Found 301 results
Open Access
Article
10 July 2024Documenting the Changing Floodplain of Nileas Basin in North Euboea (Greece) before and after Storms Daniel and Elias
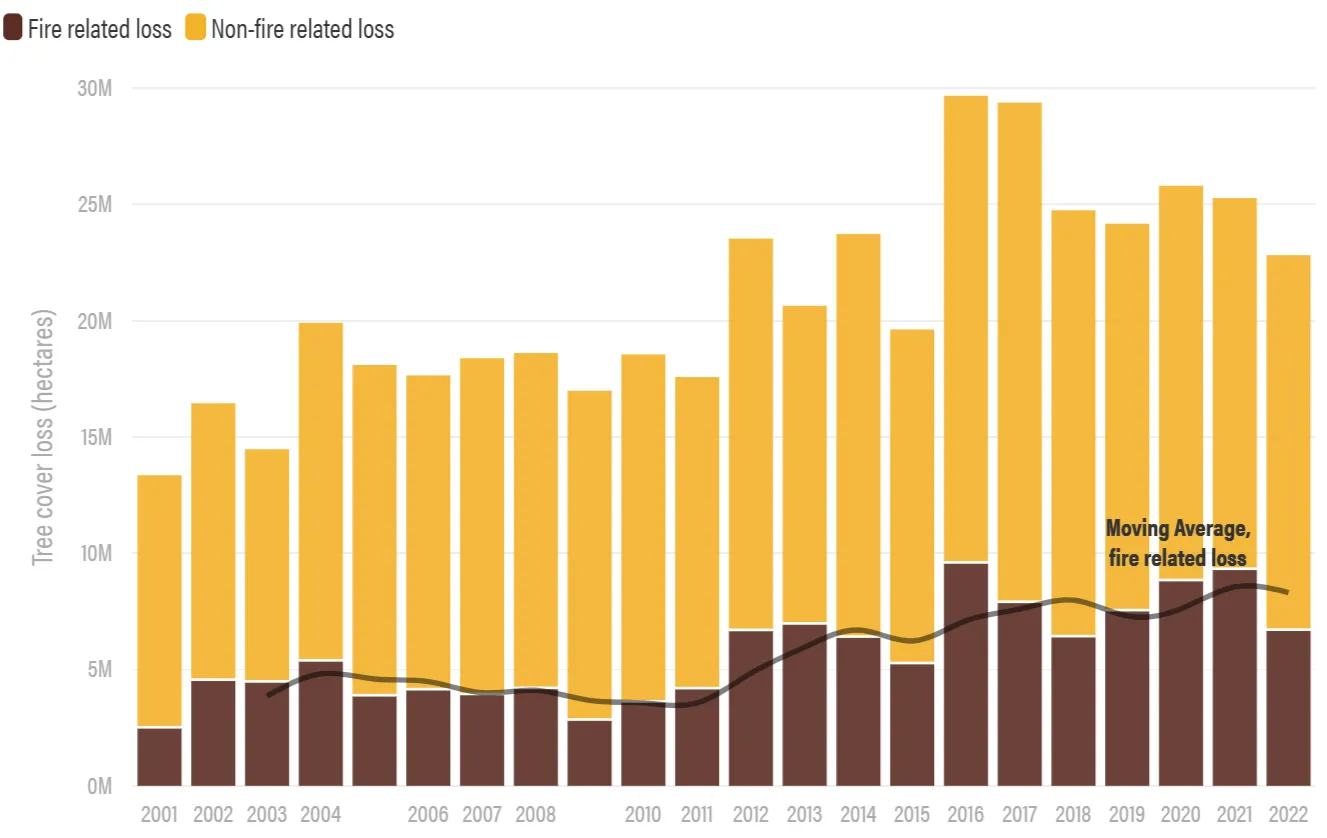
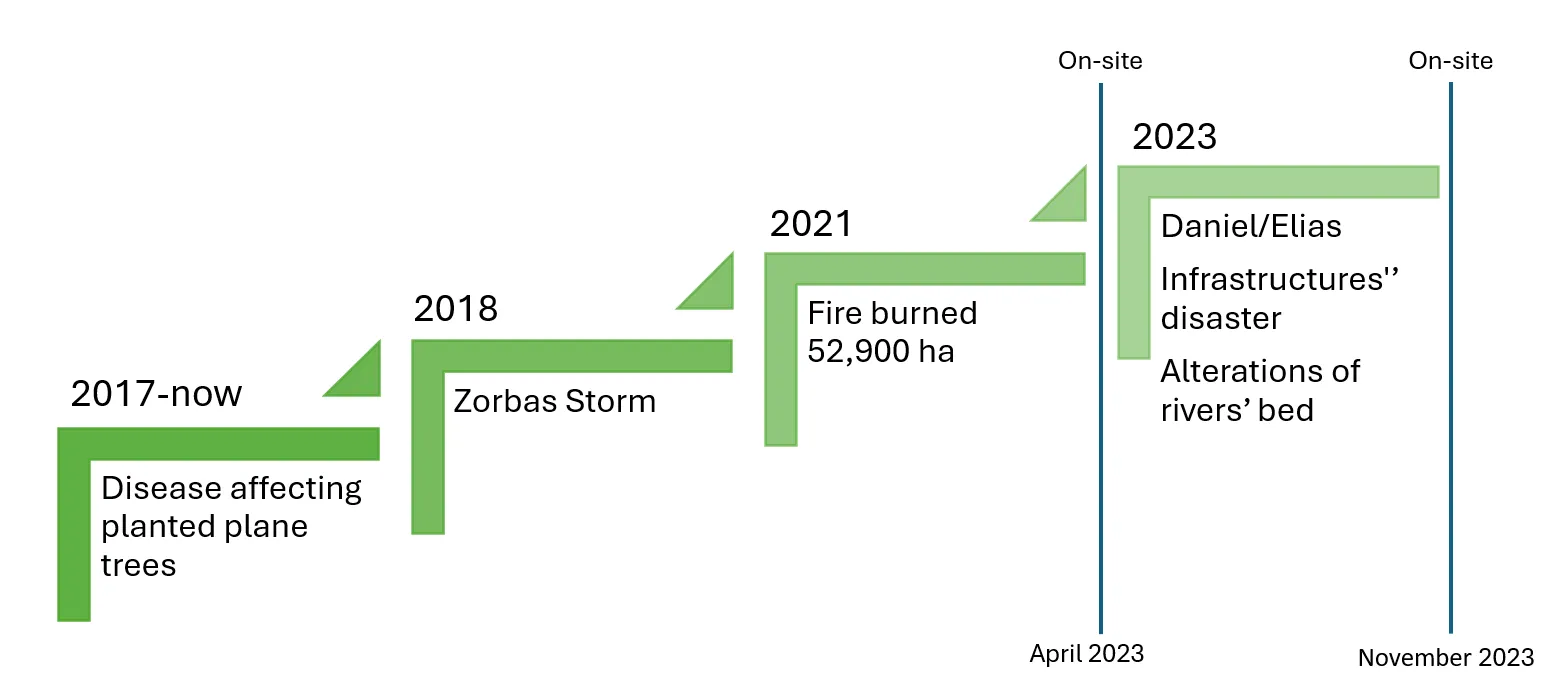
The area of north Euboea is characterized by its intense relief, dense hydrographic network, and rich flora and fauna. In the mid-2010s, the region was struck by a plane tree disease that withered the large population of plane trees in the area, while in 2021, a large wildfire completely burned the forest. These unfortunate events depleted the landscape’s natural ability to manage and mitigate flood phenomena. Observing the landscape’s vulnerability to floods, in April 2023, we conduct on-site field inspections in the rivers of the area. In September 2023, a major flood hit the area, causing in dramatic changes to the landscape. Therefore, in November 2023, we conducted follow-up on-site field inspections in the area, in order to trace the differences, present the damages the phenomenon left behind. These inspections allowed to document the landscape changes from the combination of all previous events and identify any associated pathologies. Site visits and comparisons before and after the Daniel/Elias storm revealed dramatic changes in the riverbed width at lower altitudes, significant sediment accumulation in the Voudouros River delta, alterations in the natural landscape along the river and its floodplain, destruction of the arable land, and road collapses in several locations.
Open Access
Book Review
09 July 2024
Open Access
Article
02 July 2024Early Risk Indicators for DSM-IV Diagnoses in Adolescents and Young Adults with Intellectual Disabilities
To identify risk indicators at ages 6–18 years that are associated with DSM-IV diagnoses in adolescents and young adults with intellectual disabilities five years later. To assess the potential health gain and efficiency of preventive interventions targeting these risk indicators. Parents reported on potential child, parental, and environmental risk indicators. Five years later, parents were interviewed using a standardised psychiatric interview schedule (DISC-IV) to assess DSM-IV diagnoses in children with ID (N = 614) at the age of 11 to 24 years. Logistic regression and linear probability models were used to test the contribution of risk indicators to the prediction of DSM-IV diagnoses. Deviant levels of internalising and externalising problems, inadequate adaptive behaviour, and parental psychopathology predicted psychiatric disorder. Children/adolescents exposed to multiple risk indicators were at greater risk of developing DSM-IV disorders. Strategies aiming for the risk reduction of psychiatric disorders in children/adolescents with ID should focus on intervening at an early age, improving psychopathology and adaptive behaviour skills of the children/adolescents, and supporting their parents.

Open Access
Article
28 June 2024Shifting Prospects: Views and Strategies for Transforming Livestock and Meat Value Chains in a Dynamic Location
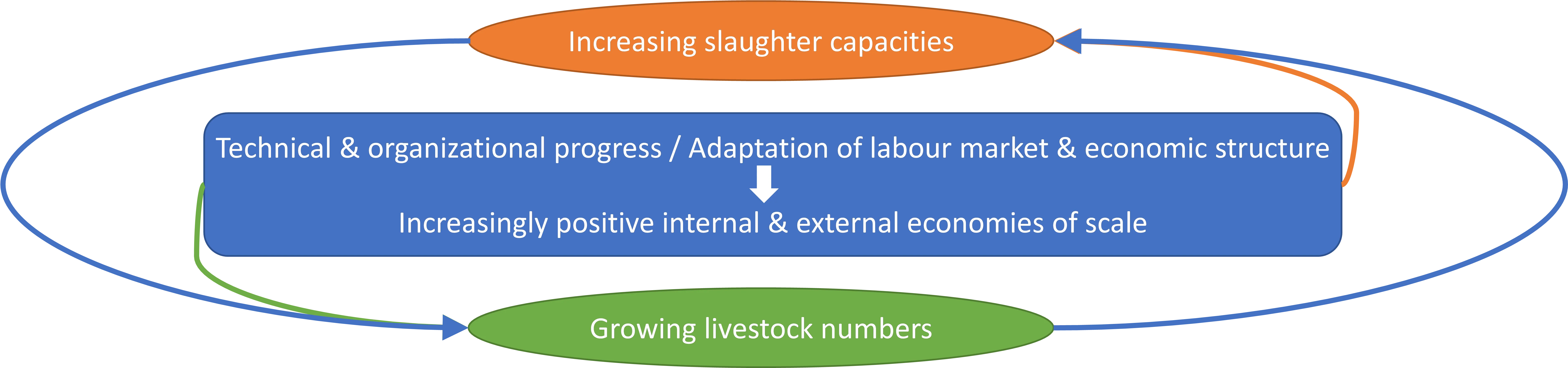
Rural areas characterized by resource-dependent industries often experience growth but also lock-in and transformation pressures. We ask what strategies industries and businesses pursue that successfully exploit the transformative potential of such a location and what prevents other industries and businesses from doing the same. Based on interviews with stakeholders and experts from the livestock and meat sector in a highly specialized location, we explore the will, resources, and capabilities of industries and actors to transform their businesses and entire value chains in ways that can stabilize the local growth regime. The analysis is based on a conceptual framework derived from resource-based and dynamic capability theories at the micro level and the concept of Strategic Action Fields (SAFs) at the meso level. The results suggest that incumbents from the old industrial core tend to counteract the transformation of the SAF with conservative strategies. Challengers from former support activities, in contrast, want to move away from cost competition towards new markets. Their product variation and horizontal diversification can exploit favorable cluster characteristics to develop future-proof capabilities. This should be encouraged, along with new entrepreneurial activity, even if the region is then no longer hosting the core industries of the transformed field.
Open Access
Opinion
26 June 2024Prospective Approaches for Ecosystem Sustainability Including Climate Mitigation
A summary, based upon foresight, futures, ideation and frontier technology studies of prospective approaches to foster ecosystem sustainability including climate mitigation at the technology and societal levels which are at scale and profitable. Approaches summarized include halophytes/salt plants grown on deserts/wastelands using saline/seawater, to address land, water, food, energy and climate, frontier energetics, nascent climate mitigation concepts, cellular agriculture, materials optimization, the virtual age, efficiency and redesigning the ecosystem for the Anthropocene. Solution/mitigation approaches are targeted at deforestation, desertification, pollution writ large (land, sea, air, space), and extensive urbanization along with soil salination, ocean acidification, mining, and water scarcity.

Open Access
Perspective
24 June 2024High Entropy Oxides: Next-Generation Air Electrodes for Reversible Protonic Solid Oxide Cells
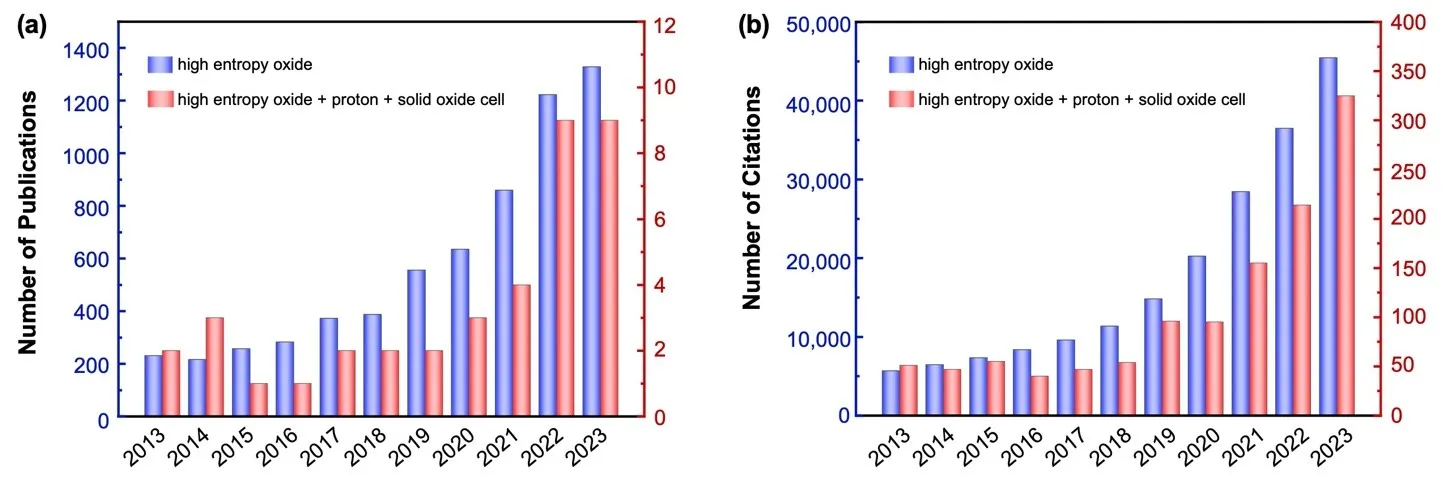
Reversible protonic solid oxide cell (P-SOC) operating at intermediate-temperature exhibits excellent potential as a power generation and green hydrogen production device in fuel cell and electrolysis cell modes because of the high conversion efficiency. However, the lack of efficient air electrodes is the main challenge to obtain P-SOC with remarkable performance. Typically, air electrodes should possess high proton, oxygen ion and electron conductivity, outstanding catalytic ability for oxygen reduction reaction and H2O splitting, and also long-term durability. Recently, high entropy oxides (HEO) have become popular due to their various potential applications in terms of outstanding properties, including catalysis ability, conductivity, thermal stability, etc. HEO air electrodes have been confirmed to show good electrochemical performance in P-SOC, but the complex compositions and structure make it difficult to study HEO by traditional experimental methods. Machine learning (ML) has been regarded as a powerful tool in materials research and can solve the drawbacks in the discovery of HEO in a traditional way. In this perspective, we not only discuss the current utilization of HEO in P-SOC but also provide a possible process to use ML to guide the development of HEO.
Open Access
Commentary
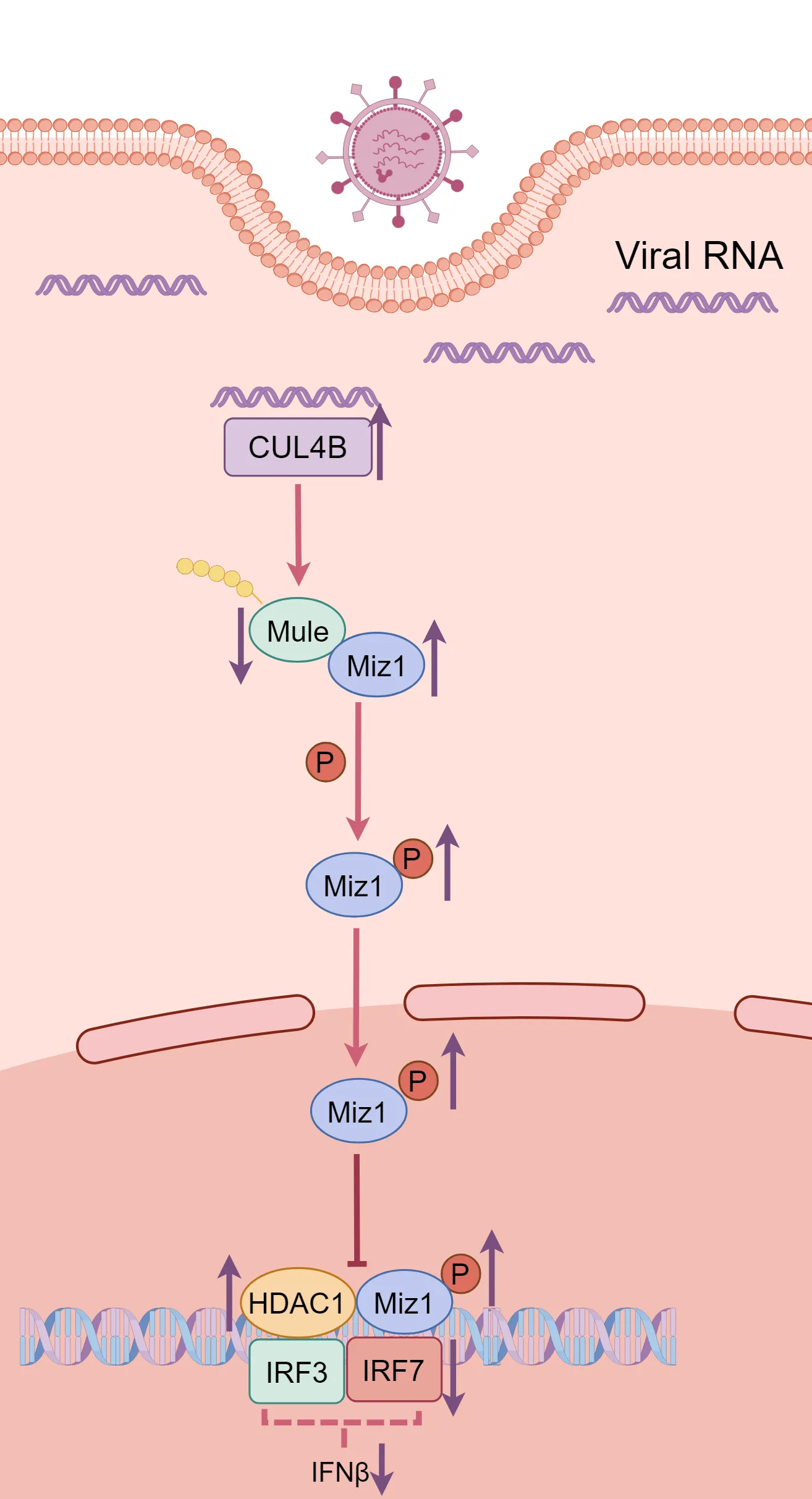
17 June 2024Unraveling Novel Strategies: Targeting Miz1 for Degradation to Enhance Antiviral Defense against Influenza A Virus
The ubiquitin system has been shown to play an important role in regulation of immune responses during viral infection. In a recent article published in Science Signaling, Wu and colleagues revealed that transcriptional factor Miz1 plays a pro-viral role in influenza A virus (IAV) infection by suppressing type I interferons (IFNs) production through recruiting HDAC1 to ifnb1 promoter. They show that a series of E3 ligases combinatorially regulates Miz1 ubiquitination and degradation and modulates IFNs production and viral replication.
Open Access
Review
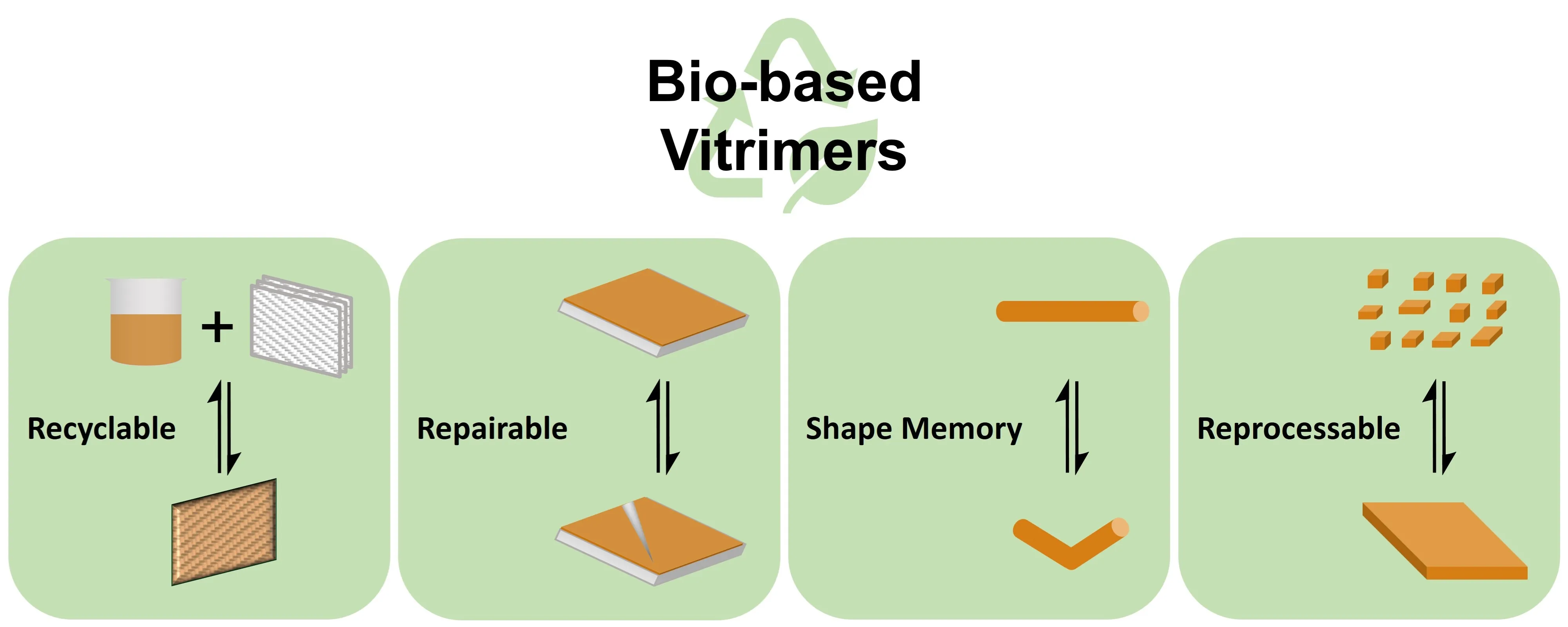
14 June 2024Biobased Vitrimers: A Sustainable Future
Vitrimers are crosslinked polymers containing dynamic covalent linkages. Because of their crosslinked structure, they are stable as thermosets at their service temperatures. At high enough temperatures, dynamic exchange reactions occur and rearrange the polymer network, thus vitrimers become malleable and reprocessable like thermoplastics. The dynamic covalent bonds can also undergo dissociative cleavage reactions under specific conditions, so vitrimers are inherently degradable. To achieve a sustainable future, various biomass resources have been used as raw materials in vitrimer preparation. This review summarizes recent developments in biobased vitrimers and highlights their preparation methods. The limitations of current biobased vitrimers are also discussed.
Open Access
Article
13 June 2024Optimizing Performance and Design Simulation of a 100 KW Single Rotor Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine
As wind energy becomes increasingly vital in global energy strategies, optimizing wind turbine design is essential. This research focuses on the development of a 100 kW single rotor horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT) tailored to meet the energy needs of Jamshoro, Pakistan. The turbine design leverages SolidWorks for structural modeling and is validated through comprehensive simulations using ANSYS and Q-Blade. Operating at an optimal wind speed of 6.9 m/s, the turbine achieves maximum efficiency, as indicated by the highest power factor. This efficiency translates to an estimated power output of approximately 100 kW, suitable for common household consumption. The study integrates regional climatic data and wind conditions to enhance turbine performance and durability. The findings offer a sustainable energy solution for Jamshoro, contributing to Pakistan’s renewable energy infrastructure and addressing local energy demands effectively. The focus of this study will be Jamshoro, a region in Pakistan as a case study. The software simulations will consider a variety of elements, including as wind speeds, variable loads, and environmental factors unique to the chosen region (Jamshoro). This research proposes a sustainable solution for addressing the energy demands in Jamshoro by integrating accurate data based on software analysis with real-world concerns, adding to the larger goal of developing sustainable sources of energy in Pakistan.
Open Access
Article
05 June 2024An Architecture for Early Wildfire Detection and Spread Estimation Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, Base Stations, and Space Assets
This paper presents, an autonomous and scalable monitoring system for early detection and spread estimation of wildfires by leveraging low-cost UAVs, satellite data and ground sensors. An array of ground sensors, such as fixed towers equipped with infrared cameras and IoT sensors strategically placed in areas with a high probability of wildfire, will work in tandem with the space domain as well as the air domain to generate an accurate and comprehensive flow of information. This system-of-systems approach aims to take advantage of the key benefits across all systems while ensuring seamless cooperation. Having scalability and effectiveness in mind, the system is designed to work with low-cost COTS UAVs that leverage infrared and RGB sensors which will act as the primary situational awareness generator on demand. AI task allocation algorithms and swarming-oriented area coverage methods are at the heart of the system, effectively managing the aerial assets High-level mission planning takes place in the GCS, where information from all sensors is gathered and compiled into a user-understandable schema. In addition, the GCS issues warnings for events such as the detection of fire and hardware failures, live video feed and lower-level control of the swarm and IoT sensors when requested. By performing intelligent sensor fusion, this solution will offer unparalleled reaction times to wildfires while also being resilient and reconfigurable should any hardware failures arise by incorporating state of the art swarming capabilities.