Found 301 results
Open Access
Article
09 October 2025Preparation of CdS-BaZrO3 Heterojunction for Enhanced Photocatalytic Water-Splitting Hydrogen Production
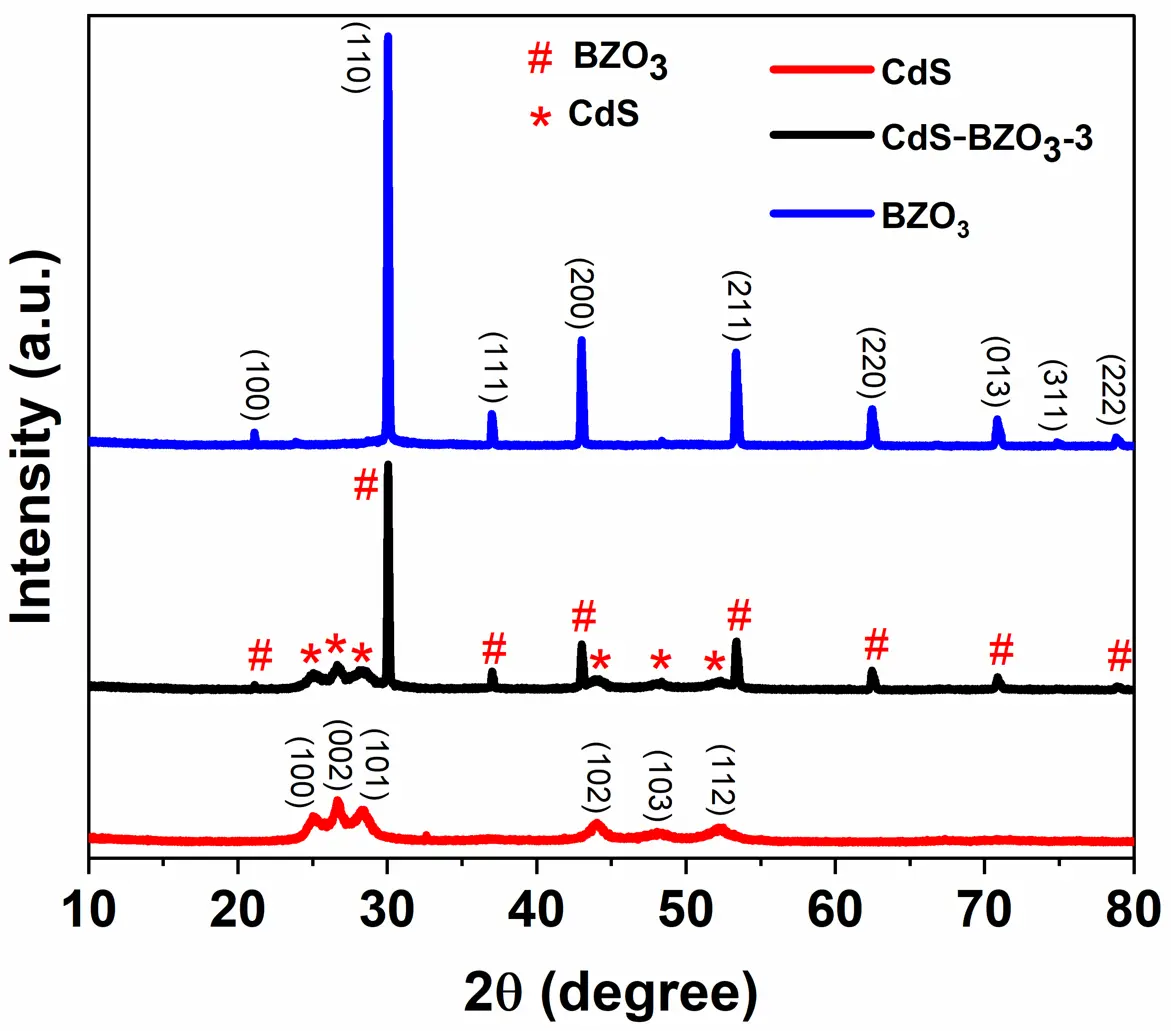
Photocatalytic water splitting using solar light, a promising technical approach for hydrogen production. However, the slow charge transfer and rapid recombination of photogenerated charge carriers in photocatalysis limit their practical application. To address these issues, in this work, we successfully prepared a novel CdS-BaZrO3 (CdS-BZO3) heterojunction via a simple chemical-bath deposition method. The as-prepared heterojunctions facilitate the separation and transportation of photogenerated charges, while also maintaining the high redox-oxid ation ability of the photocatalysts. As a result, CdS-BZO3 heterojunctions show enhanced photocatalytic water-splitting hydrogen production ability without a co-catalyst. Especially, the optimized CdS-BZO3 sample exhibits high photocatalytic activity with a hydrogen production rate of 44.77 μmol/h, which is 4.4 and 2.9 times higher than that of BZO3 and CdS, respectively. At the same time, the CdS-BZO3 heterojunction exhibits good stability in the photocatalytic hydrogen production cycle test. This work provides a reference for the heterostructure construction of perovskite-based photocatalysts to improve photocatalytic performance.
Open Access
Article
29 September 2025Multivariant Time-Series Forecasting Methodology for Product Demand Using Deep Learning and Large Language Models
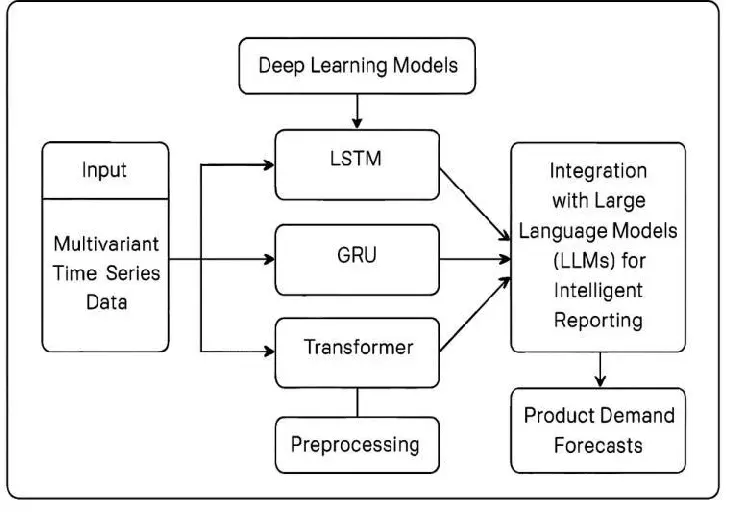
Accurate demand Soothsaying is a crucial element in force chain operation and business planning. Traditional statistical ways don’t consider the nonlinear, dynamic, and interdependent nature of variables that drive product demand, including deal history, prices, seasonality, elevations, request changes, and profitable pointers. This design presents a sophisticated soothsaying frame for guidance from an artificial intelligence system, integrating soothsaying using deep literacy models together with large language models(LLMs), that can negotiate both accurate soothsaying and give practicable intelligence. The deep literacy infrastructures used in this study include Long Short Term Memory(LSTM), Reopened intermittent Units(GRU), and other Motor models for timeseries soothsaying, which optimize temporal dependences and the complex cross-variable relations. To further increase interpretability of the vaticinations, LLMs are useful agents to convert the specialized cast affair into a completely automated and enhanced mortal-readable textbook and reports to develop intelligence for decision timber. Prophetic modeling and naturally generated reporting lead to better delicacy and practicable intelligence for their businesses. This intelligence empowers businesses to create better procurement processes, improve inventory management, and develop more resilient supply chains relevant to today’s business environment.
Open Access
Review
29 September 2025Robot Grinding: From Frontier Hotspots to Key Technologies and Applications
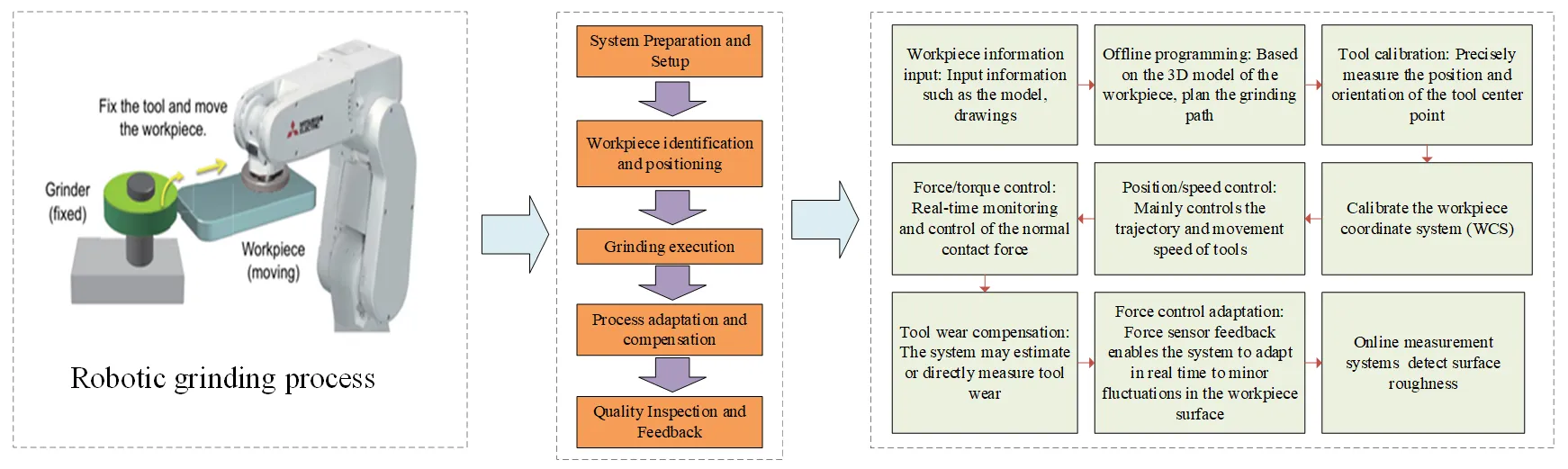
Robot grinding technology has shown broad application prospects in the field of machining complex curved parts due to its high flexibility, strong adaptability, and high automation. However, industrial robots are generally only suitable for rough machining, and for semi-finishing and finishing, improving the machining accuracy of robots and the surface quality of parts is a key issue. This paper summarizes the current research status of robot grinding and provides a reference for realizing robot precision grinding. At present, the research on robot grinding technology mainly focuses on robot pose control, force/position hybrid control strategy, intelligent machining path planning, vibration suppression technology, compliance control, and so on, aiming at solving the key bottleneck problems such as low machining accuracy, large grinding force fluctuation and poor surface quality consistency caused by insufficient robot stiffness. Firstly, the development history of the robot grinding system and the research status of process technology are summarized systematically. Secondly, the analysis focuses on grinding path planning, programming technology, and robot compliance force control technology. Finally, the current status of optimization research in robot grinding technology is summarized. The overarching purpose of this paper is to provide a systematic analysis and a comprehensive reference framework, aiming to address the core challenges hindering the achievement of high-precision, consistent surface quality in robotic grinding manufacturing. Based on the summarized state-of-the-art, robot grinding technology development trend is also predicted.
Open Access
Article
28 September 2025Integrated Consensus Framework for Task Assignment and Path Planning of a Degraded UAV Fleet
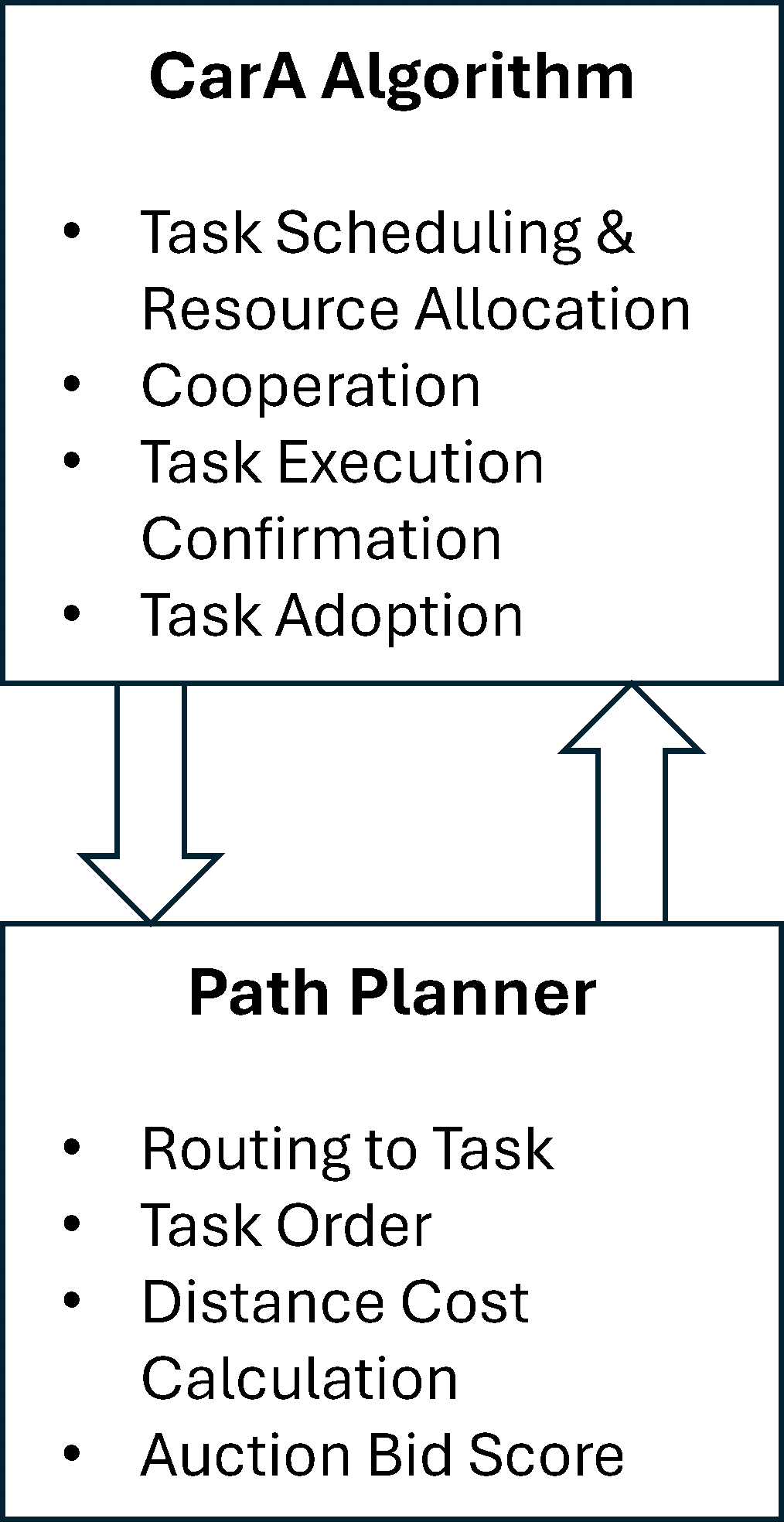
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) systems can fail during civil and military operations. This presents a significant challenge for human teleoperators (remote pilots) in determining task reallocation after member loss within the fleet. To alleviate the high cognitive load on teleoperators in critical situations, a decentralized strategy was developed to resolve the combined task assignment and vehicle routing problems. This Integrated Consensus Framework (ICF) not only solves the combined problem but also adds a unique ability to identify the loss of a vehicle and dynamically reroute agents to abandoned tasks to achieve a satisfactory solution. ICF is a two-tiered approach that combines a novel algorithm, the Caravan Auction (CarA) algorithm, with a path-planning strategy to identify when UAVs are lost and reallocate orphaned tasks. The CarA Algorithm consists of three phases: auction, consensus, and validation phases. An experiment using Monte Carlo simulations was conducted to determine the performance of ICF. Teleoperators assigned to complete multiple tasks with UAVs in dangerous environments can allow the proposed system to perform task assignments and reallocation while offering only supervisory control as needed. The results indicate this novel approach provides comparable performance to existing strategies, doing so with the addition of randomized UAV loss.
Open Access
Commentary
28 September 2025From Crisis to Coordination: How AI Transformed Public Health Policies during COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic showed the shortcomings of traditional policy-making procedures and highlighted serious flaws in international public health institutions. Artificial intelligence (AI) became a transformative force in response to the crisis’s urgency, allowing for data-driven, flexible, and better-coordinated public health measures. This viewpoint article examines how AI improved communication, accelerated vaccine development and distribution, enhanced decision-making, and optimized healthcare delivery during the COVID-19 pandemic. These advancements collectively contributed to significant changes in public health policy. Real-time analysis of large, complex datasets, ranging from case numbers and mobility patterns to hospital capacities and disinformation trends, was made possible by AI technologies including machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP). Timely interventions like resource allocation, targeted lockdowns, and control of misinformation were made possible by this capability. AI also played a crucial role in forecasting infection trends, identifying vulnerable populations, and informing evidence-based decisions. AI-powered solutions further enhanced public involvement and cross-sector cooperation through chatbots and digital platforms delivering trustworthy health information. Additionally, AI-powered solutions enhanced public involvement and cross-sector cooperation, including the use of chatbots and digital platforms to provide trustworthy health information. AI sped up supply chain optimization and candidate screening in vaccine development, guaranteeing efficient, and quick delivery. However, ethical issues including bias, data privacy, and equity in healthcare access were also brought about by the integration of AI. This study emphasizes the need for open, inclusive, and morally sound AI governance by highlighting AI’s twin roles as a technological enabler and a tool for policy. The pandemic provides a fundamental lesson for countries preparing for future health emergencies: AI may be a key instrument in creating public health systems that are more robust, responsive, and equitable if it is applied properly.

Open Access
Article
25 September 2025Detection and Classification of Faults in a Photovoltaic System—A New Hybrid Algorithm
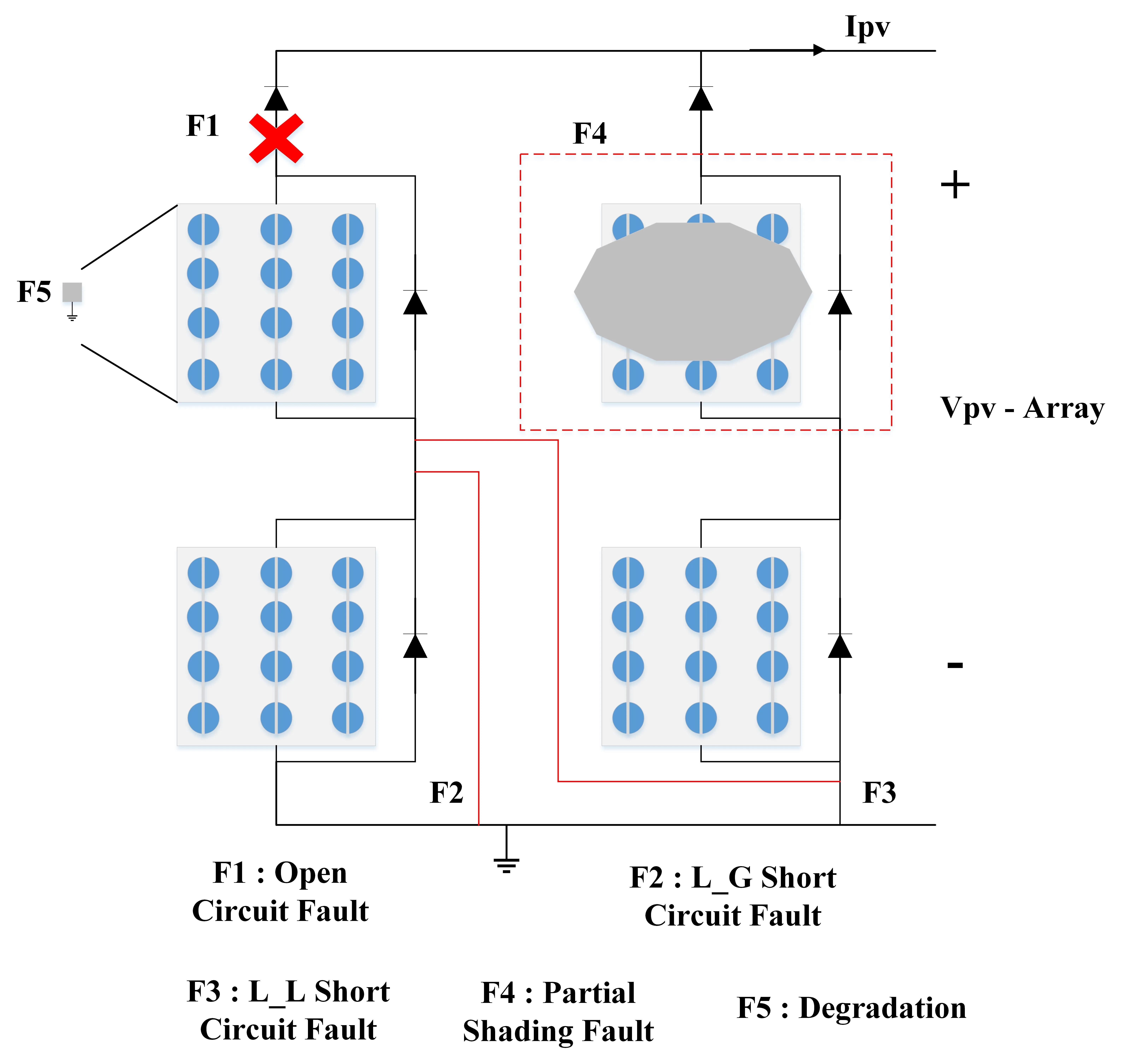
Four main types of faults can occur at the DC side of any Photovoltaic System (PVS). These faults are quite dangerous and can cause permanent damage to the photovoltaic modules if not addressed promptly. The faults include open circuit, short circuit, degradation, and partial shading. Short circuit faults are classified into line-to-line (L-L) and line-to-ground (L-G). Detecting these faults requires specialized algorithms. This paper tackles this complex issue through (1) fault-finding equations and the placement of current sensors, and (2) a new hybrid algorithm based on data from the fault-finding equations and current sensors. Numerous simulations using PSIM 2021 were conducted to verify this proposed solution. The hybrid algorithm presented here is original compared to previous studies. It is easy to understand, responds quickly, and can be implemented in systems with photovoltaic arrays of any size.
Open Access
Article
25 September 2025An Angles-Based Design of an Island-Type Fishway and Its Hydraulic Properties Inside the Channel
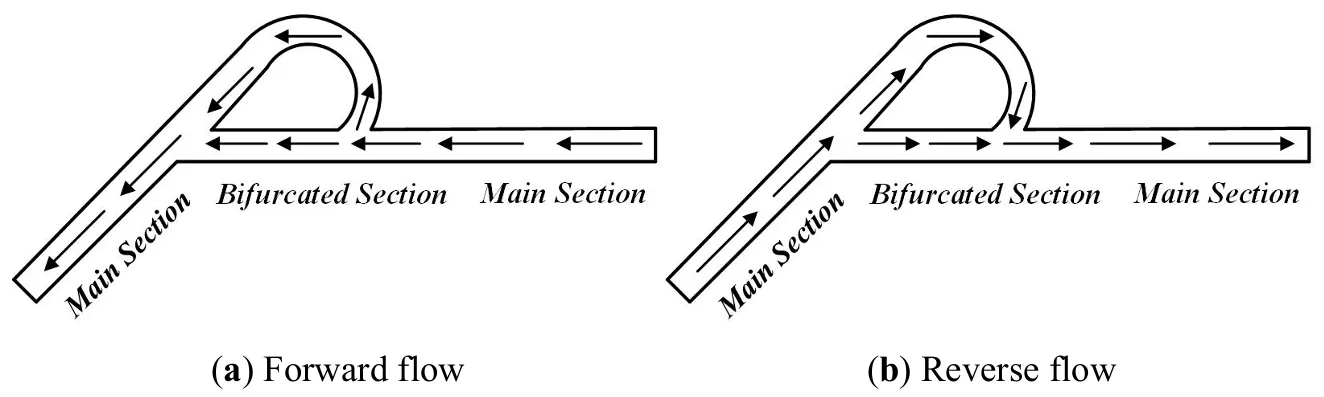
With the development of hydraulic and hydroelectric projects, the connectivity of natural rivers has been disrupted, impeding the migration of migratory fish and affecting their reproduction and population sustainability. This study investigates a novel island-type fishway, where combinations of island structures and arc configurations dissipate water flow energy and reduce flow velocity, thereby minimizing resistance to upstream fish migration. The research focuses on the influence of island angles on the hydrodynamic characteristics within the island-type fishway. Experimental results indicate that low-velocity regions downstream of the island exhibit larger areas when the island angle is −60° or 60°. Meanwhile, at an island angle of 0°, the maximum flow velocity and the average flow velocity are reduced. Additionally, turbulence kinetic energy in the fishway chambers is effectively suppressed, with both maximum and average turbulence kinetic energy maintained at low levels. The water level variations caused by changes in island angles are minor, with an advantage observed when the island angle is set to 0°. These findings provide a reference for the further development of island-type fishways.
Open Access
Article
23 September 2025Side Chain Piperidinium Functionalized AEMs with an Ethylene Oxide Spacer for Improving Ion Conductivity and Alkaline Stability
In this work, grafting alkaline stable piperidinium cations via ethylene oxide (EO) spacers onto an aryl ether-free poly(oxindole terphenylene) backbone was adopted as a strategy for designing self-aggregating side chain AEMs with optimized alkaline stability. Aryl ether-free poly(oxindole terphenylene) backbones were synthesized via superacid-catalyzed step-growth polycondensation and were subsequently functionalized with either piperidinium containing hydrophilic, dipolar EO or hydrophobic alkyl spacer, aiming to explore the effect of side chain-engineering on conductivity and alkaline stability of the resulting AEMs. The AEM membrane containing dipolar ethylene oxide spacer, despite its lower ion exchange capacity (IEC), exhibited a more pronounced microphase separated morphology as evidenced by TEM, and higher ionic conductivity (reaching up to 30.5 mS cm−1 at 80 °C) compared to the hydrophobic alkyl spacer-containing AEM membrane. This was attributed to its higher water uptake stemming from the EO hydrophilic nature and the formation of interconnected ion-conducting channels due to piperidinium–EO interactions. Additionally, the hydrophilic nature of the ethylene oxide groups endowed the membrane with enhanced alkaline stability, preserving its mechanical integrity and retaining 71.5% of its initial conductivity after 3 weeks of immersion in 2 M KOH at 80 °C. In contrast, the AEM with an alkyl spacer experienced severe degradation under the same conditions. These results suggest that incorporating flexible alkoxy-containing spacers onto an aryl ether-free backbone is a promising and simple route for fabricating mechanically and chemically robust AEMs with sufficient conductivity.

Open Access
Article
23 September 2025Promoting Sustainable Development through Community Education on Flood- and Storm-Resistant Architecture
Pakistan is experiencing climate-induced disasters such as floods and storms with an increased frequency and intensity every single year. This study aims to explore the integration of resilient architecture into environmental education as a pathway toward sustainable development and disaster risk reduction. The research examines current levels of understanding regarding flood- and storm-resistant building practices and identifies key barriers to their adoption in high-risk regions of Pakistan. The study used a mixed-methods approach by administering surveys. These surveys were administered to 500 community members in different cities of Sindh and Punjab. The study also incorporated two in-depth case studies: the Heritage Foundation’s low-cost housing initiative in Makli, Sindh, and the Aga Khan Agency for Habitat’s Safe Housing Program in Chitral, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. These cases provide valuable insights into effective, culturally appropriate, and scalable models of resilient construction in Pakistan. Findings of the present study reveal that public awareness of resilient architecture is below a satisfactory level, with common misconceptions. Challenges, including high costs, lack of technical knowledge, and minimal government support, were identified as significant obstacles. Despite these issues, communities showed strong interest in learning about safer building practices when exposed to practical examples and local success stories. The study recommends integrating resilient construction education into community outreach, school curricula, and builder training programs. It also advocates for greater government involvement, financial incentives, and replication of proven models to foster widespread adoption of resilient architecture for long-term sustainability.

Open Access
Article
23 September 2025A Survey on XR-Based Drone Simulation: Technologies, Applications, and Future Directions
This paper presents a comprehensive survey of Extended Reality (XR)-based drone simulation systems, encompassing their architectures, simulation engines, physics modeling, and diverse training applications. With a particular focus on manual multirotor drone operations, this study highlights how Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are increasingly vital for pilot training and mission rehearsal. We classify these simulators based on their hardware interfaces, spatial computing capabilities, and the integration of game and physics engines. We analyze specific platforms such as Flightmare, AirSim, DroneSim, Inzpire Mixed Reality UAV Simulator, and SimFlight XR are analyzed to illustrate various design strategies, ranging from research-grade modular frameworks to commercial training tools. In this paper, we also examine the implementation of spatial mapping and weather modeling to enhance realism in AR-based simulators. Finally, we identify critical challengesthat remain to be addressed, including user immersion, regulatory alignment, and achieving high levels of physical realism, and propose future directions in which XR-integrated drone training systems can advance.