Found 5 results
Open Access
Article
26 November 2025Machine Learning in Forensic Anthropology: Sex Classification of Fingerprints
A Fingerprint plays an important role in identifying an individual in forensic and criminal investigations. Fingerprint ridge density is considered one of the most important features for sex classification. The present study intends to classify sex using fingerprint ridge density through a machine learning model, i.e., Random Forest. A total of 2040 fingerprints of 204 participants (102 males and 102 females) were collected from the north Indian population using a standard methodology. Ridge density in the three topological areas of fingerprints,i.e., radial, ulnar, and proximal areas, was assessed. Taking all the areas into consideration, the data of fingerprint ridge density was used to train the Random forest algorithm. The training and testing of the model data were taken in a ratio of 70:30, respectively (training dataset = 1428; testing dataset = 612). Random forest provided an accuracy of 81.53% in sex classification using fingerprint ridge density. The paper discusses the evaluation report of the accuracy of the parameters of the Random forest in detail. The study concludes that the machine learning models, such as Random forest can be utilized for sex classification from fingerprint ridge density. The study proposes its direct application in forensic examinations, especially when there is no clue about the perpetrator, and the sex of the perpetrator can be predicted from fingerprints recovered from the crime scene using the present customized model.
Open Access
Article
25 September 2025Detection and Classification of Faults in a Photovoltaic System—A New Hybrid Algorithm
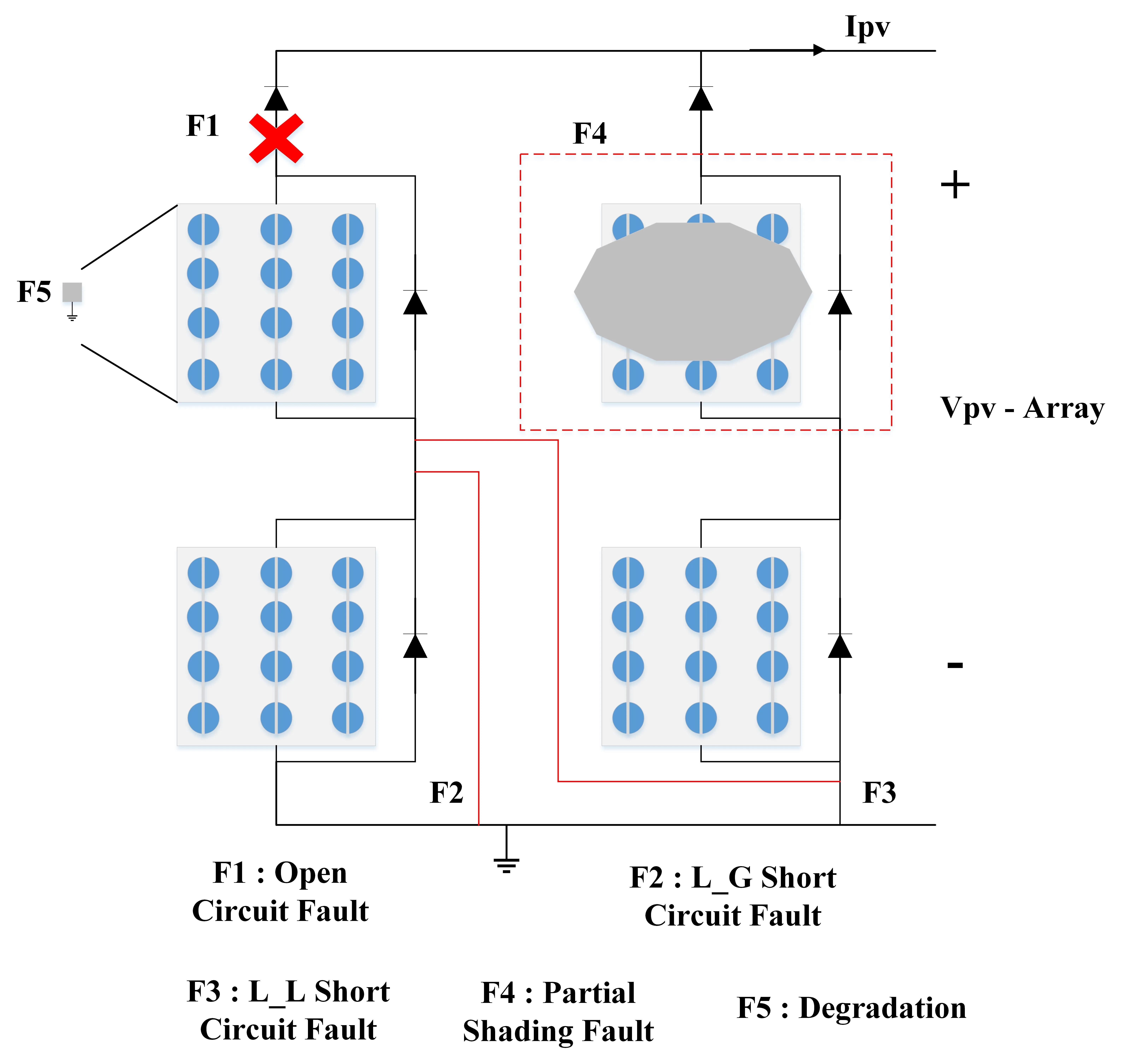
Four main types of faults can occur at the DC side of any Photovoltaic System (PVS). These faults are quite dangerous and can cause permanent damage to the photovoltaic modules if not addressed promptly. The faults include open circuit, short circuit, degradation, and partial shading. Short circuit faults are classified into line-to-line (L-L) and line-to-ground (L-G). Detecting these faults requires specialized algorithms. This paper tackles this complex issue through (1) fault-finding equations and the placement of current sensors, and (2) a new hybrid algorithm based on data from the fault-finding equations and current sensors. Numerous simulations using PSIM 2021 were conducted to verify this proposed solution. The hybrid algorithm presented here is original compared to previous studies. It is easy to understand, responds quickly, and can be implemented in systems with photovoltaic arrays of any size.
Open Access
Article
27 August 2025Statistical Analysis of GSR Particles Morphometry Using the CART Method
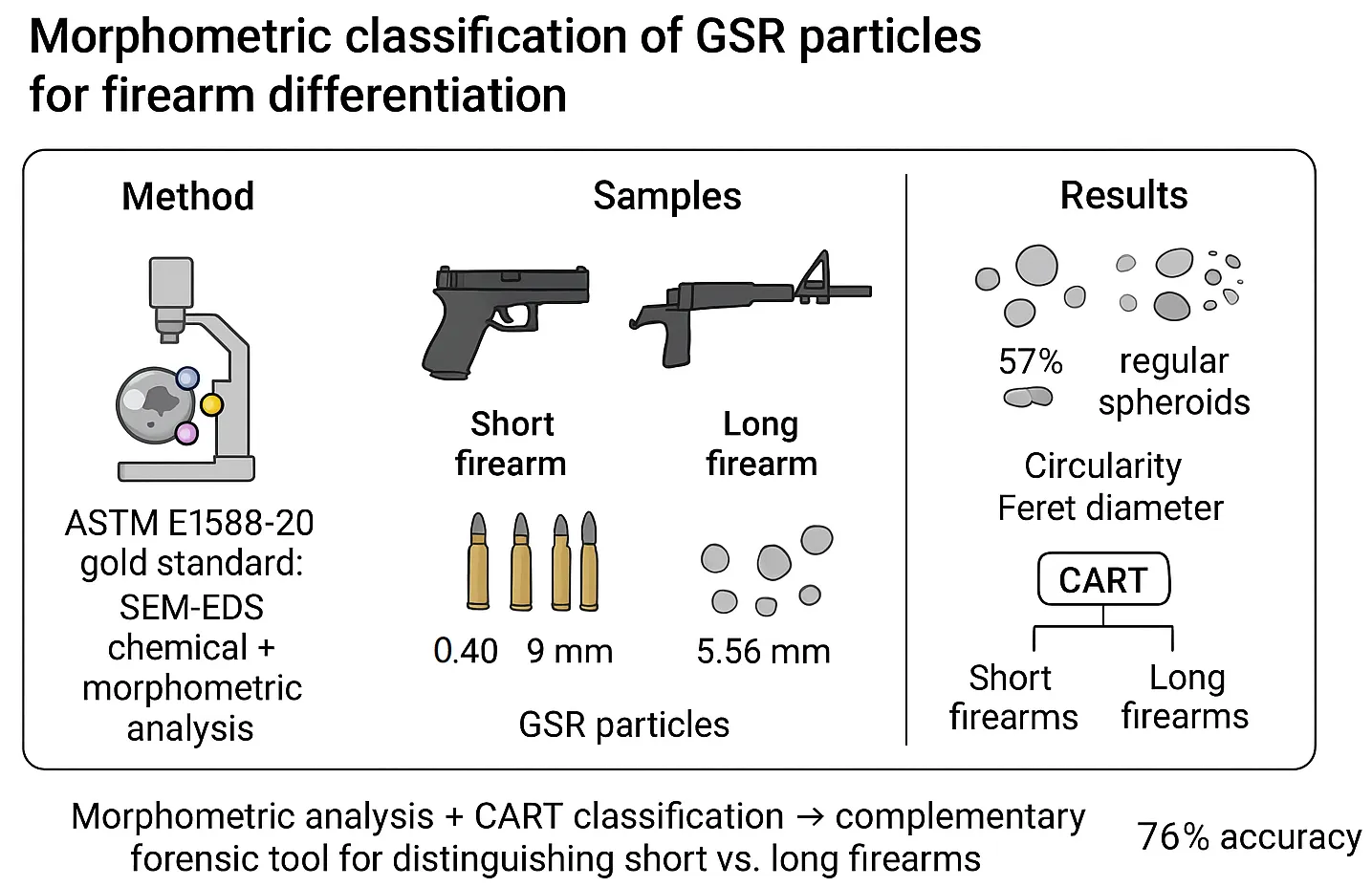
According to ASTM E1588-20, gunshot residue (GSR) particles can be unequivocally identified through chemical and morphometric analysis using scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), the gold standard technique for GSR detection. Recent studies have reported the presence of characteristic GSR particles—containing lead (Pb), barium (Ba), and antimony (Sb)—on vehicle occupants exposed to airbag deployment, underscoring the need for complementary analytical approaches. While elemental composition remains the primary criterion for GSR identification, morphometric analysis enhances the ability to differentiate GSR from other environmental particles. Furthermore, detailed characterization of GSR particle morphology may assist in determining the type of firearm used in a shooting incident. This study systematically analyzed characteristic GSR particles originating from four Brazilian-manufactured ammunition, establishing an initial framework for differentiating between two classes of firearms (short and long) based on morphometric features using the Classification and Regression Tree (CART) method. CART is well-suited for scenarios where interpretability and ease of implementation are priorities. Two short firearms—Taurus G2C pistol (0.40 caliber) and Glock G23 pistol (9 mm caliber) and two long firearms—Colt M16A2 rifle (5.56 mm caliber) and IMBEL FAL rifle (7.62 mm caliber) were tested: Ammunition types included CBC 0.40 S&W CSCV 160 gr, CBC 9 mm copper bullet (batch BNC10), CBC 5.56 mm AXO46 (batch A0142946), and CBC 7.62 × 51 mm Common. Morphometric analysis revealed distinct variations in characteristic GSR particle profiles across different ammunition calibers. A new four-category classification system for characteristic GSR particles was developed, with 57% identified as regular spheroids. Using CART analysis, a statistical model achieved 76% accuracy in distinguishing between short and long firearms based on morphometric parameters, particularly circularity and Feret diameter. Further research with expanded datasets and alternative predictive methods is recommended to enhance model performance and generalizability. These findings reinforce the potential of morphometric classification as a complementary tool in forensic ballistics.
Open Access
Article
08 August 2023Where Do Chinese Doublets Come From?—The Doublets from Prehistory to the Era of the Book of Poetry
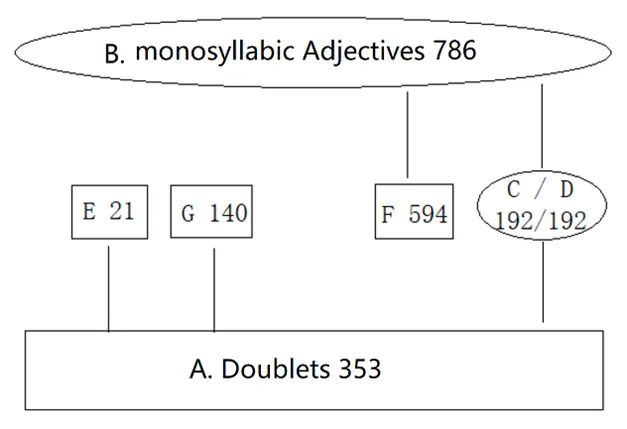
The earliest writing in China is the oracle bone inscriptions of the Shang Dynasty, which records early Chinese, also known as oracle bone Chinese, which are all monosyllabic-words (1300 BC). In the Bronze Inscriptions of the Western Zhou Dynasty and later handed down documents, doublets appear (beginning in 1046 BC). At present, the philological academy believes that the doublets recorded with two Chinese single-characters come from reduplication of two single-character symbols, but there is no complete argument and reliable evidence. This article, by using the opposite method of argument, reversely assumes that the single-characters (monosyllabic words) come from doublets and tries to demonstrate it. The article proves the truth of the origin of doublets based on the word distribution and semantic correspondence between doublets and single-characters in “the Book of Poetry”, that is, doublets are the source and single-characters are flows. Among them, 39.66% of the doublets have no corresponding single-characters, and they are the characters created to record doublets; 41.92% of the meanings of doublets have nothing to do with the meanings of single-characters, which proves that the doublets does not come from the combination of single-characters; 12.46% of the meanings of doublets are interpreted as the meanings of single-characters, which are the subjective errors of later generations of interpreters; the remaining 5.66% are only associated with proclitics and enclitics rather than single-characters. Finally, the article proposes that doublets originate from a unique mechanism of expressive morphology, which is a new type of etymological theory outside the morphological grammar system, and can create various polysyllabic ideophones, including the onomatopoeia or mimetic words. The article proves that a language begins with the creation of words. In the prehistoric period before the oracle bone inscriptions, Chinese ancestors had invented a large number of distinctive doublets (AA), couplets (AB) and other polysyllabic words (xA, or ABB, ABA’B), or ideophones. Due to the difficulty of writing, the doublets were hidden in spoken language for hundreds of years. It was not until the time of “Book of Poetry” and “Book of History” in the bronze inscriptions of the Western Zhou Dynasty that it entered the history and has continued to this day. Doublets are the earliest Chinese words and the beginning of Chinese civilization.
Open Access
Article
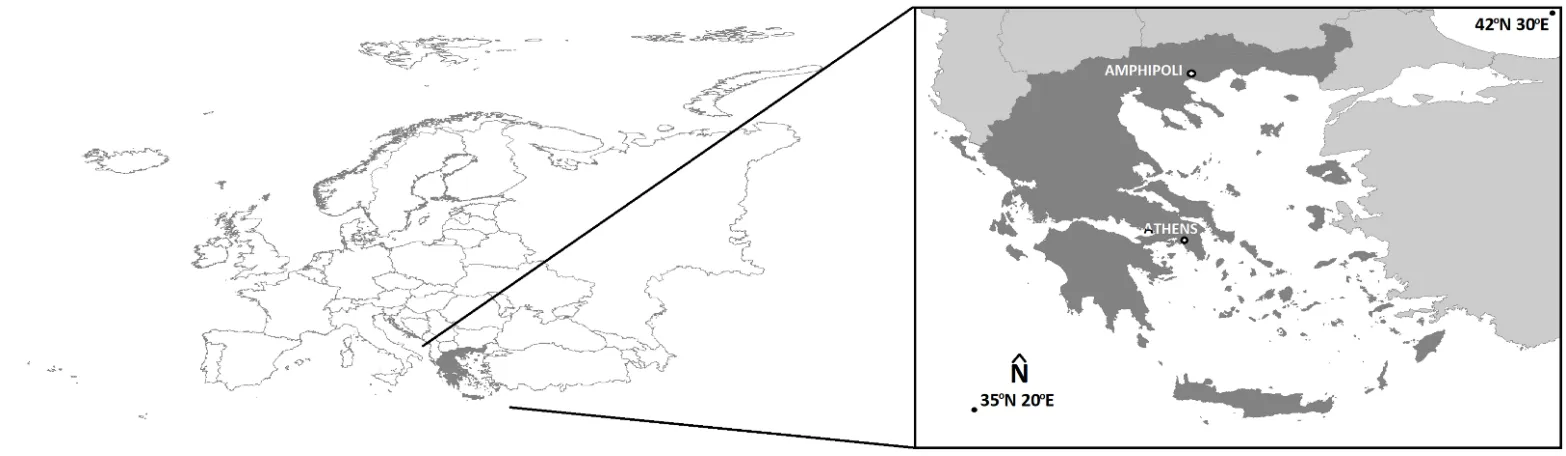
22 December 2022Image Fusion Capability from Different Cameras for UAV in Cultural Heritage Applications
In this paper, image fusion is performed by utilizing images derived from different cameras for the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). By producing the fused image, the spatial resolution of the multispectral (MS) image is improved on the one hand and the classification accuracy on the other hand. First, however, the horizontal and vertical accuracy of the generated products, orthophoto mosaics, and digital surface models, is determined using checkpoints that do not participate in the processing of the image blocks. Also, the changes of these accuracies with a 50% increase (or decrease) of the UAV's flight height are determined. The study area is the Early Christian Basilica C and the flanking Roman buildings, at the archaeological site of Amphipolis (Eastern Macedonia, Greece).