Found 8 results
Open Access
Article
28 October 2025The Role of Knowledge Transferred between Rural Inhabitants and Newcomers in the Development of Rural Areas
The purpose of this study is to find the answer to the question: What is the role of the transfer of knowledge between the permanent and new residents of the countryside. The results are based on qualitative inquiry, carried out in 18 Polish villages, situated in socially and historically diverse regions and outside of the metropolitan areas. Knowledge, which is transmitted in the contacts between the two groups considered, has a very clearly informative character. This concerns primarily the basic information pieces, meant to ensure satisfaction of the daily needs of the groups of inhabitants considered. Knowledge transfer is relatively little intensive and takes place during sporadic encounters, mainly in public spaces—a street, a central square, a shop. This, presumably, exerts an influence on the nature and quality of knowledge and information exchange. The permanent residents are, first of all, the source of current information and practical knowledge, concerning broadly conceived village life, answering the fundamental questions of what, where, and when. On the other hand, the newcomers, side by side with informative knowledge, provide also knowledge of advisory and non-material character. Knowledge and information provided by permanent rural residents serve the needs of daily life and the satisfaction of current necessities, while newcomers introduce new lifestyles and behaviors, leading to increased social activity in the countryside.

Open Access
Commentary
17 September 2025Shades of Grey: A Continuum of Biodiversity Understanding from Dark to Bright Diversity
This commentary introduces a conceptual framework that reinterprets biodiversity assessment as a continuum, spanning from Dark diversity, representing the unobserved or uncolonized potential of species ecologically suited to a system, to Bright diversity, conceived as an aspirational, fully integrated upper bound of biodiversity knowledge. Bright diversity encompasses not only observed components and their intricate interactions, but also a profound understanding of the reasons for species' presence or absence, including the inferred insights from Dark diversity across taxonomic, functional, phylogenetic, and genetic facets. Situated in between is Grey diversity, which characterizes the predominant state of partial knowledge and inherent uncertainty in real-world ecological assessments as an epistemic gradient. By delineating this epistemological gradient, the framework offers a heuristic tool for ecologists and conservationists to critically evaluate the clarity, completeness, and uncertainty embedded in biodiversity data, and an operational basis for “epistemic cartography”, i.e., the spatial mapping of knowledge sufficiency and uncertainty. It facilitates the identification of knowledge gaps, guides research priorities, and informs conservation actions, especially under conditions of incomplete information, through a compact workflow and transparent indicators. This conceptual spectrum serves as both an epistemological reflection and a practical guide for advancing biodiversity science, while outlining a forward-looking agenda that leverages multi-faceted “bands of biodiversity knowledge” to support robust biodiversity planning.

Open Access
Article
03 June 2025Ecosystem Service Importance, Contributions, and Trends: Perspectives from Farmers in the Mountains of Nepal
Understanding farmers’ perceptions of local ecosystem services is crucial for developing effective ecosystem management strategies and policy interventions to improve the overall welfare of residents. Although there is widespread recognition of the linkages between ecosystem services and human well-being, empirical studies examining farmers’ perceptions and contributions to local ecosystem services, particularly at the micro level in mountainous regions, remain limited. To address these knowledge gaps, we conducted an empirical study employing focus group discussions (n = 6), key informant interviews (n = 12), and household surveys (n = 370) in Mid-Marsyangdi watershed, Lamjung, Nepal. The study revealed that farmers perceive high dependency on regulating followed by provisioning, supporting, and cultural ecosystem services such as freshwater, nutrient cycling, water regulation and purification, timber production, livestock fodder, and natural hazard regulation. Their contributions are notably high in managing freshwater, nutrient cycling, and timber production. Farmers’ practices like forest conservation, agroforestry, inter-cropping, terracing, terrace improvement, multi-year cropping, and organic composting enhance ecosystem services. A significant discrepancy exists between perceived importance and actual contribution, particularly in water regulation, purification, and wild edible food, highlighting areas needing greater attention. The study showed a significant difference (p < 0.001) between perceived importance and contribution across all ecosystem services, with perceived importance consistently higher. Further, a study showed the influence of socio-demographic variables on the farmers’ perception. These findings can inform more effective policy-making for farmer welfare, mountain development, and environmental management.

Open Access
Article
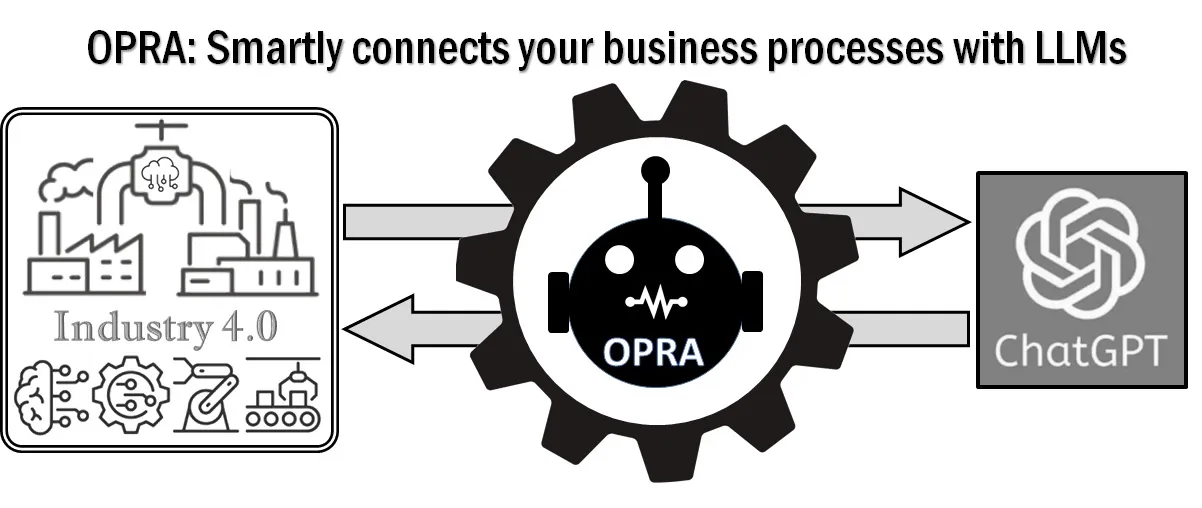
14 March 2025A Conceptual Design of Industrial Asset Maintenance System by Autonomous Agents Enhanced with ChatGPT
This article introduces OPRA (Observation-Prompt-Response-Action) and its multi-agent extension, COPRA (Collaborative OPRA), as frameworks offering alternatives to traditional agent architectures in intelligent manufacturing systems. Designed for adaptive decision-making in dynamic environments, OPRA enables agents to request external knowledge—such as insights from large language models—to bridge gaps in understanding and guide optimal actions in real-time. When predefined rules or operational guidelines are absent, especially in contexts marked by uncertainty, complexity, or novelty, the OPRA framework empowers agents to query external knowledge systems (e.g., ChatGPT), supporting decisions that traditional algorithms or static rules cannot adequately address. COPRA extends this approach to multi-agent scenarios, where agents collaboratively share insights from prompt-driven responses to achieve coordinated, efficient actions. These frameworks offer enhanced flexibility and responsiveness, which are critical for complex, partially observable manufacturing tasks. By integrating real-time knowledge, they reduce the need for extensive training data and improve operational resilience, making them a promising approach to sustainable manufacturing. Our study highlights the added value OPRA provides over traditional agent architectures, particularly in its ability to adapt on-the-fly through knowledge-driven prompts and reduce complexity by relying on external expertise. Motivational scenarios are discussed to demonstrate OPRA’s potential in critical areas such as predictive maintenance.
Open Access
Article
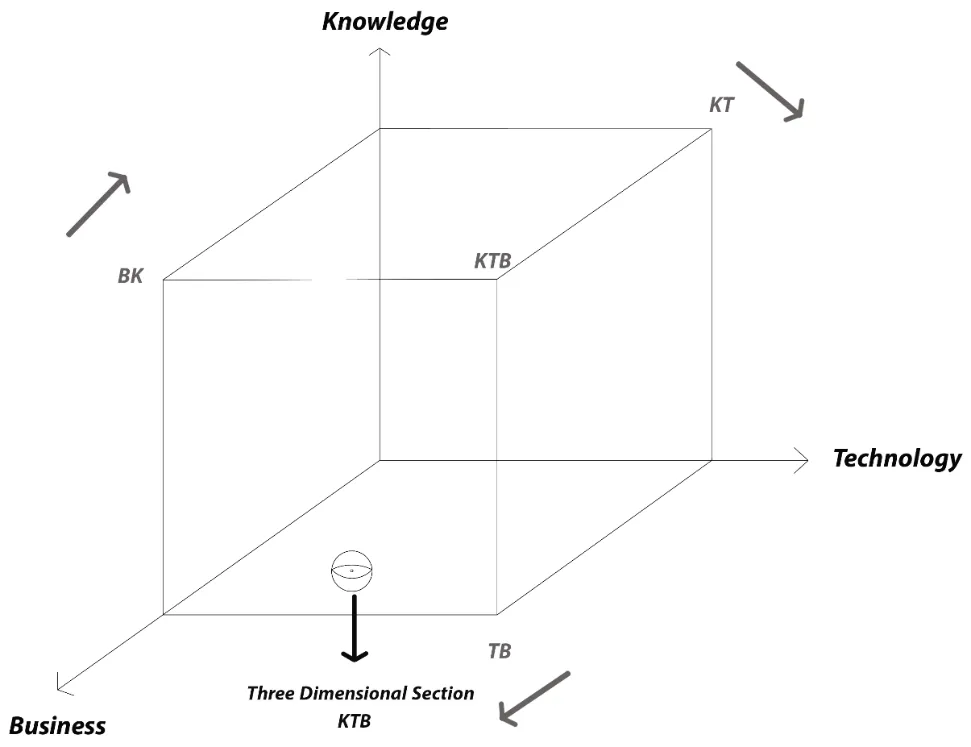
10 December 2024Sailing the X.0 Wave Theory: Navigating the Future of Civilization
This paper delves into the X.0 Wave/Tomorrow Age Theory, a comprehensive framework conceived, invented, introduced, and developed by Prof. Dr. Hamid Mattiello between 2010 and 2017, to analyze the evolution of human civilization through distinct epochs of knowledge, technology, and business (KTB). The theory segments history into transformative waves, from the first development (X.0 ≤ 1.0) and Agricultural Age (X.0 = 1.0) and the X.0 Wave/Tomorrow Age Theory (2.1 ≤ X.0 ≤ 2.2) spanning the 17th Century to 1870, to the current Age of Artificial Intelligence (X.0 = 4.0). It also projects into the anticipated Human Age (X.0 = 5.0) and Transhuman Age (X.0 = 6.0) and beyond (6.0 ≤ X.0). Each wave represents a revolutionary phase characterized by significant advancements that shape societies, industries, and technologies. The X.0 Wave Theory integrates these historical phases with the Seven Pillars of Sustainability (7PS) to evaluate their societal impacts. The paper explores how these waves influence future developments by examining historical roots, emerging technological paradigms, and socio-economic dynamics. It examines how advancements in AI, biotechnology, and virtual reality are reshaping industries and global business practices, while also addressing the ethical and sustainability considerations essential for navigating these changes. By forecasting future trends, confronting current challenges, and preparing for potential crises, the X.0 Wave Theory offers a robust framework for understanding and adapting to the rapid pace of technological evolution. This paper provides deep insights into how these transformative waves shape our past, present, and future, offering valuable perspectives for navigating the complexities of an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
Open Access
Article
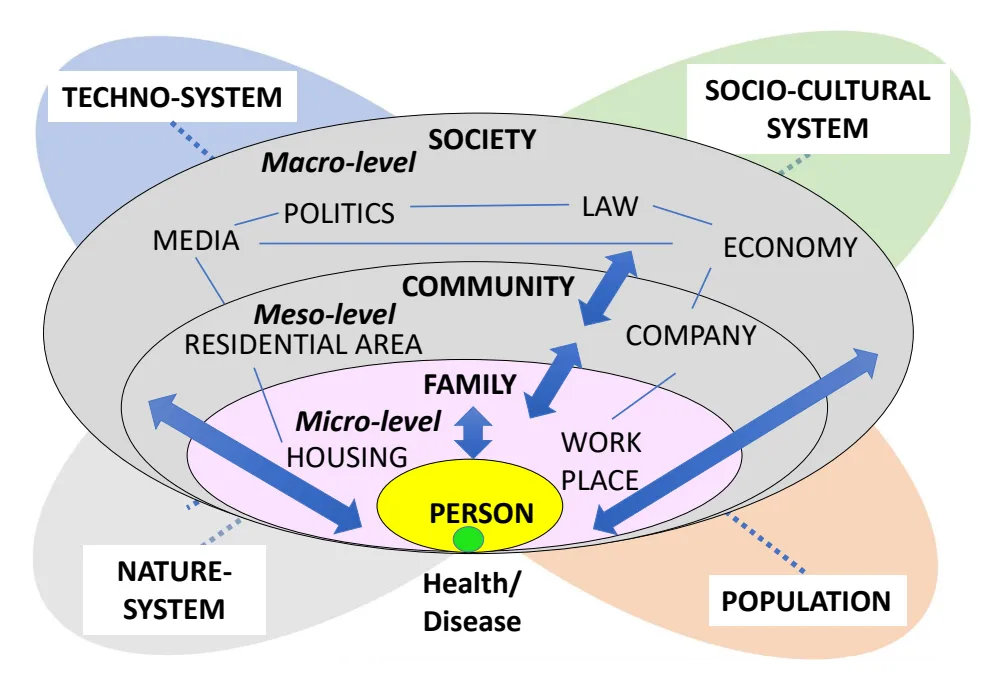
23 May 2024Proposal for A Systemic Human Ecological Turn for Health Science and Medicine
Industrial development processes, accompanied by extreme growth processes, regards world population, pollution, food production and the exploitation of natural resources have caused severe ecological problems. This has been well known since 1972 through the study ‘The Limits to Growth’, in which humanity and the world society was called upon to make an ecological turn and to change its consumption model and the type of economic development that was not suited to finite natural resources (or a finite planet). However, the relationships between the state of the environment and human health have hardly been considered, although an ecological view of health was already proposed by Hippocrates, and as in the meantime, the technical terms “Environmental Health” and “Environmental Medicine” have become established at universities. It is only in recent times that global terms such as climate medicine, One Health, Eco Health, etc. have become powerful pragmatic and action-oriented initiatives. They can be understood as calls for a worldwide health-related ‘ecologization’ of (health) culture. Regarding these approaches we highlight theoretical and metatheoretical aspects, since in general, any real action is only as good as the analytical quality of the plan that serves as a guide for that action. From this point of view, we find that these approaches exhibit striking weaknesses. These are, among other things: the neglect of epistemological challenges combined with inconsistent conceptualizations of the category environment, the very superficial models of human beings, weaknesses of ecological frameworks in relation to the macro-, meso- and micro-eco-social levels of the targeted topics, and a vague notion of systems methodology. Following on from this, we call for an explicit social-/human-ecological framework (New Viennese School, Australian School) for environmental health issues as it has been established for decades in the field of environmental, sustainability and transformation sciences.
Open Access
Article
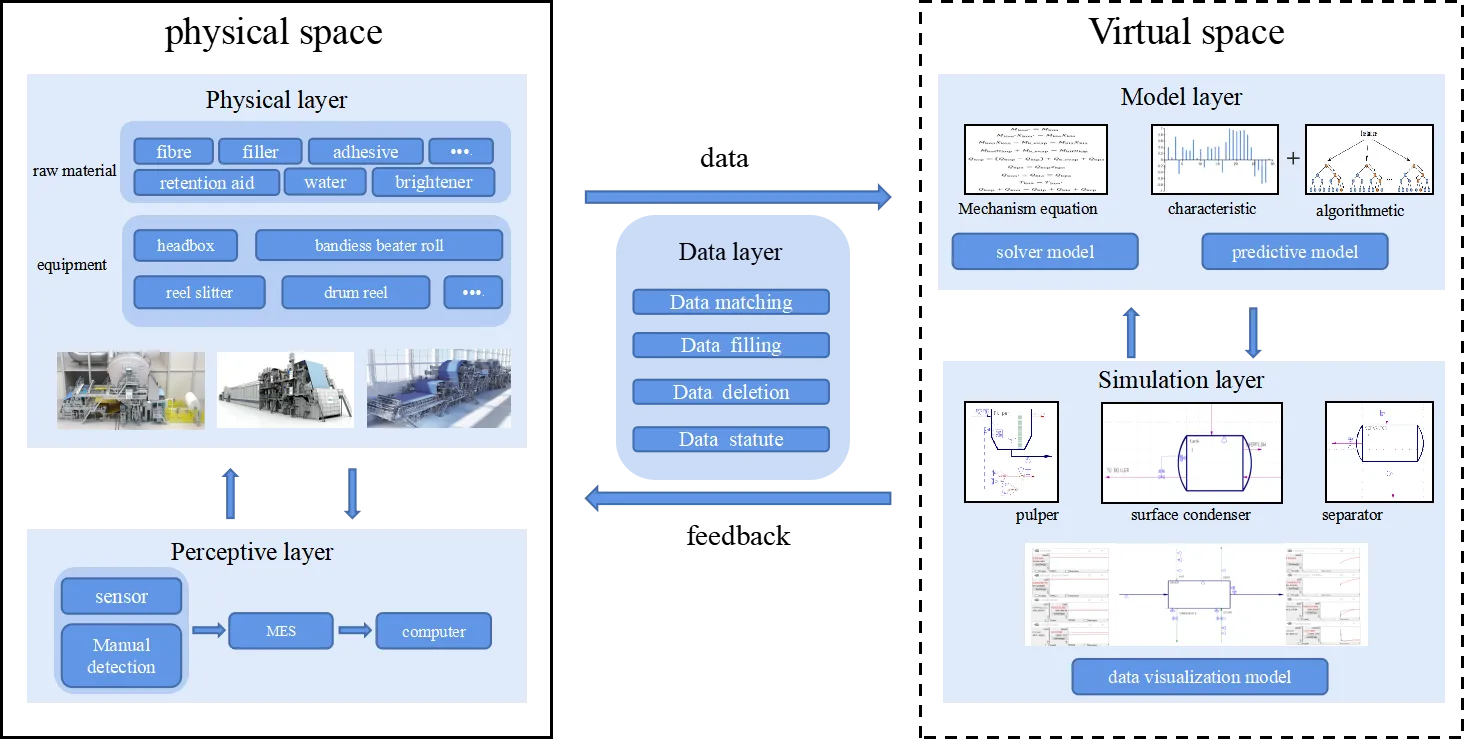
27 February 2024Knowledge-data Collaborated Digital Twin Model of Papermaking Process
The structure of the drying section in papermaking process is complex and too compacted to install sensors. In order to monitor the parameters in dynamic and manage the process practically with virtual simulations instead of physical experiments, a digital twin-based process parameter visualization model is constructed in this study. Regarding to the possible missing data in the modeling framework, it is proposed to combine industrial data, and knowledge of mechanism with intelligent algorithms to fill in the missing parameters. Upon which, a digital twin-based data visualization model is established using CADSIM Plus simulation software. Both of the knowledge -based mechanism solution model and the random forest-based parametric prediction model perform well, and the predicted parameters can support the digital twin visualization model in CADSIM Plus. Visual modeling of surface condenser in the paper drying section was realized for example, and results show that the model is capable of monitoring the dynamic changes of parameters in real time, so as to support the optimization and decision making of papermaking process such as formation, drying, et al.
Open Access
Article
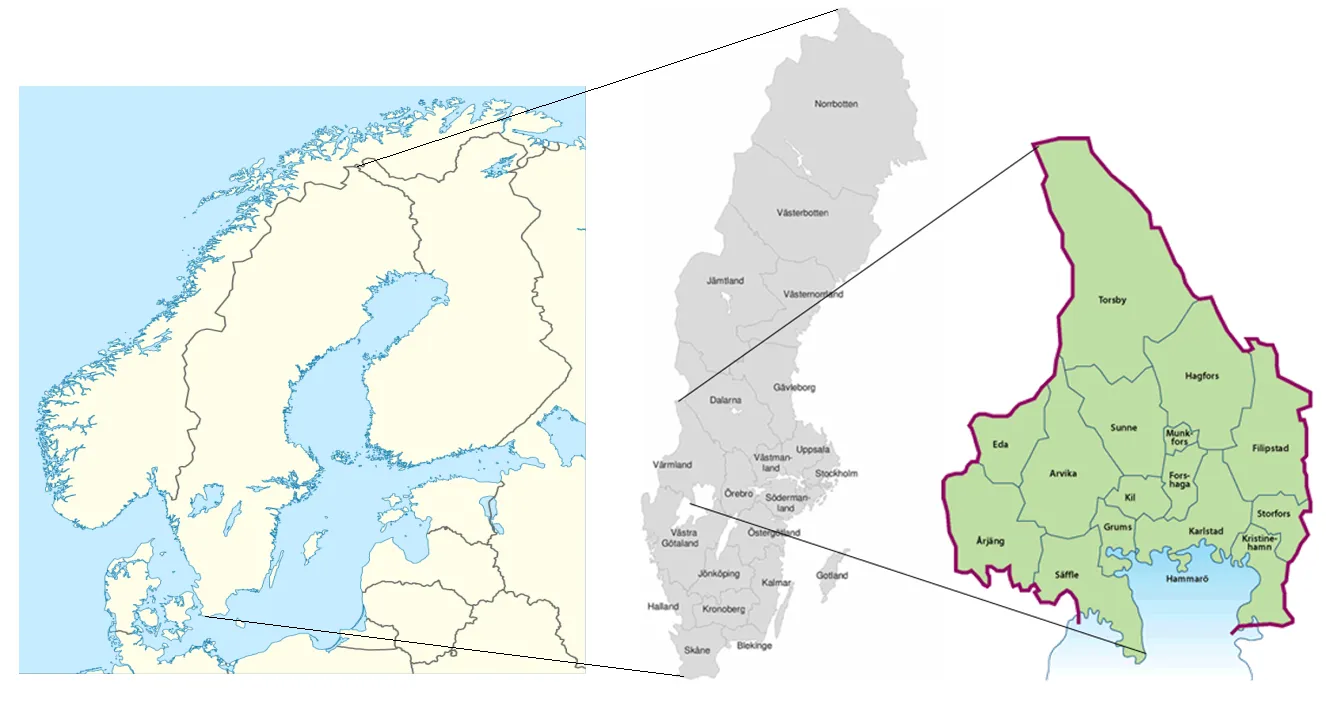
06 February 2024Geographical Discrepancies in Higher Education in Sweden
There is a growing awareness of the importance of higher education in Sweden to reduce social differences in society. There are also various mechanisms that individuals relate to that favour either the status quo or change based on an ideal of higher education. Individuals live in a geographical context with a number of ‘key actors’ who influence the perception of higher education with varying degrees of intensity. Paradoxically, despite several reforms to broaden recruitment, it can be seen that relative inequalities persist in terms of residents with higher education in Sweden, not least from a regional perspective. The purpose of this article is to shed light on geographical differences in the higher education level of the population over time from a Swedish perspective. The study shows that higher education has a geographical centre-periphery perspective, but not exclusively. There are thus additional influencing factors that in various ways relate to the social context in which the individual is located. We can conclude from our empirical data that the reforms implemented to broaden recruitment have not had the desired effect, especially for the group of men. We find it likely that what differentiates women and men is who their individual ‘key players’ are and how they interact. From an academic education perspective and as an intermediary of higher education, there is therefore a challenge to be able to identify who these “key players” are in order to be able to be an important actor in contributing to the desired broader recruitment that the government is striving to achieve.