
Open Access
Article
17 September 2025Environmental Management Based (EMB) on Local Wisdom for Sustainable Utilization of Natural Resources in the Environmental Rescue Movement (ERM) in Villages, South Konawe, Indonesia
This study uses a qualitative approach with a case study strategy in four villages in South Konawe Regency, Indonesia, to explore environmental management practices based on local wisdom with the Building Village Index (BVI) instrument, which includes social, economic, and environmental resilience dimensions. The study results show that local wisdom, such as traditional planting patterns, customary law, and water and natural resource management through traditional rituals, play a significant role in maintaining the balance of the village ecosystem while strengthening cultural identity. The integration of local wisdom with appropriate technology has been proven to increase ecological awareness, strengthen social solidarity, and support equitable distribution of resources, although improvements in waste and energy governance are still needed. Theoretically, these findings enrich the literature on village resilience based on local wisdom, while practically providing evidence-based policy recommendations to strengthen ecological conservation and sustainable village development.

Open Access
Commentary
17 September 2025Shades of Grey: A Continuum of Biodiversity Understanding from Dark to Bright Diversity
This commentary introduces a conceptual framework that reinterprets biodiversity assessment as a continuum, spanning from Dark diversity, representing the unobserved or uncolonized potential of species ecologically suited to a system, to Bright diversity, conceived as an aspirational, fully integrated upper bound of biodiversity knowledge. Bright diversity encompasses not only observed components and their intricate interactions, but also a profound understanding of the reasons for species' presence or absence, including the inferred insights from Dark diversity across taxonomic, functional, phylogenetic, and genetic facets. Situated in between is Grey diversity, which characterizes the predominant state of partial knowledge and inherent uncertainty in real-world ecological assessments as an epistemic gradient. By delineating this epistemological gradient, the framework offers a heuristic tool for ecologists and conservationists to critically evaluate the clarity, completeness, and uncertainty embedded in biodiversity data, and an operational basis for “epistemic cartography”, i.e., the spatial mapping of knowledge sufficiency and uncertainty. It facilitates the identification of knowledge gaps, guides research priorities, and informs conservation actions, especially under conditions of incomplete information, through a compact workflow and transparent indicators. This conceptual spectrum serves as both an epistemological reflection and a practical guide for advancing biodiversity science, while outlining a forward-looking agenda that leverages multi-faceted “bands of biodiversity knowledge” to support robust biodiversity planning.

Open Access
Article
11 September 2025Investigation of Structure of the High-Entropy Alloy Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi
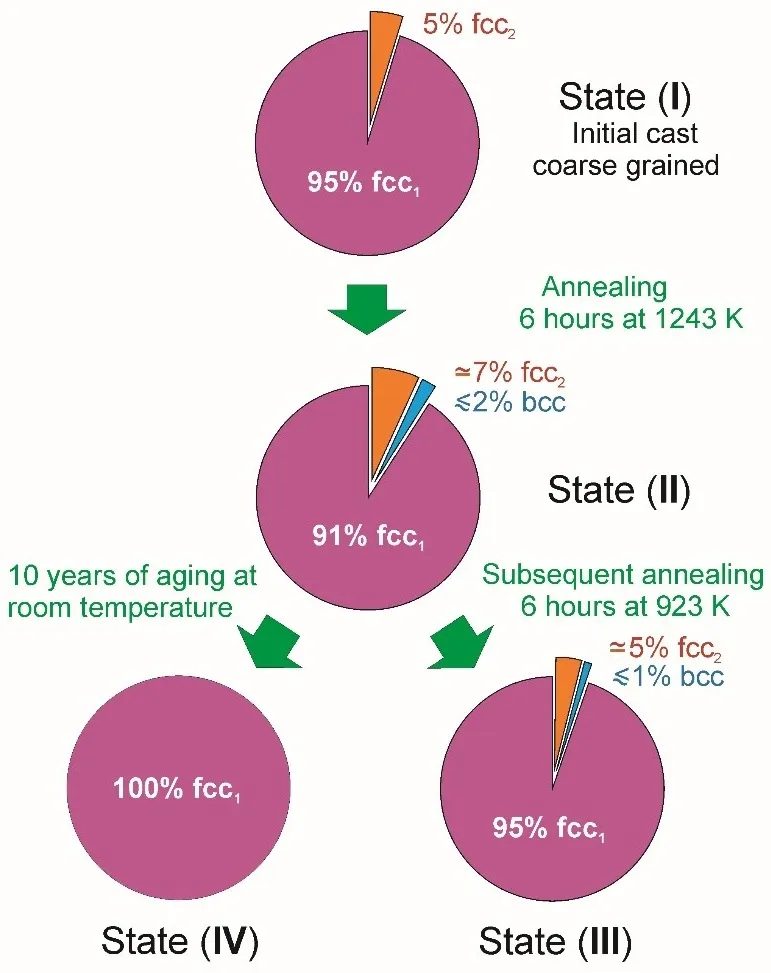
A detailed examination of the structure of the high-entropy alloy Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi at room temperature was carried out using different methods of optical microscopy, electron microscopy and X-ray structural analysis techniques. Numerical estimates of the dislocation density ∼5⋅1015 m−2, the mean size of the ordered (crystalline) domains ~18 nm and lattice micro strain ∼3⋅10−3 were obtained through Williamson-Hall analysis of XRD patterns. The estimates of the dislocation density were found to correlate with the estimates of the total length of dislocation segments per unit volume, which effectively interact with elastic vibrations of the sample ∼4⋅1013 m−2, as previously determined from acoustic relaxation measurements. This is consistent with the idea that a significant portion of dislocations are concentrated in grain boundaries, and only dislocation segments located inside grains and having a favourable orientation with respect to the direction of sound wave propagation can effectively interact with cyclic deformation of the sample.
Open Access
Article
08 September 2025Open Water in Winter: An Influential but Underestimated Ecosystem in Northern Boreal Mountain Regions
Patches of open water (polynyas) persist throughout six-month winters on many ice-covered lakes in boreal mountain ecoregions of northwestern North America. We explored their distribution, hydrological correlates, and the diversity of species using them from freeze-up to break-up. In headwater drainages, lakes with outflow polynyas were significantly larger than those without, but many small lakes also had polynyas. There was a consistent threshold in upstream catchment size below which outflow polynyas were absent and above which they persistently occurred in downstream lakes. Outflow polynyas depend on winter-long through-flow of water, likely maintained by the hydraulic head of higher elevation ground water in perched water tables in this region of very limited permafrost. Based on camera trapping, two species, the American dipper and river otter, used polynyas heavily throughout winter foraging. Polynyas likely provided crucial forage for at least 9 species of migratory waterfowl (Anatidae) to complete their spring migration or to prepare for reproduction on local lakes. Cameras recorded additional 5 bird and 11 mammal species, as foragers, scavengers, or incidentally. We report previously undocumented significance of these spatially-limited and seasonal polynya ecosystems in expanding the diversity of winter ecological opportunity for numerous species on small to medium-sized lakes.

Open Access
Article
05 September 2025A Green Way for the Synthesis of Ester Oil by an Ionic Liquid as Both a Catalyst and Lubricant Additive
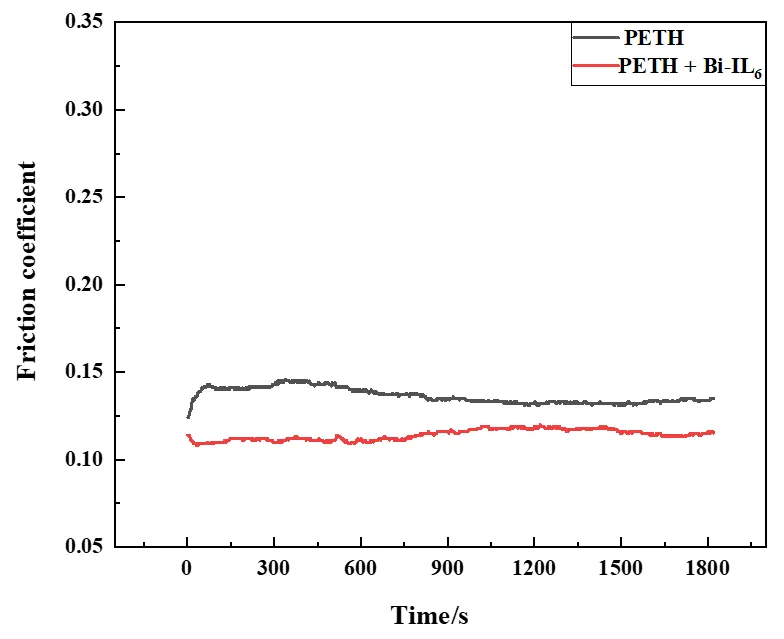
A series of ionic liquids 1-alkyl-3-methylim idazole bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate, were prepared, and the catalytic performance of ionic liquids was evaluated through the esterification reaction of pentaerythrotol and hexanoic acid at a stoichiometric ratio as a model reaction. The results showed that the [BMIM][DEHP] and [HMIM][DEHP] exhibited good catalytic activity. The [HMIM][DEHP] was chosen as a lubricant additive to further investigate the tribological properties after the reaction, and the results for both COF and WSD and wear volume indicate that the introduction of [HMIM][DEHP] has improved the friction reducing and anti-wear properties of pentaerythrotol tetra-hexanoate.
Open Access
Review
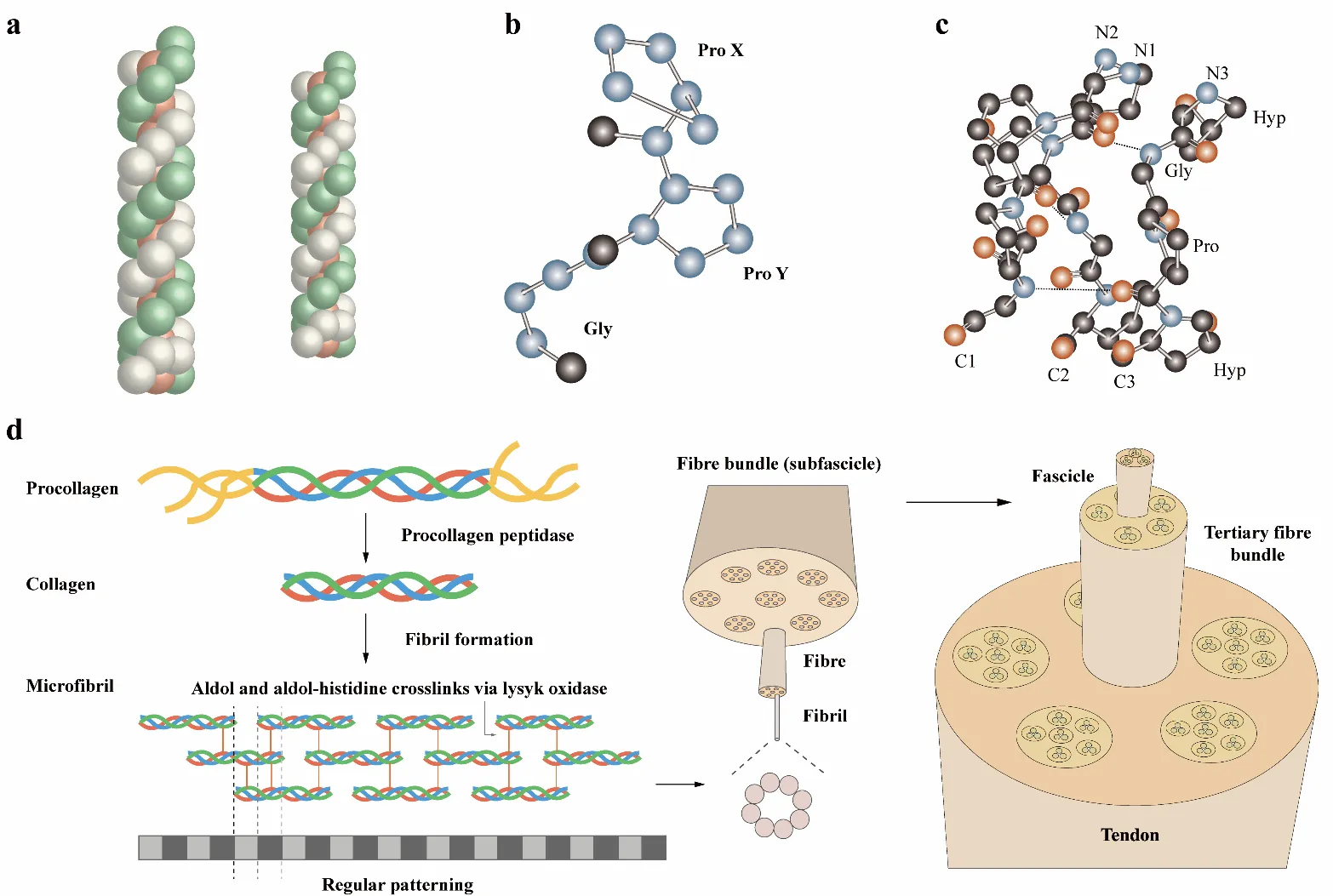
04 September 2025Collagen Biosynthesis to Engineered Biomaterials: Molecular Design, Synthetic Strategy, and Biomedical Application
Collagen, a principal component of the extracellular matrix, provides mechanical strength and stability to tissues and organs through its structural organization. Its biocompatibility has established it as a crucial material in biomedical applications such as drug delivery systems, cell culture matrices, and tissue engineering scaffolds. However, the use of animal-derived collagen carries risks of pathogen transmission, which has driven research towards developing synthetic collagen alternatives. Advances in AI-assisted protein engineering are accelerating the design of synthetic collagens and their applications in biomaterials. This review examines collagen’s structural characteristics, biosynthesis strategies, biological activities as well as AI-assisting engineering.