Artiles
Open Access
Review
09 December 2024Synthesize and Applications of Biodegradable Plastics as a Solution for Environmental Pollution Due to Non-Biodegradable Plastics, a Review
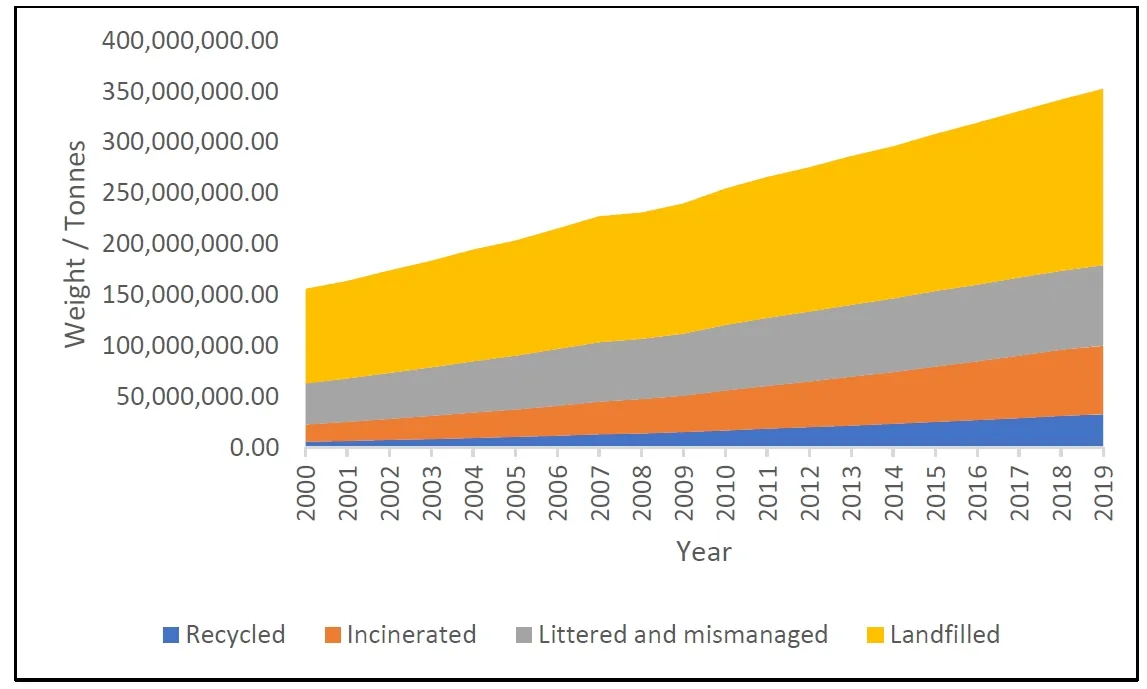
Biodegradable plastics are a potential sustainable alternative to conventional petrochemical-based non-degradable plastics. Due to their lightweight, flexibility, durability, versatile applications, chemical inertness, electrical and heat insulation, and conductivity, plastics have become an essential material for many industries, with annual production currently exceeding 450 million tons. However, these materials are non-biodegradable, leading to detrimental consequences such as the formation of microplastics from improper disposal and the generation of toxic gases, including furans, dioxins, mercury, and polychlorinated biphenyls, from burning plastic waste. This results in environmental pollution, affecting land, water bodies, and the atmosphere. In response, studies where the focus has been on creating bio-degradable polymers such as polylactic acid, polyhydroxy alkanoates, Polycaprolactone, Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate), and Polybutylene succinate, which were extracted from renewable resources or chemically modified as biodegradable polymers. Biodegradable polymers exhibit a wide range of properties and can now be modified to be used in various applications suitable for substituting some conventional plastic products. Thus, the article highlights the critical issue of environmental pollution caused by non-biodegradable plastics and provides a comprehensive overview of the synthesis processes, properties, novel applications, and challenges associated with the use of biodegradable plastics.
Open Access
Review
09 December 2024The Multifaceted Roles of Neutrophil Death in COPD and Lung Cancer
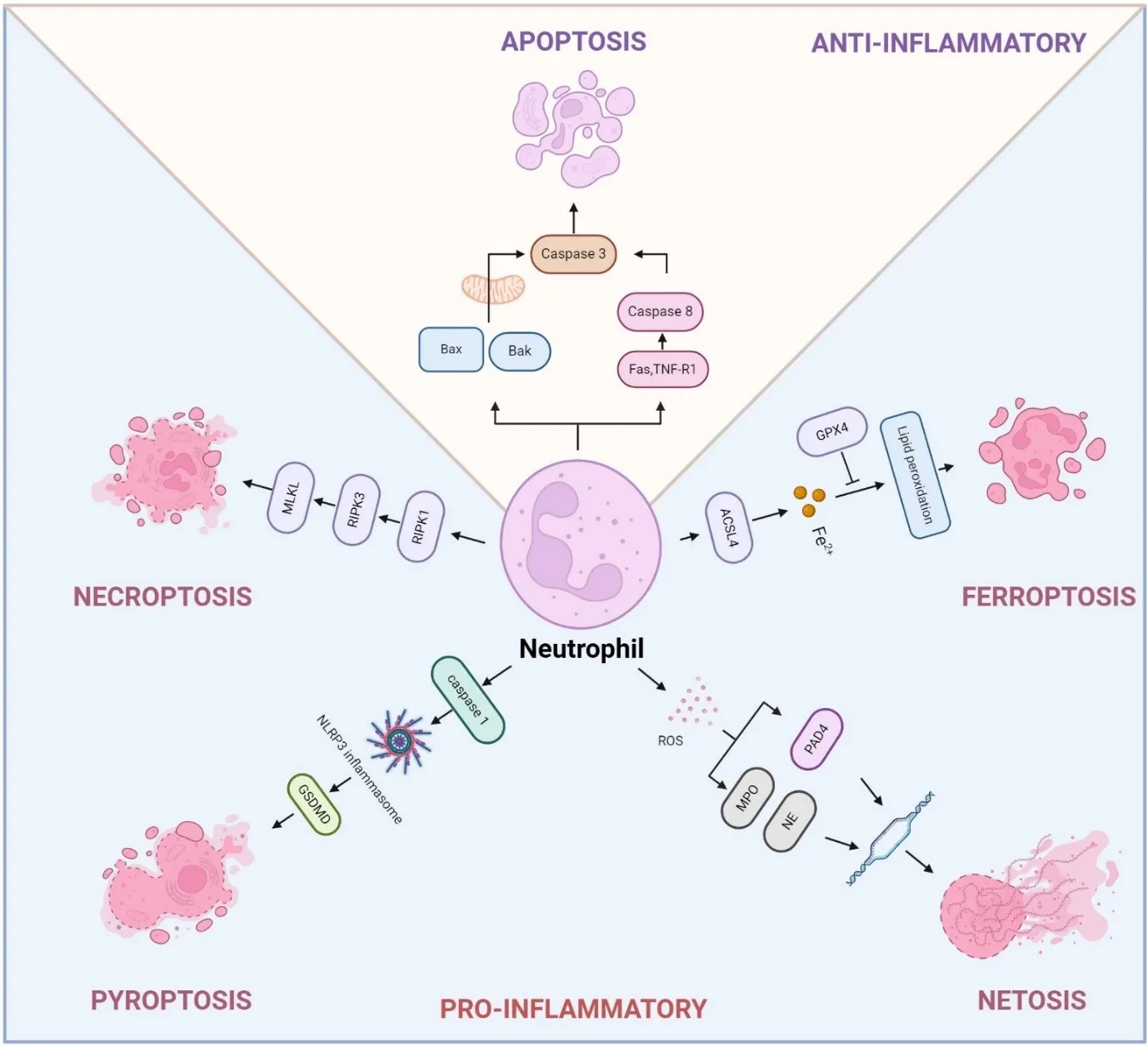
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer are closely linked, with individuals suffering from COPD at a significantly higher risk of developing lung cancer. The mechanisms driving this increased risk are multifaceted, involving genomic instability, immune dysregulation, and alterations in the lung environment. Neutrophils, the most abundant myeloid cells in human blood, have emerged as critical regulators of inflammation in both COPD and lung cancer. Despite their short lifespan, neutrophils contribute to disease progression through various forms of programmed cell death, including apoptosis, necroptosis, ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and NETosis, a form of neutrophil death with neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) formation. These distinct death pathways affect inflammatory responses, tissue remodeling, and disease progression in COPD and lung cancer. This review provides an in-depth exploration of the mechanisms regulating neutrophil death, the interplay between various cell death pathways, and their influence on disease progression. Additionally, we highlight emerging therapeutic approaches aimed at targeting neutrophil death pathways, presenting promising new interventions to enhance treatment outcomes in COPD and lung cancer.
Open Access
Review
06 December 2024Recent Progress of High Safety Separator for Lithium-Ion Battery
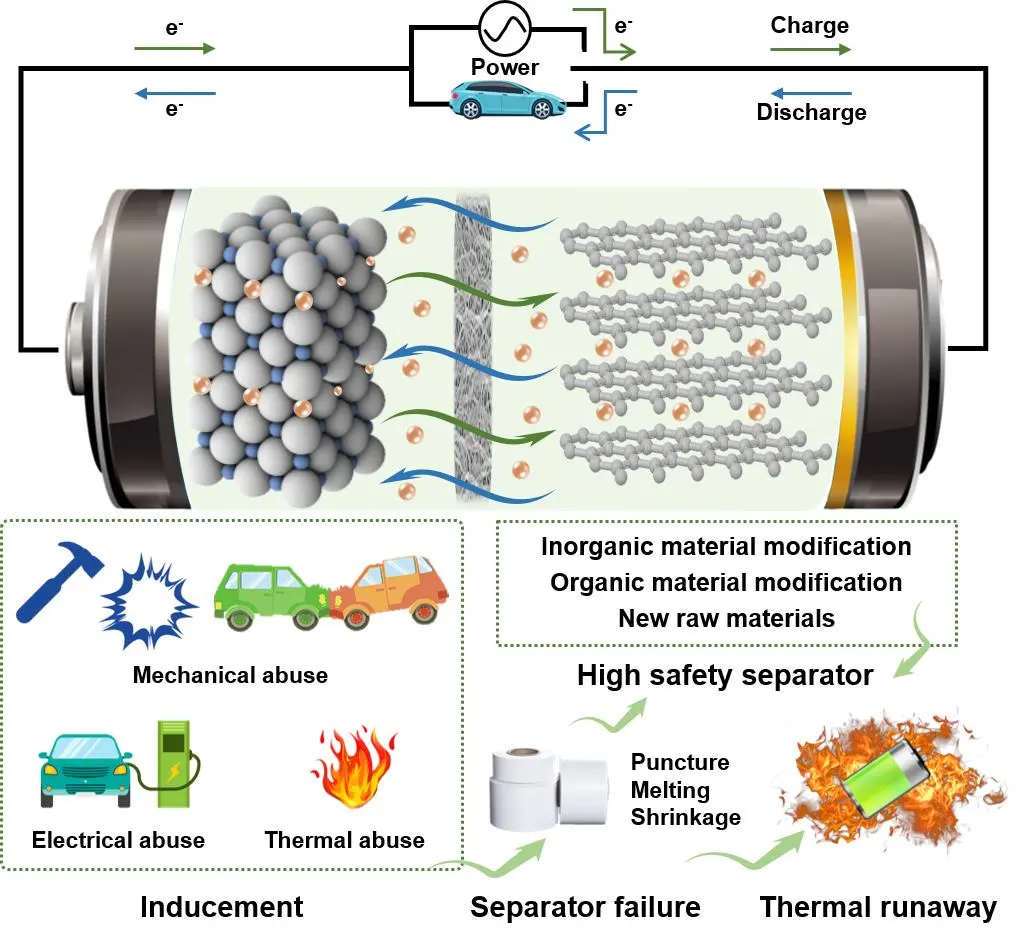
With the rapid increase in quantity and expanded application range of lithium-ion batteries, their safety problems are becoming much more prominent, and it is urgent to take corresponding safety measures to improve battery safety. Generally, the improved safety of lithium-ion battery materials will reduce the risk of thermal runaway explosion. The separator is a key component of lithium-ion batteries. It plays a crucial role in battery safety, serving as one of the most effective measures against internal short circuits.Separator failure is a direct cause of the thermal runaway and can be specifically divided into three categories: puncture, melting, and thermal shrinkage. The requirements for an ideal lithium-ion battery separator have a synergistic effect on the electrochemical performance, safety, and scalability of lithium-ion batteries. Focus on the separator, this review summaries the mechanism of separator in thermal runaway process, and reports the recent progress of high safety separator from the perspective of material preparation.
Open Access
Article
06 December 2024Population Dynamics and Stock Assessment of the Spottail Mantis Shrimp Squilla mantis (Linnaeus, 1758) in the North Aegean Sea, Greece
In Greek waters, the spottail mantis shrimp Squilla mantis (Linnaeus, 1758) presents significant ecological and low to moderate economic value. This study investigates the population dynamics and stock assessment of the species in the north Aegean Sea. A total of 856 individuals were collected using commercial bottom trawls between April 2021 and April 2023. Key population parameters such as size distribution, sex ratio, growth, size at maturity and spawning seasonality were assessed. Results indicate a relatively stable population with a slight male dominance and peak spawning activity occurring in late spring to early summer. Growth parameters were estimated using the von Bertalanffy growth model, revealing moderate growth rates and a maximum length slightly higher than previously recorded for this species in other Mediterranean regions. Stock assessment, conducted through yield-per-recruit analysis, suggests that the current exploitation levels are approaching sustainable limits. However, potential overfishing risks necessitate continuous monitoring and the implementation of adaptive management strategies. This study underscores the importance of integrative approaches combining biological and fisheries data to ensure the sustainable management of S. mantis populations in the Aegean Sea.
Open Access
Commentary
05 December 2024Improving Postmortem Dental Profiling: The Integration of Intraoral Scanners in Dental Autopsies
Forensic odontology plays a crucial role in human identification, particularly in cases where traditional identification methods face challenges such as severe trauma, decomposition, skeletonization, or carbonization. The evolution of digital dentistry has significantly advanced dental autopsies, particularly through the use of intraoral scanners (IOSs). These devices provide a non-invasive and efficient method for capturing detailed impressions of dentition and photographic images of teeth. The benefits of intraoral scanning in analyzing human remains in forensic odontology are endless. Digital impressions can be easily stored, shared, and transmitted electronically, eliminating the need for physical storage or transportation of dental models. This technology also enables remote postmortem dental profiling. By combining digital models with antemortem dental records, forensic odontologists can more efficiently identify matches and discrepancies, with the added benefit of future advancements in artificial intelligence(AI). Intraoral scanning should be considered a routine process in all dental autopsies to improve postmortem dental data collection and archive. Forensic odontologists should be equipped with a portable X-ray device, a digital sensor, and an IOS.

Open Access
Meeting Report
04 December 2024Progress and Gaps in Respiratory Disease Research and Treatment: Highlights of the IRM 2024 in Shanghai
Respiratory diseases pose a major public health challenge globally, necessitating collaborative efforts between basic researchers and clinicians for effective solutions. China, which is heavily impacted by a broad spectrum of respiratory disorders, has made notable strides in both research and clinical management of these diseases. The International Respiratory Medicine (IRM) meeting was organized with the primary goal of facilitating the exchange of recent research developments and promoting collaboration between Chinese and American scientists in both basic and clinical research fields. This article summarizes key insights from IRM2024, held in Shanghai, where a wide range of topics were discussed, including lung tissue development, disease mechanisms, and innovative therapeutic strategies. By integrating perspectives from basic, translational, and clinical research, IRM2024 highlighted recent advancements, addressed persistent challenges, and explored future directions in respiratory science and clinical practice. The insights gained from IRM2024 are poised to be pivotal in shaping future research and therapeutic approaches, further reinforcing the global commitment to enhancing respiratory health and improving patient outcomes.
Open Access
Article
03 December 2024Pathway Engineering of E. coli for Production of Fritschiellaxanthin and Other Carotenoids with α-Carotene Backbone and Their Singlet Oxygen-Quenching Activities
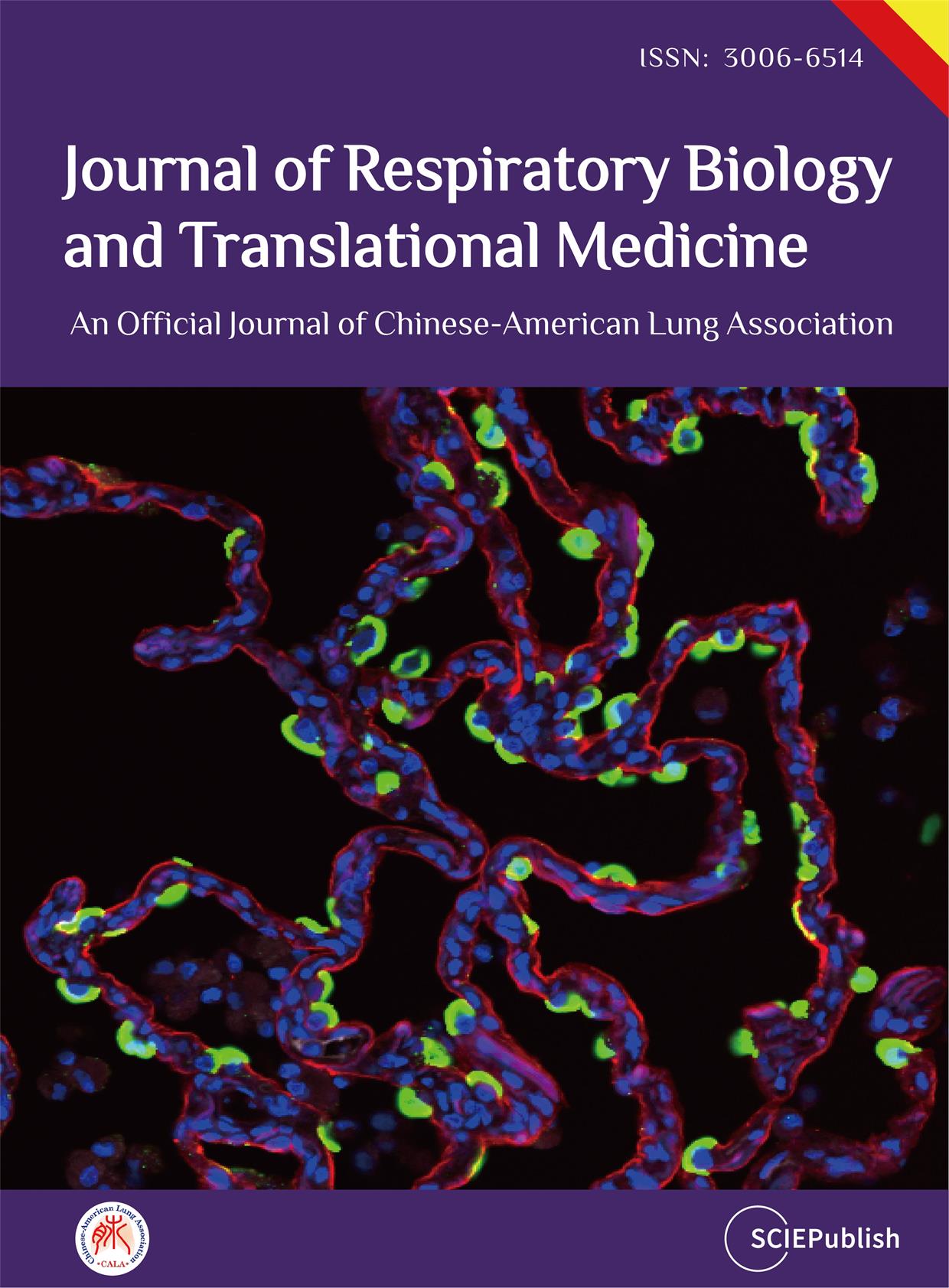
Some photosynthetic organisms are capable of biosynthesizing carotenoids (xanthophylls) with α-carotene backbone, that is, α-carotene-derived carotenoids, such as (3R,3′R,6′R)-3,3′-dihydroxy α-carotene (lutein). Except for lutein, such carotenoids are minor compounds in nature. In this study, α-carotene-derived carotenoids were produced with E. coli. To achieve this, carotenoid biosynthesis genes from the bacterium Pantoea ananatis containing the 4-β-ketolase (crtW) gene with/without the 3-β-hydroxylase (crtZ) gene, in addition to crtEBI genes, and biosynthesis genes (MpLCYb, MpLCYe, and MpCYP97C) from liverwort Marchantia polymorpha, along with the HpIDI gene, were cloned into plasmids. The transformed E. coli cells biosynthesized (3S,3′R,6′R)-3,3′-dihydroxy-4-keto-α-carotene (fritschiellaxanthin (4-ketolutein)), (3′R,6′R)-3′-hydroxy-4-keto-α-carotene (4-keto-α-cryptoxanthin), and (3′R,6′R)-3′-hydroxy-α-carotene (α-cryptoxanthin), as carotenoids that have not been produced by a heterologous microbial system so far. These carotenoids show potent singlet oxygen-quenching activity.
Open Access
Review
02 December 2024The Interplay of Heart Failure and Lung Disease: Clinical Correlations, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Implications
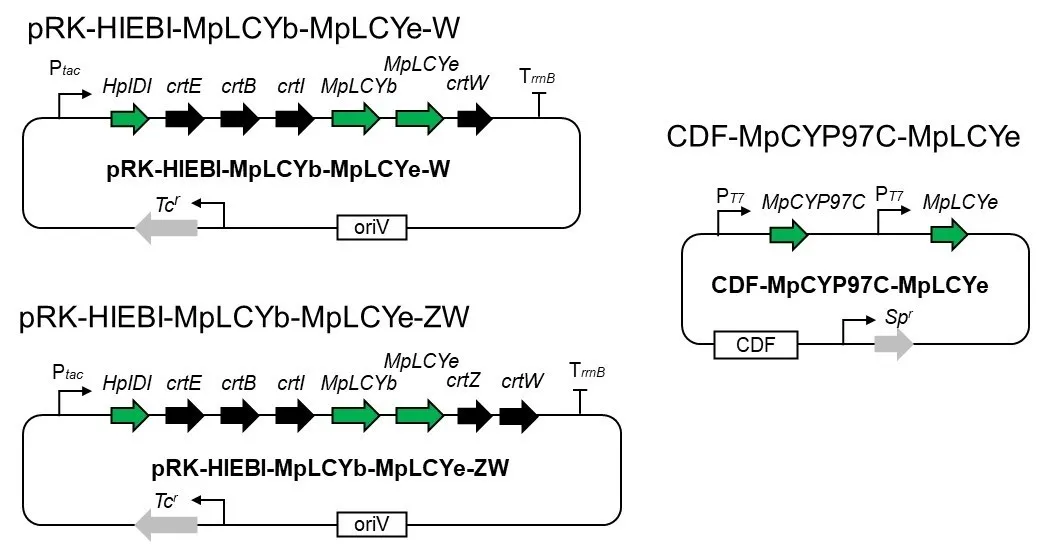
Heart failure (HF) is a common clinical syndrome marked by reduced cardiac output, elevated intracardiac pressures, and heart dysfunction. Chronic HF (CHF) is a syndrome characterized by a lack of blood flow and impaired pumping ability to the heart over time, while acute HF (AHF) arises suddenly due to incidents like myocardial infarction or cardiac arrest. HF has a significant impact on pulmonary health and function, leading to conditions such as pulmonary edema and restrictive lung patterns. Clinical evidence highlights the bidirectional relationship between HF and lung dysfunction. Declining lung function serves as a predictor for HF progression and severity, while HF contributes to worsening lung health. Animal models that induce HF through surgical methods further demonstrate the connection between heart and lung pathology. The main mechanisms linking HF and lung dysfunction are pressure overload and chronic systemic inflammation, with changes in the extracellular matrix (ECM) also playing a role. Additionally, environmental factors like air pollution exacerbate lung inflammation, increasing the risk of both HF and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) incidence. Combined treatment approaches involving pharmaceutical drugs such as statins, Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) may benefit by reducing inflammation. This review will explore the complex interplay between HF and lung function, emphasizing their interconnected pathophysiology and potential integrated treatment strategies.
Open Access
Article
28 November 2024Correlations of System Degradation, Losses and Significant Parameters for 49 MW Large Scale Solar Plant with Real Site Data Validations
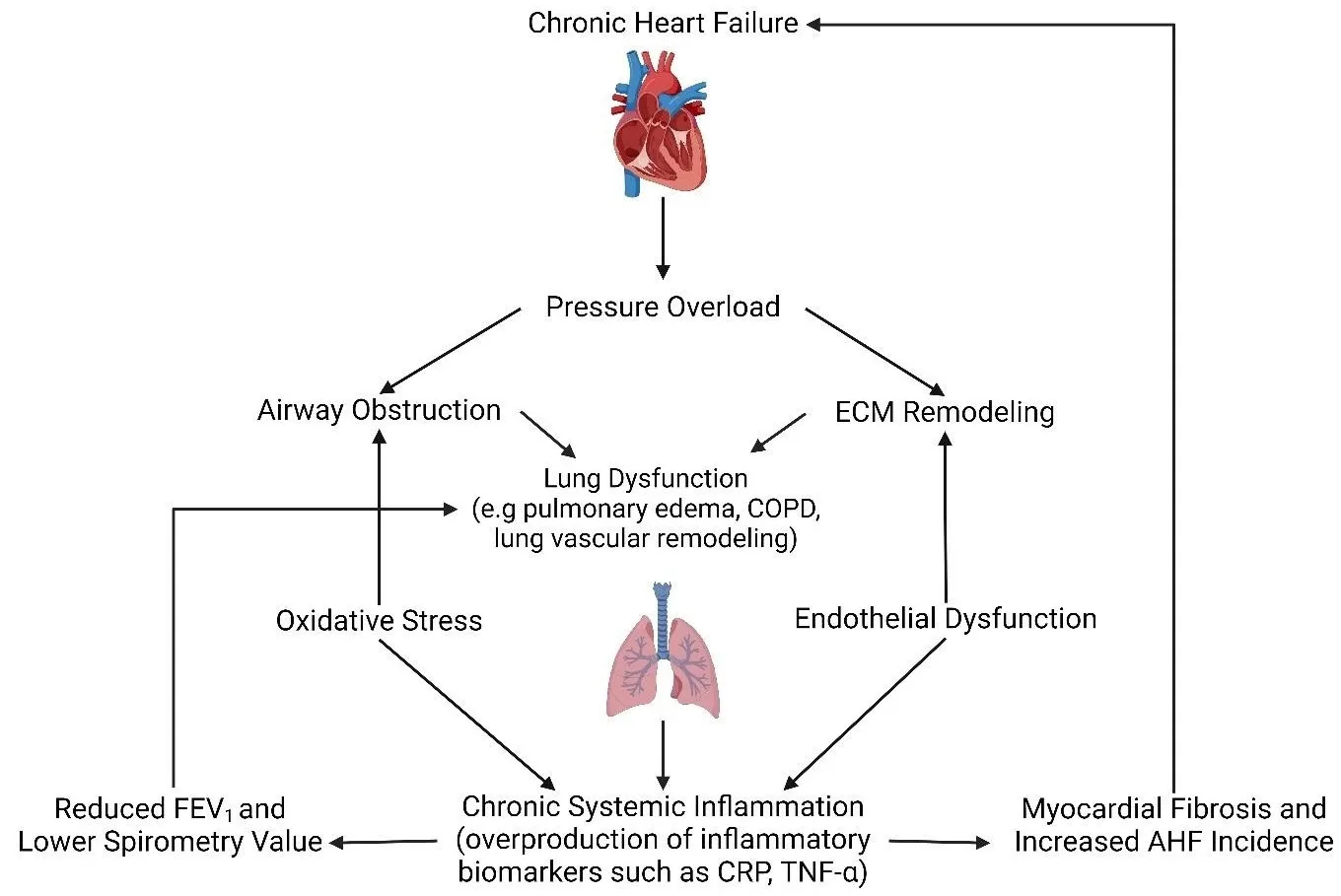
A smooth transition towards a clean and sustainable environment will heavily rely on the continuous increase of renewable energy (RE) integration. Malaysian authorities have set targets to increase the RE capacity to 31% by the end of 2025 and achieve 40% by 2035, specifically through the power generation plan. Solar PV systems have been widely used, from industries to residential homes, because Malaysia receives a high irradiation potential of up to 5000 Wh/year. The increase in the potential of solar PV usage has allowed solar companies to provide this system regardless of its complexity and system size. However, a drop in efficiency due to system parameters within the photovoltaic (PV) system is evident over time. This study aims to analyze the relationship between solar PV system parameters and their energy performance, particularly in a tropical climate region, for a large-scale solar (LSS) plant. This project was undertaken with two objectives: First, it is to develop an optimum solar PV system by adhering to and implementing GCPV standards in Malaysia. Stage 1 will primarily focus on managing and manipulating various PV system parameters to ensure the optimum energy yield received from the plant. The system parameters analyzed are tilt angle, module technology and its effect on different temperatures, the effect of the optimizer, sizing and thermal loss. Stage 2 will then incorporate the industry data of the LSS plant by creating a Pearson’s Correlation model on how energy yield is correlated against real time system parameter values obtained. An optimum tilt angle of 10°, monocrystalline module and inclusion of optimizer increases the overall energy production from 88,986 MWh/year to 89,782 MWh/year and performance ratio (PR) from 78.9% to 79.8%. The outcome of this study demonstrates the significant parameters of the PV system to maximize the energy output to the grid. This will further support the government’s plan to reduce GHG emissions by 45% through the use of renewable energy, with the aim of producing up to 2.5 GW from LSS systems by 2030.
Open Access
Article
28 November 2024A Review of the Energy Policy in Greece in the Last 50 Years and Its Implications for Prosperity
This paper elucidates the development of electricity production and distribution in Greece from the 1950s to date, in correlation with national and European energy policy. During this period, Greece experienced a multifaceted energy transition, including both the transition of ownership of energy generation companies from public to private and a transition from an energy mix in which coal (lignite) served as a major and inexpensive resource to a mix in which wind power, solar power and natural gas gained a primary role, but with high costs for energy generation. The correlation between electrical energy consumption and economic growth is explored in this context, revealing an increase in consumption before the 2009 recession and a decline thereafter. The study investigates the correlation between escalating electricity prices and legislative dependencies that mandated the purchase of wind- and solar-generated electricity at exorbitant rates, the closure of cost-effective lignite units, and the reliance on natural gas—a commodity susceptible to geopolitical shifts. It also shows that, given the structure of the Greek energy mix, the increase in the share of wind and solar energy in the mix is directly related to the increase in the price of electricity. Highlighting the importance of energy costs for prosperity, this paper underscores, through the detailed review of the Greek energy “landscape”, that the major determinants of electricity prices are both the accessibility to natural resources but also their proper and judicious management.
