Found 301 results
Open Access
Article
23 April 2025Evaluating Everyday Prospective Memory in School-Age Children through Parent- and Self-Reports: Validating Questionnaires and Examining Relations to Executive Functions and Autistic Traits
Prospective memory (PM) refers to the ability to remember to complete everyday tasks, and in adults, PM is often assessed using the Prospective and Retrospective Memory Questionnaire (PRMQ). However, this questionnaire has not been validated in children, and whether it is effective in detecting subtle PM and retrospective memory (RM) difficulties in subclinical populations remains unclear. Study 1 first validated the parent-reported PRMQ for children (PRMQC-p) and developed a self-reported version (PRMQC-s), and Study 2 examined the relationships among PM, executive functions, and autistic traits using parent-reported questionnaires. The study recruited 1127 children aged 6–12 years and their parents. Parents completed questionnaires assessing PM, executive functions, and autistic traits, while children completed the PRMQC-s. Confirmatory factor analysis indicated that both versions of PRMQC showed good reliability and supported the PM-RM correlated factor model. Preliminary norms were generated to allow quick evaluation of children’s everyday PM and RM performance. Importantly, higher autistic traits were associated with more frequent PM errors and executive functions completely mediated this relationship. These findings suggest that the PRMQC is a valid and useful tool for evaluating children’s everyday PM performance and emphasizes the critical role of executive functions in daily PM.

Open Access
Article
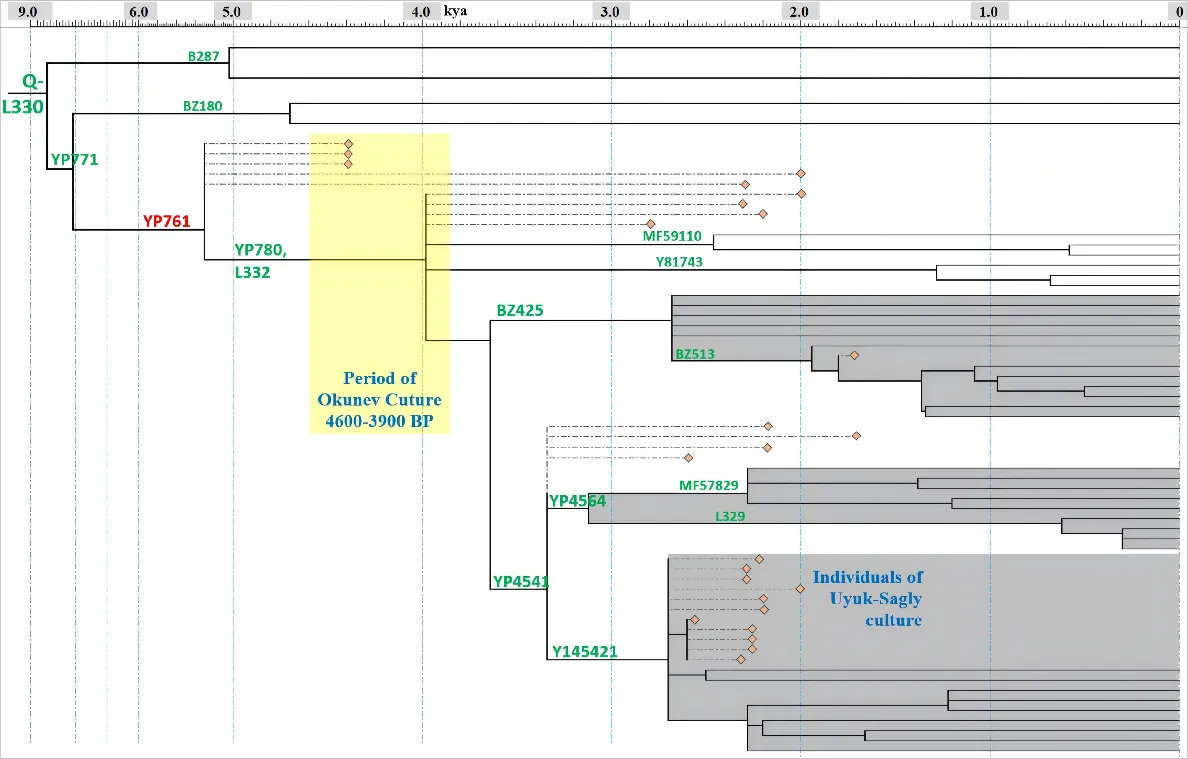
18 April 2025Demographic History of Ancient Okunev People and Their Kin across Eurasia: A Patrilineal Perspective
The ancient Okunev culture in South Siberia is renowned for its mysterious artistic and cultural legacy and belief system. Many later, Eurasian steppe peoples are thought to have inherited elements of the Okunev culture, but its origins and evolution remain unclear. Previous research of ancient DNA (aDNA) indicated that the primary paternal lineage of the ancient Okunev people was Q-L330-YP761. In this study, we sequenced 25 modern samples from this haplogroup and analyzed them alongside 26 ancient samples and 10 modern samples from public sources. The updated, high-resolution phylogenetic tree shows paternal lineage Q-L330-YP761 expanded significantly during the Okunev culture. Its downstream subclade Y145421 was the main paternal type of the Chandman culture. Phylogeographic analysis indicates that Q-L330-YP761 largely integrated into the Xiongnu, Tiele, and Han Chinese populations after the Okunev culture. Many downstream branches of Q-L330-YP761 also migrated westward to Central Asia and Europe. In summary, Q-L330-YP761 is considered one of the genetic lineages that have migrated across the Eurasian steppe since the Bronze Age.
Open Access
Article
18 April 2025Strata Use in a Canopy Beetle Community of a Lowland Neotropical Rainforest in Southern Venezuela
Stratification of tropical rainforests and their arthropods is highly pronounced. I hypothesize that the occurrence of rainforest canopy beetles in the understory is not random but related to the ecology of the taxa, such as feeding guilds and larval development. Therefore, the ecological characteristics of stratum generalists recorded in both the canopy and the lower understory were analyzed. Adult beetles were collected manually and with traps in the northern part of the Amazonian rainforest for a cumulative year. Seventy out of a total of 862 canopy beetle species from 45 families associated with 23 tree species were shared between both strata. The beetle families represented by most species in the canopy and ground samples were Curculionidae, Chrysomelidae, and Carabidae. For Elateridae and Scarabaeidae, the proportion of shared species between the strata was ≥20%. In contrast, the species-rich families (≥20 canopy species) Cerambycidae, Mordellidae, and Buprestidae did not comprise species sampled in both strata. Thus, beetle families comprising many stratum generalists are either largely predatory, or their larvae often develop in the soil.

Open Access
Review
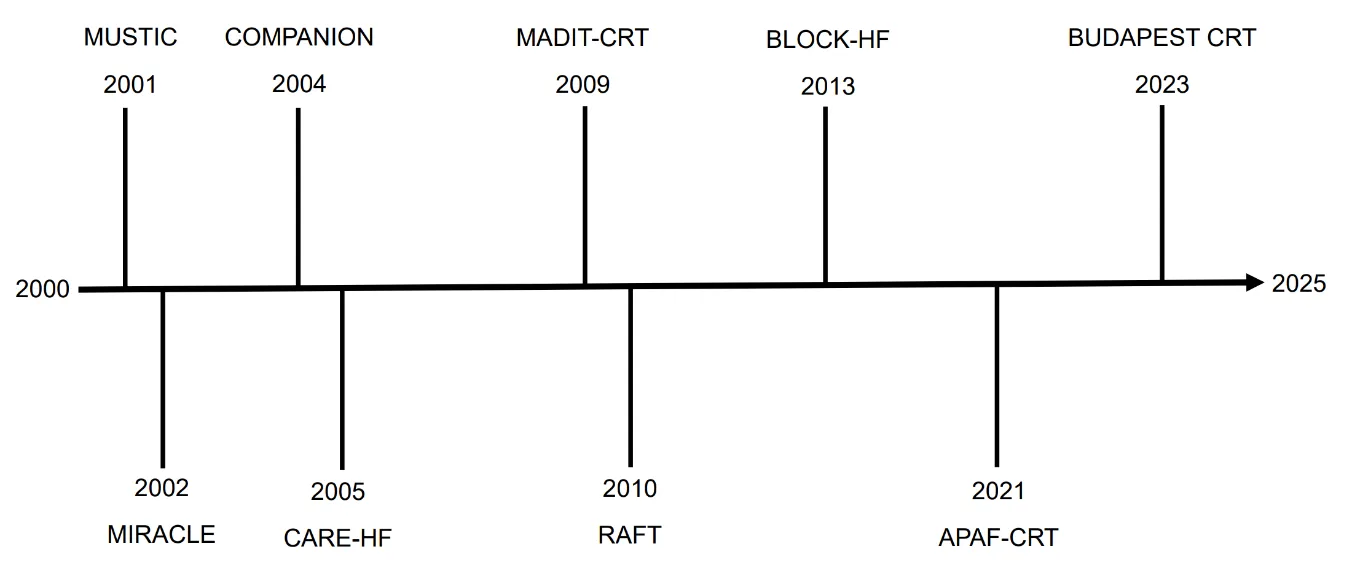
17 April 2025Advances in Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy
Cardiac resynchronisation therapy (CRT) has emerged as a transformative treatment in heart failure management, particularly for patients with significant left ventricular systolic dysfunction in the context of electrical dyssynchrony. Over time, CRT has evolved to address broader patient populations and more complex clinical scenarios. Despite its well-documented benefits in improving survival, reducing hospitalisation and enhancing quality of life, approximately 30% of patients fail to respond, making ongoing research critical for optimising outcomes. This review provides a comprehensive update on the evolving landscape of CRT therapy. Focus is placed on expanding indications, novel assessment techniques for dyssynchrony, application in special populations and innovations in device programming.
Open Access
Article
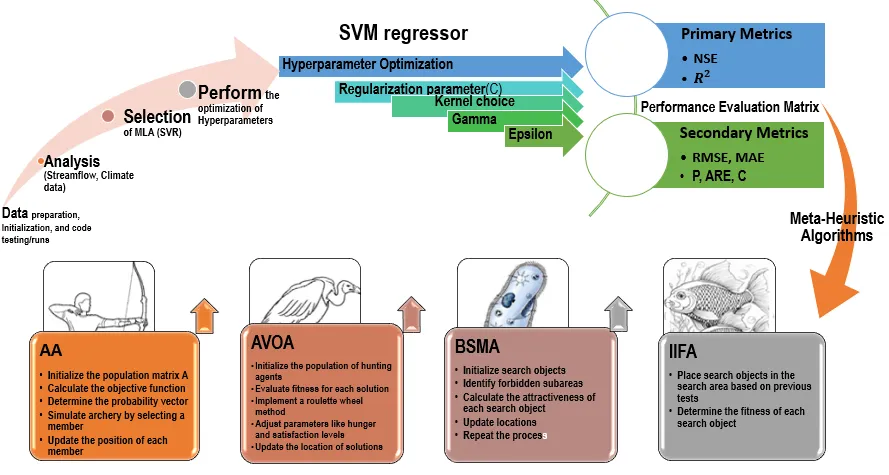
15 April 2025Enhancing Streamflow Forecasting in Major West African Rivers by Utilizing Meta-Heuristic Algorithms and Climate Data Time Lag Analysis
Accurate streamflow prediction is essential for irrigation planning, water allocation, and flood risk management, particularly in water-scarce regions like the Niger River Basin. However, the complexity of hydrological processes and data limitations make reliable predictions challenging. This study optimizes Support Vector Machine (SVM) hyperparameters for daily streamflow prediction using time-lagged climate data and four metaheuristic algorithms—Binary Slime Mould Algorithm (BSMA), African Vulture Optimisation Algorithm (AVOA), Archery Algorithm (AA), and Intelligent Ice Fishing Algorithm (IIFA). Model performance was assessed using eight evaluation metrics, with results showing that AA and IIFA consistently outperform the others, achieving Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) values between 0.986–0.999 and 0.893–0.999, respectively. AVOA and BSMA show less consistent performance, with NSE ranges of 0.524–0.999 and 0.863–0.965, respectively. The study highlights the novel integration of multiple metaheuristic algorithms for optimizing machine learning models, offering insights into their effectiveness for hydrological prediction. By demonstrating the superior performance of AA and IIFA, this research provides a robust framework for enhancing long-term streamflow forecasting. These findings support improved water resource management in West Africa, helping policymakers address climate variability, water scarcity, and hydrological uncertainty.
Open Access
Review
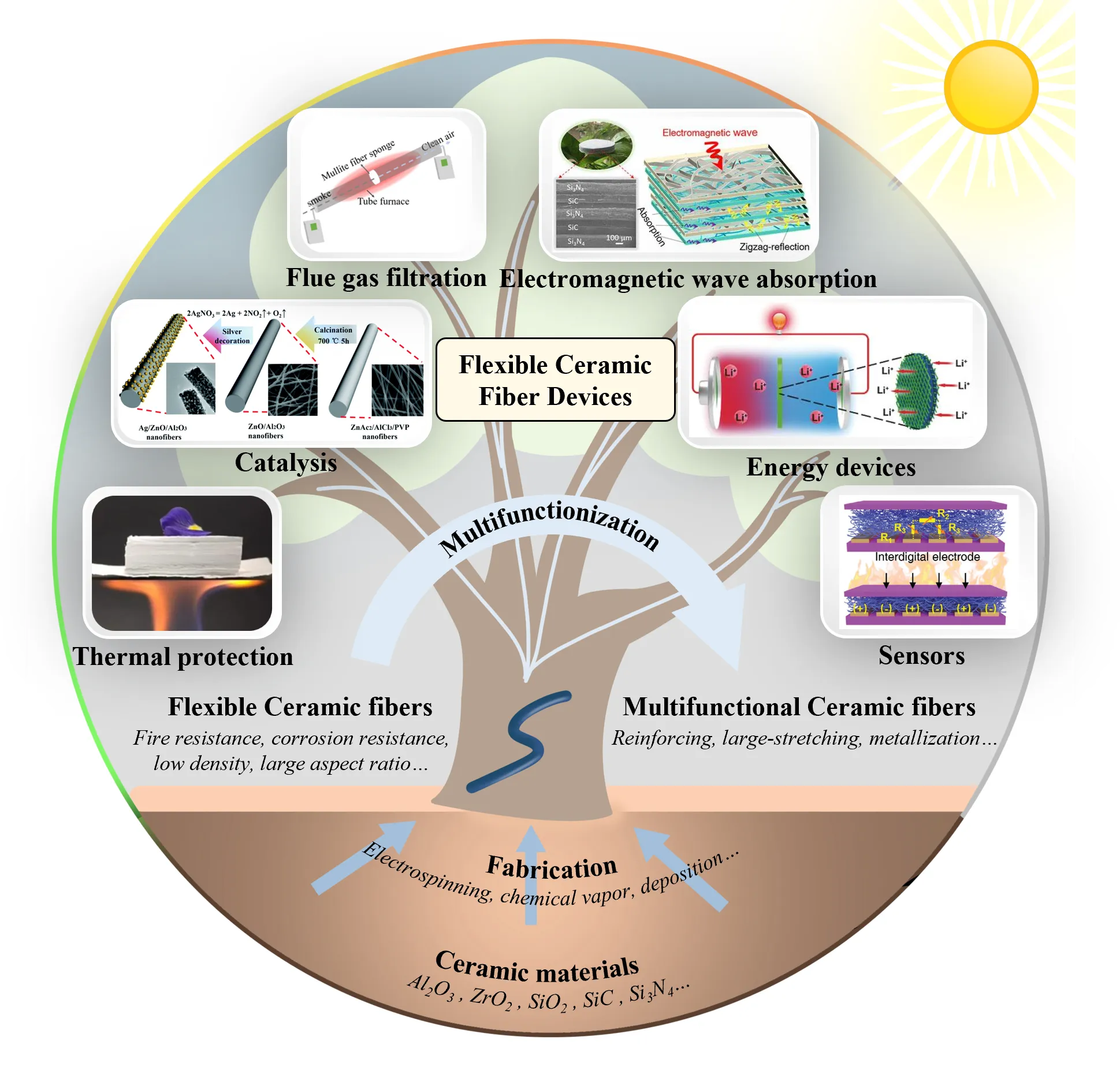
14 April 2025Advancements in Flexible Ceramic Fibers for High-Temperature Applications: A Comprehensive Review
Flexible ceramic fibers (FCFs) have emerged as a highly promising material for high-temperature applications, effectively combining the excellent thermal stability of ceramic materials with the robust mechanical properties of flexible fibers. This review provides a comprehensive overview of recent advances in multifunctional FCF devices, focusing on innovative methods across material selection, structural design, and fabrication techniques to enhance their functional properties. These improvements, i.e., mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and oxidation resistance, make FCFs particularly suitable for a wide range of applications, including energy storage, sensing, and high-temperature filtration. Notably, advancements in fabrication techniques have enabled the creation of novel FCF devices for thermal insulation and high-temperature sensing, such as stretchable ceramic membranes and printable ceramic fiber papers. The review concludes by discussing the future potential of FCFs, especially in multifunctional applications in high-temperature environments, where they can serve as essential components of advanced technologies. This work highlights the versatility and potential of FCFs as a transformative material for next-generation high-temperature applications.
Open Access
Article
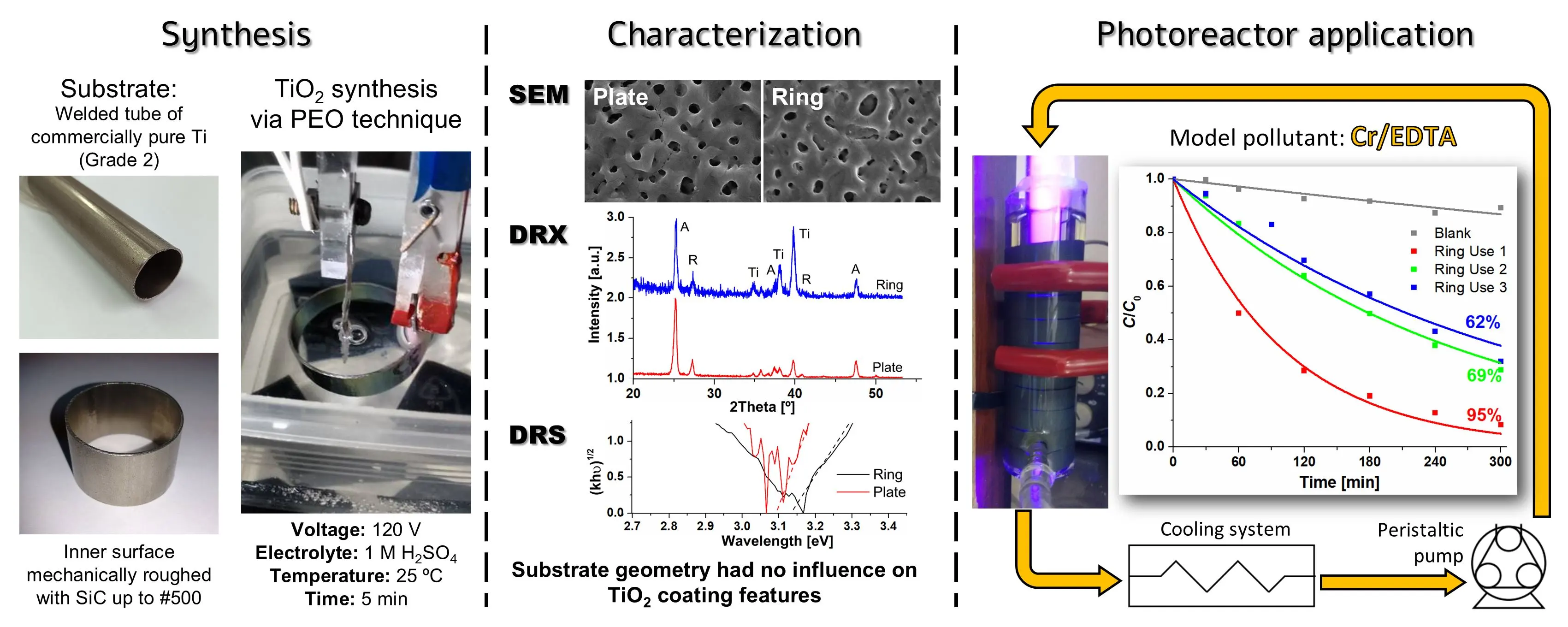
03 April 2025Design, Building and Performance of a New Photocatalytic Reactor Using TiO2-Coated Rings Synthesized by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation
An annular UV photocatalytic reactor with recirculation in batch was designed and built. The design considered low construction, simple operation and maintenance costs, availability and durability of the materials used, easy cleaning, and high standards of hygiene and safety. The TiO2 photocatalysts were synthesized by plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) on commercial Ti rings were compared with coatings obtained on Ti plates as a reference, and no influence of the substrate geometry on the morphology, crystallinity, or bandgap of the coatings was observed. The efficiency of the photocatalytic reactor using 10 TiO2-coated rings was tested by Cr(VI) transformation in the presence of EDTA. The Cr(VI) transformation after 5 h irradiation attained 95%; a rather high photocatalytic activity (62%) was maintained after the third use of the rings without reactivation of the photocatalyst. These coatings synthesized by PEO have not been applied in modular photocatalytic reactors until now.
Open Access
Review
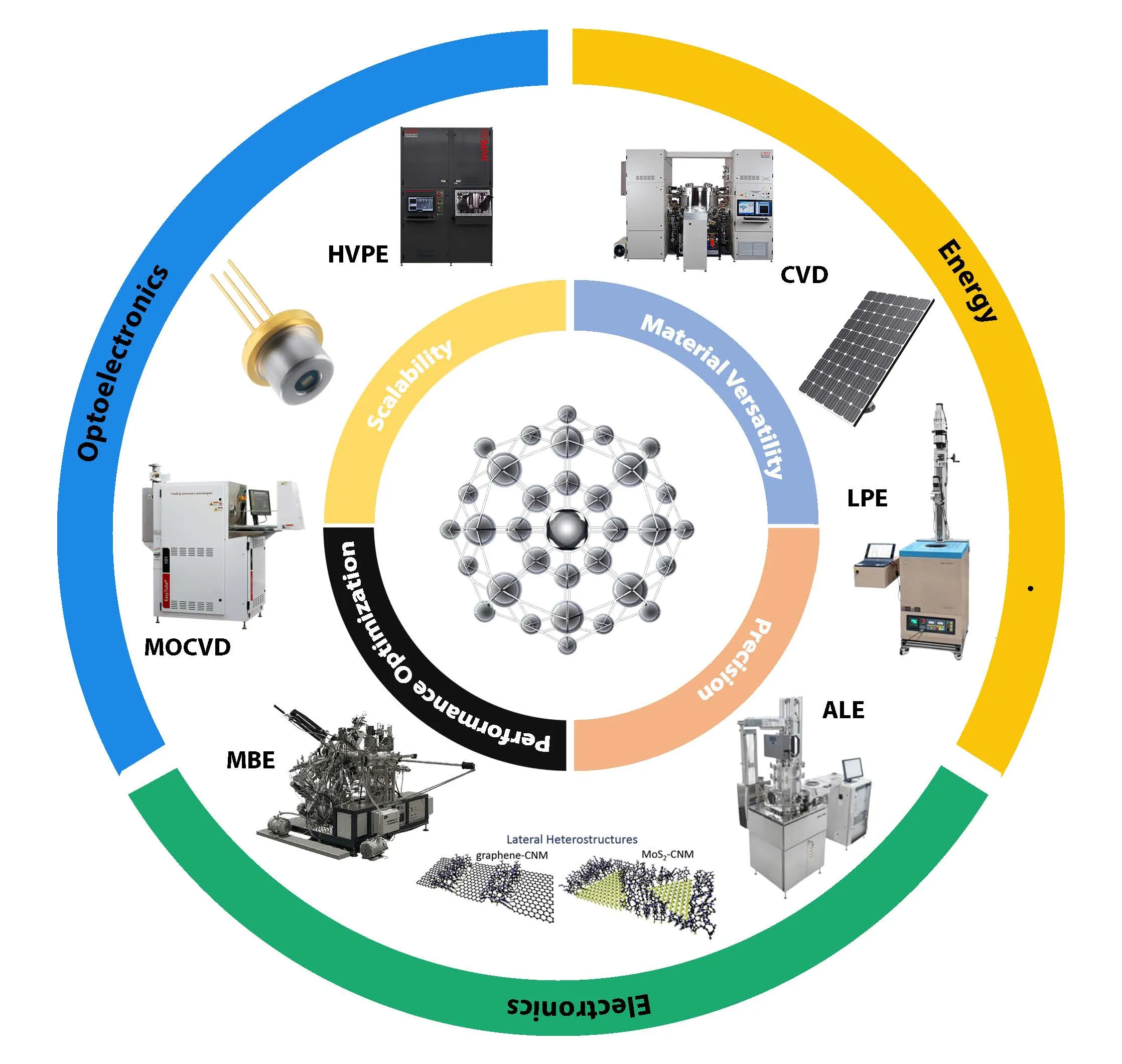
02 April 2025Wide-Bandgap Semiconductors: A Critical Analysis of GaN, SiC, AlGaN, Diamond, and Ga2O3 Synthesis Methods, Challenges, and Prospective Technological Innovations
The increasing demand for high-performance Wide-Bandgap (WBG) semiconductors, including GaN, SiC, and emerging Ultrawide-Bandgap (UWBG) materials such as Ga2O3 and diamond, has driven significant advancements in epitaxial growth techniques. However, achieving scalability, defect-free growth, and sustainability remains a major challenge. This review systematically evaluates Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE), Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD), Hydride Vapor Phase Epitaxy (HVPE), and other novel growth and hybrid growth techniques, emphasizing energy efficiency, defect control, and environmental impact. Industry 4.0-driven AI-based process optimization and closed-loop recycling have emerged as transformative strategies, reducing waste and improving manufacturing efficiency. Key findings reveal that HVPE enables rapid defect-free GaN fabrication, Hot-Filament CVD enhances SiC growth with superior thermal properties, and Atomic Layer Epitaxy (ALE) achieves sub-nanometer precision crucial for next-generation quantum and RF applications. Despite these advancements, p-type doping in UWBG materials, substrate compatibility, and thermal management remain unresolved challenges. Future research must focus on scalable eco-friendly epitaxy, novel doping mechanisms, and policy-driven sustainability efforts. This review provides a comprehensive roadmap for sustainable WBG semiconductor manufacturing, bridging materials innovation, energy efficiency, and industrial adoption to support the next generation of power electronics and optoelectronics.
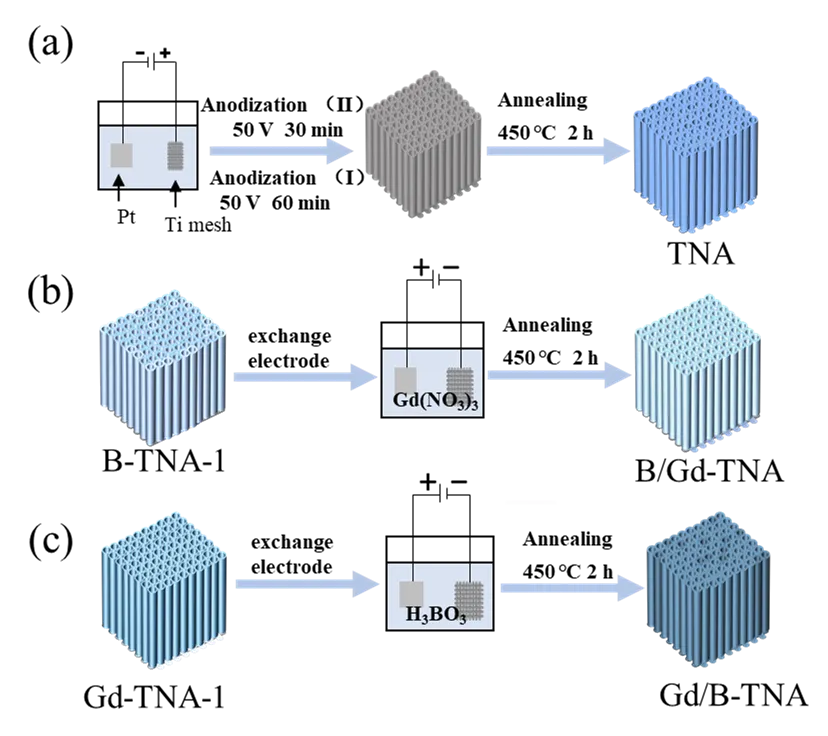
Open Access
Article
01 April 2025B, Gd Co-Doped TiO2 Nanotube Arrays for Efficient Degradation of Gaseous Toluene under Visible Light Irradiation
Although photocatalytic degradation of VOCs has attracted widespread attention, the efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation performance remains a challenge. This work presents the visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of gaseous toluene over B, Gd co-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays prepared via a controllable electrochemistry method. It was found that B and Gd co-doping strategy not only enhances the visible light responsiveness of TiO2 nanotube arrays but also introduces moderate oxygen vacancies on the surface of TiO2, which is beneficial to the formation of free hydroxyl radicals and their attack on toluene molecules. The doping order also affects the photocatalytic performance. The optimized sample achieves an enhanced degradation efficiency for toluene under visible light irradiation and exhibits considerable stability. This work may provide an efficient TiO2-based photocatalyst for the removal of volatile organic compounds for air purification and give an understanding of the mechanism of photocatalytic degradation of toluene over co-doping TiO2.