Found 301 results
Open Access
Review
30 May 2024A Review on Design of Sustainable Advanced Materials by Using Artificial Intelligence
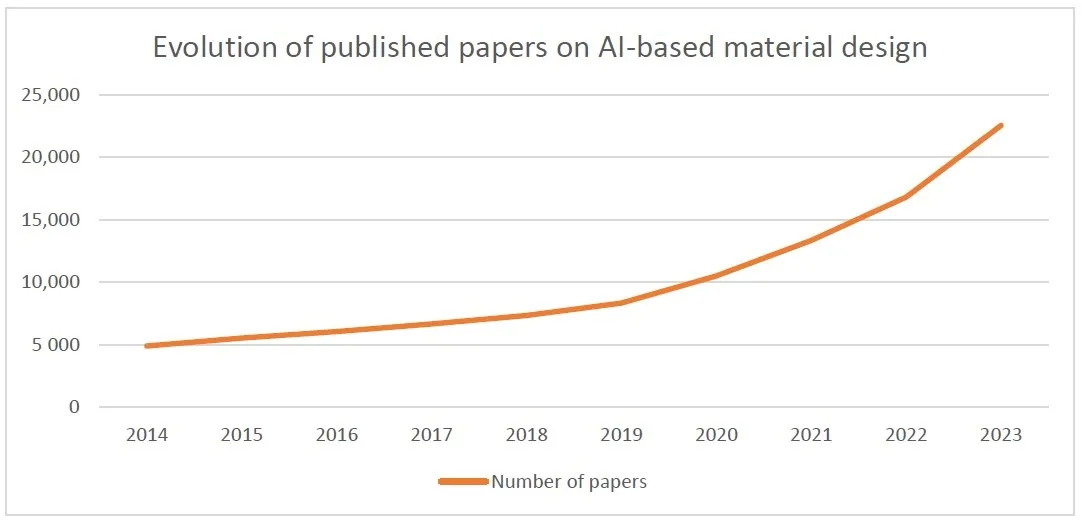
This paper gives a comprehensive review of scientific interests and current methodologies of artificial intelligence applied to advanced material design and discovery by taking into account multiple sustainable design criteria such as functionalities, costs, environmental impacts, and recyclability. The main research activities include predicting material properties, compositions, and structures with data mining, new material discovery, hybrid modeling approaches combining AI techniques and classical computational formulations based on physical and chemical laws, and multicriteria optimization of materials. Based on this review, a short analysis is provided on the perspectives of this research area in the future, aiming at creating an everything connected material life cycle with real-time traceability systems
Open Access
Communication
30 May 2024A Novel Animal Model for Pulmonary Hypertension: Lung Endothelial-Specific Deletion of Egln1 in Mice
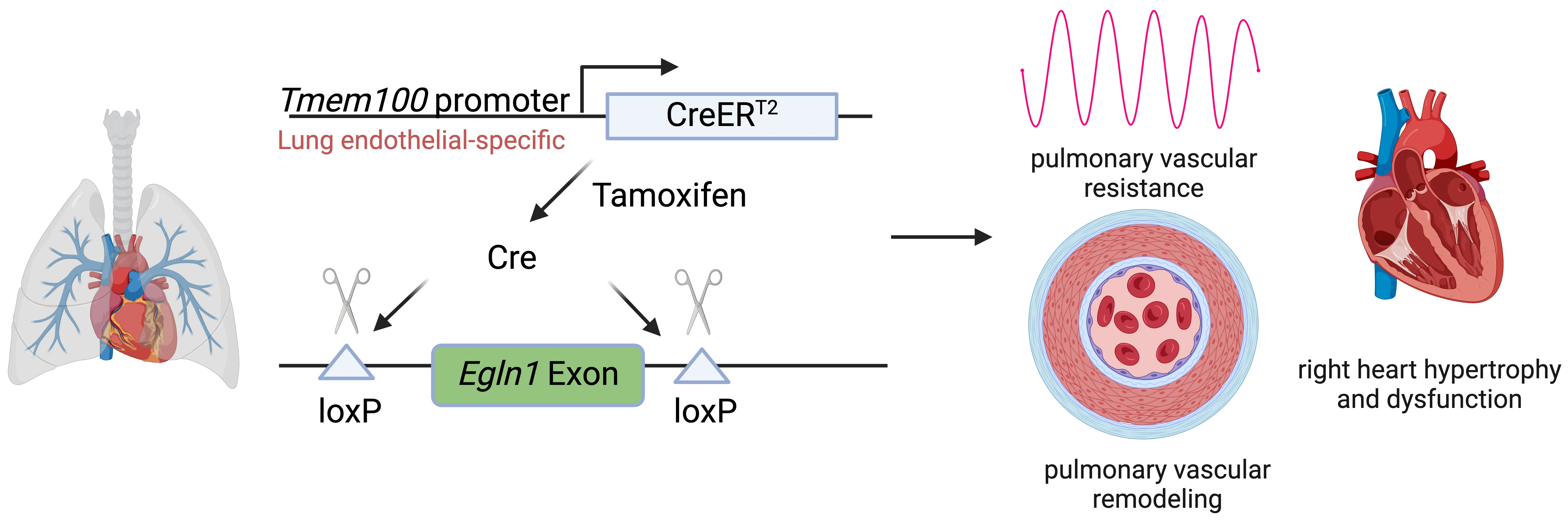
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a devastating disease characterized by high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries, which can potentially lead to heart failure over time. Previously, our lab found that endothelia-specific knockout of Egln1, encoding prolyl 4-hydroxylase-2 (PHD2), induced spontaneous pulmonary hypertension (PH). Recently, we elucidated that Tmem100 is a lung-specific endothelial gene using Tmem100-CreERT2 mice. We hypothesize that lung endothelial-specific deletion of Egln1 could lead to the development of PH without affecting Egln1 gene expression in other organs. Tmem100-CreERT2 mice were crossed with Egln1flox/flox mice to generate Egln1f/f;Tmem100-CreERT2 (LiCKO) mice. Western blot and immunofluorescent staining were performed to verify the knockout efficacy of Egln1 in multiple organs of LiCKO mice. PH phenotypes, including hemodynamics, right heart size and function, pulmonary vascular remodeling, were evaluated by right heart catheterization and echocardiography measurements. Tamoxifen treatment induced Egln1 deletion in the lung endothelial cells (ECs) but not in other organs of adult LiCKO mice. LiCKO mice exhibited an increase in right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP, ~35 mmHg) and right heart hypertrophy. Echocardiography measurements showed right heart hypertrophy, as well as cardiac and pulmonary arterial dysfunction. Pulmonary vascular remodeling, including increased pulmonary wall thickness and muscularization of distal pulmonary arterials, was enhanced in LiCKO mice compared to wild-type mice. Tmem100 promoter-mediated lung endothelial knockout of Egln1 in mice leads to development of spontaneous PH. LiCKO mice could serve as a novel mouse model for PH to study lung and other organ crosstalk.
Open Access
Article
28 May 2024Efficacy and Cytocompatibility of a Pressure Garment—Silicone Composite Dressing Material for Scar Healing
Pressure garment therapy (PGT) and silicone gel sheeting (SGS) predominate non-invasive interventions for burn injuries, but the market lacks a composite solution combining pressure garment fabric (PGF) and medical-grade silicone (e.g. Biopor®AB) for multi-therapeutic efficacy. To address this gap, a versatile composite dressing of PGF-Biopor®AB was developed. PGF-Biopor®AB incorporates dual PGF-SGS therapy, mechanotherapy, and active moisture management, to facilitate recovery of hypertrophic subsidiary structures. The PGF structure enables the application of PGT, while the Biopor®AB silicone characteristics enforce silicone gel therapy (SGT). The PGF-SGS efficacy optimization not only reduces tension but also facilitates water vapor and oxygen penetration, along with hydration of the stratum corneum. Mechanotherapy, involving tension-shielding and pressure redistribution, promotes the reorganization of the collagen-fiber network. For active moisture management, the incorporation of a microchannel structure with active nylon absorbency facilitates effective moisture control through water absorption, retention, and cellular pathways of transport. In this study, the microscale features in the structure were further investigated. Under ISO 10993-5 standard, an over 70% cell viability in 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay containing the L929 cell line verified the enhanced cell growth and inhibited proliferation, endorsing the safe usage of PGF-Biopor®AB. Patient studies of one-month efficacy in both high and low-cell-density samples and an early scarless healed wound suggest that over 70% cell viability is sufficient for optimal scar therapeutics. The multifaceted scar repair roles are fulfilled by addressing persistent inflammation, insufficient oxygenation, low levels of perfusion, and scar-healing tension, hence realising the multi-therapeutic efficacy of the composite dressing.
Open Access
Review
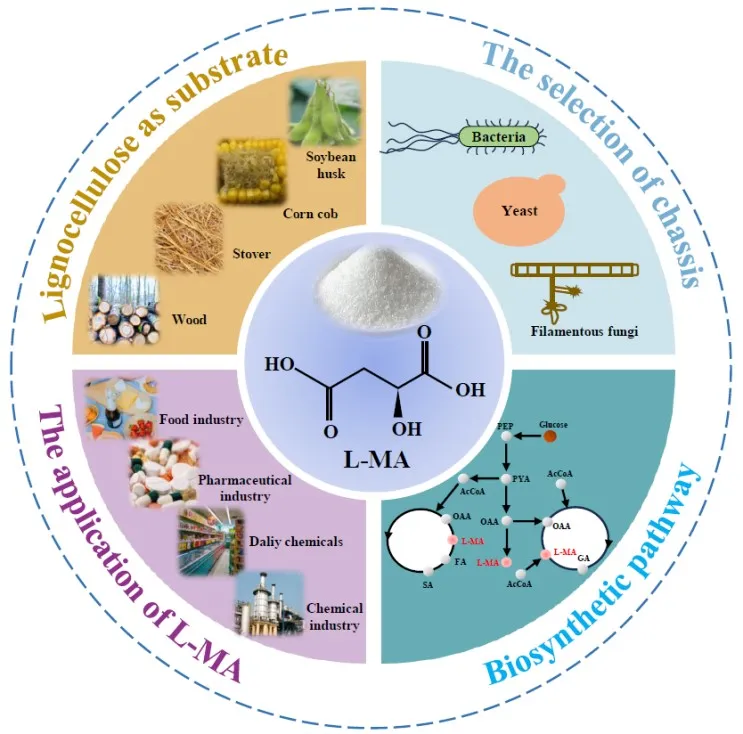
24 May 2024Current Progress on Microbial l -malic Acid Production
As an important
intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle,
Open Access
Article
08 May 2024Assessing Drone Return-to-Home Landing Accuracy in a Woodland Landscape
While aerial photography continues to play an integral role in forest management, its data acquisition can now be obtained through an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly referred as a drone, instead of conventional manned aircraft. With its feasibility, a drone can be programed to take off, fly over an area following predefined paths and take images, then return to the home spot automatically. When flying over forests, it requires that there is an open space for a vertical takeoff drone to take off vertically and return safely. Hence, the automatic return-to-home feature on the drone is crucial when operating in a woodland landscape. In this project, we assessed the return-to-home landing accuracy based on a permanently marked launch pad nested in a wooded area on the campus of Stephen F. Austin State University in Nacogdoches, Texas. We compared four models of the DJI drone line, with each flown 30 missions over multiple days under different weather conditions. When each drone returned to the home launch spot and landed, the distance and direction from the launch spot to the landing position was measured. Results showed that both the Phantom 4 Advanced and the Spark had superior landing accuracy, whereas the Phantom 3 Advanced was the least accurate trailing behind the Phantom 4 Pro.

Open Access
Article
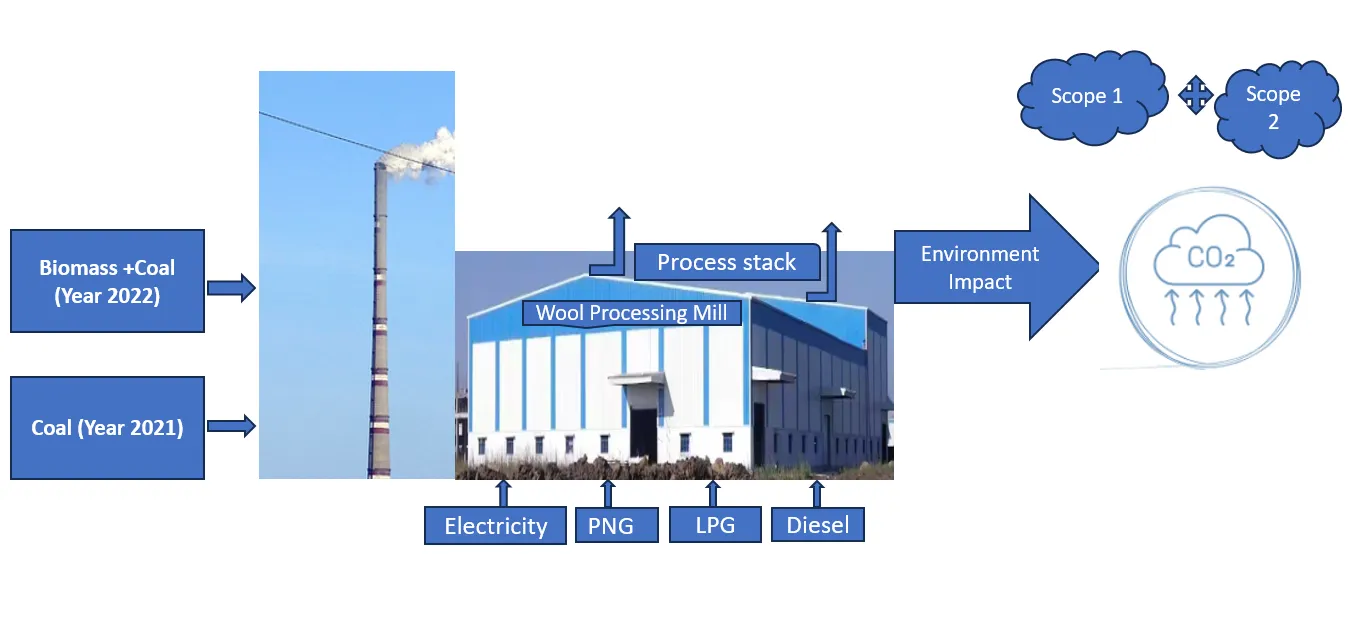
06 May 2024Assessing Energy Emissions and Environmental Impact of Wool Processing: A Case Study of an Indian Textile Mill
The objective of this study is to investigate and analyze the effect of varying sources of energy inputs and their impact on carbon emissions during wool fiber processing. The method involved industrial visits to the textile wool processing mill and interaction with the manufacturing as well as commercial sourcing teams to gather relevant data. The results and outcome of this analysis indicate that wool wet processing is responsible for a significant carbon emission of about 0.031 tCO2e/unit of production. Coal as a source of energy has the highest carbon emission 0.066 tCO2e/product, while the use of biomass and Pressurized Natural Gas (PNG) had significantly lower CO2 emissions. Further, this study evaluated the scope 1 and scope 2 category emissions produced at the wool processing stage which accounted for 56303.2 tCO2e and 1817.10 tCO2e respectively.
Open Access
Article
26 April 2024Exact and Heuristic Approaches to Surveillance Routing with a Minimum Number of Drones
The rising cost and scarcity of human labor pose challenges in security patrolling tasks, such as facility security. Drones offer a promising solution to replace human patrols. This paper proposes two methods for finding the minimum number of drones required for efficient surveillance routing: an ILP-based method and a greedy method. We evaluate these methods through experiments, comparing the minimum number of required drones and algorithm runtime. The findings indicate that the ILP-based method consistently yields the same or a lower number of drones needed for surveillance compared to the greedy method, with a 73.3% success rate in achieving better results. However, the greedy method consistently finishes within one second, whereas the ILP-based method sometimes significantly increases when dealing with 14 more locations. As a case study, we apply the greedy method to identify the minimum drone surveillance route for the Osaka-Ibaraki Campus of Ritsumeikan University.
Open Access
Commentary
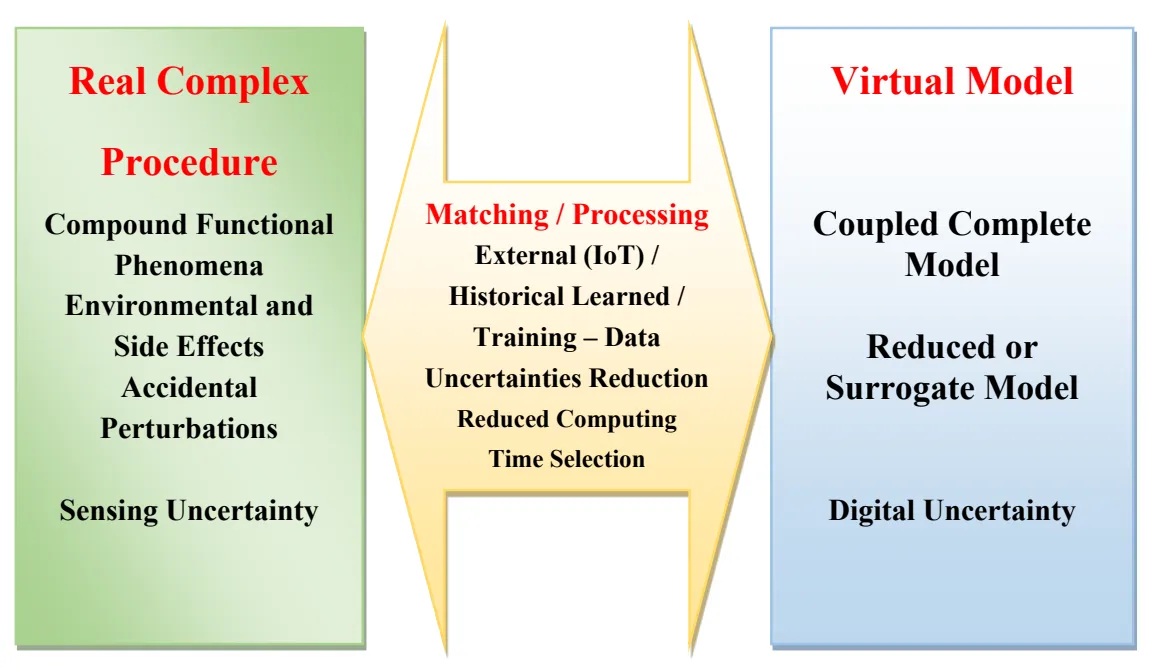
25 April 2024Monitoring Complexity in Clean Energy Systems Applications
Clean energy applications often involve systems with technological process monitoring. This supervision aims to optimize operation, in particular efficiency, performance and compatibility with dedicated criteria. Most of these energy systems involve complex procedures. A complex procedure is an arrangement of compound processes interacting in interdependent behaviors. The supervision of these complex procedures focuses on the interaction of compound processes, their digital coupling and the handling of uncertainties in their detection and digital tools. Real-virtual pairs, such as digital twins, could carry out such surveillance. This commentary aims to analyze and illustrate such supervision in clean electromagnetic energy systems based on a review of the literature. The notion of complexity and the interactions of the compound processes involved are first addressed and detailed. The modeling of these interactions is presented through the mathematical coupling of the electromagnetic equations with other equations of the phenomena involved. These phenomena are linked to the functional or environmental behaviors of the systems. Compound process monitoring in complex procedures is then analyzed taking into account threats, unsolicited external events and uncertainties related to the sensing and digital tools involved. This contribution illustrated several points relating to, the relationship between the complexities of a real energy procedure and its coupled virtual model, the dependence of the model reduction strategy on each specific application and the reduction of uncertainties through the matching of real-virtual pairs. The different analyses are supported by literature references permitting more information when necessary.
Open Access
Article
23 April 2024Visible Light-Driven H2O2 Photoelectrocatalytic Synthesis Over a Tandem Electrode Strategy
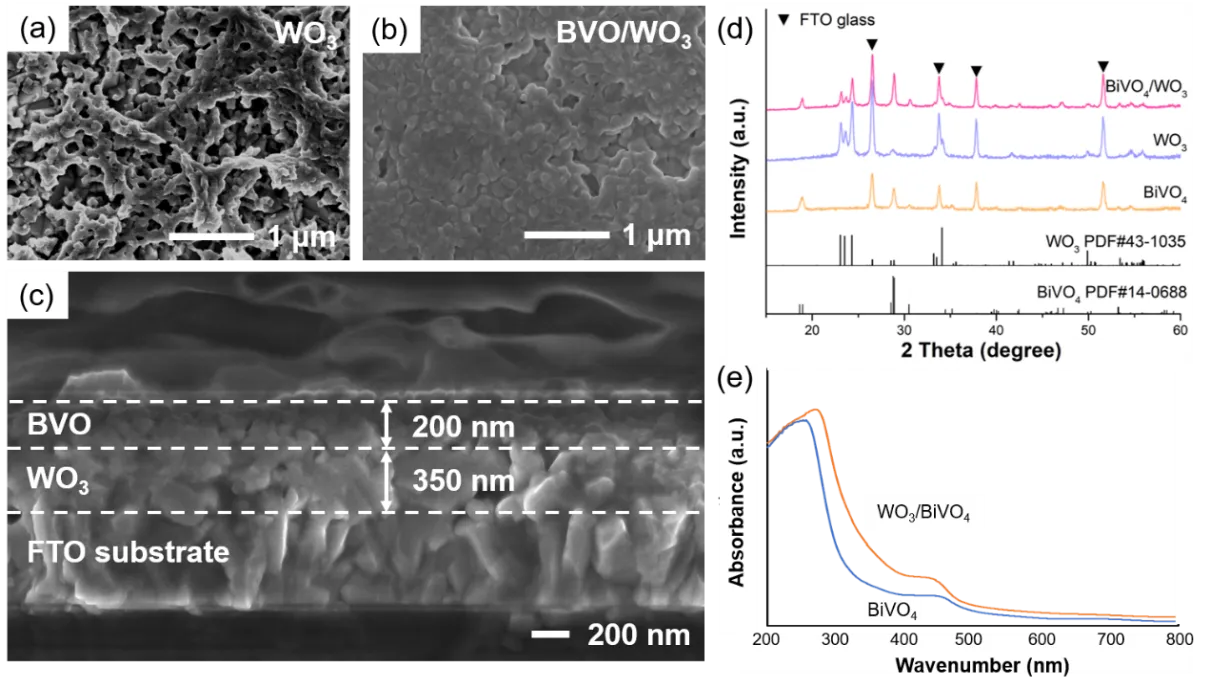
Photocatalytic synthesis of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) can be an environmentally friendly and energy-saving solution. However, the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) rate is limited due to the low solubility of O2 in water. In this study, a modified BiVO4 (BVO) photoanode combined with an Sn-coordinated phthalocyanine gas diffusion electrode (SnPc-GDE) was employed for the synthesis of H2O2, and the oxy-gen reduction reaction rate was increased through a unique three-phase interface system. When visible light was irradiated on the BVO photoanode, the hole-electron pairs were excited and the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) was driven through the holes, and the excited electrons were transferred to the SnPc-GDE to reduce O2 for the synthesis of H2O2. Oxygen vacancy enrichment on the BVO electrode was achieved by photoetching and annealing under an N2 atmosphere, which effectively improved the carrier separation efficiency. Complexation with a WO3 layer formed a built-in electric field, which further promoted the electron-hole pair separation. The SnPc catalyst-modified GDE electrode has the best selectivity for ORR and remains stable during long-term reactions. Under bias-free conditions, the generation rate of H2O2 reached 952.5 μM·L−1·h−1, with a Faradaic efficiency of 48.4%. This study provided a practical strategy for designing a highly efficient BVO/SnPc-GDE photoelectrochemical system to produce H2O2 based on improvement in electron-hole transmission efficiency and product selectivity.
Open Access
Article
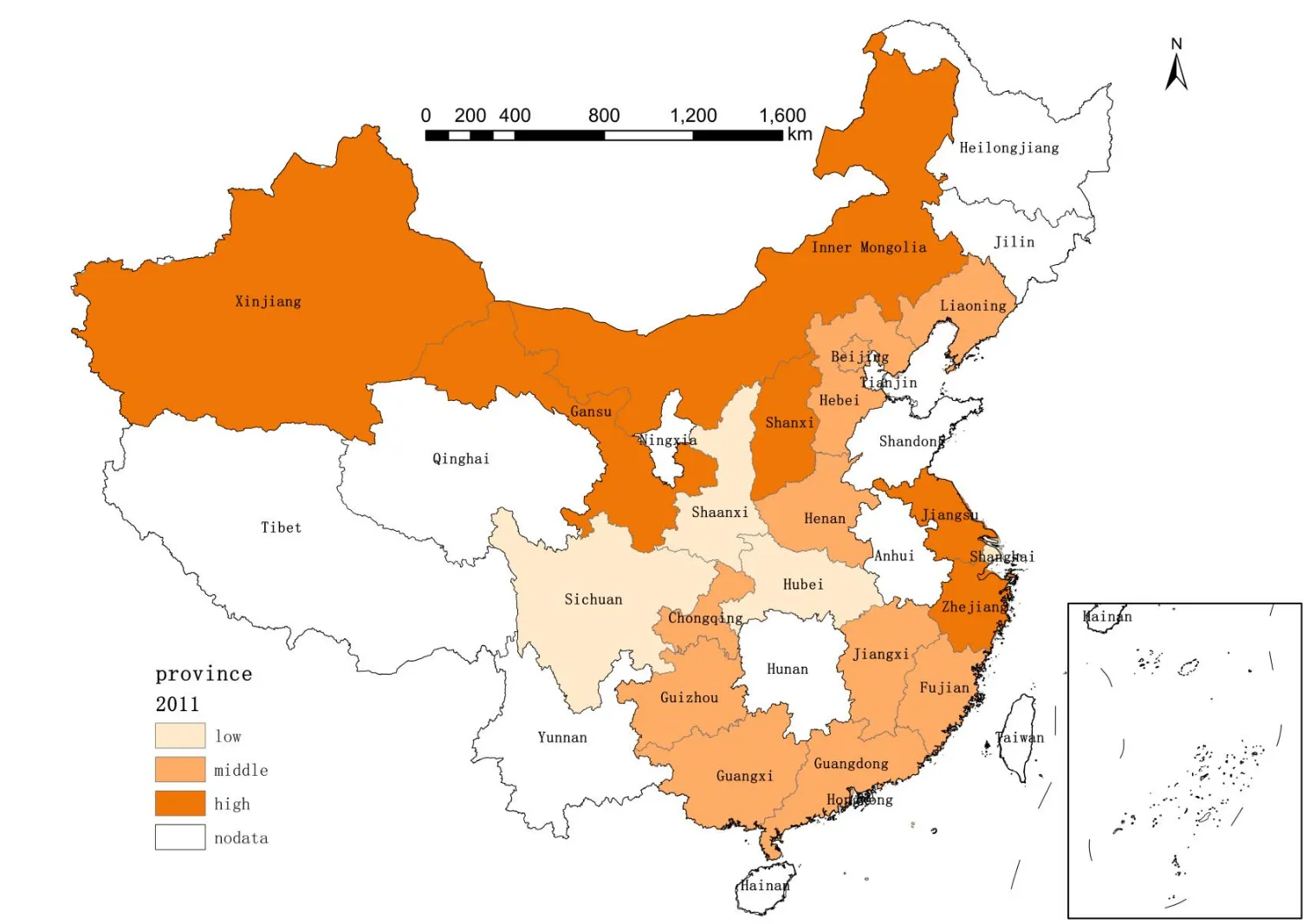
19 April 2024Can Digital Village Construction Reduce Rural Income Disparity?—Empirical Analysis Based on Inter-provincial Panel Data in China
Cutting the income disparity within rural areas is one of the key priorities in seeking common prosperity in China. Based on the panel data of 20 provinces in China from 2011 to 2020, we empirically analyze the impact of digital village construction on rural income disparity by building a digital village construction level indicator system which represents three dimensions of digitalization in rural areas, i.e., digitalization of rural infrastructure, digitalization of agricultural development and digitalization of rural residents’ life. Overall, the level of digital village construction in rural China has shown a development trend of gradual improvement, while the development level in various regions is unbalanced and varies greatly. The results of the fixed-effect model show that, digital village construction can significantly reduce the income disparity in rural areas, whereas the effect is significant in eastern China, insignificant in central and western China. It is recommended to increase the investment in funds and talents and take full consideration and advantage of local conditions, while promoting the development of new rural digital economy, so to achieve the development goal of common prosperity of rural residents.