Value Engineering in the Era of Industry 4.0: From Gap Analysis to Research Methodologies and Strategic Framework
Received: 29 August 2025 Revised: 10 October 2025 Accepted: 24 October 2025 Published: 07 November 2025
© 2025 The authors. This is an open access article under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
1. Introduction
Value Engineering (VE) is a systematic, function-driven methodology designed to maximize value by achieving the desired performance at the lowest total cost. It emerged in the 1940s at General Electric, where Lawrence D. Miles developed what was initially called value analysis in response to material shortages during World War II. His approach aimed to identify alternative solutions that could deliver required functions at reduced costs without compromising quality, performance, or reliability. Over the decades, VE evolved into a comprehensive, interdisciplinary practice applied across a wide range of sectors, including manufacturing, construction, healthcare, transportation, and public infrastructure. According to SAVE International, VE is defined as “the systematic application of recognized techniques by a multidisciplinary team to identify the functions of a product or service, establish a worth for those functions, and generate alternatives that achieve the necessary functions at the lowest total cost of ownership”. This definition underscores VE’s core principles: function-based reasoning, stakeholder collaboration, and lifecycle cost optimization [1,2,3].
Value Engineering (VE) is based on the principle that value equals function over cost, emphasizing that value can be increased by improving functionality, reducing cost, or both. Unlike conventional cost-cutting approaches, VE preserves essential features, safety, and user satisfaction by focusing on holistic value optimization. VE has evolved beyond its traditional applications in manufacturing and construction to encompass product development, supply chain management, and service industries, reflecting its adaptability to complex, multidisciplinary challenges. As shown in Figure 1, the Value Engineering Cycle comprises three interconnected phases: Value Discovery, Value Realization, and Value Optimization. Value Discovery identifies improvement opportunities through systematic analysis of stakeholder needs, functional requirements, and cost-performance trade-offs. Value Realization translates these insights into feasible, cost-effective solutions aligned with project objectives and technical constraints. Value Optimization ensures sustained value through continuous evaluation, lifecycle feedback, and adaptive refinement, enabling organizations to respond to evolving requirements and technological advancements. VE is executed through a structured Job Plan comprising six phases: Information, Function Analysis, Creative, Evaluation, Development, and Presentation. This approach allows multidisciplinary teams to generate innovative, cost-efficient alternatives, integrating analytical rigor with creative problem-solving to enhance design quality, reduce waste, and maximize value across the product or service lifecycle [1,4,5]. By integrating technical analysis, stakeholder engagement, and strategic decision-making, VE provides a robust framework for achieving operational excellence, innovation, and sustainable competitiveness in both traditional and modern industrial contexts.
VE has proven to be a strategic tool across industries. In manufacturing, it contributes to leaner product designs, material savings, and faster time-to-market. In construction and infrastructure, VE supports better constructability, improved scheduling, and long-term cost savings. Across public and private sectors, it facilitates early design interventions, interdisciplinary decision-making, and continuous improvement. Its structured, repeatable methodology makes VE particularly valuable in complex projects where performance, cost, and stakeholder alignment must be carefully balanced [6,7].
However, as industrial ecosystems rapidly digitize, traditional VE practices are increasingly misaligned with the realities of Industry 4.0. Conventional VE remains largely analog, sequential, and document-based—limiting its ability to respond to the interconnected, data-intensive, and real-time demands of smart manufacturing and digital service systems. VE is still frequently deployed as a one-time, event-driven initiative rather than as a dynamic, embedded process. Moreover, it operates independently of advanced modeling tools, enterprise platforms, and live data environments, which restricts its capacity to evaluate complex trade-offs, integrate customer feedback, or optimize lifecycle performance in real-time. Critically, VE remains underutilized in its engagement with enabling technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), Digital Twins, Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), and Big Data analytics—technologies that could significantly enhance function modeling, scenario simulation, and predictive optimization.
These limitations underscore the urgent need to transition from conventional VE toward a more integrated, intelligent, and adaptive methodology. This shift marks the emergence of VE 4.0—a digitally empowered paradigm that fuses classical function-based logic with the transformative potential of Industry 4.0 technologies. VE 4.0 facilitates real-time, data-driven, and collaborative value creation across the product–process–service continuum. It repositions VE from a cost-reduction tool to a strategic system for continuous value optimization aligned with customer expectations, sustainability goals, and business agility. By integrating digital capabilities, VE 4.0 enables dynamic function modeling, stakeholder co-creation, and informed decision-making within cyber-physical environments.
In this context, the present study explores the evolution of VE and its redefinition in light of digital transformation imperatives. It examines how VE can be reimagined to meet the performance, resilience, and sustainability challenges of Industry 4.0. The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 reviews the theoretical foundations and historical development of VE, highlighting its emerging transformation. Section 3 presents a critical analysis of current limitations in VE practice and identifies barriers to VE 4.0 adoption. Section 4 proposes a strategic framework for VE 4.0 that integrates function-based thinking with digital technologies and Lean Six Sigma principles. Finally, Section 5 offers concluding insights and outlines a research agenda to advance VE 4.0 as a foundational methodology for digital value management in future-ready industrial systems.
2. Literature Review
This section examines the theoretical foundations of Value Engineering (VE), its applications across diverse sectors, and the emerging evolution toward VE 4.0 within the Industry 4.0 paradigm. A systematic literature review (SLR) was conducted to analyze the development, conceptual underpinnings, and practical applications of Value Engineering. Insights were synthesized across disciplines and industries, highlighting key methodologies, emerging trends, and technological enablers shaping the field. Peer-reviewed articles published between 2015 and 2025 were systematically retrieved from Scopus, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect using targeted search terms, including Value Engineering (VE), Value Optimization, Industry 4.0, VE 4.0, Digital Engineering, Function-Oriented Design, Lifecycle Cost Optimization, Lean Six Sigma (LSS), and DMAIC. The selection adhered to rigorous inclusion and exclusion criteria, prioritizing empirical studies, conceptual frameworks, and applied research relevant to Industry 4.0 contexts. The analysis identified critical research gaps, including limited empirical validation, underexplored areas, and insufficient alignment with contemporary challenges such as digitalization, sustainability, and smart manufacturing ecosystems. By integrating these insights, the study provides a comprehensive understanding of the field. It establishes a foundation for a forward-looking framework that bridges theory and practice, advancing innovation, operational resilience, and sustainable competitiveness in Industry 4.0 ecosystems.
2.1. Review of Value Engineering
Value Engineering (VE) is a systematic and function-oriented methodology that aims to maximize value by optimizing the relationship between performance and cost. Originally conceived in the 1940s at General Electric by Lawrence D. Miles as “value analysis”, VE emerged in response to wartime material shortages and rising production costs. It focused on identifying cost-effective alternatives that maintained or enhanced functionality. The formalization of VE through the founding of the Society of American Value Engineers (now SAVE International) in 1958 standardized its practices and enabled its global adoption across industries such as manufacturing, construction, aerospace, and infrastructure. At its core, VE is grounded in the classic value equation (Value = Function/Cost), which emphasizes enhancing value either by improving function, reducing cost, or both, without sacrificing quality, reliability, or stakeholder satisfaction [1,7,8].
Unnecessary project costs frequently arise from functional inefficiencies, fragmented decision-making, and misaligned stakeholder priorities. A team-based, problem-solving approach has proven effective in overcoming these challenges by fostering collaboration, cross-disciplinary insight, and structured analysis [9]. VE embodies this approach by forming cohesive, multidisciplinary teams dedicated to achieving clearly defined objectives. At the core of VE is the Job Plan, a systematic and phased methodology that guides the team in analyzing functions, exploring alternatives, and optimizing value. This structured process improves decision quality and ensures efficient resource allocation by delivering required functions at the lowest feasible lifecycle cost. Simultaneously, VE integrates the owner’s value considerations—such as aesthetics, environmental performance, safety, flexibility, reliability, and schedule—ensuring that technical solutions are aligned with broader project goals and stakeholder expectations [8].
VE operates through a disciplined, phased process known as the Job Plan, typically comprising eight stages: Preparation, Information, Function Analysis, Creative, Evaluation, Development, Presentation, Implementation, and Follow-up (Janani, 2018). This structured methodology enables multidisciplinary teams to systematically dissect products, processes, or systems into their basic and secondary functions and develop innovative, cost-effective alternatives. Key tools supporting this process include brainstorming, cause-and-effect matrices, and the Function Analysis System Technique (FAST). FAST diagrams are particularly valuable, as they graphically represent logical relationships among functions using “How” and “Why” logic, thereby enhancing problem clarity, encouraging multifunctional design thinking, and identifying value gaps [10,11].
VE has been widely applied across diverse sectors. In the construction industry, it is instrumental in enhancing constructability, reducing lifecycle costs, and aligning design decisions with project objectives. In manufacturing, VE supports lean product design, material efficiency, and design-to-cost strategies. In civil engineering, VE is especially effective when conducted during early project phases, where functional decisions have significant cost and performance implications. Late-stage VE application often results in increased costs, delays, or suboptimal solutions [1,11]. Beyond these sectors, VE has been successfully implemented in the automotive industry [12], IT and software engineering [13], and large-scale industrial systems [1]. Numerous empirical studies affirm VE’s impact on improving functional outcomes, enhancing project coordination, and achieving measurable cost savings [14,15,16,17,18,19].
Despite its effectiveness, VE is often misinterpreted as a cost-reduction tool and conflated with Value Management (VM). While VM encompasses broader project values and stakeholder perspectives, VE remains narrowly focused on functional optimization through structured analysis and team-based creativity [1,2]. Traditional VE, however, has significant limitations in today’s increasingly digital and dynamic industrial environments. It remains largely sequential, analog, and documentation-heavy, limiting its responsiveness to real-time data and its integration within agile development or smart production environments. VE processes are rarely embedded in digital enterprise systems or continuously informed by evolving operational, environmental, and customer data, thereby reducing their strategic relevance in cyber-physical contexts.
Industry 4.0 introduces a suite of transformative technologies—Artificial Intelligence (AI), Building Information Modeling (BIM), the Internet of Things (IoT), Digital Twins, Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), and Big Data analytics—that offer powerful opportunities to enhance VE. These technologies facilitate real-time sensing, predictive analytics, dynamic simulation, and cross-functional integration. For example, BIM allows early-stage modeling of function-cost-performance trade-offs; AI supports automated function recognition, optimization algorithms, and intelligent decision-making; and Digital Twins provide real-time synchronization between digital and physical systems, enabling predictive and lifecycle-aware value assessments. IoT platforms and big data environments further support continuous feedback loops and context-aware decision-making, expanding VE’s capacity to adapt to real-time changes in stakeholder requirements, operational constraints, or environmental conditions.
In light of these developments, the concept of VE 4.0 has emerged as a digitally empowered evolution of the classical VE framework. VE 4.0 integrates function-based thinking with real-time data intelligence, automation, and cyber-physical connectivity to enable continuous, agile, and sustainable value creation. Rather than remaining a discrete, event-driven intervention, VE 4.0 becomes an embedded, dynamic process that is responsive to changing contexts and complex trade-offs. This transformation repositions VE as a strategic methodology aligned with the goals of digital transformation, operational excellence, and systems innovation. As industrial ecosystems move toward smart, connected, and human-centered paradigms, VE 4.0 offers a foundational approach to optimize value holistically—across the entire lifecycle of products, processes, and services.
2.2. Review of Industry 4.0 Features and Technologies
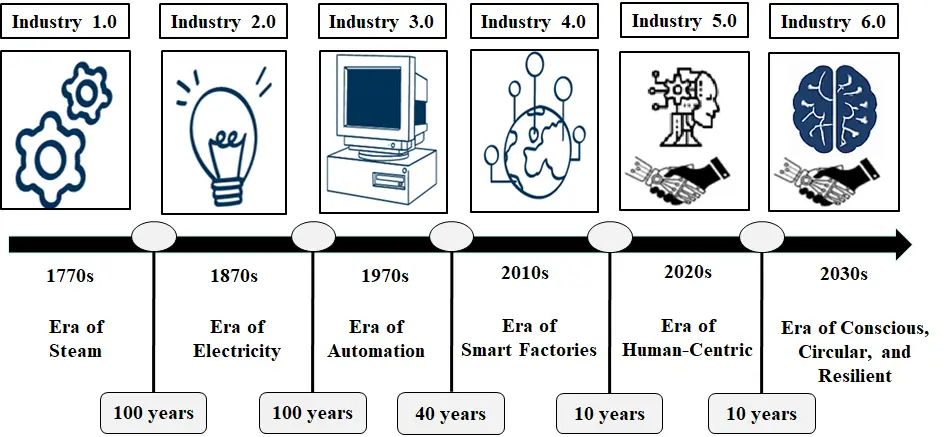
The evolution of industrial revolutions reflects humanity’s progressive integration of technology, intelligence, and sustainability into production systems, demonstrating a continuous drive toward efficiency, innovation, and societal value. As shown in Figure 2, this transformation begins with Industry 1.0, characterized by mechanization through steam engines and basic labor-saving tools, and progresses to Industry 2.0, which introduced mass production, assembly lines, and electrical power. Industry 3.0 brought automation, digital computing, and programmable logic controllers, enhancing productivity and reducing human intervention in repetitive tasks. Industry 4.0 represents the convergence of cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, and real-time intelligence, enabling interconnected, adaptive, and self-optimizing industrial ecosystems. Emerging paradigms such as Industry 5.0 and the conceptual framework of Industry 6.0 mark a pivotal shift—moving beyond digital efficiency toward human-centric, ethically governed, and regenerative industrial ecosystems. These next-generation paradigms emphasize human-machine collaboration, resilience, social value creation, and environmental sustainability, integrating technological advancement with societal and planetary well-being [20,21,22]. Overall, the evolution of industrial revolutions illustrates a trajectory toward increasingly intelligent, integrated, and sustainable production paradigms, providing a conceptual foundation for frameworks such as Value Engineering 4.0, which aligns value optimization with the ethical, regenerative, and digital dimensions of modern industry.
Industry 4.0 marks a paradigm shift in industrial systems, driven by the integration of digital technologies with physical operations to create intelligent, self-organizing, and interconnected production environments. First introduced at the Hannover Messe in 2011 and formally defined in 2013, Industry 4.0 harnesses technologies such as Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and big data analytics to enable real-time monitoring, predictive decision-making, and adaptive control [23,24]. These capabilities redefine conventional manufacturing by embedding intelligence across the value chain.
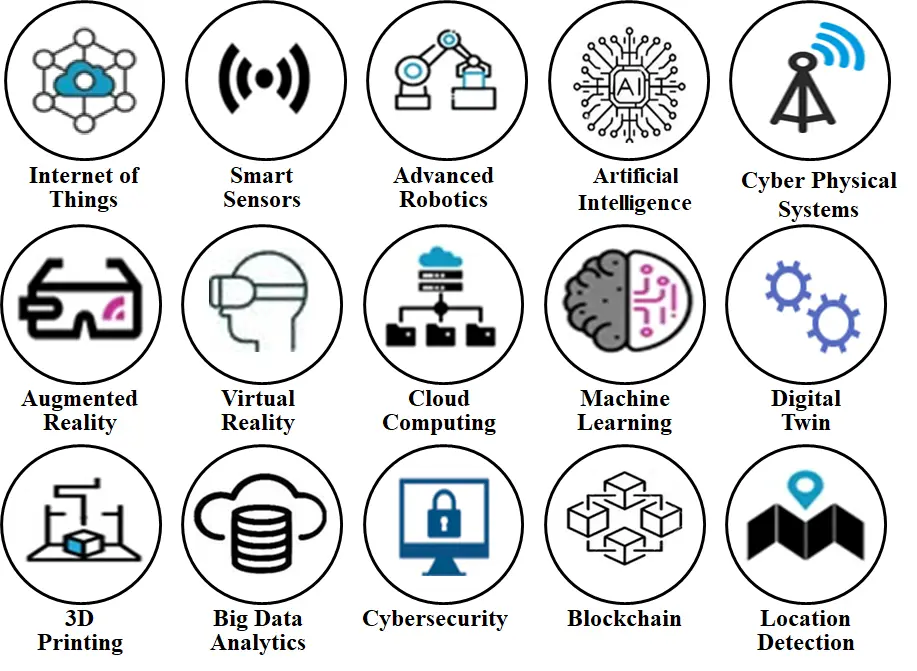
Industry 4.0 is enabled by a powerful convergence of advanced technologies that integrate physical and digital systems, reshaping traditional manufacturing into intelligent, connected, and adaptive environments. As illustrated in Figure 3 and supported by recent studies, the core technologies underpinning this transformation include the Internet of Things (IoT), which facilitates real-time connectivity and data exchange among devices, systems, and machines, and smart sensors, which enable continuous monitoring and data acquisition. Advanced robotics enhances precision, flexibility, and automation in production processes, while artificial intelligence (AI) supports intelligent decision-making and process optimization through data-driven learning. Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) bridge the physical and virtual worlds by integrating digital models with physical assets for real-time control and coordination. Immersive technologies such as Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) enhance design, training, and maintenance applications. Cloud computing provides scalable infrastructure for data storage and processing, complemented by machine learning (ML) for predictive analytics and system adaptability. Digital twin technology enables dynamic simulation and lifecycle optimization through virtual representations of physical systems. Additive manufacturing (3D printing) allows for rapid prototyping, customization, and efficient material use. Big data analytics transforms vast, heterogeneous datasets into actionable insights, while cybersecurity ensures the protection and integrity of interconnected systems. Blockchain technology offers secure, transparent, and decentralized data management, while location detection technologies, such as GPS and RFID, enhance traceability and operational visibility. Together, these technologies form the technological backbone of Industry 4.0, enabling smart, resilient, and sustainable industrial systems [25,26,27,28].
Industry 4.0 moves beyond centralized control and isolated systems by promoting distributed intelligence, machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, and seamless integration across organizational levels. Smart manufacturing environments foster dynamic interaction among connected assets, enabling mass customization, reduced lead times, and accelerated innovation [29,30]. Vertical, horizontal, and end-to-end integration ensures that design, production, logistics, and customer systems operate in harmony, enhancing agility and responsiveness.
Global adoption of Industry 4.0 is expanding rapidly, with market size projected to grow from $66.7 billion in 2016 to over $227 billion by 2025 [31]. Advanced economies are driving adoption through national strategies such as Germany’s Industrie 4.0, China’s Made in China 2025, and Japan’s Society 5.0 [20,32]. However, developing countries face significant challenges—ranging from infrastructural deficiencies to workforce gaps—which hinder the full-scale integration of Industry 4.0 technologies [33,34].
Beyond performance optimization, Industry 4.0 plays a critical role in advancing sustainability. Economically, it enhances asset utilization and resource efficiency. Environmentally, it supports circular production, waste minimization, and energy efficiency. Socially, it improves workplace safety, fosters digital upskilling, and promotes inclusive design [35]. Increasingly, sustainability is embedded as a guiding principle in Industry 4.0 implementation strategies [35].
Core enabling technologies—including digital twins, edge computing, IoT, and cloud platforms—facilitate real-time simulation, optimization, and predictive analytics [36]. These tools allow organizations to anticipate disruptions, enhance product quality, and improve resilience. Nonetheless, implementation barriers persist, such as cybersecurity vulnerabilities, interoperability limitations, and organizational resistance. Effective deployment requires not only technological readiness but also cultural transformation, leadership alignment, and change management [37].
While Industry 4.0 emphasizes automation, interconnectivity, and efficiency, Industry 5.0 introduces a complementary focus on human-centricity, ethical innovation, and sustainability. This next paradigm seeks to harmonize technological advancement with human values, autonomy, and inclusion, promoting deeper collaboration between people and machines [21]. It redefines industrial success by embedding circularity, resilience, and societal well-being into future production systems.
Industry 4.0 technologies have significantly impacted key industrial functions. In supply chains, IoT and big data enhance visibility, real-time tracking, and predictive logistics [38]. In lean manufacturing, advanced analytics support waste elimination and just-in-time production [39]. AI-driven predictive maintenance minimizes downtime and extends asset lifecycles [40]. Smart products communicate usage data; smart machines adapt in real-time; and augmented operators, supported by AR and wearables, optimize performance. These developments enable high-mix, low-volume production and reinforce systemic agility [41].
Recent literature highlights both the transformative potential and emerging risks of Industry 4.0. Choudhary and Nandy (2024) [42] identified sixteen sustainability risks, extending the conventional triple bottom line to include organizational and systemic dimensions. Barata and Kayser (2023) [21] traced the evolution of Industry 5.0 literature, emphasizing circularity, ethical AI, and human-machine collaboration. Rijwani et al. (2025) [43] reviewed enabling technologies—blockchain, cobots, 6G, edge computing—highlighting their benefits and integration challenges. Gomaa (2024) [22] proposed a strategic framework combining AI, digital twins, and collaborative robotics to drive agile, resilient, and human-centered smart manufacturing.
The convergence of Industry 4.0 technologies with Value Engineering (VE) offers a compelling opportunity to reconfigure VE as a dynamic, digitally enabled methodology. Traditionally reliant on static analysis, VE can be enhanced through integration with real-time data, digital twins, and AI to support continuous value optimization across the product and process lifecycle. This synergy enables predictive function modeling, automated trade-off analysis, and lifecycle-based decision support, aligning engineering innovation with strategic, economic, and sustainability imperatives. As such, VE 4.0 represents an evolutionary leap—embedding intelligent systems into value optimization and transforming VE into a core enabler of smart, adaptive, and value-centric manufacturing ecosystems [44,45,46,47,48,49].
3. Research Gap Analysis for Value Engineering 4.0
As Value Engineering (VE) integrates with Industry 4.0 technologies, several critical challenges must be addressed to unlock its full transformative potential. While tools such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and digital twins offer new capabilities for enhancing VE, significant gaps remain in both theoretical development and practical application. Bridging these gaps is essential to advancing VE 4.0 as a dynamic, intelligent, and collaborative methodology tailored for smart manufacturing and digital engineering contexts. Table 1 identifies key deficiencies and emerging priorities across four thematic areas that require focused research and strategic innovation [50,51,52,53,54,55].
- (1)
- Conceptual Foundations: There is a lack of an integrated theoretical framework that coherently embeds Industry 4.0 technologies into the VE process. Most existing models remain fragmented, limiting the potential for systemic digital transformation within VE. Additionally, there is a shortage of empirical studies evaluating the effectiveness, scalability, and cross-sector applicability of VE 4.0. Future research must develop unified models that clearly define VE 4.0’s principles, scope, and interaction with cyber-physical and data-driven systems.
- (2)
- Technology-Driven Optimization: Conventional VE remains largely manual, linear, and disconnected from real-time data environments. Function analysis and value modeling are not currently supported by AI, machine learning, or predictive analytics—limiting the agility and precision of decision-making. VE practices also tend to focus on initial cost reduction rather than total lifecycle value. Digital twins, big data, and simulation technologies can enable continuous function tracking and adaptive optimization. Furthermore, collaborative digital platforms leveraging AR/VR, cloud PLM, and remote engineering tools are needed to support cross-functional value co-creation. VE should also expand to address product–service systems (PSS), enabled by IoT and servitization models.
- (3)
- Human-Centric and Ethical Dimensions: Despite the rise of automation and autonomous decision-making, VE must remain grounded in human creativity, ethical reasoning, and inclusivity. Current VE methods insufficiently incorporate sustainability criteria, circular economy principles, or environmental key performance indicators (KPIs). Digital technologies can be leveraged to embed these considerations into early design and value assessment phases. Moreover, frameworks for human-in-the-loop governance and ethical AI integration are necessary to maintain transparency, trust, and responsibility in VE 4.0 applications.
- (4)
- Organizational Readiness and Capacity Building: The successful implementation of VE 4.0 depends on an organization’s digital maturity and strategic alignment. However, standardized maturity models and assessment tools to evaluate VE 4.0 readiness are still lacking. Organizations require clear guidance on how to benchmark capabilities, identify gaps, and develop transformation roadmaps. Simultaneously, education and training systems must evolve to reflect the competencies needed for VE 4.0—such as digital modeling, systems thinking, data-driven design, and ethical innovation. New curricula, digital learning platforms, and interdisciplinary training programs are essential to prepare engineers, designers, and decision-makers for the future of value engineering.
In conclusion, addressing these interconnected gaps is vital for repositioning VE as a digitally enabled, human-centered, and sustainability-oriented methodology. VE 4.0 has the potential to play a central role in the design and management of smart, adaptive, and resilient industrial systems. Advancing this transformation will require collaborative research, empirical validation, intelligent tools, and ethically grounded frameworks that align VE with the broader vision of Industry 4.0.
Table 1. Key research gaps & future research directions for VE 4.0.
|
Group |
# |
Research Area |
Gap |
Future Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1. Conceptual Foundations |
1 |
Framework Integration |
Lack of an integrated framework linking Industry 4.0 technologies to VE phases |
Develop an integrated VE 4.0 framework, aligning digital technologies with VE processes. |
|
2 |
Empirical Validation |
Limited real-world validation and benchmarking |
Conduct cross-industry case studies to demonstrate VE 4.0 impact and benefits. |
|
|
2. Technology-Driven Optimization |
3 |
Intelligent Function Analysis |
Predominance of manual and static function analysis methods |
Utilize AI, machine learning, and big data for automated, dynamic function modeling |
|
4 |
Lifecycle Value Optimization |
Focus on upfront costs rather than full lifecycle value |
Employ digital twins and predictive analytics for continuous lifecycle value management |
|
|
5 |
Collaborative Platforms |
Insufficient digital tools for agile, cross-functional VE collaboration |
Build cloud-based platforms integrating AR/VR, PLM, and real-time simulation tools |
|
|
9 |
Product-Service Systems Integration |
VE is limited to products and lacks integration with digital product-service systems. |
Extend VE to hybrid product-service models leveraging IoT and servitization. |
|
|
3. Human-Centric & Ethical Dimensions |
6 |
Sustainability & Circularity |
Weak incorporation of sustainability and circular economy metrics |
Embed environmental KPIs and circular economy principles via IoT and lifecycle analysis |
|
7 |
Human & Ethical Integration |
Limited focus on human factors, creativity, and ethical AI |
Develop human-in-the-loop and ethical AI frameworks to enhance collaboration and trust |
|
|
4. Organizational Readiness & Capacity |
8 |
Maturity & Readiness |
No standardized tools to assess VE 4.0 readiness |
Design maturity models and diagnostic tools to guide VE 4.0 adoption |
|
10 |
Education & Training |
Outdated VE education lacking Industry 4.0 focus |
Develop updated curricula and digital training platforms to build VE 4.0 competencies. |
4. Research Methodology for Value Engineering 4.0 Implementation
VE 4.0 signifies a strategic advancement of classical value engineering by integrating Industry 4.0 technologies to enable intelligent, real-time, and lifecycle-oriented value creation. As a function-driven, data-intelligent, and human-centric methodology, VE 4.0 supports continuous value optimization across products, processes, and services. The proposed methodology is structured around six interrelated components that collectively form a comprehensive, adaptive, and future-oriented framework.
-
Foundational principles that emphasize digital integration, data adaptability, lifecycle sustainability, human-centric collaboration, and organizational readiness;
-
Digital transformation of VE processes through IoT, AI, digital twins, and big data analytics for predictive and connected decision-making;
-
Enhancement of the traditional VE Job Plan using digital tools such as NLP, AR/VR, and blockchain to improve speed, precision, and lifecycle alignment;
-
A phased implementation roadmap that ensures strategic alignment and scalability through assessment, planning, piloting, scaling, and continuous improvement;
-
An enhanced Lean Six Sigma DMAIC framework that incorporates smart technologies to enable continuous, real-time value optimization; and
-
A set of enablers and mitigation strategies to overcome implementation challenges related to leadership, digital competency, IT infrastructure, and cybersecurity.
In summary, VE 4.0 redefines value engineering as a digitally empowered, ethically governed, and sustainability-aligned methodology. Uniting classical function analysis with advanced technologies and human-centered principles, it enables organizations to achieve continuous innovation, strategic agility, and long-term value. VE 4.0 thus emerges as a vital platform for optimizing performance, fostering resilience, and supporting smart, sustainable transformation in the Industry 4.0 era and beyond.
4.1. Foundational Principles of Value Engineering 4.0
VE 4.0 marks a strategic departure from traditional cost-focused methodologies, evolving into a digitally integrated, ethically governed, and systemically aligned framework for value creation. Grounded in five interdependent principles, VE 4.0 aligns advanced technologies with human insight and organizational capability to support intelligent, sustainable, and inclusive value optimization. These principles, summarized in Table 2, form the foundation for modern VE practices in Industry 4.0 environments:
- (1)
- Function-Centric Digital Integration: Advanced technologies—including AI, IoT, digital twins, and machine learning—are embedded within VE processes to enable real-time function modeling, intelligent analysis, and data-driven decision-making across the value chain.
- (2)
- Data-Driven Adaptability and Intelligence: Through big data analytics and predictive algorithms, VE 4.0 becomes adaptive and self-learning, continuously refining value trade-offs in response to real-time operational data and evolving stakeholder needs.
- (3)
- Lifecycle and Sustainability Orientation: Extending beyond cost reduction, VE 4.0 embraces total lifecycle value. It incorporates sustainability metrics, circular economy principles, and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria, aligning engineering performance with long-term environmental and social responsibility.
- (4)
- Human-Centric Collaboration and Ethical Governance: This principle underscores the critical role of human creativity, transparency, and stakeholder engagement. Digital collaboration tools and immersive technologies support inclusive decision-making while ensuring AI-driven processes remain ethical and accountable.
- (5)
- Organizational Readiness and Continuous Learning: Successful implementation of VE 4.0 depends on agile governance, digital maturity, and a culture of continuous learning. Building these capabilities is essential to sustain innovation and maximize the impact of VE across the enterprise.
Together, these principles constitute a holistic framework that unites digital technologies, human expertise, and organizational systems—positioning VE 4.0 as a transformative enabler of smart, sustainable, and resilient value engineering in the digital era.
Table 2. Core principles underpinning Value Engineering 4.0.
|
# |
Core Principle |
Objective |
Description |
Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Function-Centric Digital Integration |
Deliver continuous, precise function analysis |
Harness AI, IoT, digital twins, and machine learning for real-time, accurate evaluation and optimization of functions and value drivers throughout the lifecycle. |
AI, IoT, Digital Twins, Real-Time Function Modeling |
|
2 |
Data-Driven Adaptability and Intelligence |
Enable proactive, dynamic value optimization |
Leverage real-time data, big data analytics, and predictive algorithms to simulate alternatives, balance trade-offs, and support agile, informed decision-making. |
Big Data Analytics, Predictive Modeling, Machine Learning |
|
3 |
Lifecycle and Sustainability Orientation |
Integrate comprehensive lifecycle and sustainability criteria |
Embed economic, environmental, and social metrics across design, production, use, and disposal phases, aligned with circular economy and ESG standards for lasting value. |
Lifecycle Management, Circular Economy, ESG Metrics |
|
4 |
Human-Centric Collaboration and Ethical Governance |
Promote inclusive teamwork and ethical accountability |
Facilitate cross-disciplinary collaboration via AR/VR and cloud platforms, ensuring AI systems are transparent, fair, and explainable to build trust and accountability. |
AR/VR Collaboration, Human-in-the-Loop, Ethical AI |
|
5 |
Organizational Readiness and Continuous Learning |
Cultivate capabilities and governance for sustained success |
Implement maturity models, targeted upskilling, and agile leadership to foster innovation, resilience, and effective integration of VE 4.0 practices. |
Maturity Models, Skills Development, Agile Governance |
4.2. Digital Transformation of the Value Engineering Process
VE process is undergoing a fundamental transformation driven by Industry 4.0 technologies, shifting from traditional, static methods to dynamic, data-enabled, and lifecycle-integrated systems. These advancements reshape VE into a continuous, collaborative, and real-time value optimization practice. Table 3 outlines a framework mapping key Industry 4.0 technologies across five strategic domains that collectively enhance the VE process.
- (1)
- Functional Insight and Data Acquisition leverages IoT, edge computing, big data analytics, and natural language processing (NLP) to provide real-time, contextual insights into product performance, system functionality, and user needs. IoT ensures continuous monitoring; edge computing enables fast, localized data processing; big data analytics identifies patterns linking function, cost, and performance; and NLP extracts actionable intelligence from unstructured data sources like reports and feedback.
- (2)
- Digital Modeling and Optimization focuses on virtual experimentation and intelligent decision support. Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) integrate digital controls with physical assets for real-time evaluation. Digital twins act as dynamic replicas to simulate and monitor system lifecycles. Simulation tools support trade-off analysis, while AI and machine learning automate function generation and complex decision-making, enhancing precision and speed.
- (3)
- Agile Prototyping and Immersive Evaluation employs additive manufacturing (3D printing), augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and advanced human–machine interfaces (HMIs) to accelerate prototype development and stakeholder engagement. These tools foster rapid iteration, immersive visualization, and intuitive interaction, promoting collaborative evaluation and informed decision-making.
- (4)
- Integrated Collaboration and Lifecycle Alignment utilizes cloud computing, Product Lifecycle Management (PLM), and Service Lifecycle Management (SLM) platforms to enable seamless, real-time collaboration and alignment across functions and lifecycle stages. This integration embeds VE as a continuous, cross-functional capability, ensuring consistent value optimization from design through operation.
- (5)
- Transparency and Process Automation enhance trust, accountability, and efficiency through blockchain and robotic process automation (RPA). Blockchain provides secure, immutable records of decisions and changes, while RPA automates repetitive tasks such as data processing and reporting, freeing VE teams to focus on strategic innovation.
Together, these technologies transform VE into an agile, intelligent, and lifecycle-driven discipline. By embedding digital tools across all VE phases, organizations can achieve enhanced innovation, operational excellence, and competitive advantage within Industry 4.0 ecosystems.
Table 3. Key Industry 4.0 technologies and their strategic impact in value engineering.
|
Strategic Domain |
Technology |
Core Capabilities |
Applications in VE |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1. Functional Insight & Data Acquisition |
Internet of Things (IoT) |
Real-time data acquisition and connectivity |
Enables continuous monitoring of product and process functionality; informs real-time value analysis |
|
Edge Computing |
Local, low-latency data processing |
Supports on-site diagnostics and responsive VE interventions in dynamic environments |
|
|
Big Data Analytics |
High-volume processing and predictive modeling |
Identifies cost-function-performance patterns; enables lifecycle value optimization. |
|
|
Natural Language Processing (NLP) |
Semantic analysis of unstructured data |
Extracts latent functional requirements and user needs from technical sources and feedback |
|
|
2. Digital Modeling & Functional Optimization |
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) |
Physical-digital integration and simulation |
Enables virtual prototyping and testing of alternative functional solutions |
|
Digital Twins |
Real-time digital representation of physical systems |
Facilitates performance tracking, scenario simulation, and continuous value alignment |
|
|
Simulation Tools |
System-level modeling and behavioral analysis |
Assesses trade-offs, uncovers value gaps, and reduces reliance on physical prototypes. |
|
|
Artificial Intelligence (AI)/Machine Learning (ML) |
Autonomous learning and decision support |
Automates function generation, ranks alternatives, and supports multi-criteria evaluation. |
|
|
3. Agile Prototyping & Immersive Evaluation |
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) |
Rapid, flexible prototype fabrication |
Accelerates testing of functional alternatives; supports customization and design agility |
|
Augmented/Virtual Reality (AR/VR) |
Immersive interaction and visualization |
Enhances stakeholder engagement and collaborative evaluation of value alternatives |
|
|
Advanced Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) |
Intuitive, adaptive digital interfaces |
Improves understanding of complex interdependencies during VE workshops |
|
|
4. Integrated Collaboration & Lifecycle Alignment |
Cloud Computing |
Scalable, real-time access to data and tools |
Enables distributed collaboration and synchronized VE activities across functions |
|
PLM/SLM Platforms |
Lifecycle-wide data integration |
Aligns functional goals across design, engineering, and operations; ensures traceability and value continuity |
|
|
5. Transparency & Process Automation |
Blockchain |
Secure, transparent, immutable data exchange |
Ensures traceability, verifiability, and trust in cost, material, and functional decisions |
|
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) |
Automation of repetitive digital tasks |
Streamlines documentation, data collection, and reporting; enables focus on high-value analysis |
4.3. Digital Enhancement of the Value Engineering Job Plan
The traditional VE Job Plan offers a structured pathway for value optimization, but the demands of today’s digitally driven industrial landscape require its evolution. VE 4.0 transforms this framework by embedding Industry 4.0 technologies, creating a smarter, more agile, and data-driven methodology that enhances precision, collaboration, and real-time decision-making across the entire product and service lifecycle. Table 4 details how advanced digital technologies integrate across each phase of the VE Job Plan, elevating traditional practices into a cohesive cyber-physical process.
- (1)
- In the Information Phase, the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, edge computing, and natural language processing (NLP) enable continuous, real-time data collection and deep contextual analysis of functional, operational, and user-related information. This data-rich foundation uncovers hidden requirements, usage patterns, and cost drivers to inform subsequent phases.
- (2)
- During the Function Analysis Phase, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), cyber-physical systems (CPS), and digital twins automate function classification, map interdependencies, and simulate system behavior. These capabilities improve accuracy and objectivity in assessing cost-value trade-offs and help prioritize high-impact functions.
- (3)
- The Creative Phase leverages AI and NLP to extract insights from past designs and stakeholder feedback, while augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) foster immersive, collaborative ideation. Additive manufacturing accelerates the rapid prototyping and testing of functional alternatives.
- (4)
- In the Evaluation Phase, digital twins, simulation tools, and AI-driven analytics model lifecycle performance and guide multi-criteria trade-off decisions. AR/VR technologies enhance visualization and stakeholder communication, supporting consensus.
- (5)
- The Development Phase integrates cloud computing and collaborative platforms, such as Product and Service Lifecycle Management (PLM/SLM), to synchronize design, manufacturing, and cost data. Additive manufacturing enables iterative refinement of prototypes.
- (6)
- Finally, the Implementation Phase employs blockchain for secure, transparent traceability, robotic process automation (RPA) for streamlined documentation and compliance, and edge/cloud computing for real-time monitoring and adaptive feedback.
Collectively, these enhancements transform the VE Job Plan into a dynamic, proactive, and cyber-physical process that supports continuous, intelligent value creation. By embedding connectivity, intelligence, and responsiveness at every step, VE 4.0 aligns fully with Industry 4.0 principles, enabling smarter, faster, and more sustainable value engineering.
Table 4. Integration of Industry 4.0 technologies across the VE job plan.
|
# |
VE Job Plan Phase |
Enabling Technologies |
Strategic Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Information Phase: Understanding context, stakeholder needs, and cost drivers |
IoT, Big Data Analytics, Edge Computing, NLP |
1. Captures real-time functional and environmental data. 2. Extracts implicit requirements from unstructured sources via NLP. 3. Identifies cost and performance patterns through big data analytics. 4. Establishes a data-driven foundation for value analysis. |
|
2 |
Function Analysis Phase: Identifying, classifying, and prioritizing functions |
AI/ML, Big Data Analytics, CPS, Digital Twins |
1. Automates function modeling and cost–value correlation using AI. 2. Maps functional interdependencies through CPS and digital twins. 3. Supports prioritization via simulation and performance analytics. |
|
3 |
Creative Phase: Generating innovative value alternatives |
AI/ML, NLP, AR/VR, Additive Manufacturing |
1. Leverages AI for ideation and functional synthesis. 2. Utilizes NLP to derive insights from prior solutions and user feedback. 3. Enhances creativity through immersive AR/VR environments. 4. Enables rapid prototyping to test functional alternatives. |
|
4 |
Evaluation Phase: Assessing and selecting optimal alternatives |
Digital Twins, Simulation Tools, AI/ML, AR/VR |
1. Simulates lifecycle performance and cost–benefit trade-offs. 2. Applies AI for multi-criteria evaluation and ranking. 3. Improves stakeholder engagement via interactive visualization. |
|
5 |
Development Phase: Refining and preparing solutions for implementation |
Cloud Computing, PLM/SLM Platforms, Additive Manufacturing |
1. Enables real-time, cross-disciplinary collaboration. 2. Integrates functional, cost, and manufacturability data across systems. 3. Supports agile development through iterative prototyping. |
|
6 |
Implementation Phase: Executing, monitoring, and sustaining value solutions |
Blockchain, RPA, Edge Computing, Cloud Computing |
1. Ensures transparency and traceability using blockchain. 2. Automates reporting and compliance via RPA. 3. Facilitates real-time monitoring and adaptive feedback through cloud/edge platforms. |
4.4. Strategic Framework and Implementation Roadmap
To fully unlock the potential of VE in the digital era, a strategic framework is required—one that fuses classical VE principles with the transformative power of Industry 4.0 technologies. Value Engineering 4.0 (VE 4.0) represents this integration, redefining VE as a function-driven, data-intelligent, and sustainability-oriented methodology for real-time value optimization across the product–process–service lifecycle. As illustrated in Table 5, the VE 4.0 framework is structured around five interrelated pillars: digital integration, intelligent function analysis, lifecycle value orientation, human-centric collaboration, and organizational enablement.
- (1)
- The first pillar, digital integration, establishes the technological foundation of VE 4.0. By embedding cyber-physical systems (CPS), the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and big data analytics across the value chain, VE becomes connected, transparent, and responsive. Digital twins enable real-time virtual modeling, performance prediction, and continuous feedback. Their integration with enterprise systems—such as Product Lifecycle Management (PLM), Building Information Modeling (BIM), and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)—ensures data consistency, traceability, and interoperability from design through deployment.
- (2)
- The second pillar, intelligent and adaptive function analysis, modernizes traditional VE practices using artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP). These technologies automate the extraction and analysis of functional requirements from diverse sources, including technical specifications, operational data, and user feedback. AI algorithms dynamically evaluate cost–function–performance relationships and support rapid generation and assessment of alternative solutions, improving the precision and agility of value-based decision-making.
- (3)
- The third pillar, lifecycle value orientation and sustainability, broadens VE’s scope beyond short-term cost reduction to encompass holistic value creation across the full lifecycle. VE 4.0 incorporates environmental performance metrics—such as energy efficiency, carbon footprint, and material recyclability—into value assessments. By aligning with circular economy principles and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) frameworks, VE 4.0 supports long-term economic, environmental, and social value, ensuring that sustainability is embedded in design, development, and operations.
- (4)
- The fourth pillar, human-centric collaboration and ethical governance, reinforces the importance of human judgment, creativity, and ethical oversight. VE 4.0 leverages collaborative digital platforms, cloud-based tools, and immersive technologies (e.g., AR/VR) to enhance real-time engagement among stakeholders. Human-in-the-loop systems ensure transparency, fairness, and inclusivity in AI-driven decision processes. Ethical AI principles—such as explainability, accountability, and stakeholder inclusiveness—are essential to fostering trust and ensuring that value decisions align with societal values.
- (5)
- The fifth pillar, organizational enablement and capability building, focuses on the cultural and structural foundations necessary for successful VE 4.0 implementation. This includes establishing governance mechanisms, digital maturity models, and transformation roadmaps aligned with enterprise strategy. Organizations must foster cross-functional coordination, develop agile teams, and invest in upskilling programs that integrate systems thinking, digital literacy, and ethical innovation. Modular education platforms and scalable certification schemes are key to developing and sustaining VE 4.0 competencies across industries.
To operationalize this framework, a phased implementation roadmap is proposed. The assessment phase evaluates current VE practices, digital infrastructure, and readiness levels. During the planning phase, organizations articulate a VE 4.0 vision, align it with strategic objectives, and map required technologies and skills. The pilot phase introduces VE 4.0 tools—such as AI-enabled function modeling and digital twin platforms—in selected projects to validate benefits and refine methods. Successful pilots lead to the scaling phase, where VE 4.0 is institutionalized across the enterprise, integrated into digital systems, and monitored through performance metrics. The continuous improvement phase sustains innovation and adaptability through feedback loops, strategic partnerships, and learning ecosystems.
Ultimately, this strategic framework positions VE 4.0 as a forward-looking methodology that moves beyond cost reduction to enable smart, resilient, and sustainable value creation. By combining classical VE logic with digital technologies, lifecycle thinking, and ethical collaboration, VE 4.0 emerges as a critical enabler of transformation in Industry 4.0 and beyond.
Table 5. Strategic framework for Value Engineering 4.0.
|
# |
Strategic Pillar |
Key Enablers |
Strategic Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Digital Integration |
• Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) • Internet of Things (IoT) • Digital Twins • Cloud Computing • Integration with PLM, BIM, and ERP systems |
• Real-time data visibility and traceability • Predictive value simulation • Seamless data flow across lifecycle stages |
|
2 |
Intelligent Function Analysis |
• Artificial Intelligence (AI) • Machine Learning (ML) • Natural Language Processing (NLP) • Optimization algorithms |
• Adaptive and automated function modeling • Continuous value analysis • Enhanced decision-making with real-time data |
|
3 |
Lifecycle Value & Sustainability |
• Digital Twin–enabled lifecycle modeling • Predictive analytics • Circular economy indicators • ESG-based assessment tools |
• Lifecycle cost and impact optimization • Sustainability integration • Alignment with circular and green innovation goals |
|
4 |
Human-Centric Collaboration |
• Collaborative cloud platforms • Augmented/Virtual Reality (AR/VR) • Human-in-the-loop decision frameworks • Ethical and explainable AI |
• Inclusive stakeholder engagement • Transparent, trusted value creation • Preservation of human agency and creativity |
|
5 |
Organizational Enablement |
• VE 4.0 maturity models • Digital transformation roadmaps • Agile governance • Interdisciplinary training and certification |
• Scalable and sustainable VE 4.0 implementation • Future-ready workforce • Strategic alignment with enterprise objectives |
4.5. Enhanced DMAIC Methodology for Value Engineering 4.0
In the era of Industry 4.0, the traditional Lean Six Sigma DMAIC (Define–Measure–Analyze–Improve–Control) framework must evolve to meet the demands of complex, data-intensive, and interconnected industrial systems. VE 4.0 addresses this need by reimagining DMAIC as a digitally empowered, function-driven, and lifecycle-oriented methodology for continuous value optimization. As outlined in Table 6, the enhanced DMAIC cycle integrates advanced technologies—such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), digital twins, edge computing, simulation tools, and collaborative digital platforms—into every phase. This transformation enables precise problem definition, real-time performance monitoring, predictive analytics, and sustainable value realization across the full product–process–service lifecycle.
- (1)
- Define: Value Clarity and Digital Alignment: This phase focuses on defining value objectives, identifying critical functions, and aligning stakeholder expectations. Digital collaboration platforms, VR/AR tools, and digital twins facilitate system visualization and early stakeholder engagement. These technologies ensure a shared understanding of functional priorities and value drivers, laying the groundwork for informed decision-making.
- (2)
- Measure: Real-Time Data Acquisition and Functional Baselines: IoT sensors, edge computing, and big data platforms enable continuous monitoring of operational parameters, usage patterns, and cost-performance metrics. These tools support accurate, real-time data capture, allowing for the establishment of robust baselines to guide targeted functional analysis and value assessment.
- (3)
- Analyze: Functional Insight and Predictive Analytics: AI, machine learning, and data mining techniques enhance functional analysis by identifying inefficiencies, modeling cost–function–performance relationships, and predicting value gaps. This phase enables a shift from retrospective evaluation to proactive diagnostics, supporting evidence-based prioritization of improvement opportunities.
- (4)
- Improve: Agile Innovation and Virtual Experimentation: Using AR/VR, simulation tools, and digital co-creation platforms, cross-functional teams can rapidly ideate, test, and validate functional alternatives. Additive manufacturing supports quick prototyping, while intelligent systems accelerate trade-off analysis. This collaborative, iterative process ensures optimal solutions are developed with greater speed, creativity, and precision.
- (5)
- Control: Lifecycle Monitoring and Adaptive Value Management: Digital twins, predictive analytics, and automated dashboards are deployed to monitor functional performance, detect deviations, and enable adaptive responses. Blockchain technology enhances transparency and traceability, while robotic process automation (RPA) ensures efficient execution and documentation. This phase secures long-term value realization and functional integrity across the lifecycle.
In conclusion, the enhanced DMAIC methodology within VE 4.0 transitions value engineering from a linear, project-specific exercise into a continuous, digital, and systemic optimization model. By embedding intelligence, agility, and connectivity into every phase, it empowers organizations to respond dynamically to change, maximize lifecycle value, and drive strategic innovation in line with the principles of Industry 4.0.
Table 6. Enhanced DMAIC methodology in VE 4.0.
|
Phase |
Strategic Focus |
Key Activities |
Enabling Technologies |
Key Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Define |
Precise value definition and stakeholder alignment |
Define project scope, identify critical functions, and engage stakeholders through digital collaboration |
Digital Twins, Virtual Reality (VR), Cloud Collaboration Platforms |
Clear objectives and aligned stakeholder expectations |
|
Measure |
Real-time, accurate data acquisition |
Deploy IoT sensors, capture continuous performance data, and establish robust data pipelines. |
IoT Sensors, Big Data Analytics, Edge Computing |
Reliable, actionable data on key value drivers |
|
Analyze |
Intelligent root cause analysis and predictive modeling |
Use AI and machine learning to analyze function-cost-performance relationships, detect inefficiencies, and forecast outcomes |
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Data Mining |
Deep insights into value drivers and predictive risks |
|
Improve |
Agile, collaborative, data-driven optimization |
Generate alternatives, perform virtual prototyping, and facilitate cross-functional collaboration. |
Simulation Software, Augmented Reality (AR), Collaborative Platforms |
Optimized solutions and faster innovation cycles |
|
Control |
Continuous monitoring and value sustainability |
Implement automated monitoring, feedback loops, and adaptive controls based on real-time insights. |
Digital Twins, Automated Dashboards, Predictive Maintenance |
Sustained value delivery and proactive process control |
4.6. Implementation Challenges and Strategic Enablers
Implementing VE 4.0 in contemporary industrial settings offers transformative potential but also introduces multifaceted challenges. While VE 4.0 leverages advanced Industry 4.0 technologies to enable real-time, lifecycle-oriented value optimization, its successful adoption demands overcoming significant technical, organizational, and cultural hurdles. As summarized in Table 7, addressing these challenges through well-defined strategic enablers is critical to unlocking the full benefits of VE 4.0 and ensuring its sustainable integration across the enterprise.
- (1)
- One of the most critical challenges lies in Leadership and Organizational Culture. Resistance to change, insufficient executive engagement, and a lack of strategic awareness often hinder the adoption of VE 4.0. Without strong leadership commitment, VE initiatives remain fragmented and underfunded. To overcome this, organizations must foster top-down sponsorship, embed VE 4.0 into digital transformation strategies, and cultivate a culture of innovation and cross-functional collaboration. Digital co-creation platforms and participatory governance structures can further reinforce engagement and alignment.
- (2)
- In the domain of Workforce Capability and Skills, the gap between traditional VE expertise and digital fluency presents a significant constraint. Many practitioners lack proficiency in AI, IoT, digital twins, and other enabling technologies, which limits their ability to leverage VE 4.0 effectively. Bridging this gap requires targeted upskilling programs, modular certification schemes, and the integration of VE 4.0 concepts into engineering and management education. Establishing maturity models and initiating pilot projects can also promote standardized, scalable implementation across departments and business units.
- (3)
- Digital Integration and System Interoperability present technical barriers that affect the seamless deployment of VE 4.0. Fragmented IT infrastructures, legacy systems, and the absence of open architecture standards can disrupt data continuity and tool interoperability. Strategic responses include investing in middleware solutions, adopting interoperable digital platforms, and aligning VE 4.0 with enterprise systems such as ERP, PLM, BIM, and digital twin ecosystems. Standardizing VE 4.0 toolkits and frameworks is also necessary to ensure consistency, repeatability, and institutional learning.
- (4)
- The increasing reliance on real-time data and cloud-based platforms introduces challenges related to Data Governance and Cybersecurity. These include concerns over data privacy, security breaches, and regulatory compliance. Organizations must implement robust cybersecurity protocols, encrypted data-sharing mechanisms, and align practices with global data protection standards. Moreover, traditional VE frameworks often overlook non-financial dimensions of value, such as environmental impact, social equity, and system resilience. Integrating ESG metrics, circular economy indicators, and stakeholder-focused KPIs enables a more holistic and forward-looking value assessment.
In summary, the successful implementation of VE 4.0 requires a balanced strategy that addresses leadership alignment, workforce readiness, digital infrastructure, and responsible data management. The strategic enablers outlined in Table 7 serve as a roadmap for overcoming these challenges and embedding VE 4.0 as a foundational pillar in smart, sustainable, and human-centric industrial transformation.
Table 7. Strategic challenges and solutions for VE 4.0 implementation.
|
Strategic Domain |
Challenge |
Solution |
|---|---|---|
|
1. Leadership & Culture |
Resistance to change and lack of executive commitment |
Promote leadership awareness of VE 4.0’s strategic value; integrate change management initiatives; foster a culture of innovation and adaptability |
|
Siloed operations and limited stakeholder engagement |
Establish cross-functional teams; adopt participatory approaches to decision-making; institutionalize co-creation frameworks. |
|
|
2. Workforce & Capability |
Inadequate digital skills and limited understanding of Industry 4.0 tools |
Design targeted training programs; incorporate VE 4.0 into academic and professional development curricula; launch digital certification pathways |
|
Uneven adoption across projects or departments |
Implement phased deployment; develop VE 4.0 maturity assessment tools; align with enterprise digital transformation strategies. |
|
|
3. Digital Integration |
Fragmented IT systems and a lack of interoperability |
Invest in modular, cloud-based infrastructure; adopt open standards and APIs; ensure seamless integration with PLM, ERP, BIM, and digital twin systems |
|
Lack of standardized VE 4.0 tools and methodologies |
Develop flexible VE 4.0 toolkits and reference models; tailor frameworks for different sectors and project types |
|
|
4. Data & Cybersecurity |
Data security risks and weak governance structures |
Implement robust cybersecurity protocols; ensure regulatory compliance; enhance trust through secure, transparent data sharing |
|
Challenges in measuring intangible value (e.g., sustainability, resilience) |
Integrate ESG metrics, circularity indicators, and stakeholder value models into VE analysis and performance evaluation. |
5. Conclusions and Future Work
This study presents Value Engineering 4.0 (VE 4.0) as a strategic evolution of classical value engineering, redefined through the lens of Industry 4.0. While traditional VE focused on optimizing the function-to-cost ratio, VE 4.0 expands its scope to enable intelligent, real-time, and lifecycle-oriented value creation. By integrating core VE principles with advanced technologies—such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), Digital Twins, Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), and Big Data analytics—VE 4.0 enables adaptive, data-driven, and collaborative approaches to value optimization across complex industrial ecosystems. This approach moves beyond static analysis toward predictive and prescriptive decision-making, allowing organizations to anticipate inefficiencies, optimize costs, and continuously improve performance. Furthermore, VE 4.0 incorporates sustainability metrics, circular economy principles, and human-centric considerations, ensuring that value creation aligns with economic, environmental, and social objectives.
The study also addresses key limitations of conventional VE practices, including fragmented digital integration, reactive implementation, and limited support for continuous decision-making. To overcome these gaps, a comprehensive VE 4.0 framework is proposed, comprising six components: (1) foundational principles emphasizing digital readiness, sustainability, human-centric collaboration, and organizational adaptability; (2) digital transformation of VE processes to support predictive and connected decision-making; (3) enhanced VE Job Plan leveraging tools such as NLP, AR/VR, and blockchain for improved analytical precision, speed, and lifecycle alignment; (4) phased implementation roadmap covering assessment, planning, piloting, scaling, and continuous improvement; (5) enhanced Lean Six Sigma DMAIC framework embedded with smart technologies for real-time optimization; and (6) enablers and mitigation strategies addressing leadership, digital competencies, infrastructure, and cybersecurity challenges.
By reconceptualizing VE as a digitally empowered, ethically governed, and sustainability-aligned methodology, VE 4.0 emerges as a key enabler of innovation, strategic agility, and long-term value creation in Industry 4.0 contexts. The framework not only extends the function-oriented nature of VE but also aligns it with the demands of dynamic, data-intensive, and interconnected industrial environments, offering both a practical roadmap and a foundation for future research.
Theoretical Implications: This study expands the conceptual scope of VE by embedding it in the digital transformation paradigm. It presents a hybrid model that integrates function-based reasoning with AI, real-time data analytics, and collaborative platforms—offering a foundation for future academic exploration in systems thinking and intelligent design optimization.
Practical Implications: The VE 4.0 framework provides actionable strategies for engineers, designers, and transformation leaders. It supports the use of digital twins, AI tools, and immersive technologies to enhance the accuracy, speed, and relevance of value-driven decisions across complex product and service environments.
Managerial Implications: For business leaders and decision-makers, VE 4.0 serves as a strategic tool for aligning engineering processes with enterprise-wide goals such as innovation, sustainability, and operational excellence. The roadmap and KPI frameworks help organizations evaluate readiness, foster cross-functional collaboration, and ensure scalable VE 4.0 deployment.
Study Limitations: As a conceptual study, this work lacks empirical validation and sector-specific case applications. Differences in digital maturity, infrastructure, and organizational culture may affect the adaptability of the framework across industries.
Future Work: Future research should focus on validating the VE 4.0 framework through empirical case studies, simulation modeling, and longitudinal analysis across sectors. The development of maturity models, training programs, and standardized toolkits will be essential for practical implementation. Moreover, the convergence of VE 4.0 with emerging Industry 5.0 paradigms—such as ethical AI, human-machine symbiosis, and regenerative systems—offers fertile ground for further inquiry and innovation.
Statement of the Use of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
While preparing this work, the author used ChatGPT to improve the writing quality of certain paragraphs. He confirms that no generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) was used in creating the content of this manuscript.
Ethics Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting this study are included within the article.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The author declares that he has no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Gomaa AH. Enhancing Product Development Using Lean Six Sigma Approach: From Continuous Improvement to Continuous Innovation. IUP J. Oper. Manag. 2024, 23, 5–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dahooie JH, Dehshiri SJH, Banaitis A, Binkytė-Vėlienė A. Identifying and prioritizing cost reduction solutions in the supply chain by integrating value engineering and gray multi-criteria decision-making. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2020, 26, 1311–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Emami K, Emami T. Value engineering: Opportunities and challenges. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 307–313. [Google Scholar]
- Masengesho E, Wei J, Umubyeyi N, Niyirora R. A review on the role of risk management (RM) and value engineering (VE) tools for project successful delivery. World J. Eng. Technol. 2020, 9, 109–127. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrahman SA, Nassar AH. Integrating Theory and Practice in Value Engineering Within Egypt’s Construction Industry. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2024, 71, 188. [Google Scholar]
- Li X, Wang C, Alashwal A. Case study on BIM and value engineering integration for construction cost control. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8849303. [Google Scholar]
- Alhumaid AM, Bin Mahmoud AA, Almohsen AS. Value Engineering Adoption’s Barriers and Solutions: The Case of Saudi Arabia’s Construction Industry. Buildings 2024, 14, 1017. [Google Scholar]
- Amoah KB. Optimizing building information modeling and value engineering synergy for construction schedule and cost worth. J. Civ. Eng. Res. 2023, 13, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lee J, Na S. Investigation of Practitioners’ Perceptions for Developing Building Information Modelling (BIM)-Based Value Analysis Model. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 301–313. [Google Scholar]
- Gomaa AH. Achieving Project Management Excellence through Lean Six Sigma. Middle East Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2025, 5, 18–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sutikno, Husin AE, Imron A. Optimizing the green building investment project mice-stadium with structural equation modeling based on value engineering and life cycle cost analysis. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2024; Volume 2710, p. 090015. [Google Scholar]
- Bock S, Pütz M. Implementing Value Engineering based on a multidimensional quality-oriented control calculus within a Target Costing and Target Pricing approach. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 146–158. [Google Scholar]
- Nucciarelli A, Li F, Fernandes KJ, Goumagias N, Cabras I, Devlin S, et al. From value chains to technological platforms: The effects of crowdfunding in the digital game industry. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 78, 341–352. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelghany M, Rachwan R, Abotaleb I, Albughdadi A. Value Engineering Applications to Improve Value in Residential Projects. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference—Canadian Society for Civil Engineering, Regina, SK, Canada, 27–30 May 2015; pp. 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Rane NL, Attarde PM. Application of Value Engineering in Construction Projects. Int. J. Eng. Manag. Res. (IJEMR) 2016, 6, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Perpetua NN. The Application of Value Engineering on Construction Projects in Abia State, Niger. Iconic Res. Eng. J. 2019, 3, 40–55. [Google Scholar]
- Mahinkanda MMMP, Sandanayake YG, Ekanayake BJ. Bridging the Theory-Practice Gap in Value Management in Sri Lankan Construction Industry. In Proceedings of the 8th World Construction Symposium, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 8–10 November 2019; pp. 147–157. [Google Scholar]
- Almansour M, Krarti M. Value Engineering Optimal Design Approach of High-Performance Residential Buildings: Case Study of Kuwait. Energy Build. 2022, 258, 111833. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed A, Abdelalim AM, Elhakeem A, Said SO. A Proposed Framework for the Integration of Value Engineering and Building Information Modeling. Eng. Res. J. 2024, 182, 322–340. [Google Scholar]
- Xu LD, Xu EL, Li L. Industry 4.0: State of the art and future trends. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 2941–2962. [Google Scholar]
- Barata J, Kayser I. Industry 5.0—Past, present, and near future. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 219, 778–788. [Google Scholar]
- Gomaa AH. Advancing Manufacturing Excellence in the Industry 4.0 Era: A Comprehensive Review and Strategic Integrated Framework. Supply Chain Res. 2024, 2, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hermann M, Pentek T, Otto B. Design Principles for Industrie 4.0 Scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2016 49th Hawaii International Conference on Systems Science, Maui, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y. Industry 4.0: A Survey on Technologies, Applications and Open Research Issues. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2017, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gomaa AH. Lean 4.0: A Strategic Roadmap for Operational Excellence and Innovation in Smart Manufacturing. Int. J. Emerg. Sci. Eng. (IJESE) 2025, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gomaa AH. LSS 4.0: A Conceptual Framework for Integrating Lean Six Sigma and Industry 4.0 for Smart Manufacturing Excellence. Indian J. Manag. Lang. (IJML) 2025, 5, 8–29. [Google Scholar]
- Pozzi R, Rossi T, Secchi R. Industry 4.0 technologies: Critical success factors for implementation and improvements in manufacturing companies. Prod. Plan. Control. 2021, 34, 138–158. [Google Scholar]
- Gomaa AH. Quality Management Excellence in the Era of Industry 4.0 (Quality 4.0): A Comprehensive Review, Gap Analysis, and Strategic Framework. MRS J. Account. Bus. Manag. 2025, 2, 18–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lasi H, Fettke P, Kemper HG, Feld T, Hoffmann M. Industry 4.0. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2014, 6, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Ghobakhloo M, Fathi M, Iranmanesh M, Maroufkhani P, Morales ME. Industry 4.0 ten years on: A bibliometric and systematic review of concepts, sustainability value drivers, and success determinants. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 127052. [Google Scholar]
- Yacout S. Industrial Value Chain Research and Applications for Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the 4th North America Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Toronto, ON, Canada, 23–25 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Siau K, Xi Y, Zou C. Industry 4.0: Challenges and opportunities in different countries. Cut. Bus. Technol. J. 2019, 32, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Ma HS, Yang JH, Wang KS. Industry 4.0: A way from mass customization to mass personalization production. Adv. Manuf. 2017, 5, 311–320. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar P, Bhadu J, Singh D, Bhamu J. Integration between lean, six sigma and industry 4.0 technologies. Int. J. Six Sigma Compet. Advant. 2021, 13, 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ghobakhloo M. Industry 4.0, digitization, and opportunities for sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119869. [Google Scholar]
- Qin J, Liu Y, Grosvenor R. A Categorical Framework of Manufacturing for Industry 4.0 and beyond. Procedia CIRP 2016, 52, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira AC, Romero F. A review of the meanings and the implications of the Industry 4.0 concept. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 13, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski K. Internet of things, big data, industry 4.0–innovative solutions in logistics and supply chains management. Procedia Eng. 2017, 182, 763–769. [Google Scholar]
- Mrugalska B, Wyrwicka MK. Towards lean production in industry 4.0. Procedia Eng. 2017, 182, 466–473. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo CJ, Ting KC, Chen YC, Yang DL, Chen HM. Automatic machine status prediction in the era of Industry 4.0: Case study of machines in a spring factory. J. Syst. Archit. 2017, 81, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou K, Liu T, Zhou L. Industry 4.0: Towards Future Industrial Opportunities and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD), Zhangjiajie, China, 15–17 August 2015; pp. 2147–2152. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary D, Nandy I. A study of sustainability risks from industry 4.0 perspective: Taxonomy and future research avenues. Compet. Rev. Int. Bus. J. 2024, 34, 1178–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Rijwani T, Kumari S, Srinivas R, Abhishek K, Iyer G, Vara H, et al. Industry 5.0: A review of emerging trends and transformative technologies in the next industrial revolution. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 2025, 19, 667–679. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Salmawi MAK, Al-Eqabi MAR. Integration Between Value Engineering Technology and Activity-Based Costing and their Impact on Reducing Costs: Applied Research in Baghdad Soft Drinks Company/Private Shareholding. Eur. J. Bus. Manag. Res. 2024, 9, 94–105. [Google Scholar]
- Fatorachian H, Kazemi H. A critical investigation of Industry 4.0 in manufacturing: Theoretical operationalisation framework. Prod. Plan. Control 2018, 29, 633–644. [Google Scholar]
- Ghobakhloo M, Iranmanesh M, Vilkas M, Grybauskas A, Amran A. Drivers and barriers of industry 4.0 technology adoption among manufacturing SMEs: A systematic review and transformation roadmap. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2022, 33, 1029–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Husal HR, Ginting R, Anizar A. Integrated Value Engineering with QFD and DFA as Product Design and Development Techniques: Literature Review. J. Sist. Tek. Ind. 2024, 26, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Janani R, Chakravarthy PK, Raj DRR. A study on value engineering & green building in residential construction. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 900–907. [Google Scholar]
- Młody M, Ratajczak-Mrozek M, Sajdak M. Industry 4.0 technologies and managers’ decision-making across value chain. Evidence from the manufacturing industry. Eng. Manag. Prod. Serv. 2023, 15, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed M. Challenges and benefits of industry 4.0: An overview. Int. J. Supply Oper. Manag. 2018, 5, 256–265. [Google Scholar]
- Othman I, Kineber AF, Oke AE, Zayed T, Buniya MK. Barriers of Value Management Implementation for Building Projects in Egyptian Construction Industry. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Sajdak M, Młody M. Technological anxiety during the implementation of Industry 4.0 technologies—A cross-case study analysis among Polish manufacturing companies. Compet. Rev. Int. Bus. J. 2024, 34, 660–679. [Google Scholar]
- Sajdak M, Młody M. Sources of Technological Anxiety During the Implementation of Industry 4.0 Technologies in the Industrial Processing Sector—A Cross-Case Study Analysis. 2023. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4330719 (accessed on 05 August 2025). [Google Scholar]
- Tortorella GL, Fettermann D. Implementation of Industry 4.0 and lean production in Brazilian manufacturing companies. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 2975–2987. [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, He J, Xu S. The application of industry 4.0 in customized furniture manufacturing industry. In Matec Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Paris, France, 2017; Volume 100, p. 03022. [Google Scholar]