Found 469 results
Open Access
Article
29 September 2024Reactions and Phase Transformations at Sintering of Cubic Boron Nitride Based Materials
Superhard cubic boron nitride (cBN) cutting materials with different contents of cBN were investigated. The compositions of cBN-based materials included ceramic and metallic binders. The sintering of materials was performed by high-temperature hot pressing (HPHT) six-anvil apparatus at pressure 4.5 GPa and temperatures 1400–1450 °C. The process of compaction and processing of superhard cBN materials is followed by numerous chemical reactions. The chemical reactions are very important in compaction and sintering. The volume transformations during chemical reactions affect the shrinkage of the materials and may also impact the residual porosity of the finished products. The adhesion between the grains also depends on these chemical reactions. The research analyzed the volume transformations of various reactions during HPHT sintering of cBN materials, which may play a significant role in forming their structure and properties.

Open Access
Article
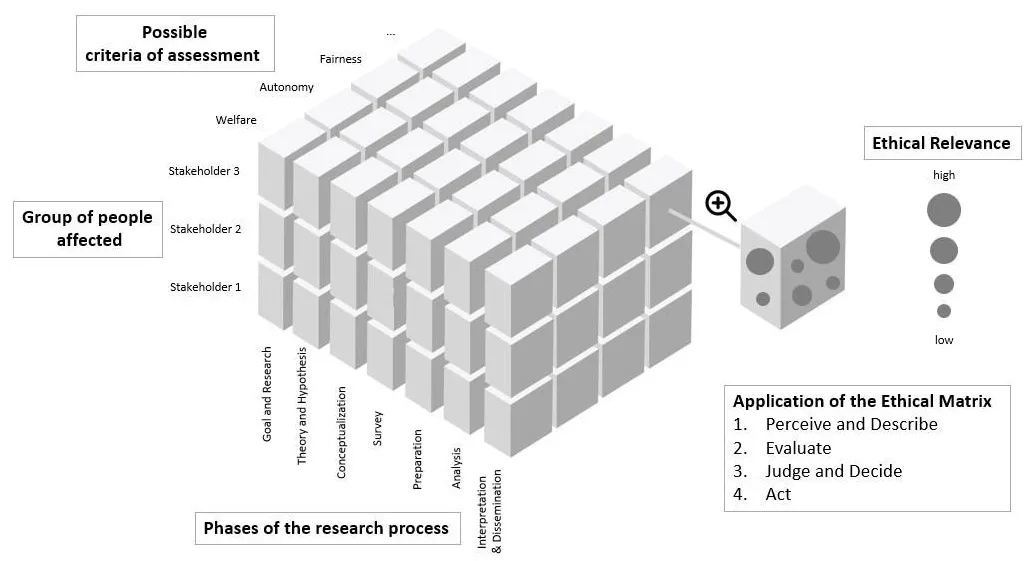
27 September 2024Responsibility as Method—A Model for Operationalizing Ethical Reflection in the Sciences
In this article, we show why the growing significance of ethics entails that the call for ethical evaluations is no longer just a specific issue for the particular discipline of academic ethics but a challenge for all academic researchers. Therefore, complex theoretical approaches must be put into practice, and the relationship between ethics and other scientific fields must be clarified. Hence, this essay shows how these requirements can be fulfilled and how to cope with the complexity of ethical consideration on a practical level. We aim to operationalize responsibility as a method. In order to achieve this, basic criteria of practical ethical reflection are elaborated. As a result, we suggest an extended ethical matrix covering the entire research process using a step-by-step model. Our ethical matrix is designed to help researchers reflect and make judgments on moral and ethical issues, enabling them to find their own solutions to these challenges without providing a formal guideline for moral decision-making.
Open Access
Article
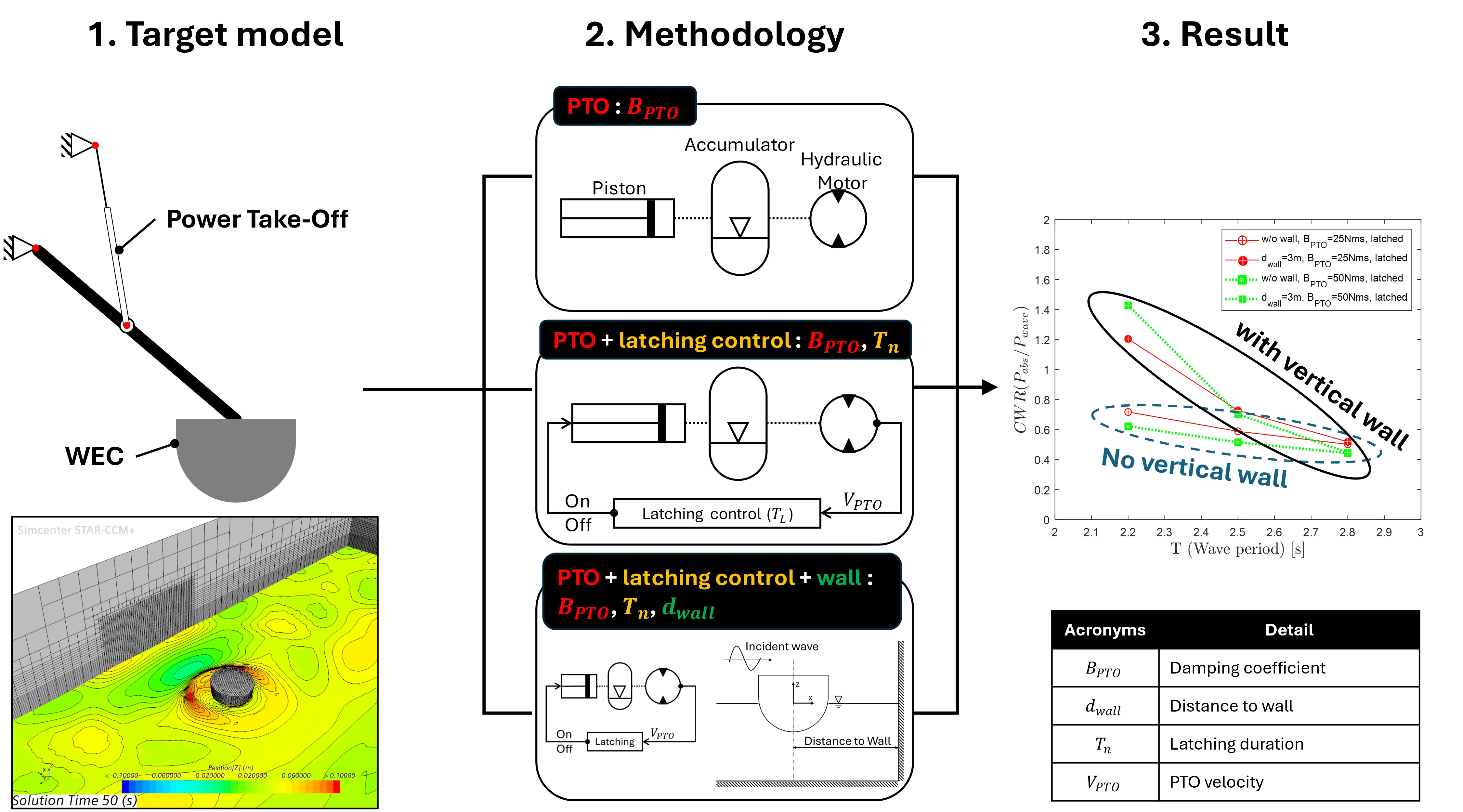
27 September 2024Numerical Investigation of a Point Absorber Wave Energy Converter Integrated with Vertical Wall and Latching Control for Enhanced Power Extraction
This study presents a numerical investigation of a point absorber wave energy converter (WEC) with a focus on improving its performance through the utilization of a vertical wall and latching control in the power take-off (PTO) system. Prior to numerical evaluations, experimental data incorporating PTO considerations and numerical simulation results were examined to validate the accuracy of the numerical methodology employed in this research. This study introduces a numerical PTO model and latching control for a further investigation. Comparative analyses were carried out on the displacement, velocity, and force of the PTO, absorbed power, and capture width ratio (CWR), considering the incorporation of a vertical wall and latching control. The results confirm that the introduction of both vertical wall and latching control significantly improves the CWR of the WEC, showing the effectiveness of incorporating a vertical wall and latching control in enhancing power extraction.
Open Access
Article
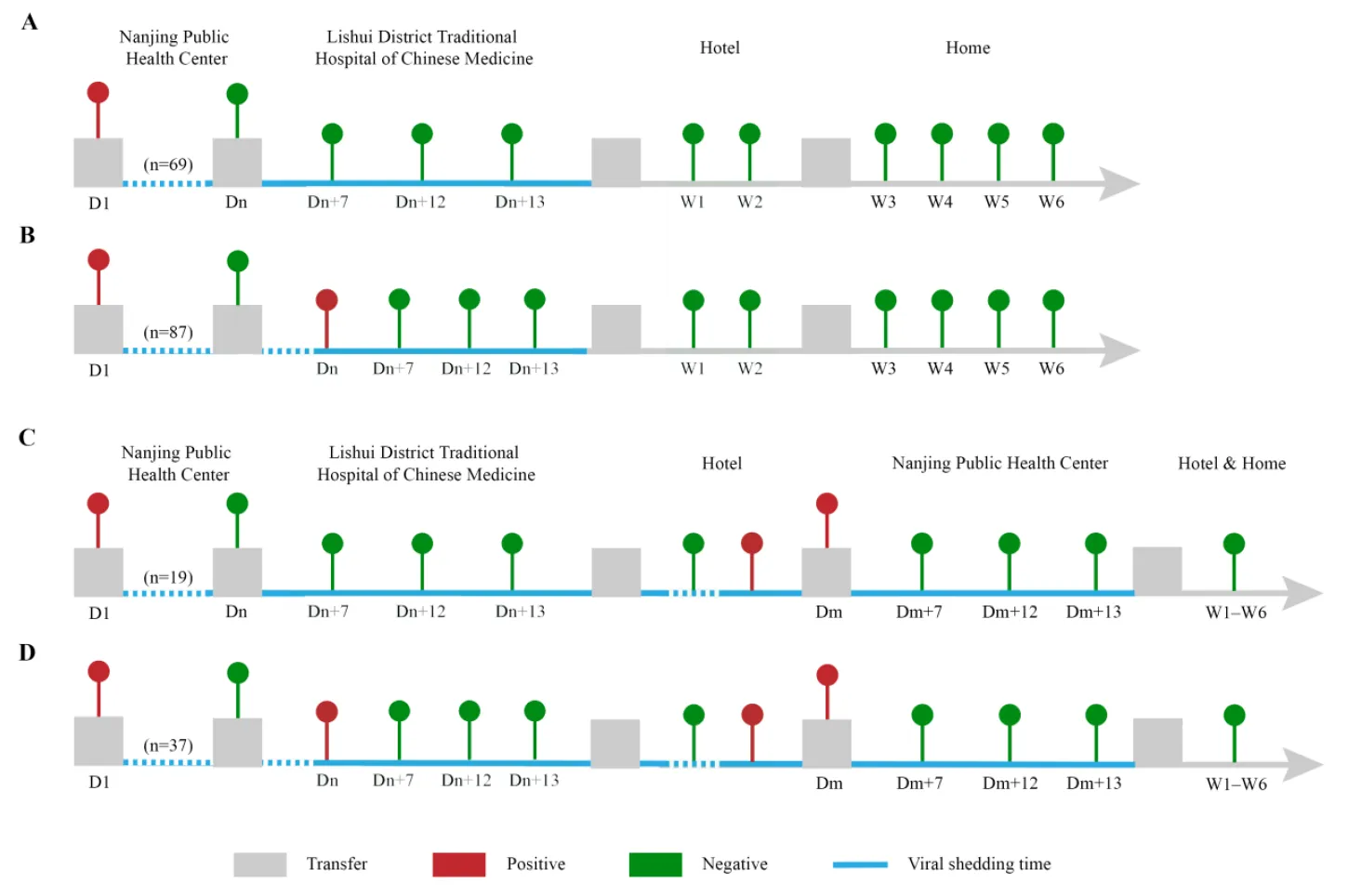
27 September 2024Evaluation of the Efficacy of Chinese Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccines against the Delta Variant in the Nanjing Outbreak: A Cohort Study
Background: The strains of COVID-19 are constantly mutating, and the effectiveness of Chinese inactivated vaccines against the COVID-19 Delta variant has not been described clearly. Methods: The clinical data of patients with the COVID-19 Delta variant in the 2021 Nanjing outbreak were retrospectively reviewed. Results: There were 212 patients with the COVID-19 Delta variant (unvaccinated, n = 56, 26.42%; vaccinated, n = 156, 73.58%) included in our cohort study. The median age was 45.5 (38, 53) years old. Eighty-seven subjects (41.04%) were airport staff, and 94 patients (44.34%) in 32 families were infected. There were 53 (25.00%) and 103 (48.58%) cases with one-dose and two-dose vaccination, respectively, and 55 (25.94%), 147 (69.34%) and 10 (4.72%) had mild, moderate and severe symptoms, respectively. The duration of viral shedding, or viral shedding time (VST), was significantly longer in unvaccinated individuals compared to vaccinated individuals (p = 0.0008). Moreover, the duration was significantly longer in patients who received one vaccine dose than those who received two doses (p < 0.0001). The mild patients had significantly shorter VSTs than the moderate subjects (p < 0.0001). Disease severity and vaccination dose were independent predictors for VST by Cox regression models. Conclusions: These results suggest that two-dose vaccination could reduce VST in patients with the COVID-19 Delta variant. Chinese inactivated vaccines may decrease the disease severity of cases with the COVID-19 Delta variant.
Open Access
Article
27 September 2024The Relationship between Negative Cognitive Processing Bias, Self-Control, and Depressive Symptoms among University Students: A Network Analysis
Depression is a heterogeneous disease, with individual symptoms uniquely associated with negative cognitive processing bias and self-control. However, studies on the relationships among them from a fine-grained level are lacking. The present study employed network analysis to explore the specific connections among the three constructs based on the dual-process model. Recruiting 1168 Chinese university students, the study estimated a regularized partial correlation network. Depression, negative cognitive processing bias, and self-control were assessed with the nine-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), the Negative Cognitive Processing Bias Questionnaire (NCPBQ), and the Brief Self-Control Scale (BSCS), respectively. Depression nodes fatigue, sad mood, and guilt were the most central symptoms. Negative memory bias, negative attention bias, and guilt were the bridge nodes. Network revealed distinct relations between different negative cognitive processing bias dimensions and depression symptoms, self-control and depression symptoms, and direct antagonistic effects between negative cognitive processing bias and self-control. The current study showed specific pathways between the three communities, and highlighted the role of dual-process model variables in depression development. Focusing on the identified critical depression nodes and related pathways could be effective for depression prevention and intervention.

Open Access
Article
26 September 2024Distribution Patterns of Tigers and Leopards in Thung Yai Naresuan (East) Wildlife Sanctuary, Western Thailand
Examining the distribution patterns of sympatric large carnivores provides critical insights into the roles of prey availability and human disturbances in shaping the landscape use of these key predators. The Thung Yai Naresuan (East) Wildlife sanctuary (TYNE) in western Thailand has been presumed to be a natural stronghold for tigers (Panthera tigris), leopards (Panthera pardus), and large ungulates, but little was known about their habitat relationships there. During April 2010–February 2012, camera trap surveys (n = 106 camera trap locations; n = 1817 trap nights) and sign surveys (n = 493 km of transects) were designed to systematically cover overlapping areas of 925 km2 and 1421 km2, respectively, to characterize and evaluate tiger and leopard distribution in TYNE. Occupancy modeling was used to estimate the potential environmental and anthropogenic factors that best explained habitats used by these large carnivores. The predictive model of tiger and leopard occupancy from surveys at the same sampling scale revealed similar relationships between limiting factors and space use. Camera surveys show that tigers are more likely than leopards to inhabit areas where gaur (Bos gaurus) and sambar (Cervus unicolor) are frequently found.. Sign surveys from across TYNE also indicated tiger distribution was characterized by the presence of large ungulates, as well by areas with high ranger patrol effort; leopard distribution was characterized by a higher occurrence of smaller barking deer (Muntiacus vaginalis) and wild boar (Sus scrofa), and by areas with low human disturbance. Our findings suggest that tigers and leopards have specific habitat preferences within the TYNE, with tigers showing a preference for areas with larger ungulates. In contrast, leopards are more likely to be found in areas with smaller prey. Human settlement areas and disturbance activities were identified as key factors influencing the distribution of both species, limiting their range to the central to the eastern part of the sanctuary.

Open Access
Article
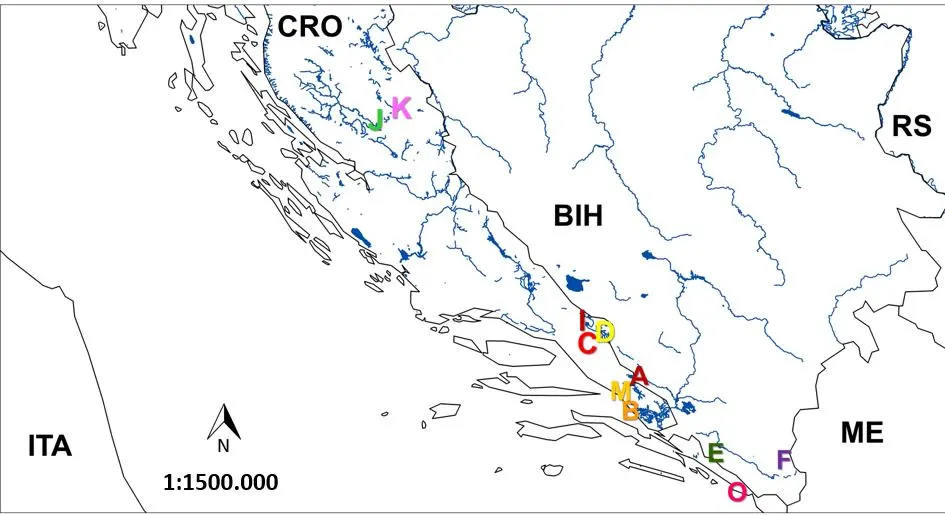
25 September 2024Evolution in the Dinarids: Phylogeography, Diversity and Evolutionary History of the Endemic Genus Delminichthys (Actinopteri; Leuciscidae)
The origin of exceptionally rich fish communities harboured within the freshwater systems of southern Europe is usually explained by allopatric speciation due to a long isolation of water basins. On the other hand, hybridization events have been recorded in several fish species, but they role in the speciation of freshwater fishes in the Southern Europe has not received significant attention. Contrary to most species within the Leuciscidae family, the genus Delminichthys inhabits a geographically restricted area (middle and southern Dinarides) and consists of only four endemic species. This study analysed the population genetic structure and demographic history of each Delminichthys species as a contribution to the understanding of the evolutionary peculiarities in Dinaric water systems. The obtained results revealed pronounced mito-nuclear and nuclear-nuclear discordance, likely the result of incomplete lineage sorting, as well as nuclear introgression observed in the Ombla River population in southernmost Croatia. In addition to allopatric speciation, ancient hybridization might have played an important role in the evolutionary history of this genus. The origin of the genus Delminichthys can be dated back to the Oligocene/Miocene boundary, to a period of significant tectonic activity in the Mediterranean region, and its ancestor likely inhabited the region of the central Dinarides. Intrageneric divergences occurred in the lower Miocene and Pliocene. Similarly, as previously proposed for Delminichthys adspersus, traces of underground migrations were found among Delminichthys ghetaldii populations, implying adaptations to underground life to be characteristic for the genus. All Delminichthys species express high levels of genetic diversity, likely as a consequence of their old origin. Size of D. adspersus is currently decreasing, while the remaining three species appear stable.
Open Access
Review
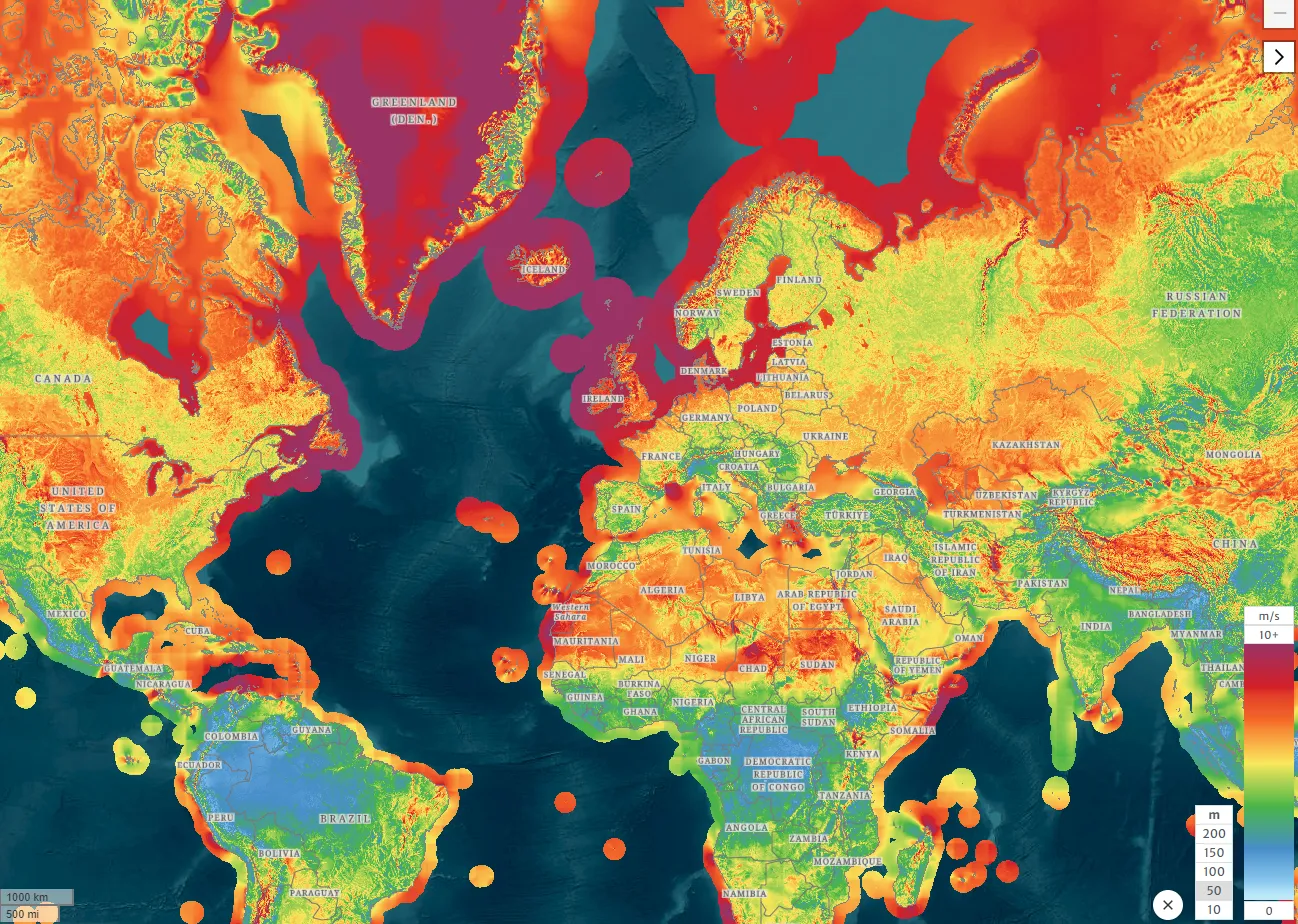
23 September 2024Icing Models and Mitigation Methods for Offshore Wind in Cold Climate Regions: A Review
Offshore wind turbines (OWTs) in cold climate regions have become increasingly significant due to the abundant wind resources with the development of renewable energy. These areas offer considerable potential for the development of OWTs. Generating energy for communities in cold climate regions involves overcoming significant challenges posed by the remote and harsh environmental conditions. This review presents the state-of-the-art research regarding prediction models for ice accretion on wind turbine components. Furthermore, this review summarizes advanced mitigation solutions, such as cold-weather packages and ice protection systems, designed to address icing issues. The present study identifies critical knowledge gaps in OWT deployment in cold climate regions and proposes future research directions.
Open Access
Commentary
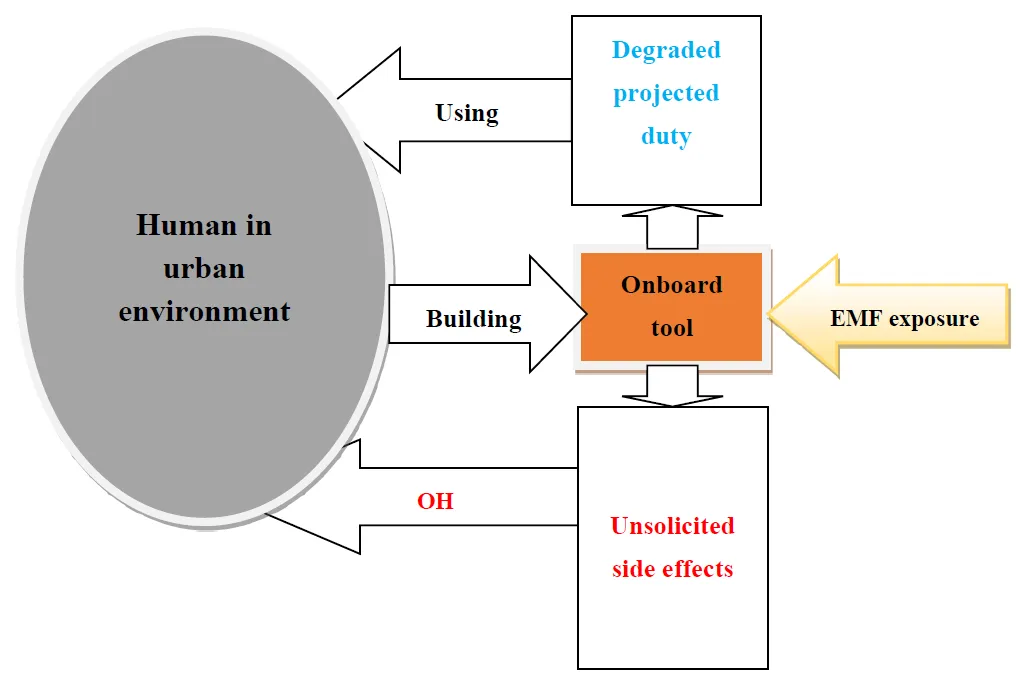
20 September 2024Sustainable Design and Integrity Control of Onboard Health Tools for Humans and Their Environmental Urban Biodiversity
Recently, onboard sensing and support devices have been used for the well-being of humans, animals, birds, plants and, more generally, biodiversity. The performance of these tools is closely linked to their electromagnetic environment, mainly artificially created by humans. Therefore, the presence of electromagnetic radiation linked to human activities near such tools constitutes a threat. The intelligent and sustainable manufacturing of these tools, which makes it possible to face such a threat, can be achieved through their design and optimization. This commentary aims to highlight the interaction of artificial electromagnetic radiation with onboard health tools involving living tissues in urban biodiversity (One Health concept) and the intelligent and sustainable construction and protection (Responsible Attitude concept) of these tools. The manuscript presents an overview of onboard devices, possible effects of electromagnetic radiation, durable construction and shielding, and analysis of electromagnetic compatibility integrity control. The main outcome of this contribution regarding sustainably designed onboard devices is that numerical analysis tools of electromagnetic fields could efficiently verify their integrity and the behavior of their necessary smart shields. These different themes are associated with examples of literature.
Open Access
Review
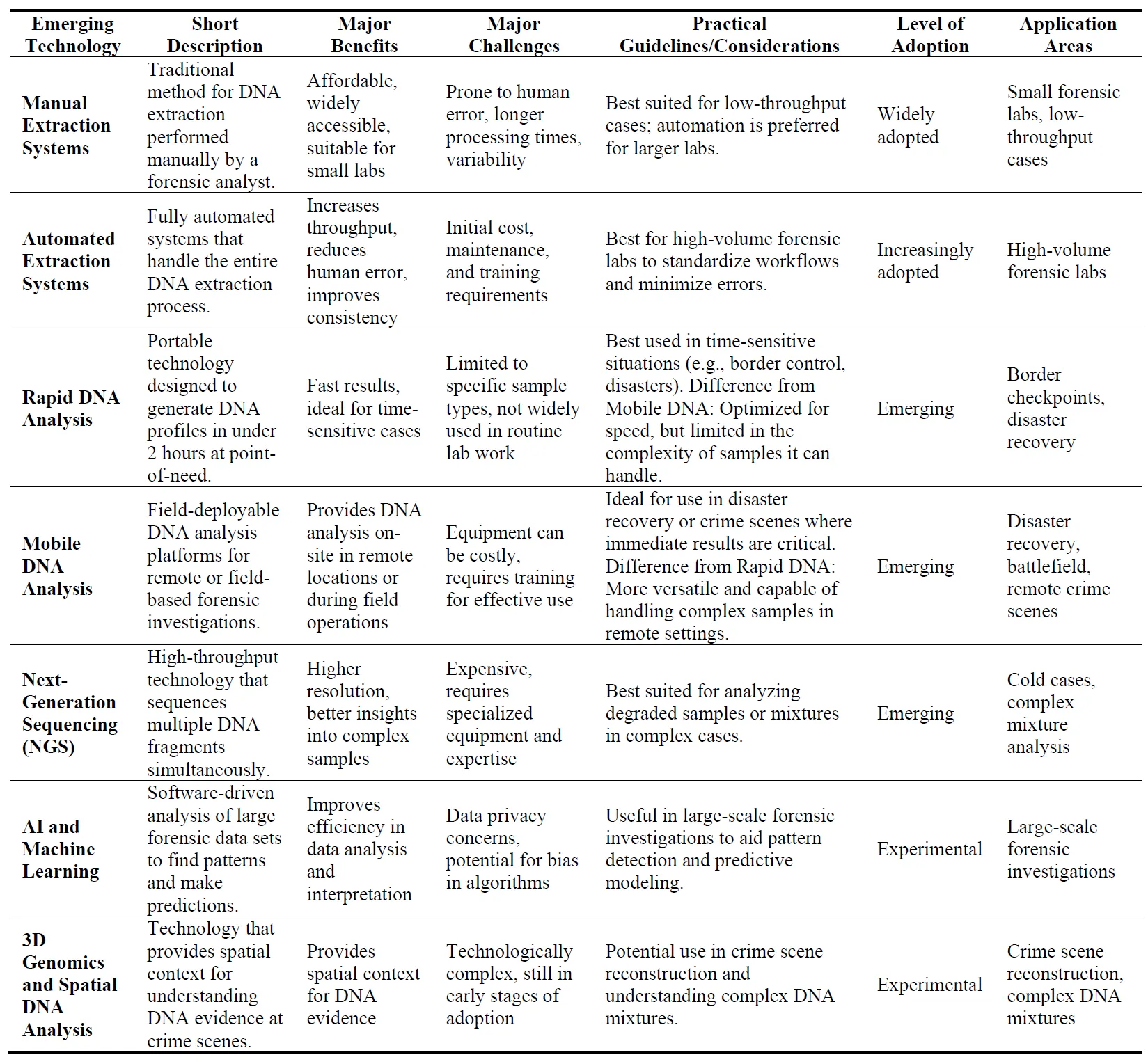
14 September 2024Emerging Technologies in Forensic DNA Analysis
Forensic DNA analysis has fundamentally transformed criminal investigations, providing an unprecedented level of accuracy in identifying suspects, exonerating the innocent, and solving cold cases. This manuscript reviews the emerging technologies that are reshaping the field of forensic DNA analysis, including next-generation sequencing (NGS), rapid DNA analysis, AI-driven forensic workflows, 3D genomics, and mobile DNA platforms. These innovations enhance the speed, precision, and scope of DNA analysis, allowing forensic scientists to process evidence more efficiently, analyze more complex samples, and conduct real-time field-based investigations. While these advancements hold great promise, they also introduce significant challenges, such as ensuring data security, maintaining the integrity of evidence, and navigating the ethical and legal implications of new forensic technologies. Issues related to privacy, consent, and potential bias in DNA databases are becoming increasingly complex as these systems expand. Furthermore, the legal admissibility of cutting-edge technologies like AI-driven DNA analysis and phenotypic prediction must be carefully evaluated to ensure the rigorous standards of forensic evidence in court are met.This review explores the opportunities and challenges associated with these emerging technologies, emphasizing the importance of responsible and ethical use. By examining advances in DNA extraction, spatial DNA analysis, and the integration of AI in forensic workflows, this manuscript provides forensic professionals with a roadmap for navigating the evolving landscape of forensic DNA analysis. The future of forensic DNA analysis lies in balancing technological innovation with the commitment to justice, ensuring that DNA evidence remains a reliable and indispensable tool in pursuing a more equitable legal system.