Found 301 results
Open Access
Article
15 May 2025Enhanced Spatial Transcriptomics Analysis of Mouse Lung Tissues Reveals Cell-Specific Gene Expression Changes Associated with Pulmonary Hypertension
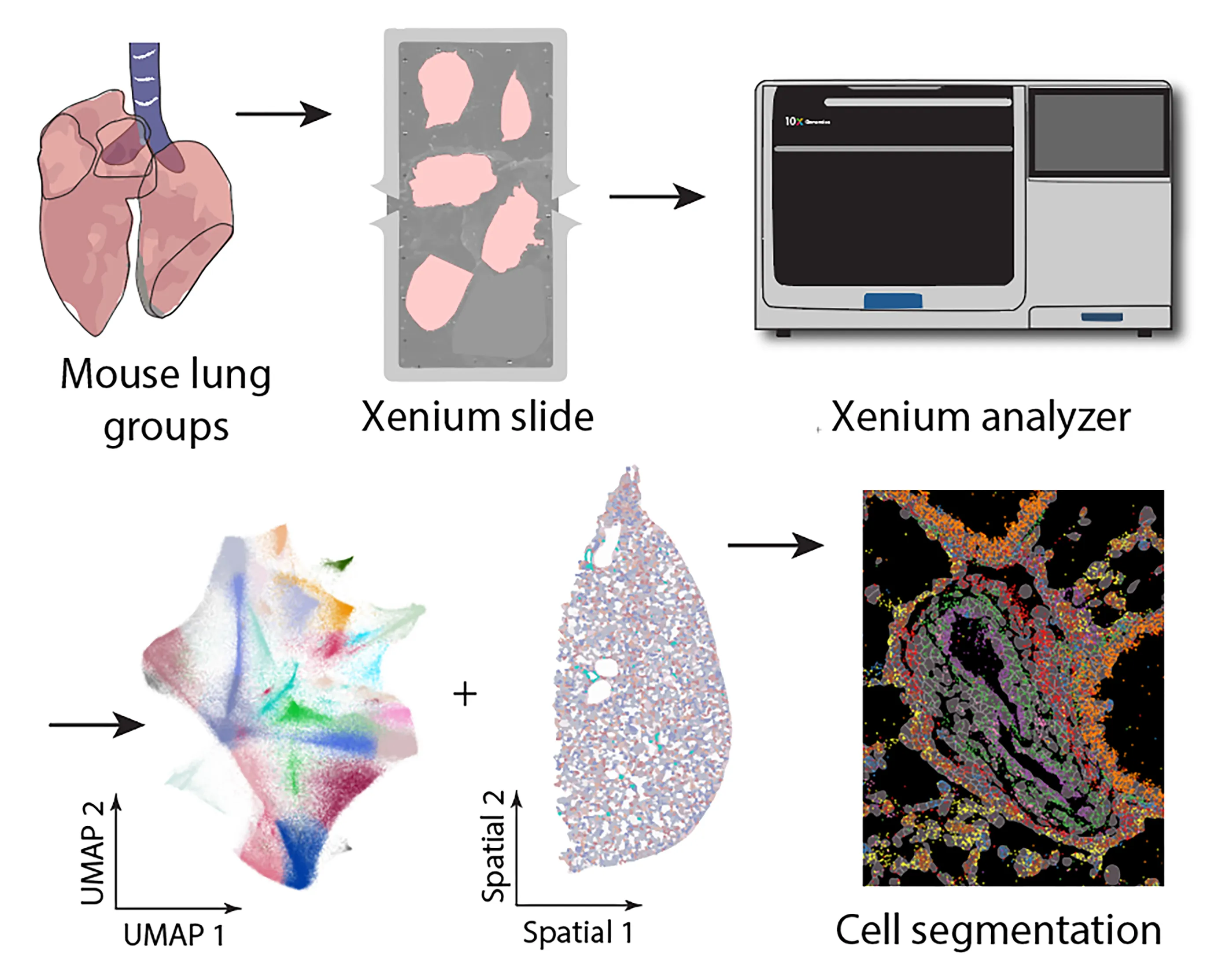
Spatial transcriptomics technologies have emerged as powerful tools for understanding cellular identity and function within the natural spatial context of tissues. Traditional transcriptomics techniques, such as bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing, lose this spatial information, which is critical for addressing many biological questions. Here, we present a protocol for high-resolution spatial transcriptomics using fixed frozen mouse lung sections mounted on 10X Genomics Xenium slides. This method integrates multiplexed fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) with high-throughput imaging to reveal the spatial distribution of mRNA molecules in lung tissue sections, allowing detailed analysis of gene expression changes in a mouse model of pulmonary hypertension (PH). We compared two tissue preparation methods, fixed frozen and fresh frozen, for compatibility with the Xenium platform. Our fixed frozen approach, utilizing a free-floating technique to mount thin lung sections onto Xenium slides at room temperature, preserved tissue integrity and maximized the imaging area, resulting in high-fidelity spatial transcriptomics data. Using a predesigned 379-gene mouse panel, we identified 40 major lung cell types. We detected key cellular changes in PH, including an increase in arterial endothelial cells (AECs) and fibroblasts, alongside a reduction in capillary endothelial cells (CAP1 and CAP2). Through differential gene expression analysis, we observed markers of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and fibroblast activation in PH lungs. High-resolution spatial mapping further confirmed increased arterialization in the distal microvasculature. These findings underscore the utility of spatial transcriptomics in preserving the native tissue architecture and enhancing our understanding of cellular heterogeneity in disease. Our protocol provides a reliable method for integrating spatial and transcriptomic data using fixed frozen lung tissues, offering significant potential for future studies in complex diseases such as PH.
Open Access
Review
14 May 2025Current Status of Biological Production Using C2 Feedstocks
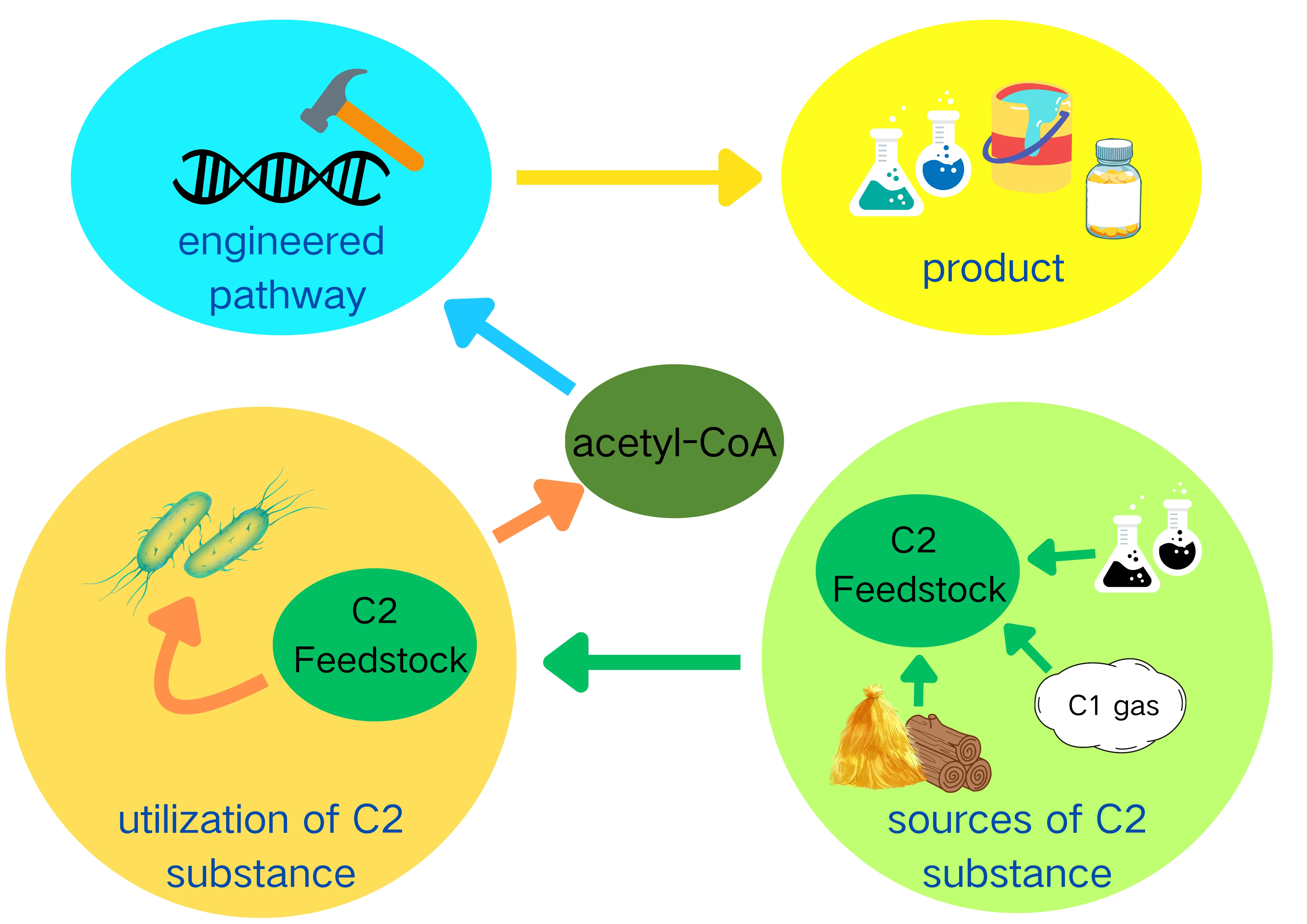
C2 feedstocks have emerged as promising carbon sources for the biological production of various value-added chemicals. Compared to the traditional C6/C5 sugars-contained/constituted feedstocks, C2 feedstocks have diverse and abundant sources, including non-food biomass, industrial by-products, and C1 gases. This diversification not only eliminates competition with human food demands but also aligns with environmental sustainability goals. Moreover, the metabolic route for C2 compounds to enter central carbon metabolism is more direct, which minimizes the carbon loss and enhances the efficiency of bio-based production processes. This review extensively analyzes three prominent C2 chemicals: ethylene glycol, ethanol, and acetate. After introducing the sources of those compounds, it details the metabolic pathways through which they are converted into acetyl-CoA in vivo. Several chemicals produced from these C2 feedstocks in fermentation are also exemplified. Furthermore, different perspectives are proposed to promote the efficient utilization of C2 feedstocks.
Open Access
Article
12 May 2025Drone Operation with Human Natural Movement
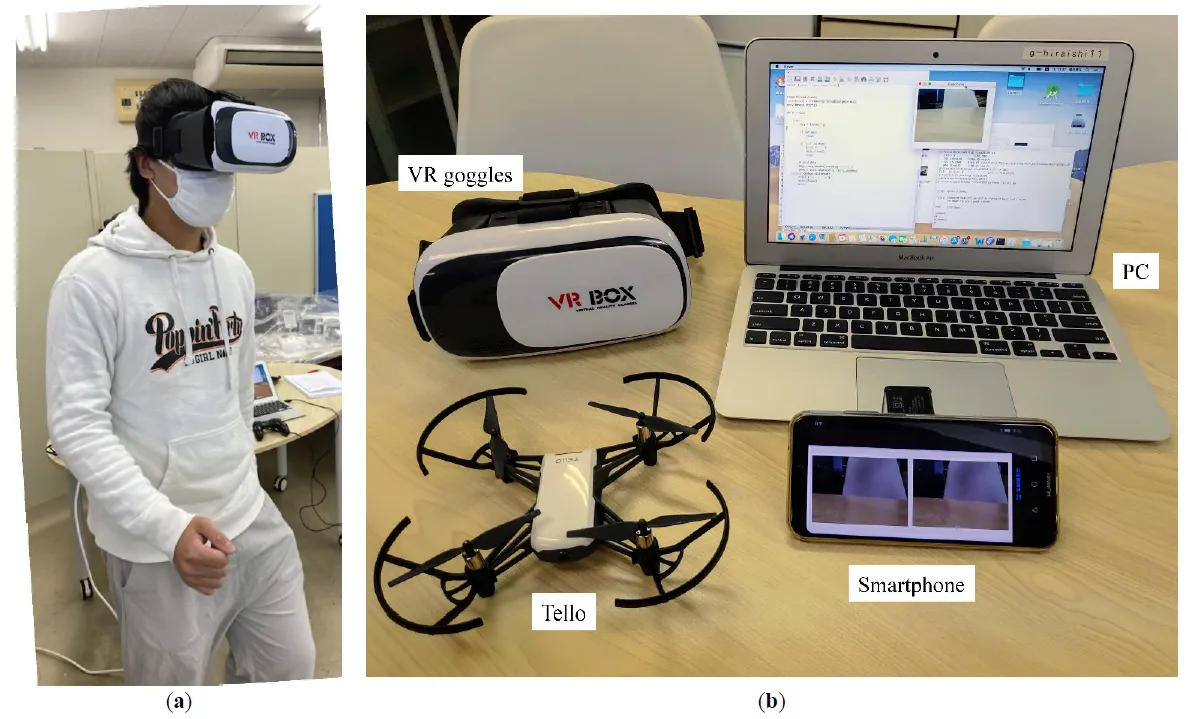
This study proposes a method for operating drones using natural human movements. The operator simply wears virtual reality (VR) goggles. An image from the drone camera was displayed on the goggles. When the operator changes the direction of his or her face, the drone changes the direction to match that of the operator. When the operator moves their head up or down, the drone rises or falls accordingly. When the operator walks in place, rather than walking, the drone moves forward. This allows the operator to control the drone as if they were walking in the air. Each of these movements was detected by the values of the acceleration and magnetic field sensors of the smartphone mounted on the VR goggles. A machine learning method was adopted to distinguish between walking and non-walking movements. Compared with operation via conventional remote control, it was observed that the remote controller performed better than the proposed approach in the early stages. However, when the participants familiarized themselves with the natural operation, these differences became relatively small. This study combined drones, VR, and machine learning. VR provides drone pilots with a sense of realism and immersion, whereas machine learning enables the use of natural movements.
Open Access
Article
09 May 2025Modeling and Assessing Economical Feasibilities for Waste to Energy Conversion/Incineration Process in Context of Municipal Solid Waste
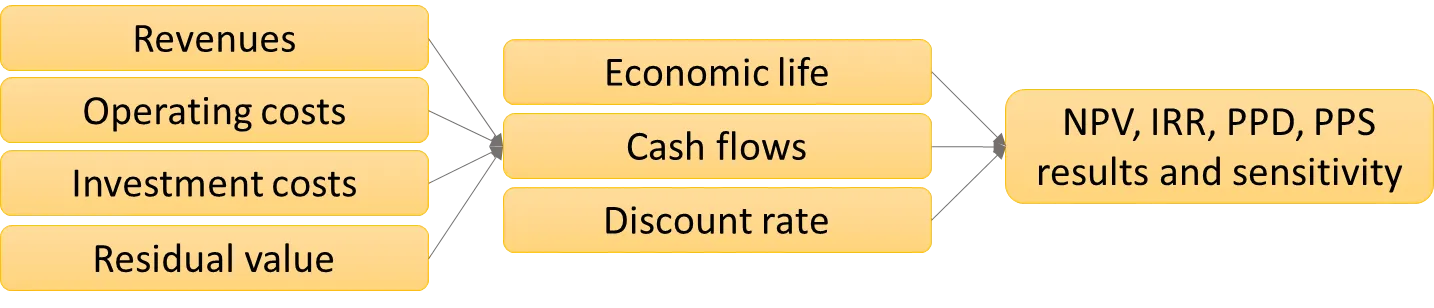
At the time of the study, most of the municipal waste, including solid municipal waste, in the city of St. Petersburg and in the connected larger Leningrad region is processed by landfilling. This sort of waste processing in open landfills causes environmental damage, uncontrollable landfill fires, bad and dangerous odors, nearby rivers/streams, groundwater pollution, CH4 and CO2 emissions, to mention a few. Additionally, landfilling is a waste of energy and material resources present in the content dumped into landfills. In this context, Waste-to-Energy (WtE) incineration is a process that we use to recover the energy the materials have back to usable form, which we use in the form of heat and electricity. Even though a lot of resources and energy are available in the (municipal solid) waste, it does not mean that recovering it would always make sense. Our study analyses and estimates the profitability of a WtE incineration plant(s) in the city of St. Petersburg and the connected Leningrad region. With the available data and following analysis, we have concluded that the WtE incineration is economically feasible in this specific region and city areas, given that the implementations follow more traditional (economically less expensive and easier) technical and process model solutions. As a note of results stability, it needs to be pointed out that the changes in estimates of gate fees, cost of electricity and heat, and so on do impact the economic feasibility a lot, and larger scale changes in the assumed revenues would have a high impact on the outcome of repeatability of the results.
Open Access
Article
08 May 2025Vulnerability Assessment of Food Crop Production and Climate Change: Implication for Agricultural Productivity and Development in Nigeria
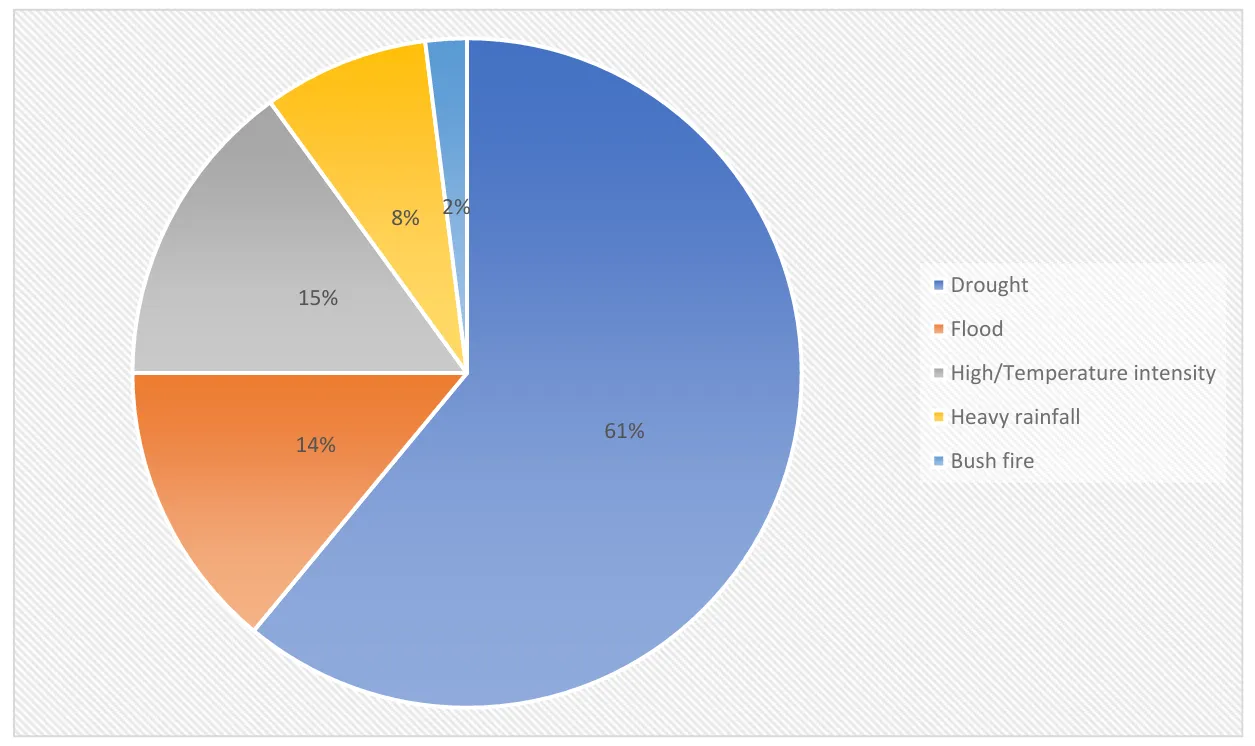
Climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture, particularly in developing nations like Nigeria, where the sector is highly dependent on vulnerable rain-fed farming systems. Extreme weather events such as prolonged droughts, erratic rainfall, flooding, and rising temperatures threaten agricultural productivity, food security, and rural livelihoods. This study examines the vulnerability of food crops to climate change, focusing on smallholder farmers’ perceptions and adaptation strategies. Using a multistage sampling technique, data were collected from 480 smallholder farmers across selected agro-ecological zones in Nigeria. The study employed descriptive statistics and a crop vulnerability scale to assess the susceptibility of key food crops—maize, cassava, sorghum, rice, millet, soybean, and yam—to climate extremes. Findings reveal that drought is the most critical climate-induced stressor affecting food crops, with maize and cassava exhibiting the highest vulnerability indices. Flooding also presents a substantial risk, particularly to maize, while temperature fluctuations have relatively less severe immediate impacts. The study highlights the importance of climate information dissemination, cooperative memberships, and extension services in enhancing farmers’ resilience. However, limited access to climate information remains a significant barrier to adaptation. Given the observed variability in crop vulnerability, it is recommended to implement targeted climate adaptation strategies such as drought-resistant crop varieties, improved drainage systems, and early warning mechanisms. This study underscores the urgent need for climate-smart agricultural policies and resilience-building measures to safeguard food production and rural livelihoods in Nigeria amid escalating climate change threats.
Open Access
Article
08 May 2025Evaluating Orthophoto Mosaic Accuracy Using RTK UAVs and AeroPoints 2 Ground Control Points: A User’s Perspective
With the growing use of Real Time Kinematics (RTK) Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and advancements in ground control points (GCPs), assessing positional accuracy of UAV derived orthophoto mosaics is crucial. This study aimed to improve UAV aerial image accuracy for more reliable orthophoto mosaics by examining the positional accuracy of orthophoto mosaics derived with (1) an RTK UAV; and (2) an RTK UAV combined with AeroPoints 2 GCPs. We tested two GPS base station methods for the RTK UAV: self-determined and manually assigned coordinates. The manually assigned coordinates resulted in significantly lower root mean square error (RMSE = 0.0729 m) compared to the self-determined method (RMSE = 1.9762 m), indicating improved accuracy. For the AeroPoints 2 GCPs, we recorded coordinates from a central GCP at a known location and four additional GCPs placed in each cardinal direction. The AeroPoints 2 system showed lower RMSE at all points compared to the RTK, with the central GCP at 0.0136 m, indicating high accuracy. These findings suggest that while RTK UAVs improve accuracy with manual base station assignment, incorporating AeroPoints 2 GCPs provides consistently higher precision across multiple locations. The study highlights the potential of AeroPoints 2 GCPs and suggests further research opportunities to enhance RTK UAV accuracy in areas lacking GPS correctional networks.
Open Access
Article
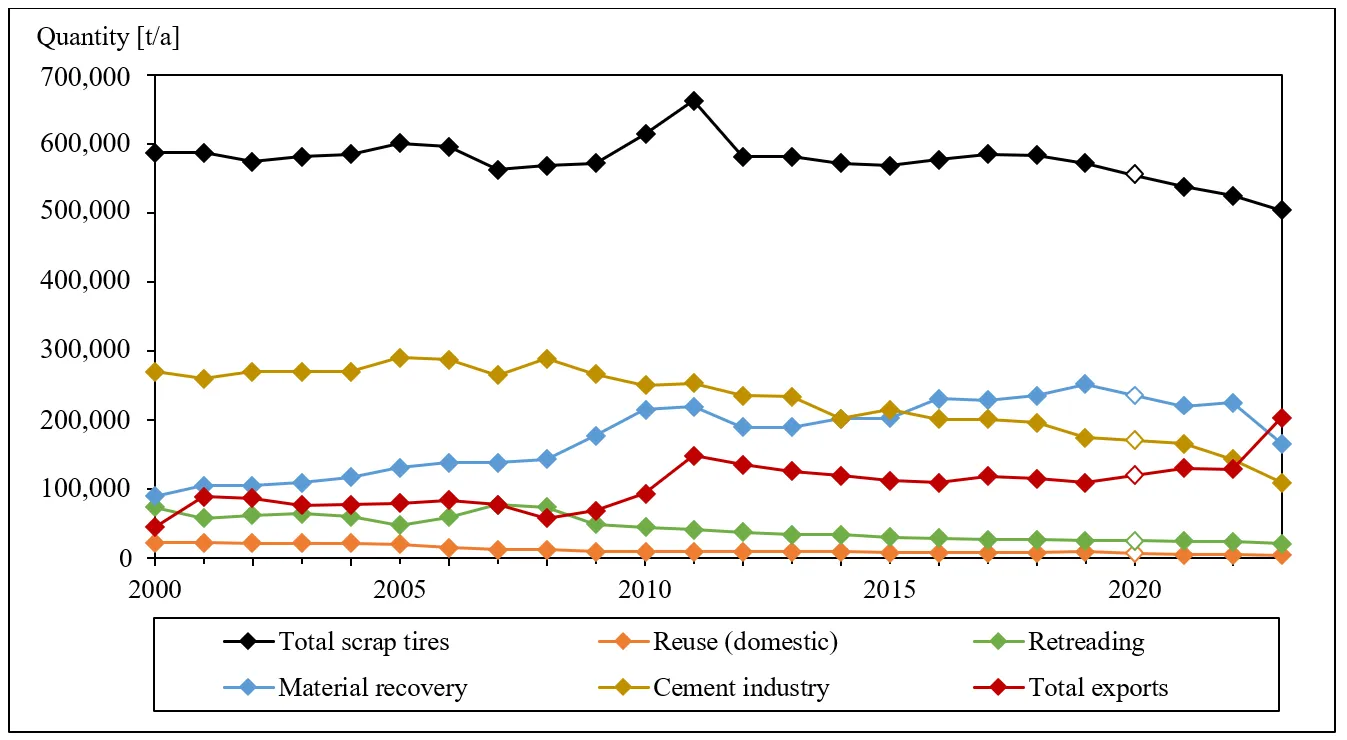
29 April 2025Application of recovered Carbon Black (rCB) by Waste Tire Pyrolysis as an Alternative Filler in Elastomer Products
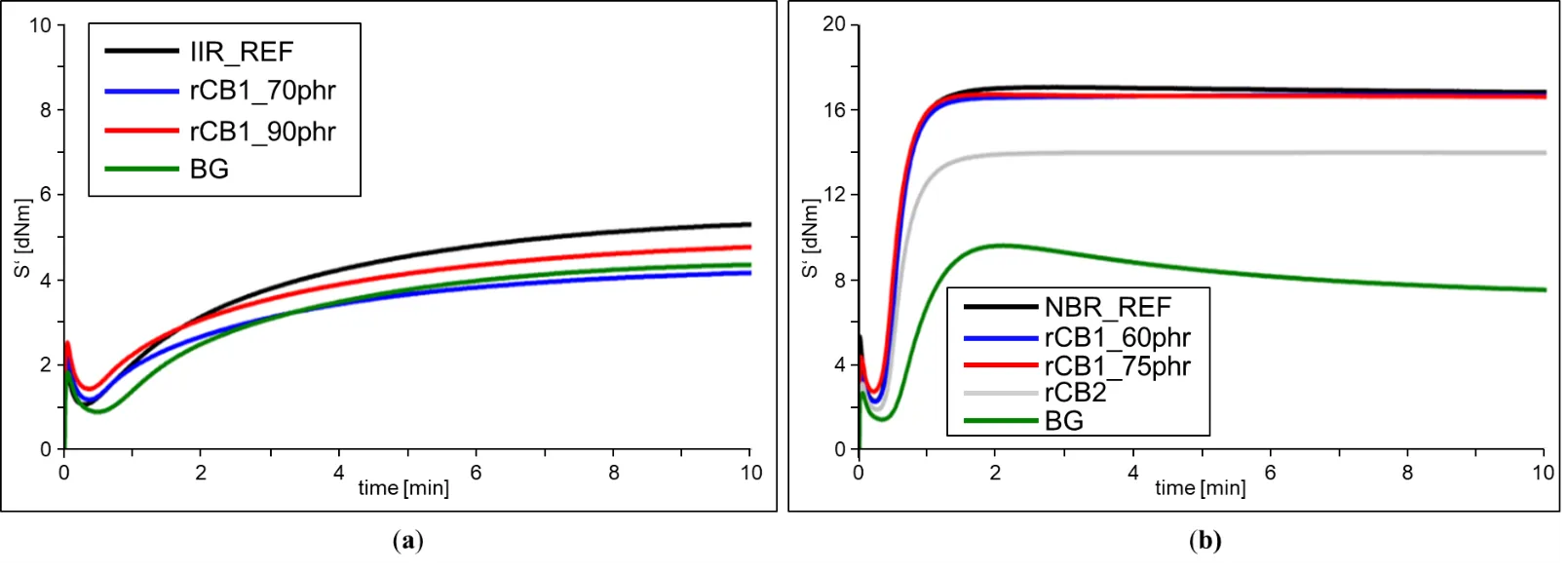
The increasing global accumulation of End-of-Life (EoL) tires and the growing demand for fossil industrial Carbon Black (CB) call for sustainable alternative solutions. In this context, tire pyrolysis and the resulting recycled raw material recovered Carbon Black (rCB), are considered potential alternatives. In the study, various rCBs were incorporated into new elastomer compounds using a laboratory internal mixer and their properties were investigated. The compounds were selected based on examples of applications such as bicycle inner tubes and hydraulic membranes. By comparing the in-rubber properties of rCB-based compounds with CB reference compounds, an initial assessment of the potential use of rCB for the chosen products was derived. Compared to industrial carbon black, the use of rCB leads to a reduction in performance. Although increasing the filler content partially compensated for the mineral content in rCB and led to a slight improvement, it could not fully offset the performance loss.
Open Access
Article
28 April 2025Production and Characterization of Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) by Waste Tire Pyrolysis as a Potential Carbon Black (CB) Substitute
Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) from scrap tire pyrolysis offers a potential alternative to fossil-based virgin Carbon Black (CB) in the context of a circular economy. This study investigated the influence of pyrolysis process parameters on rCB yield and quality at laboratory and semi-industrial scales. The resulting rCBs were characterized and found to have surface and structural properties comparable to N500 and N600 series CBs, but with higher mineral and volatile contents. The quality of rCB is influenced by the feedstock composition, particularly the ratio of organic to inorganic components as well as key process parameters such as heating rate, pyrolysis temperature and residence time. Higher heating rates accelerate degradation and shift product distribution toward increased oil yield and reduced rCB formation, while higher pyrolysis temperatures lead to lower volatile content in rCB. Additionally, reactor and process design affect heat distribution, transfer efficiency, and mixing behavior, further shaping rCB properties. However, further testing is required to evaluate the actual in-rubber properties of rCBs. Therefore, additional tests are planned, incorporating rCB into butyl and nitrile rubber-based elastomer compounds, which will be addressed in a follow-up study. In addition, data from the current experiments will support a comprehensive Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) to evaluate the environmental impacts of tire pyrolysis and rCB production compared to other recycling methods, with details to follow in a future publication.
Open Access
Article
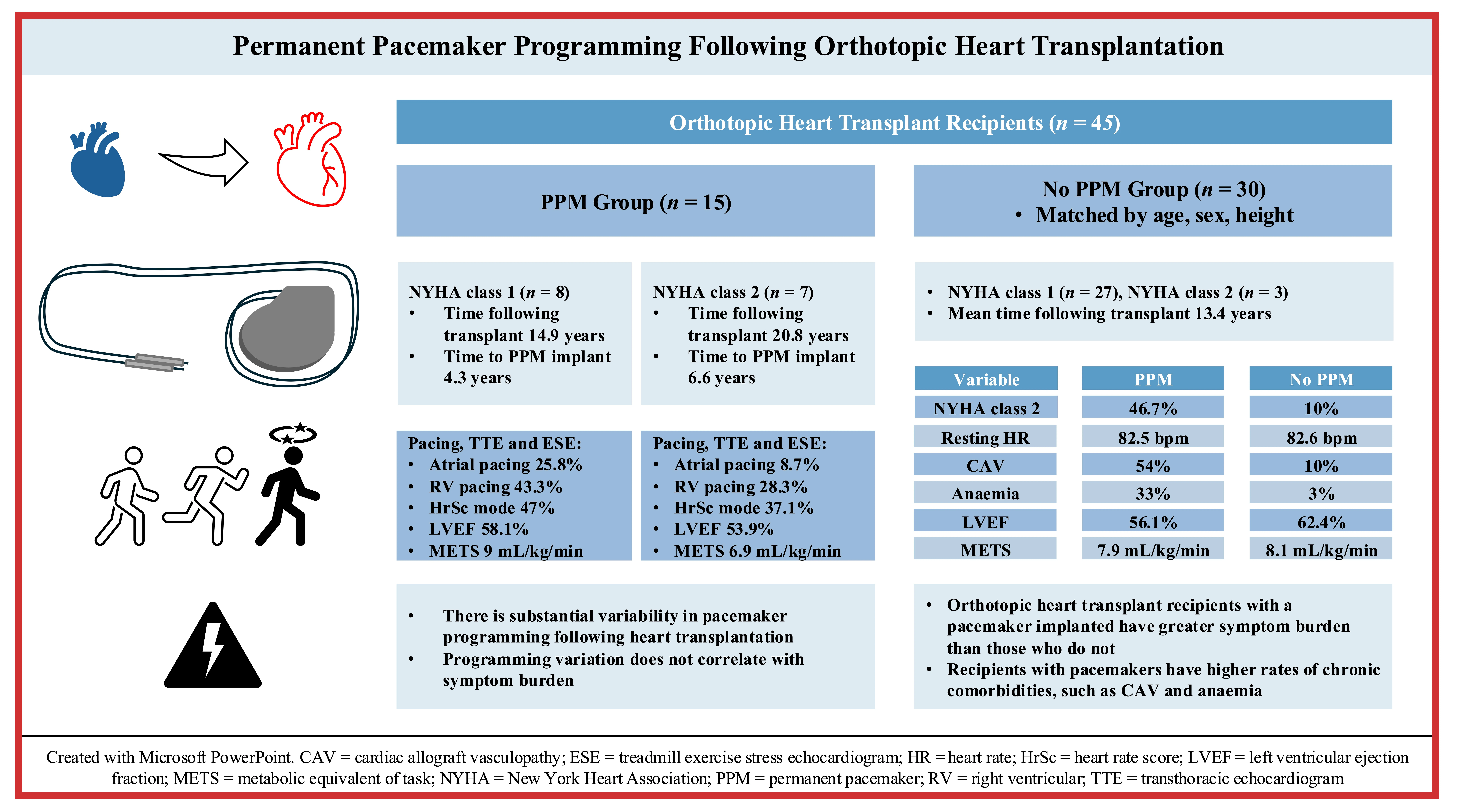
27 April 2025The Impact of Pacemaker Programming on Morbidity in Heart Transplant Recipients
Pacemaker programming recommendations in patients post-heart transplant include a higher lower rate limit, activating rate response mode, maximising battery longevity and minimising ventricular pacing in patients without atrioventricular block. This study sought to investigate how variability in pacemaker programming following orthotopic heart transplant affects morbidity. We conducted a retrospective analysis of heart transplant recipients at a single transplant centre between 1991 and 2023. Patients requiring pacemaker implantation following transplantation were matched with non-pacemaker recipients by age, sex and height. Patient and device characteristics were reviewed. Clinical outcomes, programming and physiological parameters were compared within the pacemaker group and between subject and comparator groups. Forty-five heart transplant recipients were included: 15 with pacemakers and 30 without. Within the pacemaker group, 20% were programmed with LRL > 60 bpm, rate-response mode in 47% and algorithms minimising ventricular pacing in 27%. Fifty-three percent were NYHA class I, and 46% NYHA class II; resting heart rate was similar between the groups (85 (SD14.9) and 79 (SD8) bpm: p = 0.33). NYHA class I group achieved a higher workload (METS 9 (SD2.7) vs. 6.9 (SD1) mL/kg/min: p = 0.21), and peak heart rate (135 (18.8) vs. 123 (14.8) bpm: p = 0.29) during exercise stress echocardiogram (ESE). The pacemaker group was more symptomatic than the comparator group (NYHA class II 46% vs. 10%: p = 0.016) and exhibited higher rates of cardiac allograft vasculopathy (53% vs. 10%: p = 0.005). There is substantial variability in pacemaker programming in heart transplant recipients. Patients who require a pacemaker have a greater symptom and comorbidity burden than those without. No identifiable physiological or programming differences stratified the greater morbidity within the pacemaker cohort.
Open Access
Review
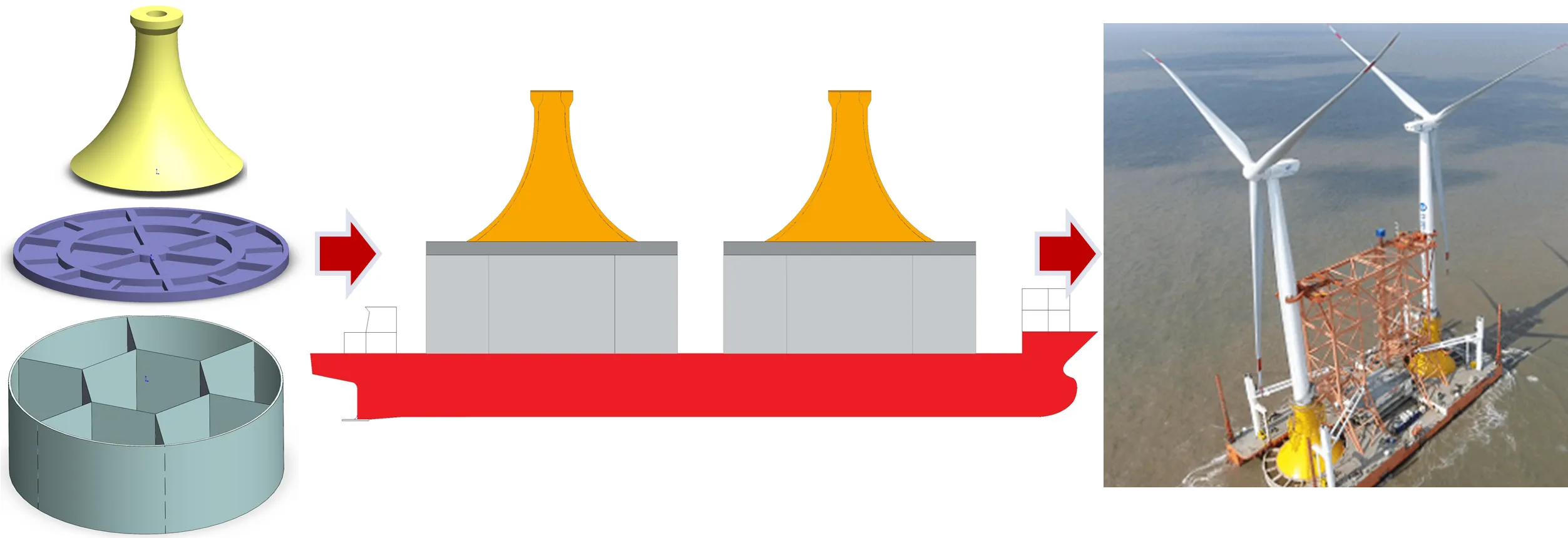
23 April 2025Research Progress on Offshore Wind Turbine Foundation Structures and Installation Technologies
Offshore wind power, as an important component of renewable energy, has gradually become one of the key technologies in global energy transition. The development of offshore wind power faces complex technical challenges, including strong wind, waves, currents, foundation bearing capacity, and installation technologies for wind turbines, among other issues. In recent years, with technological advancements, significant breakthroughs have been made in the design of offshore wind power foundation structures, installation technologies, and equipment. This paper provides a comprehensive review of the recent progress in offshore wind power technologies, deeply exploring innovative technologies in areas such as the overall development trends, foundation structures, installation technologies, and equipment of offshore wind power. Special attention is given to the design and safety analysis of wind turbine foundation structures under different foundation conditions, as well as installation technologies for wind power in complex sea conditions and deep-water areas. The paper argues that the applicable depth of fixed foundations is expected to extend beyond 50 m. The jacket foundation remains the mainstream choice for future large-scale wind turbines, with the potential to increase its applicable water depth to 100 m. Furthermore, floating foundations have significant potential for cost reduction and efficiency improvements. Developing entirely new foundation structures and installation technologies suitable for deep-water environments is also a key direction for future development.