Found 301 results
Open Access
Review
21 February 2025Cement-Free Binders in Alumina-Magnesia Refractory Castables—A Review
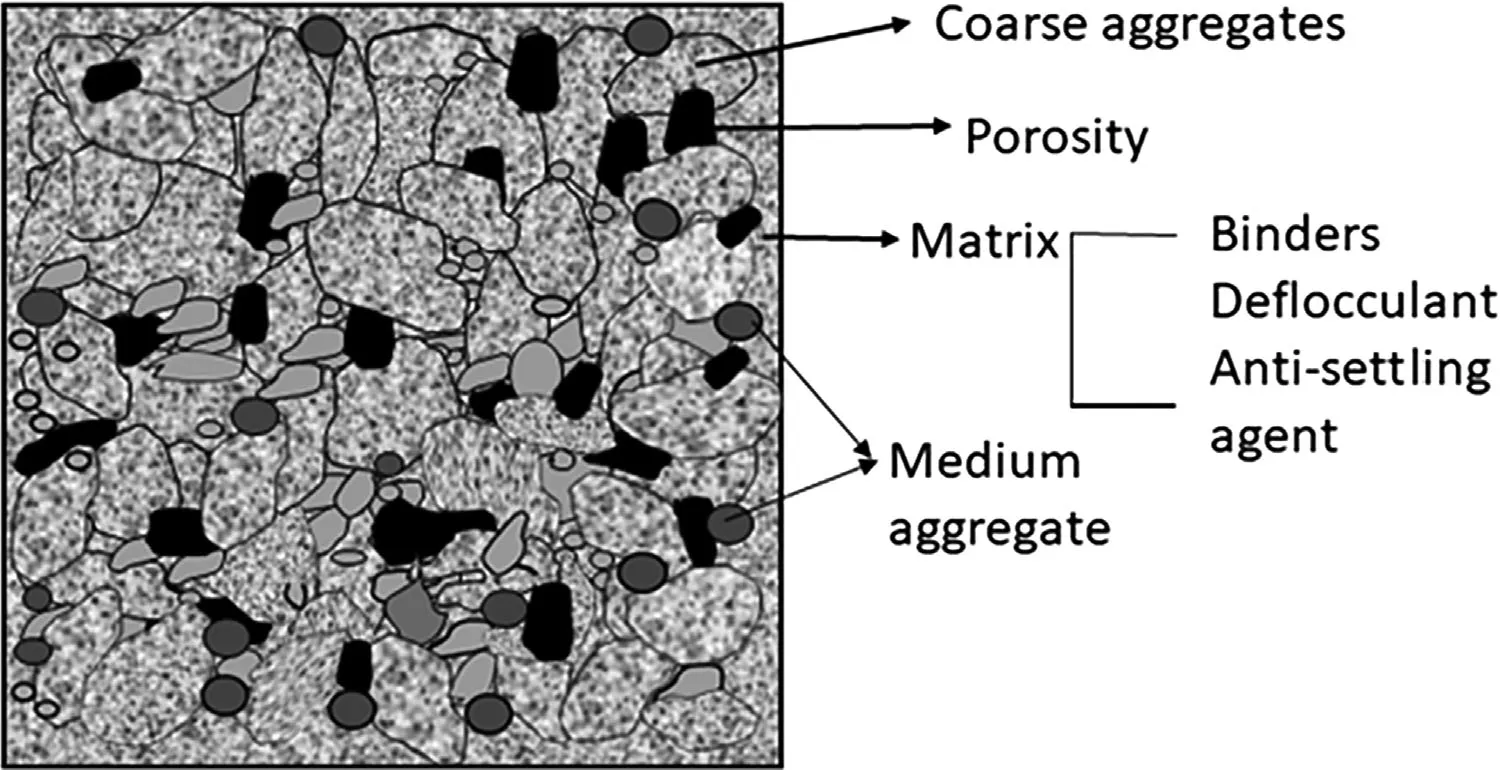
To solve the problem of the accelerated deterioration of calcium aluminate (CAC)-bonded alumina-magnesia refractory castables during the secondary refining process, the development of cement-free binders has emerged as one significant research field of castables. The hydration behavior, curing mechanism, and properties of the most recent research on cement-free binders are compared in this paper. The problems and the modification of each binder of recent research are summarized. High-temperature performance of the castables bonded by traditional hydraulic cement-free binders (ρ-Al2O3 and activated MgO) is outstanding, explosive spalling resistance of the castables bonded by sol binders (silica sol, alumina sol) is good, and the properties of the castables bonded by novel organic hydratable binder (hydratable magnesium citrate) combine the advantages of these two binders above, but the mid-temperature mechanical strength is low. Furthermore, alumina-magnesia castables bonded by organic-composited inorganic cement-free binders are expected to be a future domain.
Open Access
Review
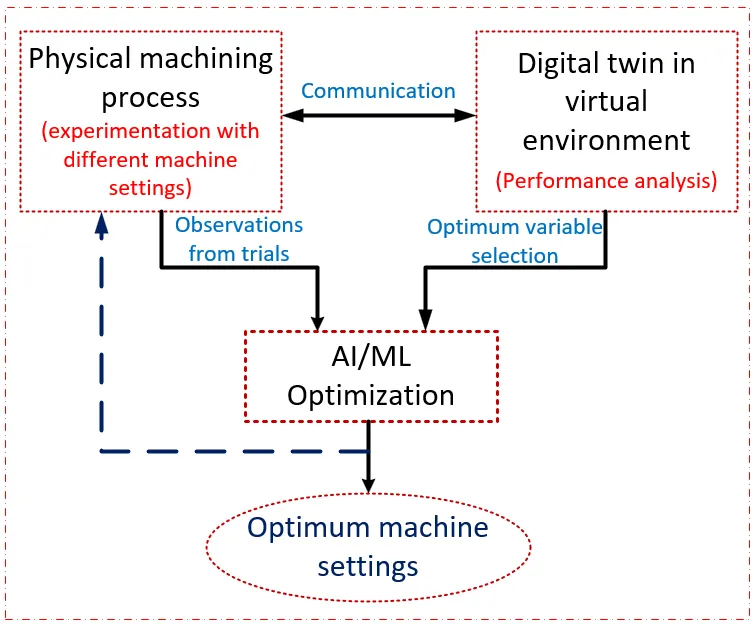
18 February 2025Digital Twin and Artificial Intelligence in Machining: A Bibliometric Analysis
The past decade has witnessed an exodus toward smart and lean manufacturing methods. The trend includes integrating intelligent methods into sustainable manufacturing systems purposely to improve the machining efficiency, reduce waste and also optimize productivity. Manufacturing systems have seen transformations from conventional methods, leaning towards smart manufacturing in line with the industrial revolution 4.0. Since the manufacturing process encompasses a wide range of human development capacity, it is essential to analyze its developmental trends, thereby preparing us for future uncertainties. In this work, we have used a Bibliometric analysis technique to study the developmental trends relating to machining, digital twins and artificial intelligence techniques. The review comprises the current activities in relation to the development to this area. The article comprises a Bibliometric analysis of 464 articles that were acquired from the Web of Science database, with a search period until November 2024. The method of obtaining the data includes retrieval from the database, qualitative analysis and interpreting the data via visual representation. The raw data obtained were redrawn using the origin software, and their visual interpretations were represented using the VOSviewer software (VOSviewer_1.6.19). The results obtained indicate that the number of publications related to the searched keywords has remarkably increased since the year 2018, achieving a record maximum of over 80 articles in 2024. This is indicative of its increasing popularity. The analysis of the articles was conducted based on the author countries, journal types, journal names, institutions, article types, major and micro research areas. The findings from the analysis are meant to provide a bibliometric explanation of the developmental trends in machining systems towards achieving the IR 4.0 goals. Additionally, the results would be helpful to researchers and industrialists that intend to achieve optimum and sustainable machining using digital twin technologies.
Open Access
Perspective
18 February 2025The Emerging “AI Artists”: Breaking the Metacrisis and the Fear of Losing Human Creativity
The emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) in the creative arts has ignited a global discourse on the intersection of technology, human creativity, and artistic expression. This paper examines the rise of “AI artists” within the broader context of neuropsychology, the metacrisis, and theories of art and creativity. Drawing on Ian McGilchrist’s hemispheric theory, it explores how AI, often associated with left-hemisphere analytical dominance, can paradoxically contribute to right-hemisphere creative processes. The study evaluates the role of AI in expanding artistic boundaries, democratizing creative expression, and redefining authorship, while addressing concerns about originality, cultural significance, and the potential devaluation of human-made art. Through an anthropological and philosophical lens, the paper argues that AI does not replace human creativity but rather augments it, offering novel tools for artistic exploration. By integrating insights from cognitive science, aesthetics, and digital humanities, this article positions AI as a collaborator in artistic evolution rather than a competitor. Ultimately, there is an assertion that the human capacity for meaning-making and emotional resonance remains irreplaceable, ensuring that human creativity persists and thrives alongside AI-generated art.

Open Access
Article
17 February 2025Comparative Study of Elastomer Nanocomposites Respectively Containing SWCNTs and MWCNTs
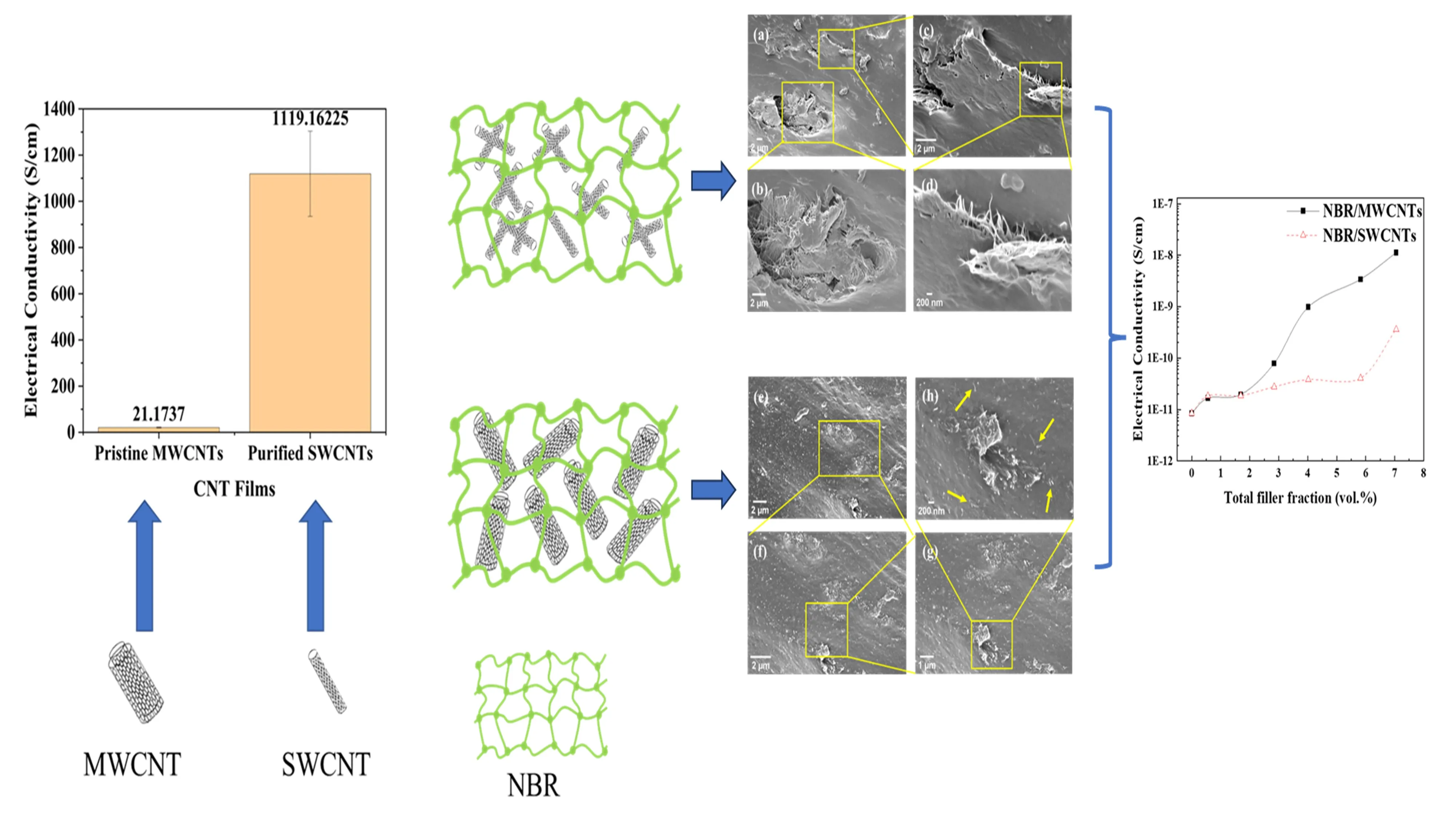
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are essential for providing polymers with mechanical reinforcement and multifunctional properties. This study investigated two groups of nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) nanocomposites containing single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), respectively. SWCNTs were purified to remove appro-ximately 20 wt.% of impurities, and both CNTs were modified with polyethylene glycol tert-octylphenyl ether (Triton X-100) before emulsion compounding and 2-roll milling with NBR. MWCNTs were found to disperse in the elastomer matrix relatively uniformly, while SWCNTs formed aggregates. Consequently, NBR/MWCNT nanocomposites exhibited superior mechanical properties, e.g. a tensile strength of 10.8 MPa at 4.02 vol.% MWCNTs, compared to 5.6 MPa for NBR/SWCNT nanocomposites. Additionally, NBR/MWCNT nanocomposites exhibited more remarkable electrical conductivity and swelling resistance to toluene. The diameter of elastomer macromolecules (0.2–0.5 nm) is close to that of SWCNTs (1–2 nm), and their single graphene wall with a hollow structure makes SWCNTs almost as flexible as elastomer macromolecules. This similarity suggests that SWCNTs should be treated as a special type of polymer. SWCNTs cannot disperse as uniformly as MWCNTs in the elastomer matrix, likely due to their smaller size and lower sensitivity to mechanical shearing during the emulsion compounding and 2-roll milling process.
Open Access
Article
11 February 2025Functionalization of 3D-Printed Plastics for the Photocatalytic Removal of Organic Pollutants in Air
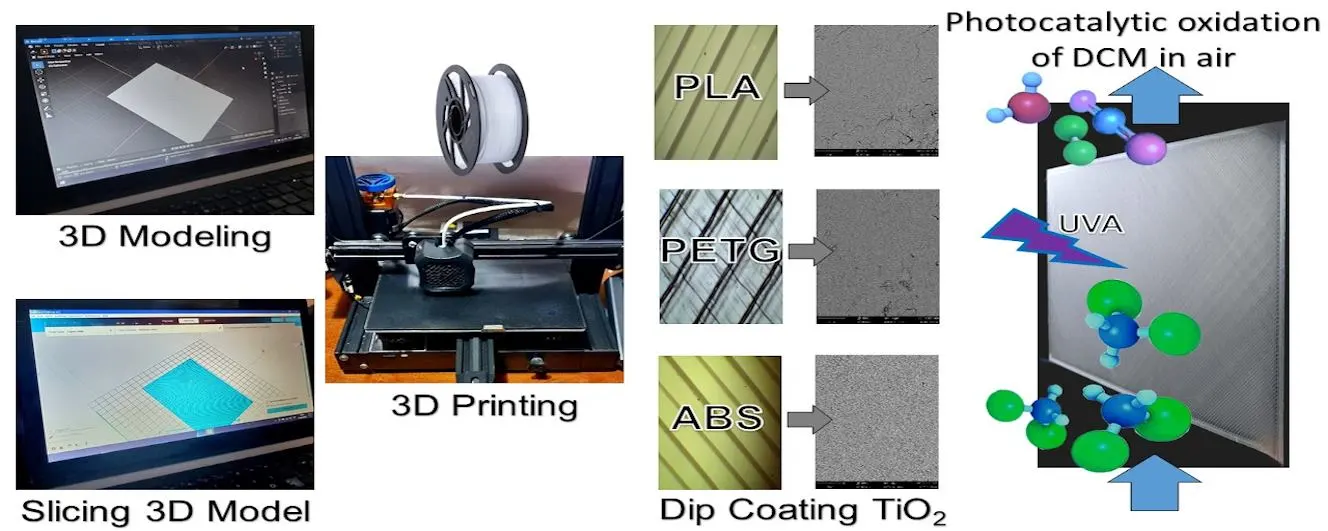
The study explored the use of 3D-printed plastics as catalyst supports for gas-phase photocatalytic applications. Specifically, it compared three commonly used plastic materials: PLA, ABS, and PETG. The process involved 3D modeling, additive manufacturing through 3D printing, and functionalization via dip-coating with titanium dioxide (TiO2). The study evaluated the loading capacity of the materials, the adhesion of the films, and the optical properties of the photocatalytic plates. Finally, the three plastic samples were tested as support materials in a laboratory-scale flat-plate reactor for the photocatalytic oxidation of dichloromethane in air. Loading capacities of around 3 mg/cm2 for TiO2 were achieved, along with radiation absorption capacities close to 65%. A correlation between loading and absorption fraction was identified, leading to the proposal of a simple saturation model; in turn, it allowed the predictive model of pollutant conversion as a function of the absorbed fraction of radiation. By analyzing both qualitative and quantitative properties and results, in order to determine the most suitable plastic material to be used in a photocatalytic wall reactor, PLA emerged as the best choice among the materials tested. These results show promise for the effective utilization of these plastics in the design of air decontamination devices.
Open Access
Article
06 February 2025Performance Impacts of Rainwater Tanks on Stormwater Drainage Systems
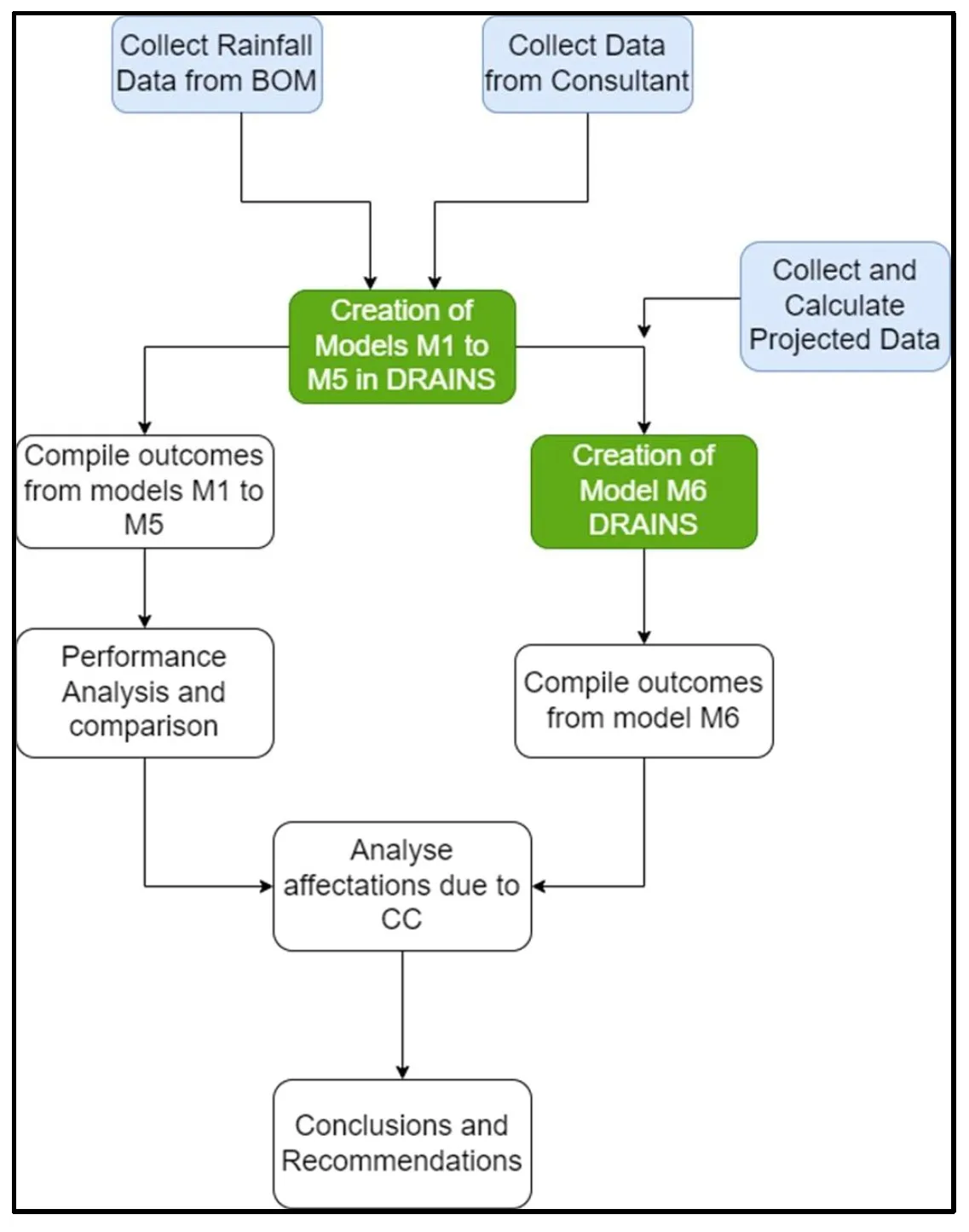
This article explores the impact of using rainwater tanks on the performance of a stormwater drainage system and the possible challenges posed by climate change and future rainfall projections. This project examines a residential development in Aldinga, South Australia. The study sets clear research objectives that include the creation and simulation of drainage systems with different conditions (e.g., with and without rainwater tanks, historical data, and projected data). The aim is to analyze performance changes in the drainage network after the inclusion of rainwater tanks. Furthermore, the incorporation of projected rainfall data is considered to study possible implications of climate change on the system performance. The methodology follows a quantitative approach, with data collection, creating different models with the use of software, and simulating various conditions such as storms with different annual exceedance probabilities and varying proportions of roof area connected to rainwater tanks. Several findings are identified in this project. When roof areas of all residential allotments are connected to rainwater tanks, substantial benefits are observed in reducing peak flows within the network and runoff volumes. This proportion of connected roof area is directly correlated with reductions in peak flow. Also, while the use of projected rainfall data slightly affects benefits in peak flow and volume reduction, they will remain relatively high at least until 2050. Other performance features, such as hydraulic gradient line, long sections, and time to peak, are also explored. Study validates the hypothesis that rainwater tanks have a significant impact on runoff reductions and flood management, particularly when 100% of roof area is connected with rainwater tanks. Also, there is an impact when projected data is used, but it remains manageable and should be considered under specific contexts to decide whether these impacts are significant. Several opportunities for future research are suggested. These include the examination of larger areas, projections to a more distant future, the use of different rainfall patterns, and the consideration of extreme rainfall events.
Open Access
Review
20 January 2025Adsorption and High-Value Transformation of Volatile Fatty Acids from Microbial Fermentation Products: A Review
To mitigate the aforementioned global environmental issues, the concept of carbon capture and storage is crucial in addressing the necessity for carbon peaking and carbon neutrality. The buildup of volatile fatty acids during anaerobic fermentation is a primary factor contributing to the suboptimal performance or outright failure of anaerobic digestion systems. In response to the pressing demand for volatile organic acid recovery and high-value conversion, we primarily outlined the sources, recovery techniques, adsorption materials, and methods for high-value conversion of volatile fatty acids. The methods of adsorbing volatile acetic acid were presented, encompassing adsorption materials, mechanisms, and interfacial modifications of the adsorbent. Furthermore, drawing from recent research advancements, we have synthesized the high-value conversion techniques for volatile fatty acids and evaluated the research challenges and future prospects in this domain.
Open Access
Article
20 January 2025Visible Monuments above and below Ground Level, a Time-Honored Site from the Late Bronze Age to Modern Times
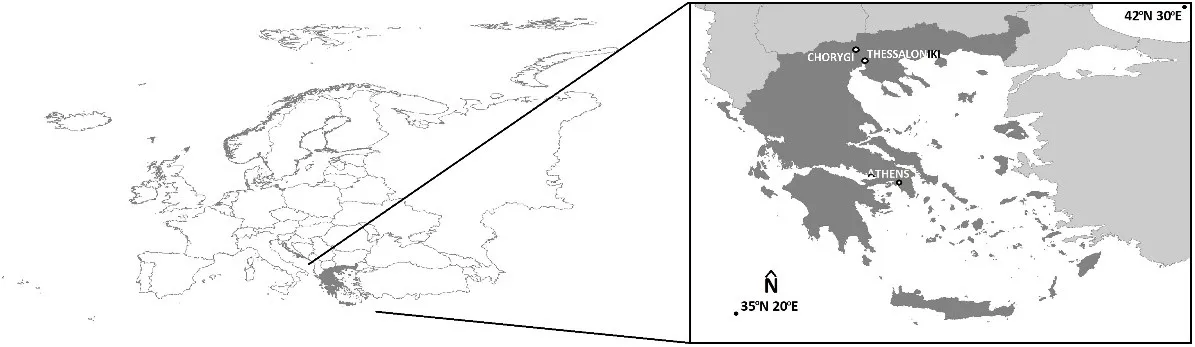
Due to the complex geometry of the monuments, it is often necessary to adapt the image collection process for their mapping. For the optimal mapping of the stronghold of Lazaritsa Chorygi (Greece) and its slopes, vertical, inclined, and horizontal images from different heights were collected using an Unmanned Aircraft System. Thus, for a monument of special archaeological/historical interest and natural beauty, a large set of high-spatial resolution data and final products (digital surface model and orthophotomosaic with spatial resolution 5.6 cm and 2.8 cm, respectively) is available. In addition, in the wider area of the fortified site, military structures (fire trenches, communication trenches, shelters, front and support trenches, and strong points) of the Great War length of 9 km were identified and mapped, which were identified in the 2003 or 2004 Google Earth Pro images, but worryingly are almost absent from the contemporary Google Earth Pro images.
Open Access
Review
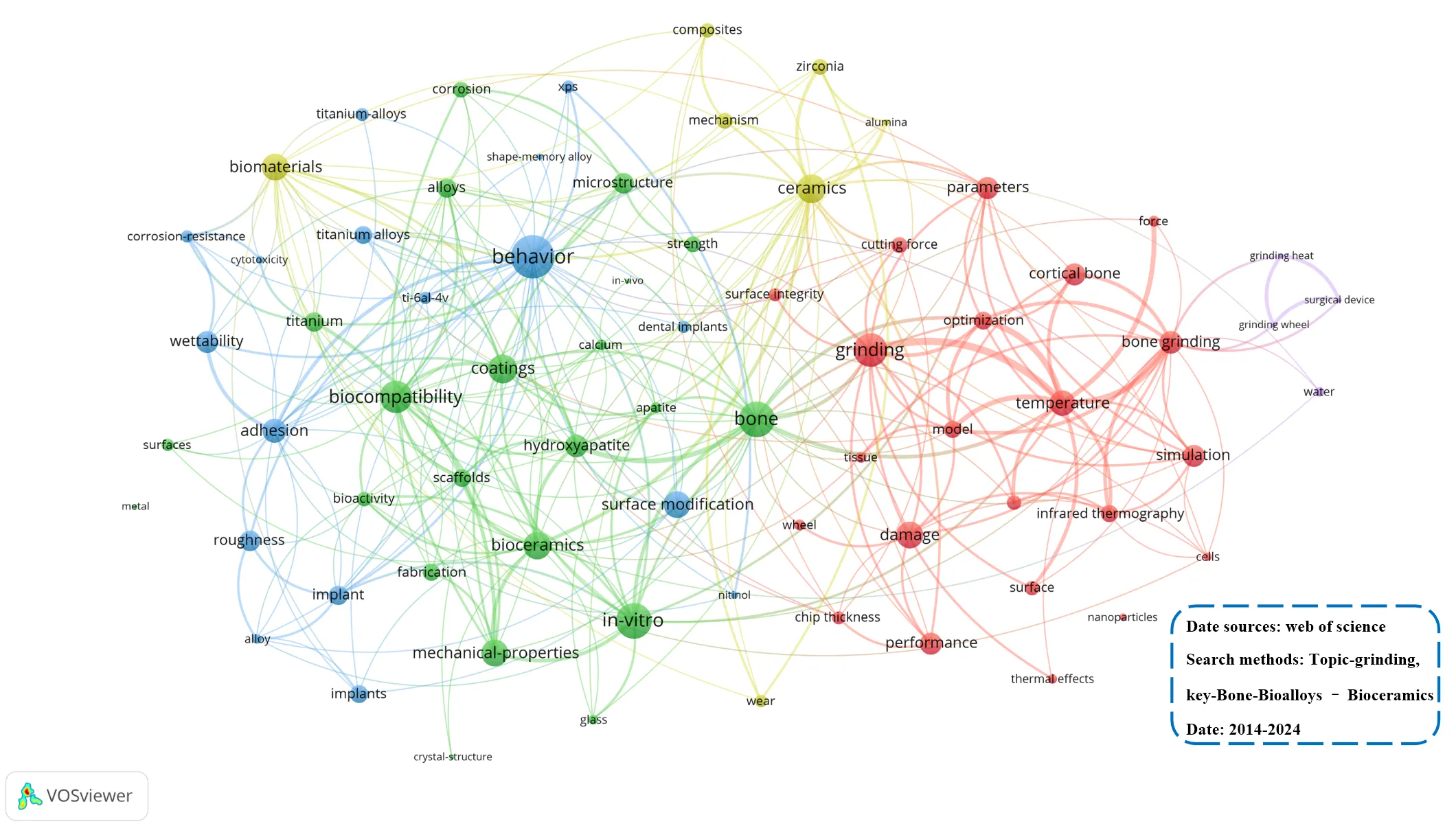
16 January 2025Biological Bone and Replacement Materials in Grinding: Force Model and Processing Capability
Grinding is widely used in orthopedic surgery to remove bone tissue material, but due to the complex and brittle structure of bone, it is prone to mechanical stresses that cause cracks and damage to the bone tissue. Furthermore, bone replacement materials typically have high hardness, strength, and brittleness, which lead to increased tool wear and damage, such as cracks and deformation during grinding. Therefore, ensuring the surface quality of bone and replacement materials during the grinding process has become a critical issue. This necessitates the development of grinding force models that consider various processing parameters, such as feed rate and cutting depth, to guide industrial production. However, currently, research on the grinding force prediction models for bone tissue and its replacement materials is relatively scarce, and there is a lack of corresponding grinding force model reviews for unified guidance. Based on this, this article focuses on bone grinding technology and, conducts a critical comparative analysis of the grinding force models for bone tissue and its replacement materials, and then summarizes the grinding force prediction models in the grinding process of bone tissue and bone replacement materials. First, according to the material types and material removal mechanisms, the materials are categorized into bone tissue, bio-inert ceramics, and bio-alloys, and the material removal process during grinding is analyzed. Subsequently, the grinding force prediction models for each material and the accuracy errors of each model are summarized. The paper also reviews the application of these grinding force prediction models, explaining how processing parameters such as feed rate and cutting depth influence grinding forces and their interrelationship. Finally, in light of the current issues in the grinding of bone tissue and replacement materials, potential future research directions are proposed, aiming to provide theoretical guidance and technical support for improving the grinding quality of bone tissue and its replacement materials.
Open Access
Review
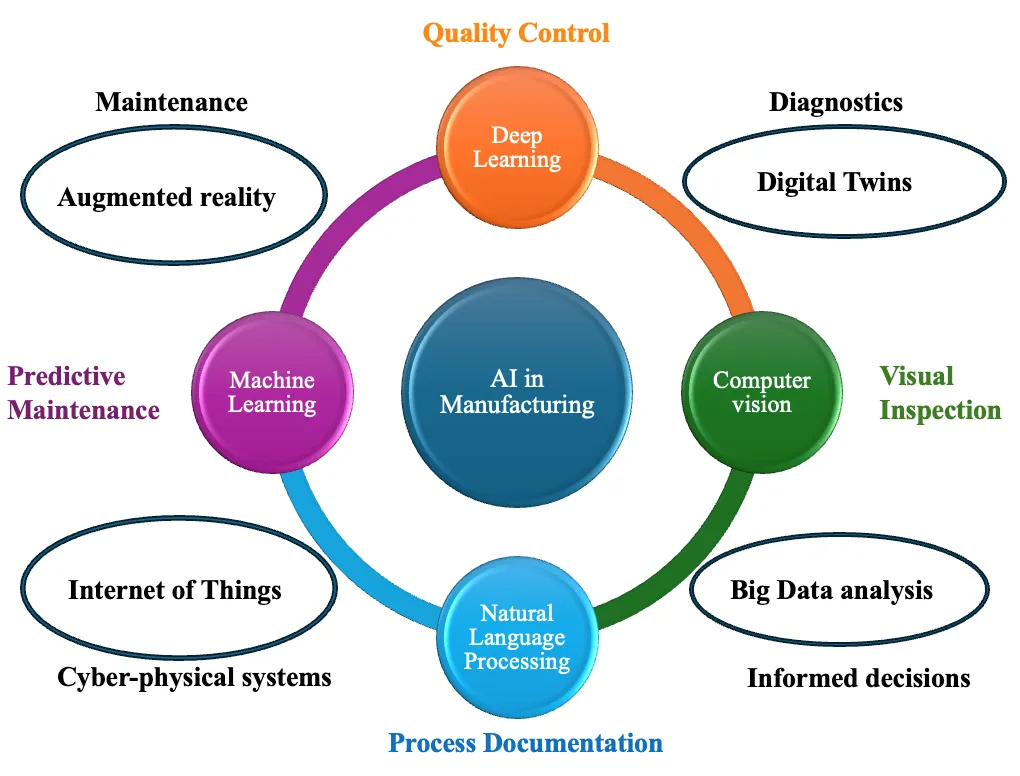
14 January 2025Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Sustainable Manufacturing: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming manufacturing processes, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance sustainability and environmental stewardship. This comprehensive review analyzes the transformative impact of AI technologies on sustainable manufacturing, focusing on critical applications, including energy optimization, predictive maintenance, waste reduction, and circular economy implementation. Through systematic analysis of current research and industry practices, the study examines both the opportunities and challenges in deploying AI-driven solutions for sustainable manufacturing. The findings provide strategic insights for researchers, industry practitioners, and policymakers working towards intelligent and sustainable manufacturing systems while elucidating emerging trends and future directions in this rapidly evolving field.