Found 56 results
Article
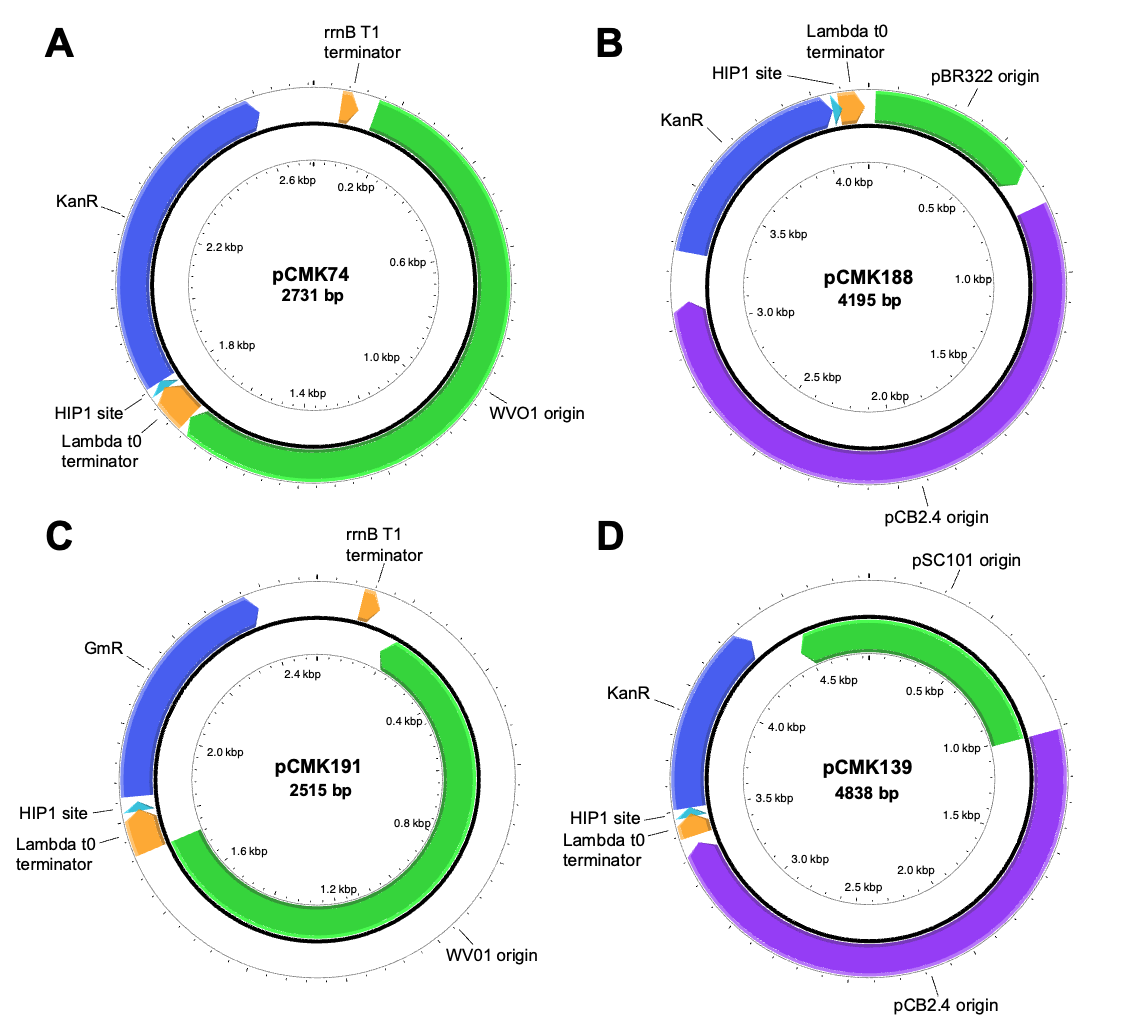
26 August 2024Delivery of Novel Replicating Vectors to Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 Via Natural Transformation of Plasmid Multimers
In most cyanobacteria, genetic engineering efforts currently rely upon chromosomal integration; a time-consuming process due to their polyploid nature. To enhance strain construction, here we develop and characterize two novel replicating plasmids for use in Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002. Following an initial screen of plasmids comprising seven different origins of replication, two were found capable of replication: one based on the WVO1 broad host range plasmid and the other a shuttle vector derived from pCB2.4 from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. These were then used to construct a set of new replicating plasmids, which were shown to be both co-transformable and stably maintained in PCC 7002 at copy numbers between 7–16 and 0.6–1.4, respectively. Lastly, we demonstrate the importance of using multimeric plasmids during natural transformation of PCC 7002, with higher order multimers providing a 30-fold increase in transformation efficiency relative to monomeric plasmids. Useful considerations and methods for enhancing multimer content in plasmid samples are also presented.
Opinion
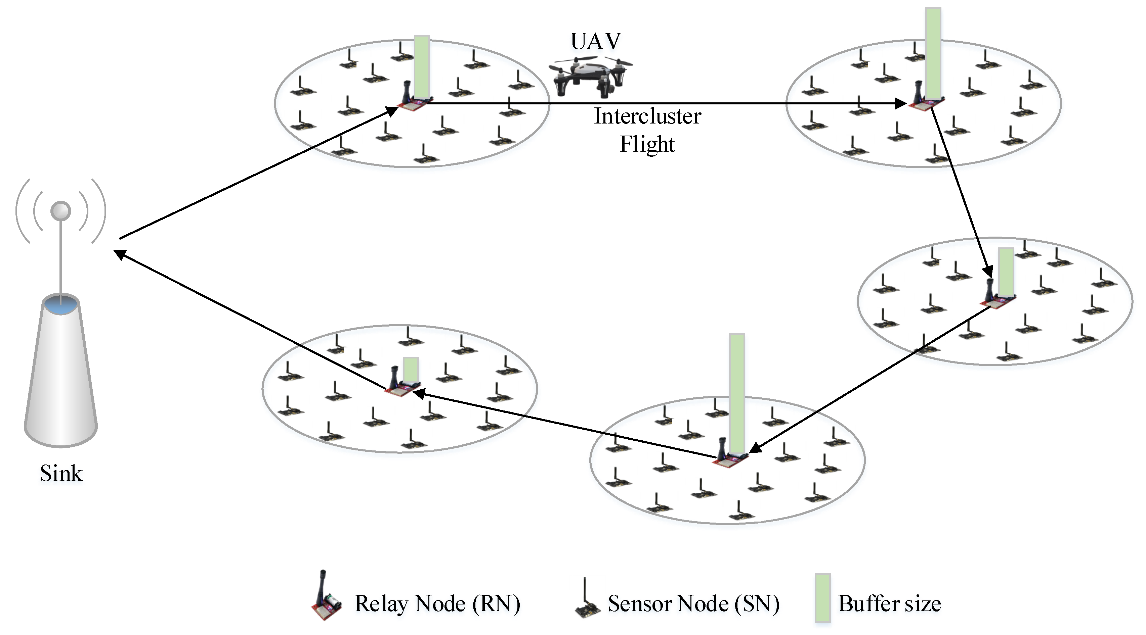
22 August 2024Medical Drones for Public Health Emergency Preparedness, Response, and Resilience: Delivering Health for All
Amid a global metacrisis of health, environmental and economic challenges, medical delivery drones (or uncrewed aerial vehicles) offer a promising method to prepare for, and rapidly respond, to future emergencies. This opinion article summarizes the current medical delivery drone landscape, evidence base, and policy implications in the context of public health emergencies, such as pandemics, natural disasters, and humanitarian crises, with a particular emphasis on the region of sub-Saharan Africa. Using a multilateral, international health policy perspective, key challenges and opportunities, such as the development of sustainable funding mechanisms, robust regulatory frameworks, and capacity building, are identified.

Article
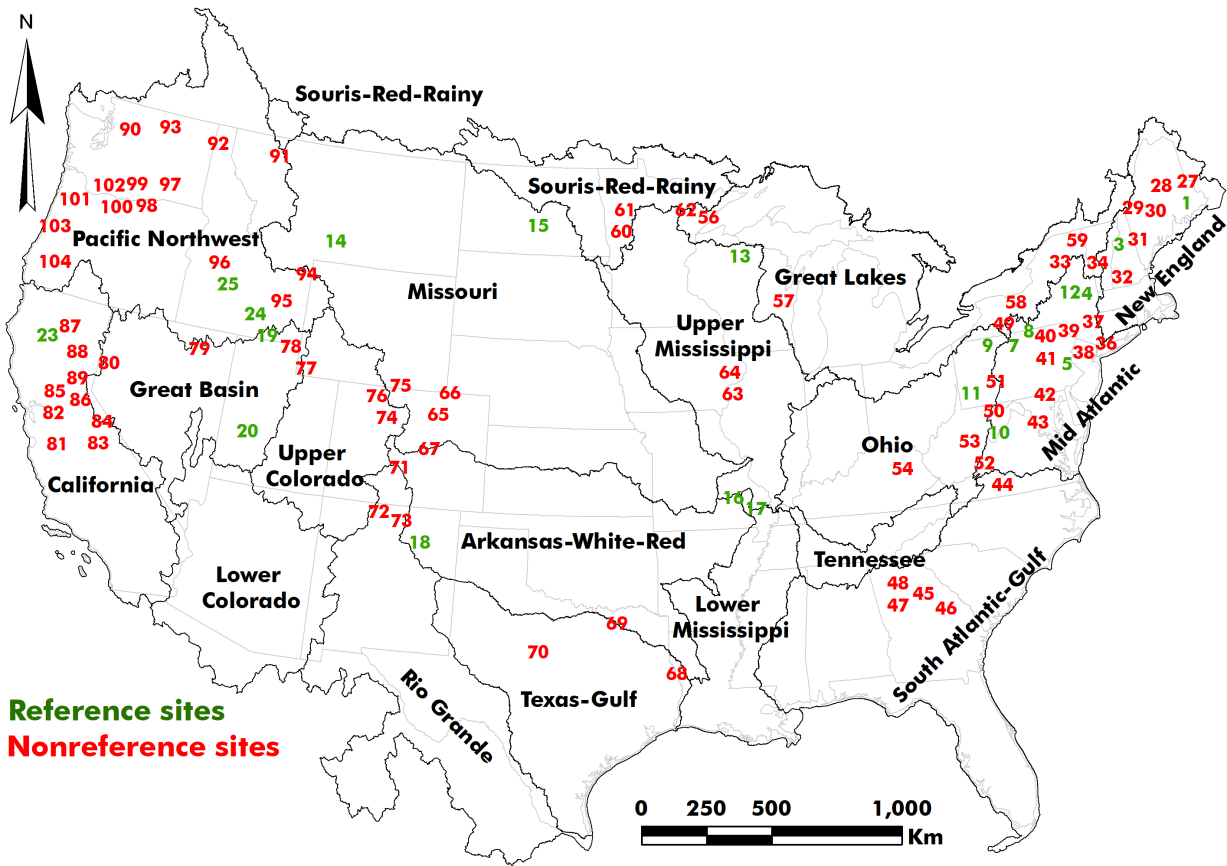
19 August 2024Differences in Flood Quantiles Estimate of Disturbed and Undisturbed Watersheds in the United States
Nonstationarity due to climate variation and anthropogenic disturbances has altered high flow regimes. However, the extent of change has not been evaluated for undisturbed versus disturbed watersheds. This article aimed to determine how partitioning watersheds into undisturbed and disturbed categories can improve the performance of probability distributions for flood analysis throughout the United States. We utilized peak flow information for 26 reference (undisturbed) and 78 nonreference (disturbed) watersheds with drainage areas ranging from 135 to 42,367 km2 and record lengths of 100 to 140 years. Results indicated that flood quantile estimates of the Log Pearson Type III (LP3) distribution were likely being overestimated for return periods of 2 to 10 years, while flood estimates of 50 years and higher might be underestimated. In contrast, the Generalized Extreme Value (GEV) distribution outperformed LP3 in estimating floods with return periods of 50 years or more. These findings enhance flood frequency analysis and forecasting under nonstationary conditions.
Editorial
16 August 2024
Review
06 August 2024Considerations for Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) Operations
This paper, intended for expert and non-expert audiences, evaluates the technical and regulatory requirements for Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) to operate beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) services. UAS BVLOS operations have the potential to unlock value for the industry. However, the regulatory requirements and process can be complex and challenging for UAS operators. The work explored the BVLOS regulatory regime in the UK, Europe and the US and found similarities in process and requirements covering themes like Detect and Avoid (DAA), Remote identification and Reliable Connectivity. A unifying goal across these jurisdictions is to operate BVLOS safely and securely in non-segregated airspace. However, operating BVLOS in segregated airspace as the default or routine mode could accelerate approval and adoption. The paper reviewed existing challenges, highlighting Coverage, Capacity and Redundancy as critical for UAS BVLOS Operations. The work also highlighted the crucial role of Non-terrestrial Network (NTN) assets like Satellites and HAPS (High Altitude Platform Station) since terrestrial networks (not optimised for aerial platform coverage) may not be reliable for BVLOS connectivity.
Review
02 August 2024A Promising and Forward-Looking Advancement Using Drones: Perspectives from Indian Sericulture
Drone integration in sericulture marks a promising advancement within the sector, leveraging recent technological strides in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) across various industries like agriculture and healthcare. While the adoption of drones in sericulture remains nascent, their potential benefits, particularly in chemical spraying tailored to sericulture’s unique environmental conditions, are increasingly recognized. This paper explores the efficacy of drone-based pesticide spraying and smart fertilization methods optimized for sericulture settings. The rapid deployment capabilities of drones facilitate enhanced network connectivity, potentially catalyzing rural development and economic prosperity within the sericulture community. However, ethical and operational concerns persist regarding drone use across industries, necessitating robust regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines. Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence augment drone capabilities, enabling automated inspections and improved performance across diverse applications. This paper underscores the need for further research and the development of standardized operating protocols to harness the transformative potential of drone technology in sericulture. Key focus areas include optimizing pesticide delivery, ensuring environmental sustainability, and addressing ethical considerations surrounding drone utilization. By leveraging UAVs for precision spraying and smart fertilization, sericulture stands poised to enhance productivity, bolster economic development, and navigate emerging challenges in agricultural production.

Article
25 July 2024A Distributed Framework for Persistent Wildfire Monitoring with Fixed Wing UAVs
Wildfires have proven to be a significantly exigent issue over the past decades. An increasing amount of research has recently been focused on the use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and multi-UAV systems for wildfire monitoring. This work focuses on the development of a decentralized framework for the purpose of monitoring active wildfires and their surrounding areas with fixed wing UAVs. It proposes a distributed fire data update methodology, a new formation algorithm based on virtual forces, fine-tuned by a Genetic Algorithm (GA), to arrange virtual agents into the monitoring area, and a control strategy to safely and efficiently guide fixed wing UAVs to loiter over the structured virtual agents. The system is tested in Software In The Loop (SITL) simulation with up to eight UAVs. The simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the system in monitoring the fire in a persistent manner and providing updated situational awareness data. The experiments show that the proposed framework is able to achieve and maintain coverage up to 100% over the area of interest, and very accurate fire representation. However, the performance is decreased for the experiments with low UAV numbers and large fire sizes.
Article
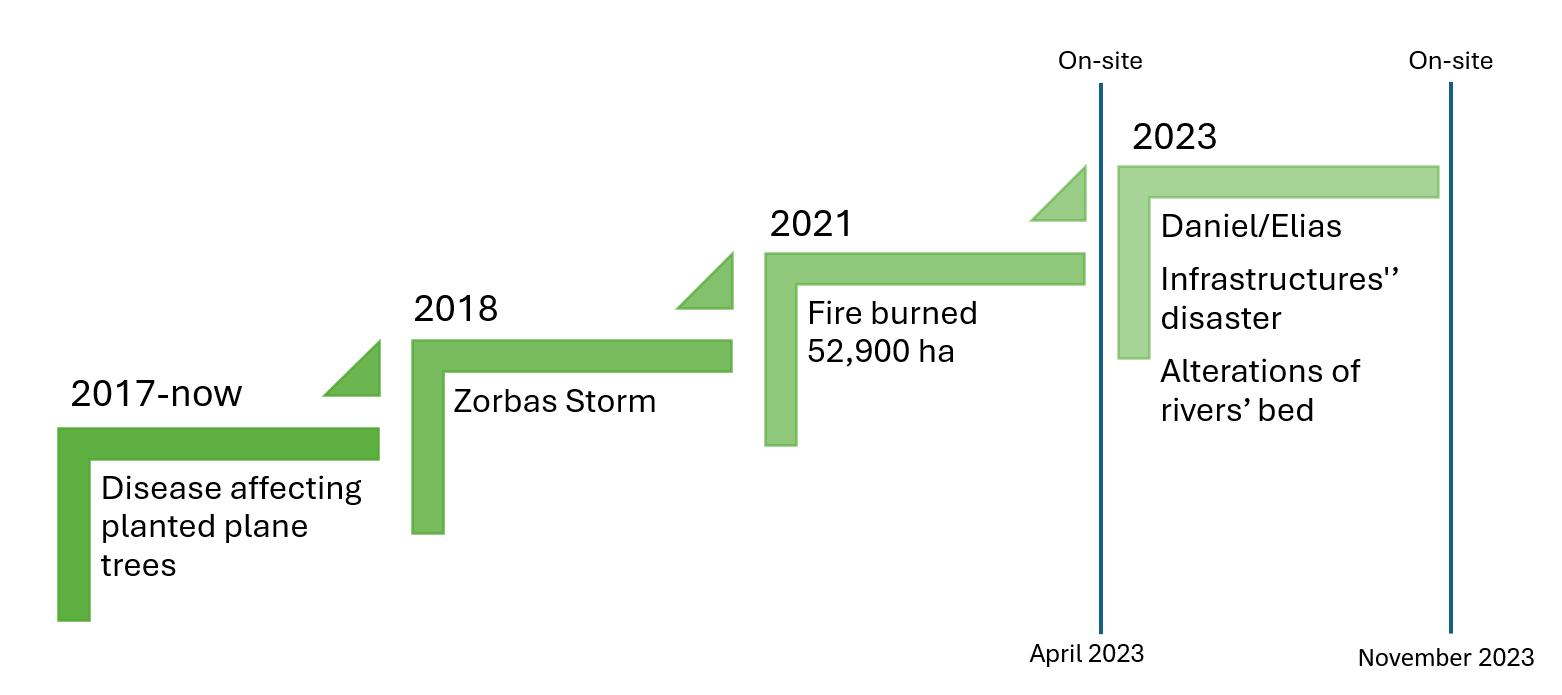
10 July 2024Documenting the Changing Floodplain of Nileas Basin in North Euboea (Greece) before and after Storms Daniel and Elias
The area of north Euboea is characterized by its intense relief, dense hydrographic network, and rich flora and fauna. In the mid-2010s, the region was struck by a plane tree disease that withered the large population of plane trees in the area, while in 2021, a large wildfire completely burned the forest. These unfortunate events depleted the landscape’s natural ability to manage and mitigate flood phenomena. Observing the landscape’s vulnerability to floods, in April 2023, we conduct on-site field inspections in the rivers of the area. In September 2023, a major flood hit the area, causing in dramatic changes to the landscape. Therefore, in November 2023, we conducted follow-up on-site field inspections in the area, in order to trace the differences, present the damages the phenomenon left behind. These inspections allowed to document the landscape changes from the combination of all previous events and identify any associated pathologies. Site visits and comparisons before and after the Daniel/Elias storm revealed dramatic changes in the riverbed width at lower altitudes, significant sediment accumulation in the Voudouros River delta, alterations in the natural landscape along the river and its floodplain, destruction of the arable land, and road collapses in several locations.
Article
28 June 2024Shifting Prospects: Views and Strategies for Transforming Livestock and Meat Value Chains in a Dynamic Location
Rural areas characterized by resource-dependent industries often experience growth but also lock-in and transformation pressures. We ask what strategies industries and businesses pursue that successfully exploit the transformative potential of such a location and what prevents other industries and businesses from doing the same. Based on interviews with stakeholders and experts from the livestock and meat sector in a highly specialized location, we explore the will, resources, and capabilities of industries and actors to transform their businesses and entire value chains in ways that can stabilize the local growth regime. The analysis is based on a conceptual framework derived from resource-based and dynamic capability theories at the micro level and the concept of Strategic Action Fields (SAFs) at the meso level. The results suggest that incumbents from the old industrial core tend to counteract the transformation of the SAF with conservative strategies. Challengers from former support activities, in contrast, want to move away from cost competition towards new markets. Their product variation and horizontal diversification can exploit favorable cluster characteristics to develop future-proof capabilities. This should be encouraged, along with new entrepreneurial activity, even if the region is then no longer hosting the core industries of the transformed field.
Article
12 June 2024Optimized Real Time Single-Drone Path Planning for Harvesting Information from a Wireless Sensor Network
We consider a remote sensing system in which fixed sensors are placed in a region, and a single drone flies over the region to collect information from cluster heads. We assume that the drone has a fixed maximum range and that the energy consumption for information transmission from the cluster heads increases with distance according to a power law. Given these assumptions, we derive local optimum conditions for a drone path that either minimizes the total or maximum energy required by the cluster heads to transmit information to the drone. We show how a homotopy approach can produce a family of solutions for different drone path lengths so that a locally optimal solution can be found for any drone range. We implement the homotopy solution in Python and demonstrate the tradeoff between drone range and cluster head power consumption for several geometries. Execution time is sufficiently rapid for the computation to be performed in real time so that the drone path can be recalculated on the fly. The solution is shown to be globally optimal for sufficiently long drone path lengths. A proof of concept implementation in Python is available on GitHub. For future work, we indicate how the solution can be modified to accommodate moving sensors.