Found 5 results
Open Access
Article
23 July 2025Evaluation and Modeling of Long-Term Endurance Measurement on Electric Double Layer Capacitors to Increase Reliability of Lifetime Predictions
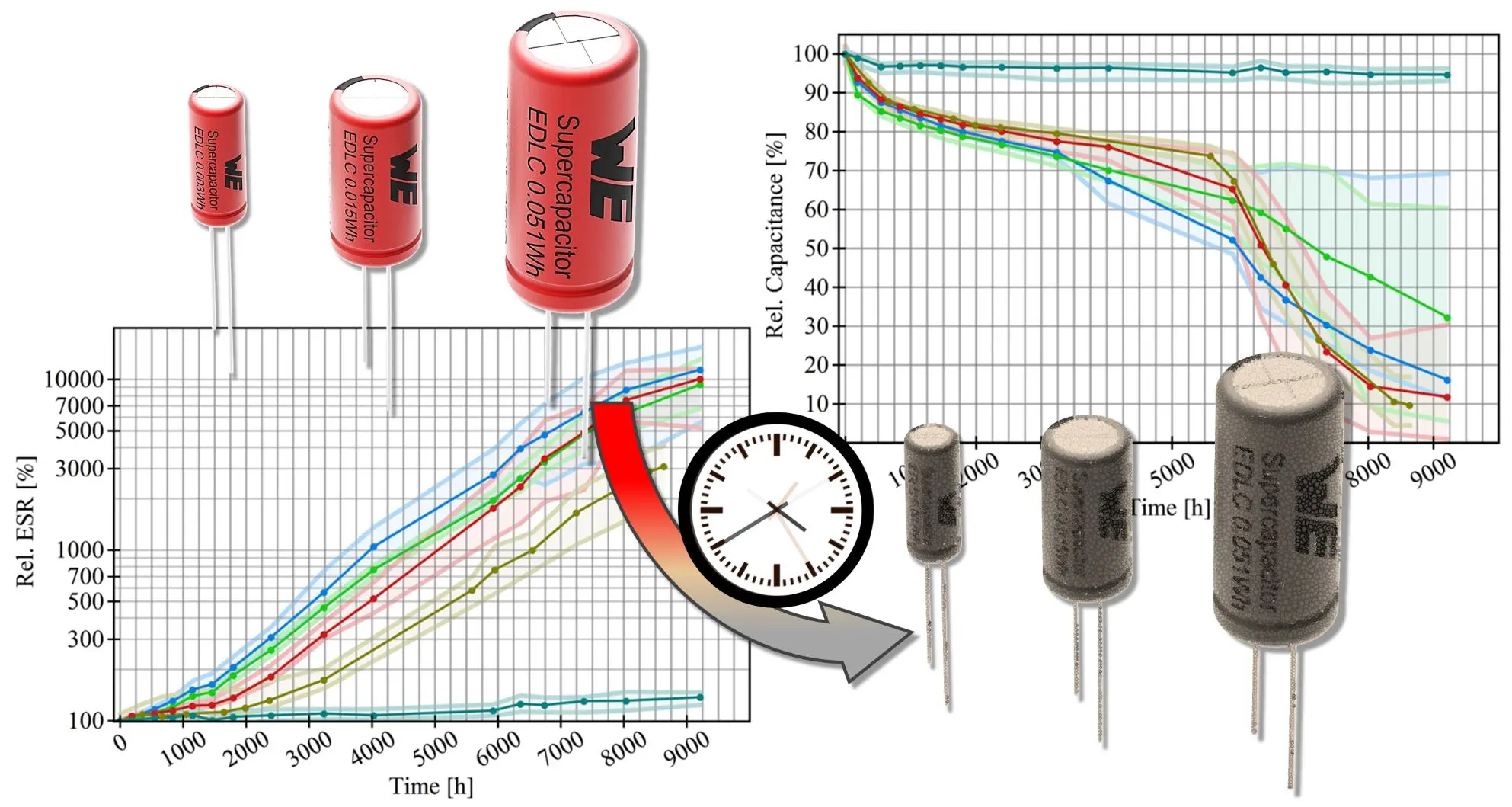
Sustainability in the electrical industry and product reliability are fundamentally dependent on product lifetime predictions. Long-term DC voltage endurance measurements at two different temperatures on various commercial electric double-layer capacitors are presented, discussed, and used to develop a deterioration model suitable for estimating lifetime. Capacitors were tested under constant voltage for approximately 1 year at 65 °C and about 4 years at room temperature. To describe the deterioration in terms of capacitance and the equivalent series resistance, a phenomenological model is proposed and tested against measurements taken at room temperature. The proposed model is based on a general exponential relation with a time-dependent deterioration rate. The model is tested against long-term measurements with constant and time-dependent temperature acceleration factors. Analysis of capacitance and equivalent series resistance measurements shows a time or deterioration dependence in the temperature acceleration factor and different phases of deterioration.
Open Access
Article
07 November 2024Fully- and Partially- Distributed Adaptive Consensus of Second-Order Multi-Agent Systems Using Only Relative Position Measurements
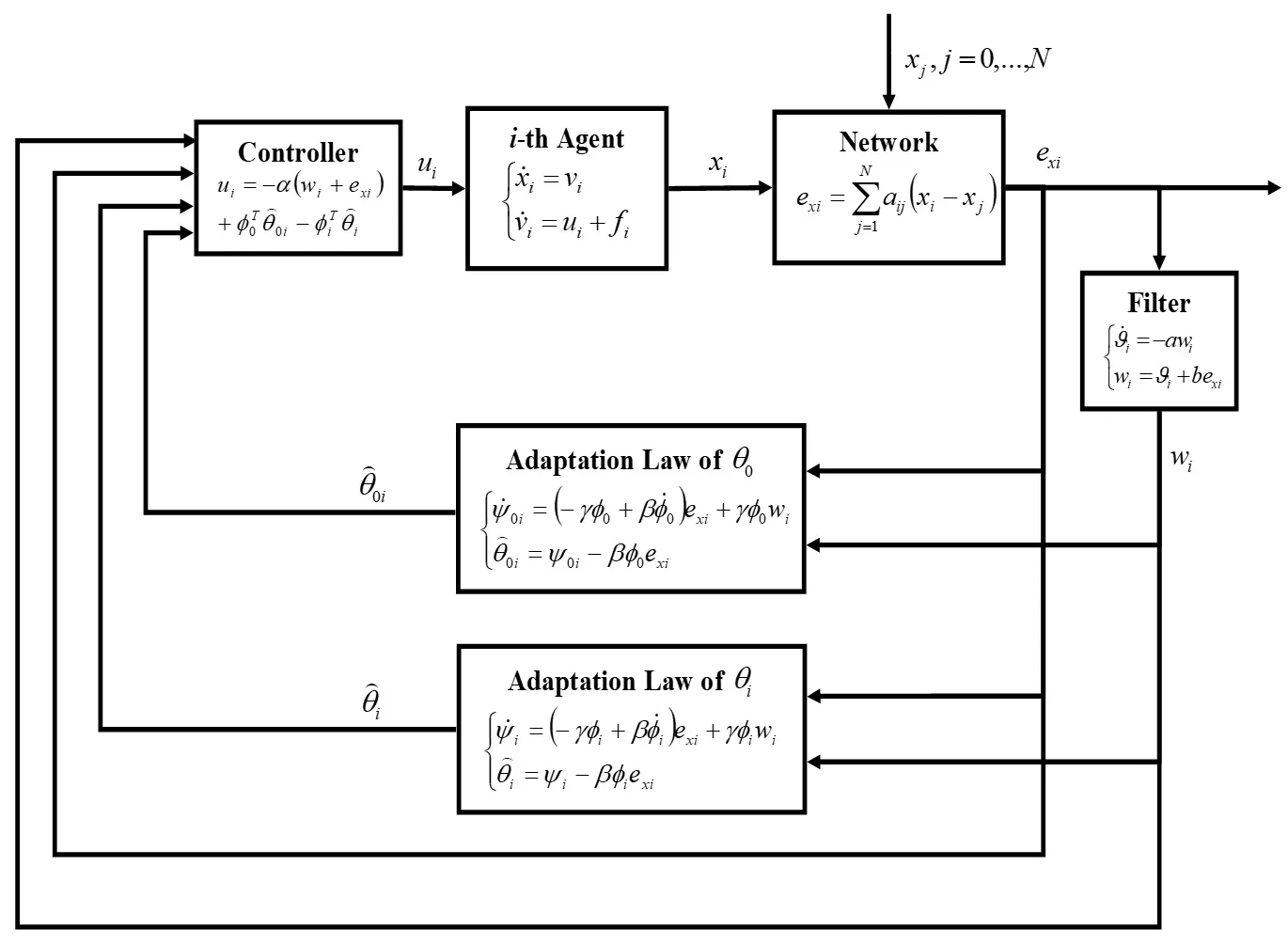
In this paper, the distributed leader-follower consensus of a group of agents with second-order dynamics under the undirected graph communication topology is studied. The main objective of this study is to solve a major practical multi-agent problem in which the acceleration of the leader is not communicated to each follower. In contrast, the follower agents include some unknown dynamics in their intrinsic structure. By assuming a linear regression structure for leader acceleration and agent’s unknown dynamics, Lyapunov-based adaptive control algorithms are devised to control the network of agents in the presence of the communication loss and modeling uncertainties. The presented study describes two multi-agent control strategies called fully-distributed adaptive control (FDAC) and partially-distributed adaptive control (PDAC) systems in the first method, the followers do not have any a priori information about the communication graph, while in the second method, some information about the eigenvalues of the communication graph is available. The mathematical manipulations required to prove the stability of the FDAC and PDAC methods are presented. Finally, illustrative simulations are conducted to render the proposed algorithms’ merits and efficiencies.
Open Access
Article
04 June 2024Initial Stages of Development of an Automated Measurement Technique on Incisors
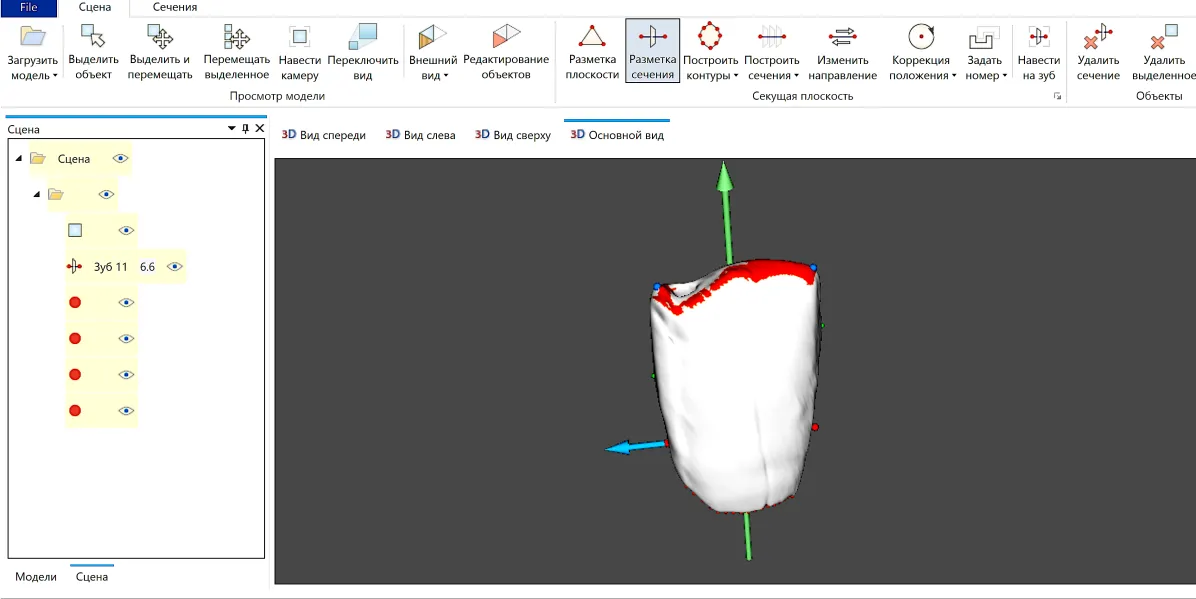
Teeth are an important object of studies in many scientific disciplines and, among various study techniques, measurements have one of the most promising prospects for further improvements supported by progress in computer sciences, imaging and image processing. Our recent work on automated odontometric algorithms for premolars and molars has gradually come to develop similar methods for another group of teeth—incisors. Using 3D reconstructions of teeth obtained through micro-focus tomographic scanning, we propose landmarks, which correspond to main morphological features of incisors and enable their formal description. In this article we present an orientation and measurement technique, based on an interpretation of incisor morphology, as a system which is able to perform in a fully automated mode. Since the primary objective of the current paper is to introduce methodological improvements, data on measurements and their results are shown at the most basic level.
Open Access
Article
14 May 2024Measurement and Structure of Common Prosperity of Urban Residents the Case of Hangzhou, China
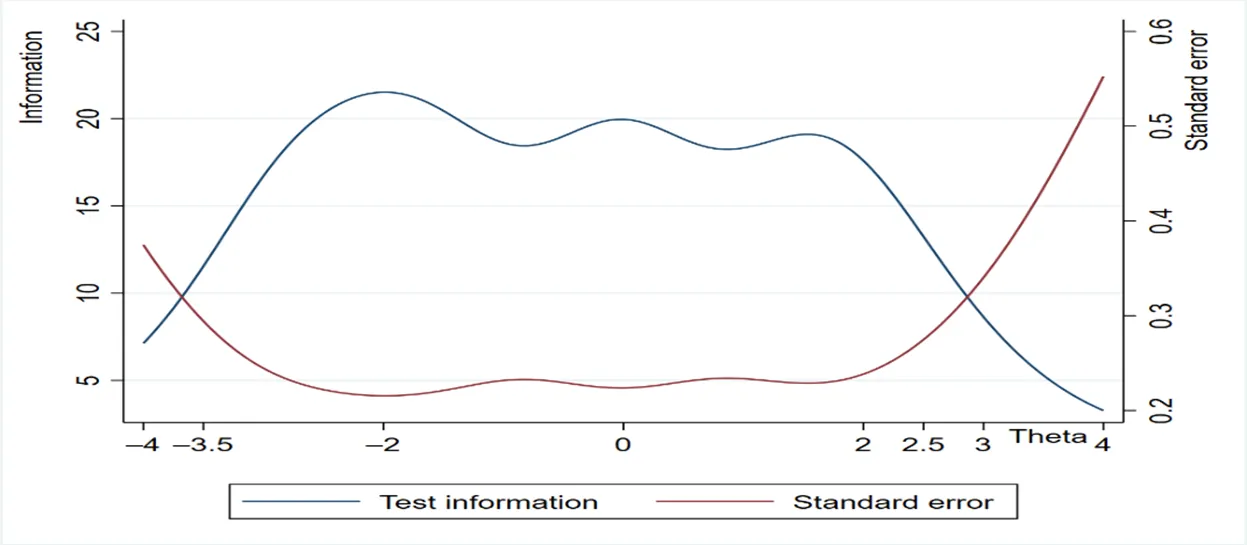
Common prosperity is an important feature of the social state that the people of the world aspire to, and an important feature of the Chinese path to modernization. Taking common prosperity as the result of income and assets does not facilitate a full understanding of people’s common prosperity, because common prosperity also includes people’s pursuit of subjective happiness such as happiness and satisfaction. From the perspective of the need for a better life in China, this study constructs a subjective evaluation system of the common prosperity of urban residents, including 5 dimensions and 25 specific indicators. It uses survey data from 460 participants and applies the graded response models to estimate parameters and predict latent variables. We find that 21 indicators are in line with the reasonable range of basic assumptions and parameters. They have a strong ability to distinguish the common prosperity of residents in different regions, but have different functional characteristics. The confirmatory factor analysis shows that the common prosperity index of residents includes four potential factors: income, education, medical care, and old-age care, and ecology, which has a good structural effect. In terms of weight, education, medical care and old-age care are the most important factors influencing common prosperity. Among them, the classification policy of high school entrance examination, the quality and fairness of primary and secondary education, the degree of medical insurance security, and the waste sorting and community security are important aspects of evaluating the Common prosperity of residents.
Open Access
Article
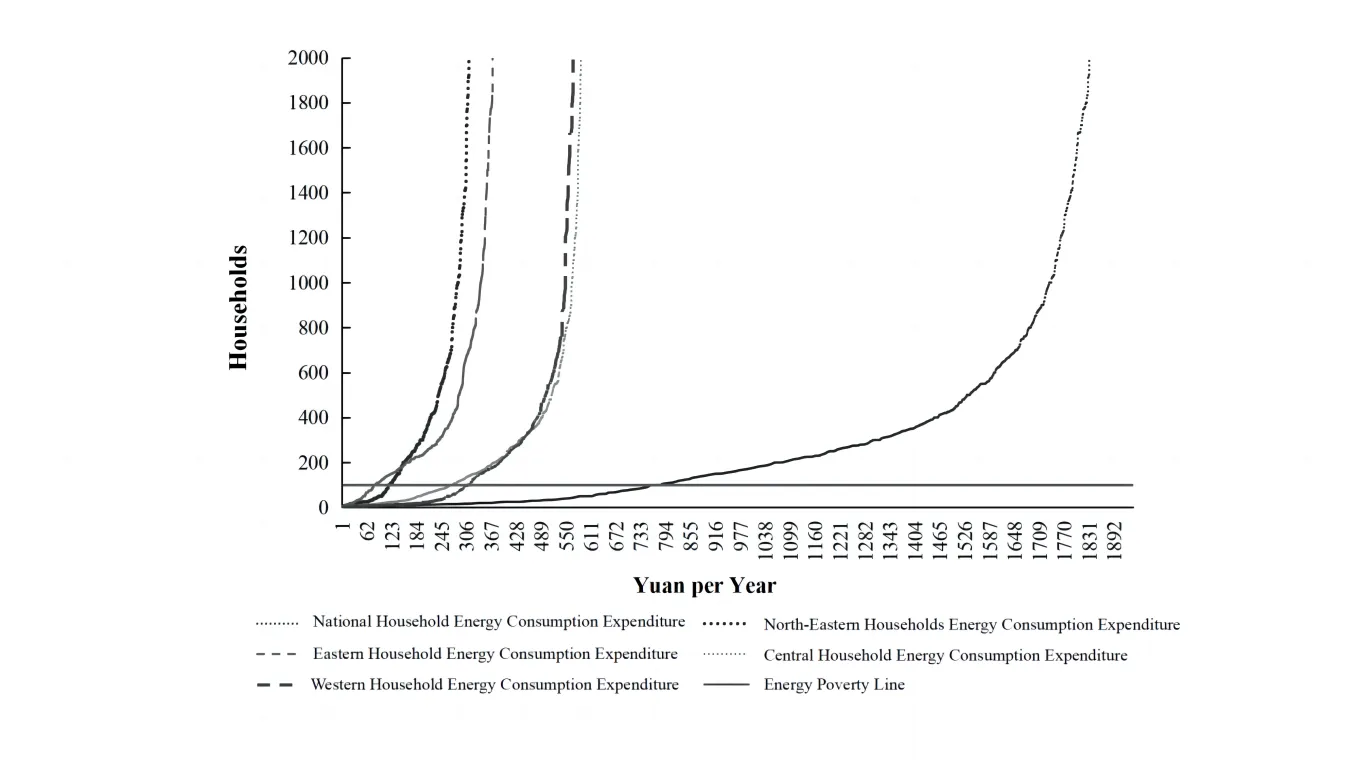
18 December 2023Measurement of Energy Poverty and Influencing Factors of Rural Households in China
Despite being the world’s largest developing country, China faces significant disparities between urban and rural areas, which exacerbates energy poverty in rural regions. This issue of energy poverty is a global concern, as millions of people lack access to modern energy necessary for a decent quality of life. This research aims to analyze the levels and structures of energy consumption in rural Chinese households, using data from the Chinese General Social Survey (CGSS) conducted in 2015 and 2018. The research employs the poverty line threshold and Theil index methods to comprehensively assess energy poverty in diverse regions. It also examines the economic, social, and familial factors influencing rural energy poverty. The findings reveal a transition in rural energy consumption towards cleaner sources, but energy poverty remains a significant issue. Factors such as energy prices and household size have a positive impact on energy poverty, while per capita income, education level, and social factors exert a negative influence.