Found 22 results
Article
29 April 2025Application of recovered Carbon Black (rCB) by Waste Tire Pyrolysis as an Alternative Filler in Elastomer Products
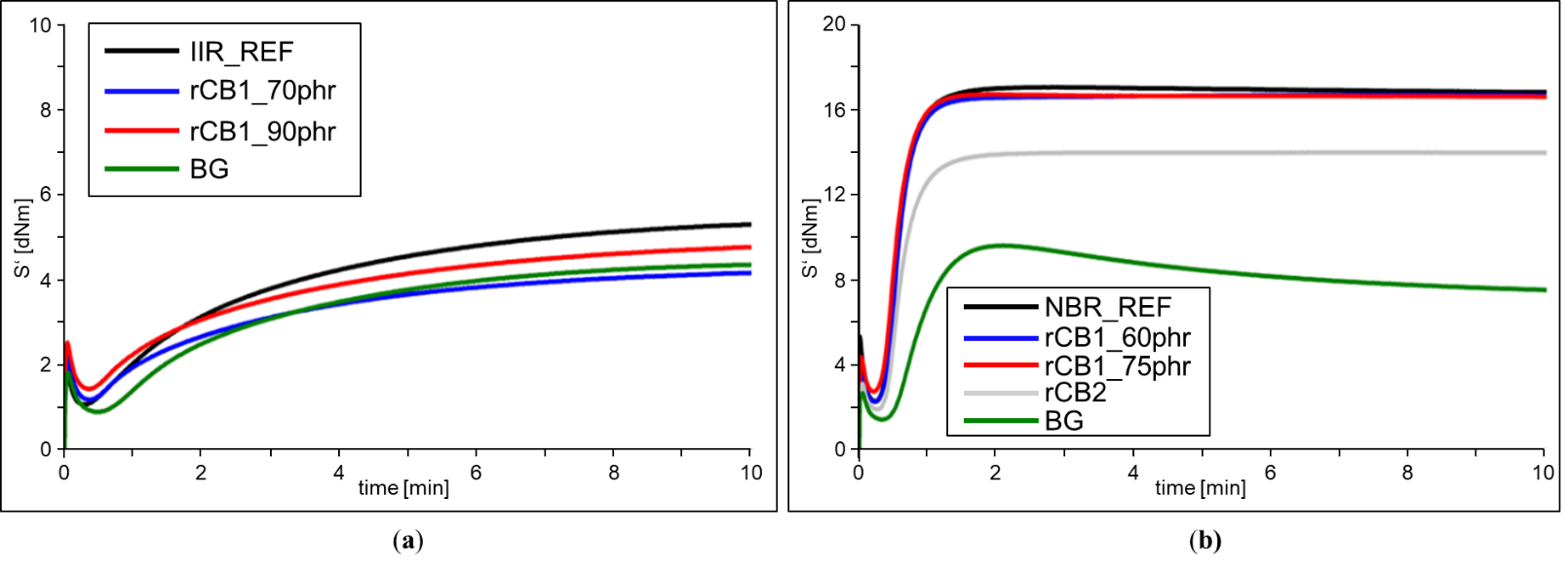
The increasing global accumulation of End-of-Life (EoL) tires and the growing demand for fossil industrial Carbon Black (CB) call for sustainable alternative solutions. In this context, tire pyrolysis and the resulting recycled raw material recovered Carbon Black (rCB), are considered potential alternatives. In the study, various rCBs were incorporated into new elastomer compounds using a laboratory internal mixer and their properties were investigated. The compounds were selected based on examples of applications such as bicycle inner tubes and hydraulic membranes. By comparing the in-rubber properties of rCB-based compounds with CB reference compounds, an initial assessment of the potential use of rCB for the chosen products was derived. Compared to industrial carbon black, the use of rCB leads to a reduction in performance. Although increasing the filler content partially compensated for the mineral content in rCB and led to a slight improvement, it could not fully offset the performance loss.
Article
28 April 2025Production and Characterization of Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) by Waste Tire Pyrolysis as a Potential Carbon Black (CB) Substitute
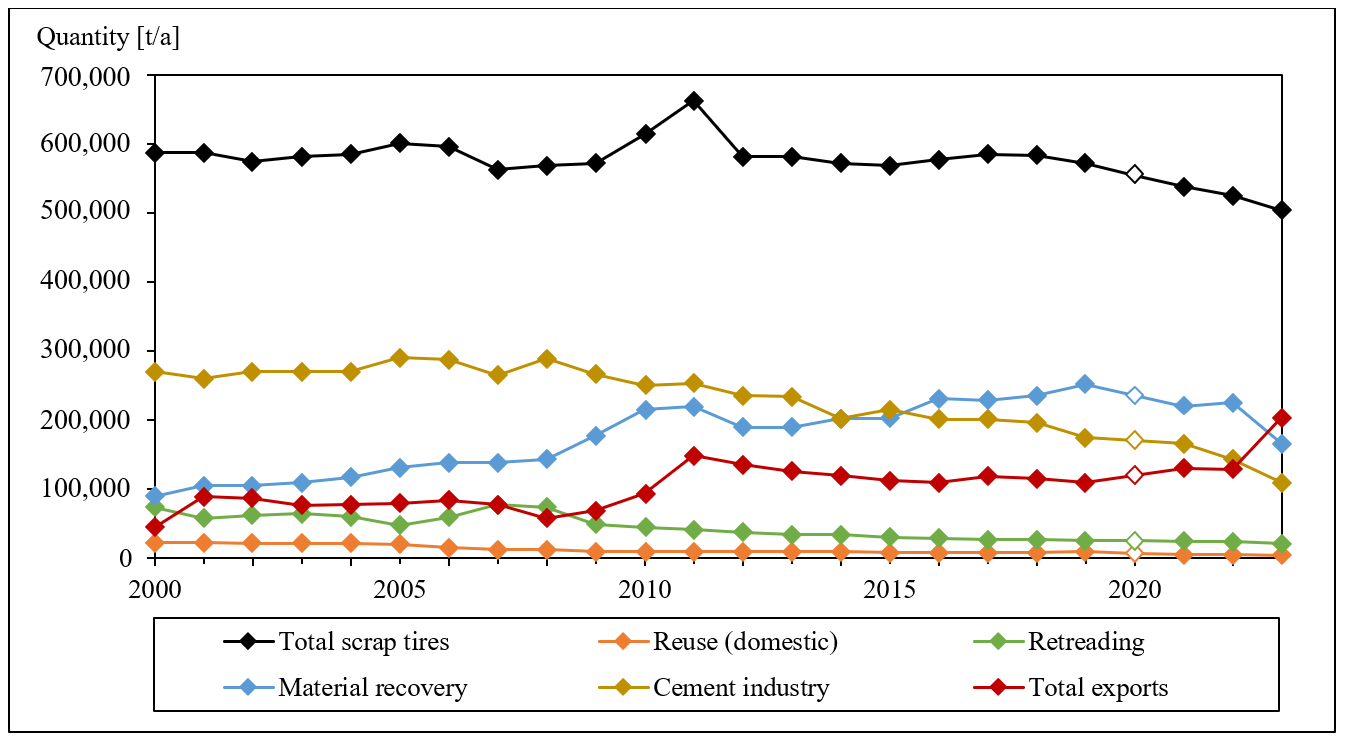
Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) from scrap tire pyrolysis offers a potential alternative to fossil-based virgin Carbon Black (CB) in the context of a circular economy. This study investigated the influence of pyrolysis process parameters on rCB yield and quality at laboratory and semi-industrial scales. The resulting rCBs were characterized and found to have surface and structural properties comparable to N500 and N600 series CBs, but with higher mineral and volatile contents. The quality of rCB is influenced by the feedstock composition, particularly the ratio of organic to inorganic components as well as key process parameters such as heating rate, pyrolysis temperature and residence time. Higher heating rates accelerate degradation and shift product distribution toward increased oil yield and reduced rCB formation, while higher pyrolysis temperatures lead to lower volatile content in rCB. Additionally, reactor and process design affect heat distribution, transfer efficiency, and mixing behavior, further shaping rCB properties. However, further testing is required to evaluate the actual in-rubber properties of rCBs. Therefore, additional tests are planned, incorporating rCB into butyl and nitrile rubber-based elastomer compounds, which will be addressed in a follow-up study. In addition, data from the current experiments will support a comprehensive Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) to evaluate the environmental impacts of tire pyrolysis and rCB production compared to other recycling methods, with details to follow in a future publication.
Review
02 April 2025Wide-Bandgap Semiconductors: A Critical Analysis of GaN, SiC, AlGaN, Diamond, and Ga2O3 Synthesis Methods, Challenges, and Prospective Technological Innovations
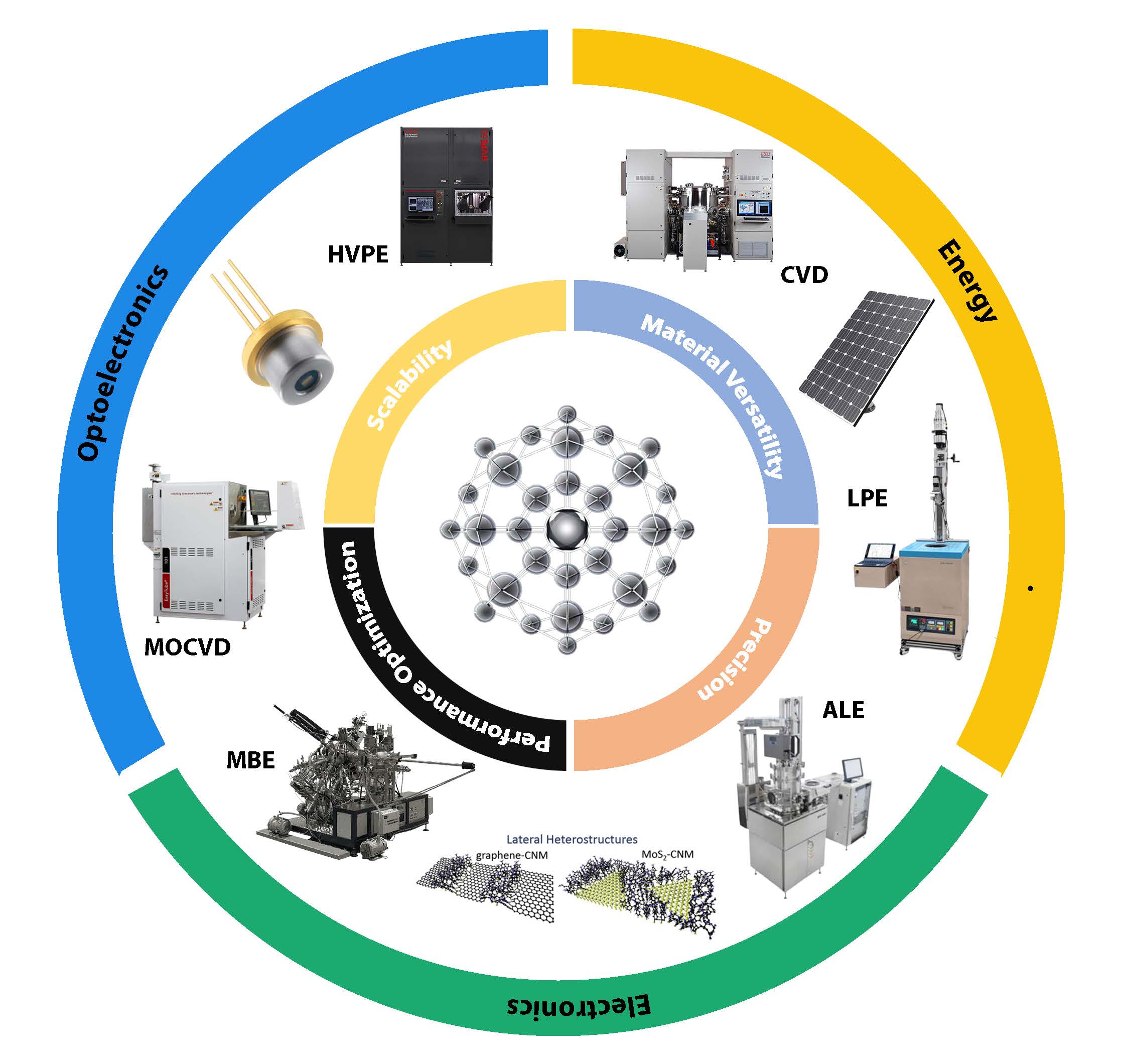
The increasing demand for high-performance Wide-Bandgap (WBG) semiconductors, including GaN, SiC, and emerging Ultrawide-Bandgap (UWBG) materials such as Ga2O3 and diamond, has driven significant advancements in epitaxial growth techniques. However, achieving scalability, defect-free growth, and sustainability remains a major challenge. This review systematically evaluates Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE), Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD), Hydride Vapor Phase Epitaxy (HVPE), and other novel growth and hybrid growth techniques, emphasizing energy efficiency, defect control, and environmental impact. Industry 4.0-driven AI-based process optimization and closed-loop recycling have emerged as transformative strategies, reducing waste and improving manufacturing efficiency. Key findings reveal that HVPE enables rapid defect-free GaN fabrication, Hot-Filament CVD enhances SiC growth with superior thermal properties, and Atomic Layer Epitaxy (ALE) achieves sub-nanometer precision crucial for next-generation quantum and RF applications. Despite these advancements, p-type doping in UWBG materials, substrate compatibility, and thermal management remain unresolved challenges. Future research must focus on scalable eco-friendly epitaxy, novel doping mechanisms, and policy-driven sustainability efforts. This review provides a comprehensive roadmap for sustainable WBG semiconductor manufacturing, bridging materials innovation, energy efficiency, and industrial adoption to support the next generation of power electronics and optoelectronics.
Review
01 April 2025Sustainable Manufacturing and Applications of Wide-Bandgap Semiconductors—A Review
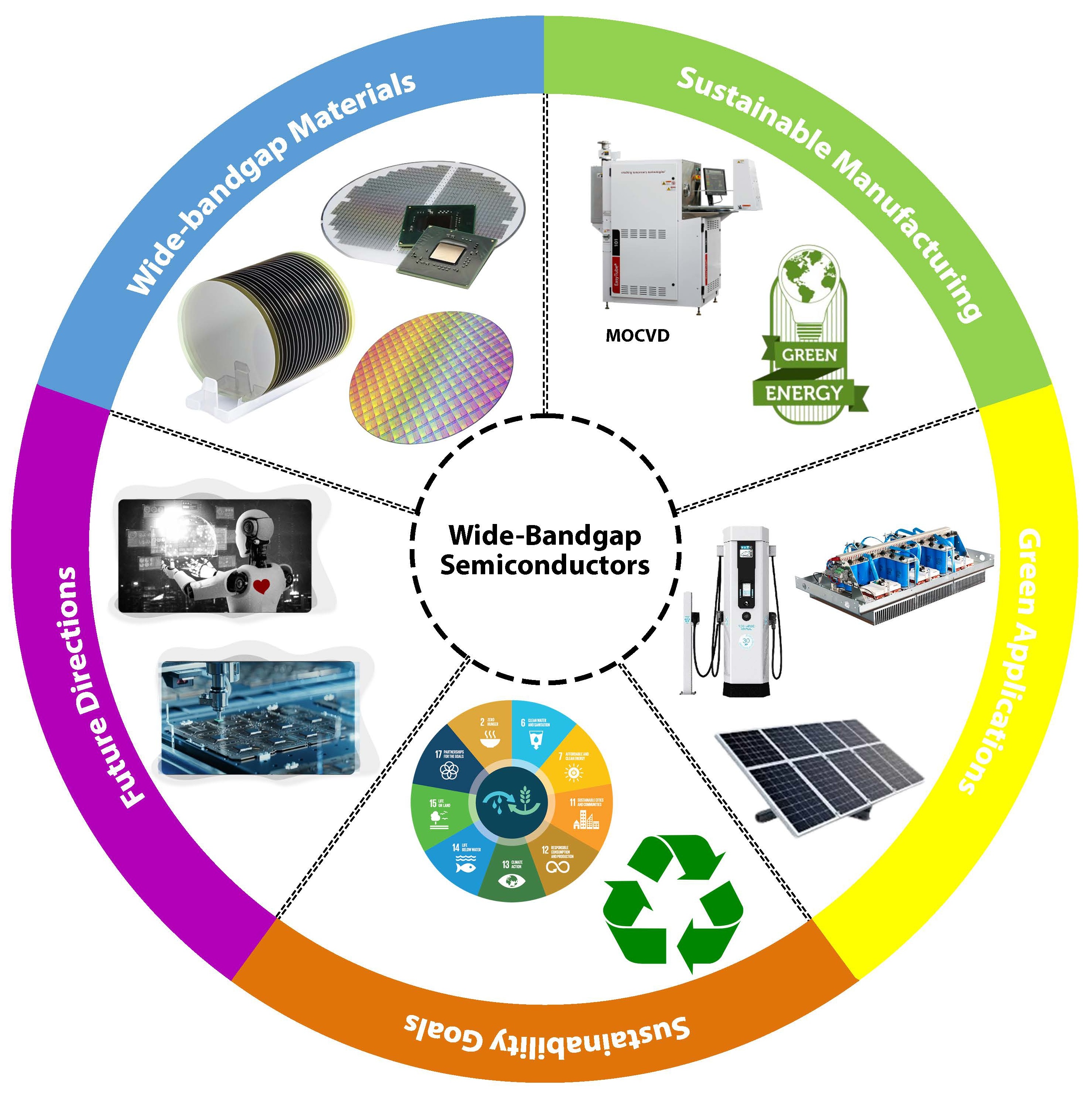
Wide-bandgap (WBG) semiconductors such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) are revolutionizing high-power electronics due to their superior thermal conductivity, breakdown voltage, and energy efficiency. These materials are critical in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and high-frequency applications like 5G infrastructure. However, their production processes are resource-intensive and present significant environmental challenges. This review evaluates recent advancements in sustainable WBG semiconductor manufacturing, focusing on low-energy epitaxial growth, closed-loop recycling, and the mitigation of toxic by-products. Additionally, it highlights the role of Industry 4.0 innovations, such as AI-driven process optimization and IoT-based resource management, in enhancing sustainability. The review identifies research gaps in cost reduction, alternative WBG materials like Gallium Oxide (Ga2O3) and Diamond, and scalable green manufacturing solutions. It underscores the necessity for industry-wide collaboration and regulatory frameworks to drive the adoption of eco-friendly semiconductor fabrication. The findings of this study provide a roadmap for advancing sustainability in WBG semiconductor production, ensuring their long-term viability in the transition toward energy-efficient technologies.
Article
17 March 2025A Strategy for Resisting the Vested Interests Driving the Collapse of the Biosphere and Civilisation
The biosphere and civilisation are facing existential and other major threats: climate change, biodiversity loss, nuclear war, social inequality/injustice, loss of human rights, and autocracy. These threats are driven by politically powerful vested interests supported by an economic system based on the exploitation of the environment and most people for the benefit of a wealthy minority. This article proposes a strategy to resist and weaken state capture, i.e., the influence of the vested interests driving the principal threats, while simultaneously facilitating the transition to a sustainable society. Despite the achievements of diverse community-based non-government organisations (CNGOs) campaigning on specific issues, scientists are now warning of the potential collapse of civilisation. As the threats are linked together in several ways, I propose a strategy to address them together to yield multiple benefits, supplementing campaigns on individual issues. A broad social movement—comprising an alliance between CNGOs devoted to the environment, social justice, human rights, and peace—could exert sufficient political power to expose and defeat the methods of state capture. Simultaneously, the movement could gain widespread community support by campaigning for a well-being economy, including universal basic services and a job guarantee, thus facilitating the transition to an ecologically sustainable, more socially just, and more peaceful civilisation.

Article
10 March 2025Leveraging Drone Technology for Precision Agriculture: A Comprehensive Case Study in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia
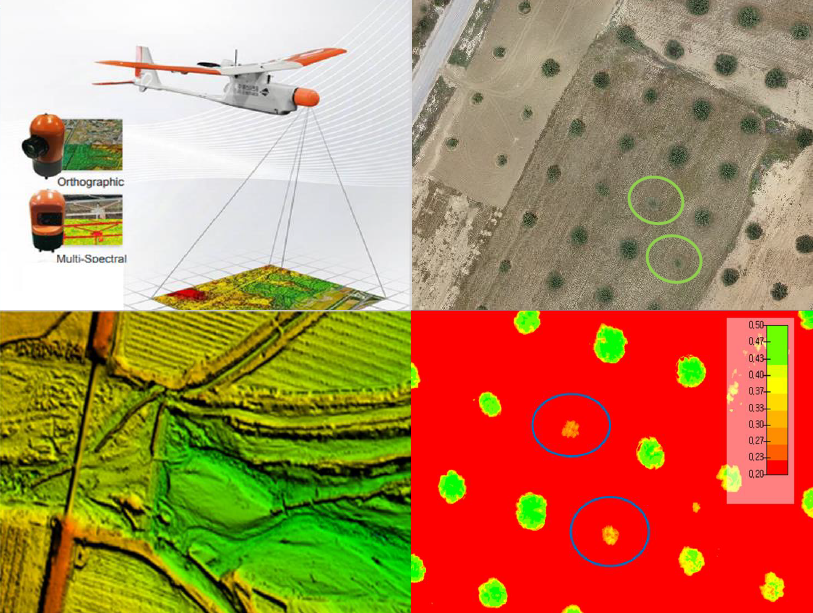
The integration of drone technology in precision agriculture offers promising solutions for enhancing crop monitoring, optimizing resource management, and improving sustainability. This study investigates the application of UAV-based remote sensing in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia, focusing on olive tree cultivation in a semi-arid environment. REMO-M professional drones equipped with RGB and multispectral sensors were deployed to collect high-resolution imagery, enabling advanced geospatial analysis. A comprehensive methodology was implemented, including precise flight planning, image processing, GIS-based mapping, and NDVI assessments to evaluate vegetation health. The results demonstrate the significant contribution of UAV imagery in generating accurate land use classifications, detecting plant health variations, and optimizing water resource distribution. NDVI analysis revealed clear distinctions in vegetation vigor, highlighting areas affected by water stress and nutrient deficiencies. Compared to traditional monitoring methods, drone-based assessments provided high spatial resolution and real-time data, facilitating early detection of agronomic issues. These findings underscore the pivotal role of UAV technology in advancing precision agriculture, particularly in semi-arid regions where climate variability poses challenges to sustainable farming. The study provides a replicable framework for integrating drone-based monitoring into agricultural decision-making, offering strategies to improve productivity, water efficiency, and environmental resilience. The research contributes to the growing body of knowledge on agricultural technology adoption in Tunisia and similar contexts, supporting data-driven approaches to climate-smart agriculture.

Article
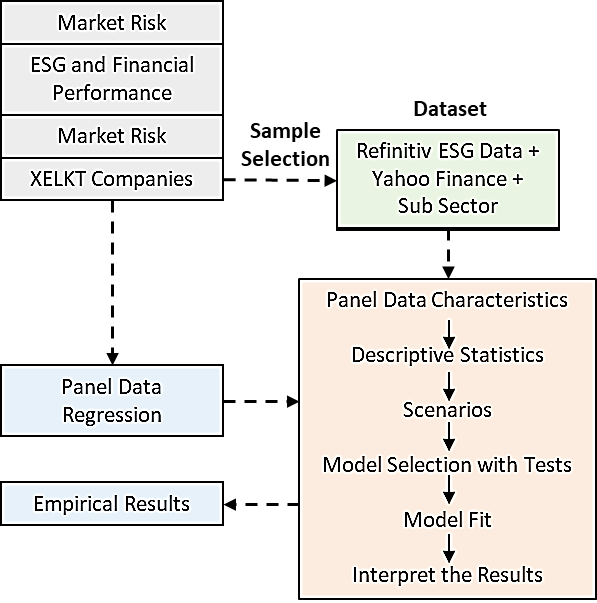
09 January 2025Sustainability Practices and Financial Performance: Evidence from BIST Electricity Index
Amidst the backdrop of heightened market risks associated with transitioning to a lower-carbon economy, this study pioneers an examination of the correlation between sustainability and financial performance within Turkish energy market generator and retailer companies. In this study, the sustainability performance, exposure to market risks and effects on the financial performance of sub-sectors of companies listed in the BIST Electricity index were analyzed using panel data regression. The findings reveal a nuanced relationship between sustainability factors and financial performance, underscoring the imperative for electricity sector companies to prioritize sustainability initiatives not only for ethical reasons but also as a strategic imperative for long-term financial success and stakeholder value creation. Finally, the possibility of impending regulatory changes underscores the importance of early adoption of sustainability practices to mitigate potential financial liabilities and navigate future market risks effectively.
Article
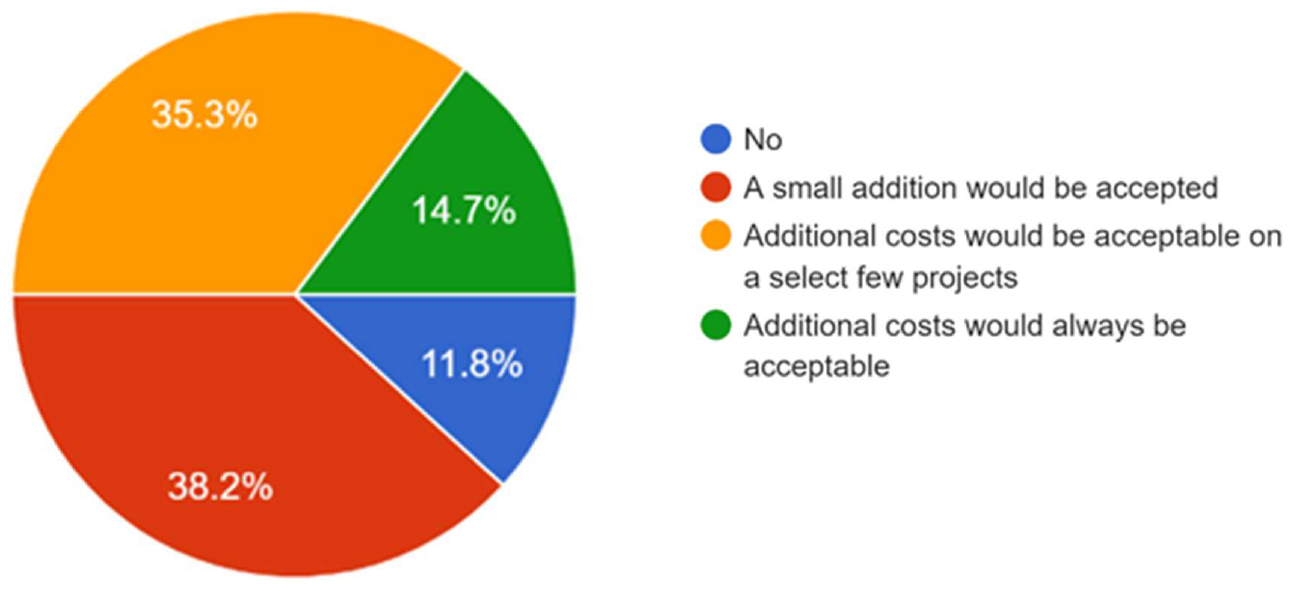
16 December 2024Exploring the Values of Sustainability and the Cost of Going Green: A Case of Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method (BREEAM)
Despite the expansion of BREEAM and the benefits of adopting sustainable building practices, there are concerns that the cost of going green may outweigh the benefits. Whilst previous studies have not provided adequate clarity in this regard, there is consensus among scholars that BREEAM provides indirect benefits that can be considered as added value. This paper aims to investigate the potential cost implication and benefits of sustainable building practices from the lens of the Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method (BREEAM) in the UK. Adopting survey research strategy, questionnaires, and interviews with 34 construction industry professionals in Southeast England were conducted to investigate their perceptions of BREEAM, the extra value it contributes to projects, and the possible limitations hindering its wider adoption. Findings show that while there is an upfront investment associated with achieving BREEAM certification, the benefits of such certification include added values such as improved environmental performance, increased market appeal, improved indoor air quality, reduced carbon emissions, and lower operational costs. This study validates the need to encourage wider adoption of sustainable building practices and promote the use of the BREEAM methodology in the UK. This research provides a foundation for future research and development in this area, with the goal of reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable development.
Article
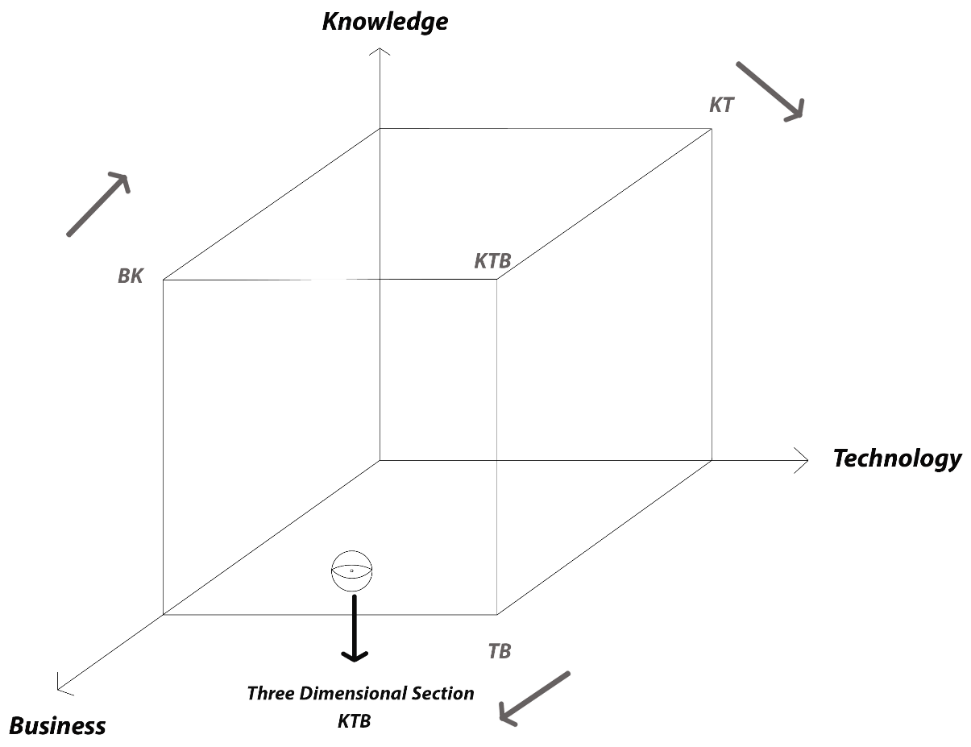
10 December 2024Sailing the X.0 Wave Theory: Navigating the Future of Civilization
This paper delves into the X.0 Wave/Tomorrow Age Theory, a comprehensive framework conceived, invented, introduced, and developed by Prof. Dr. Hamid Mattiello between 2010 and 2017, to analyze the evolution of human civilization through distinct epochs of knowledge, technology, and business (KTB). The theory segments history into transformative waves, from the first development (X.0 ≤ 1.0) and Agricultural Age (X.0 = 1.0) and the X.0 Wave/Tomorrow Age Theory (2.1 ≤ X.0 ≤ 2.2) spanning the 17th Century to 1870, to the current Age of Artificial Intelligence (X.0 = 4.0). It also projects into the anticipated Human Age (X.0 = 5.0) and Transhuman Age (X.0 = 6.0) and beyond (6.0 ≤ X.0). Each wave represents a revolutionary phase characterized by significant advancements that shape societies, industries, and technologies. The X.0 Wave Theory integrates these historical phases with the Seven Pillars of Sustainability (7PS) to evaluate their societal impacts. The paper explores how these waves influence future developments by examining historical roots, emerging technological paradigms, and socio-economic dynamics. It examines how advancements in AI, biotechnology, and virtual reality are reshaping industries and global business practices, while also addressing the ethical and sustainability considerations essential for navigating these changes. By forecasting future trends, confronting current challenges, and preparing for potential crises, the X.0 Wave Theory offers a robust framework for understanding and adapting to the rapid pace of technological evolution. This paper provides deep insights into how these transformative waves shape our past, present, and future, offering valuable perspectives for navigating the complexities of an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
Article
11 November 2024Rural Local Government Institutional Sustainability Programs and Plans in Cascadia: A Comparative Analysis
This research provides a comparative analysis of institutional sustainability programs in small and rural communities across British Columbia, Oregon, and Washington. The study reveals significant regional differences in the adoption of sustainability initiatives, with Oregon consistently leading in the implementation of various programs such as grant writing, conflict resolution, and e-government. The analysis identifies key factors influencing program adoption, including population growth, economic stability, and remoteness. Communities experiencing significant population growth and financial stability are more likely to adopt multiple sustainability programs, while remoteness and economic challenges, such as inflation, act as barriers. The study underscores the importance of regional context and local conditions in shaping the sustainability efforts of rural communities.
