Found 15 results
Open Access
Article
29 August 2024Incentive for Ecosystem Services: Governance and Policy Coherence in Nepal
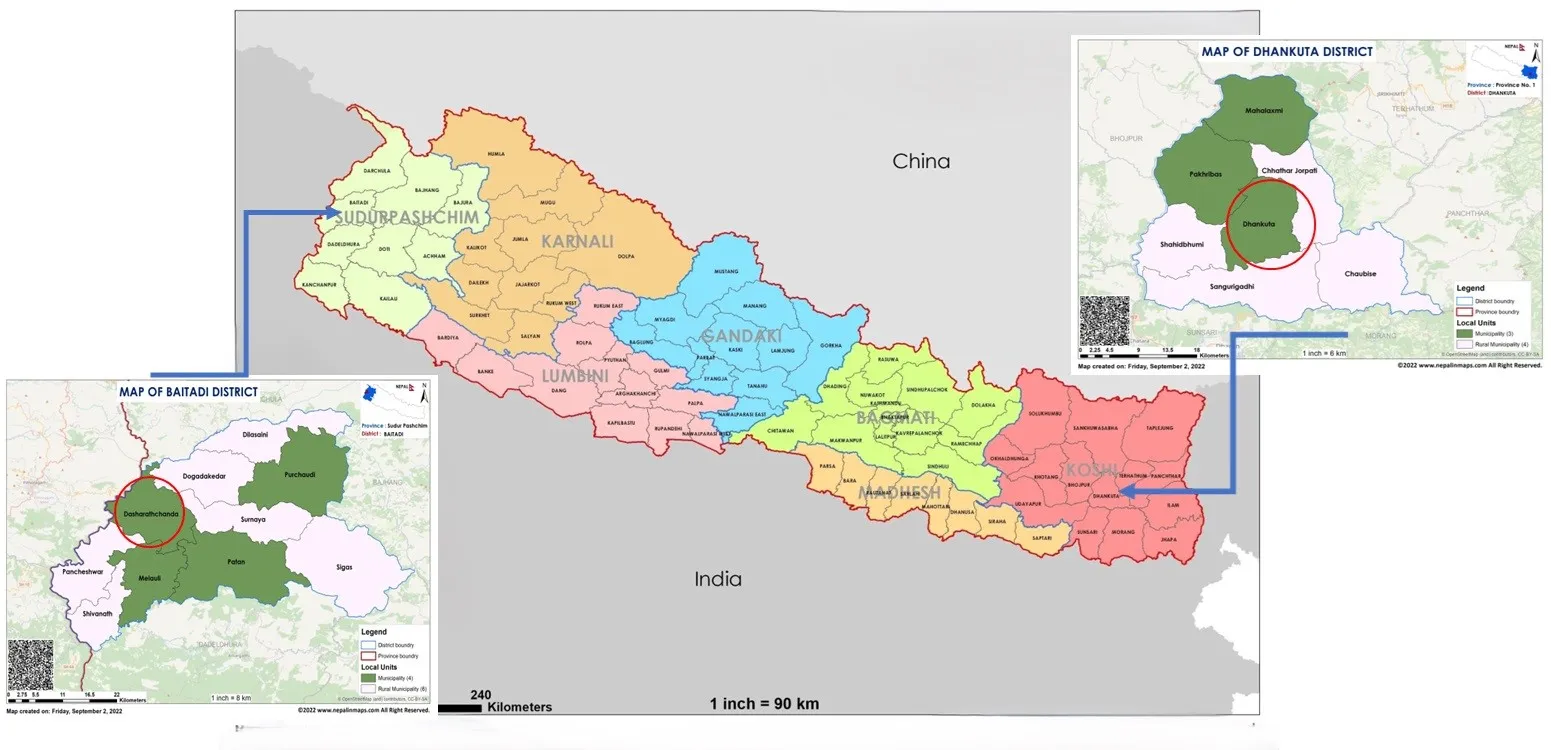
This research highlights the governance of landscape and policy coherence to ensure a sustainable supply of ecosystem services through incentives for ecosystem schemes at the municipal level in Nepal. The study was carried out in Dhankuta and Dasarath Chand municipalities representing Nepal’s Koshi and Sudur Paschim provinces. Six aggregate governance indicators adopted by the World Bank Group were assessed through interviews with primary stakeholders of selected landscapes in two municipalities, followed by Key Informant Interviews. The study indicates that implementation of the Incentive for Ecosystem service scheme is feasible, creating multi-stakeholder institutions at the local level. However, there are several governance challenges to ensure its success. In particular, incentives for ecosystem schemes must be part of local government planning, where multisectoral coordination and collaboration are essential. While municipal authorities have constitutional jurisdictions to initiate such schemes, they lack the human resources to understand ecosystem management for a sustainable supply of ecosystem services. Therefore, landscape governance is essential to make incentive schemes successful and ensure transparency and equitable benefits among ecosystem service providers.
Open Access
Opinion
22 August 2024Medical Drones for Public Health Emergency Preparedness, Response, and Resilience: Delivering Health for All
Amid a global metacrisis of health, environmental and economic challenges, medical delivery drones (or uncrewed aerial vehicles) offer a promising method to prepare for, and rapidly respond, to future emergencies. This opinion article summarizes the current medical delivery drone landscape, evidence base, and policy implications in the context of public health emergencies, such as pandemics, natural disasters, and humanitarian crises, with a particular emphasis on the region of sub-Saharan Africa. Using a multilateral, international health policy perspective, key challenges and opportunities, such as the development of sustainable funding mechanisms, robust regulatory frameworks, and capacity building, are identified.

Open Access
Article
22 March 2024Community Sport, Australian Sport Policy and Advocacy: A Qualitative Study of Stakeholder Perspectives
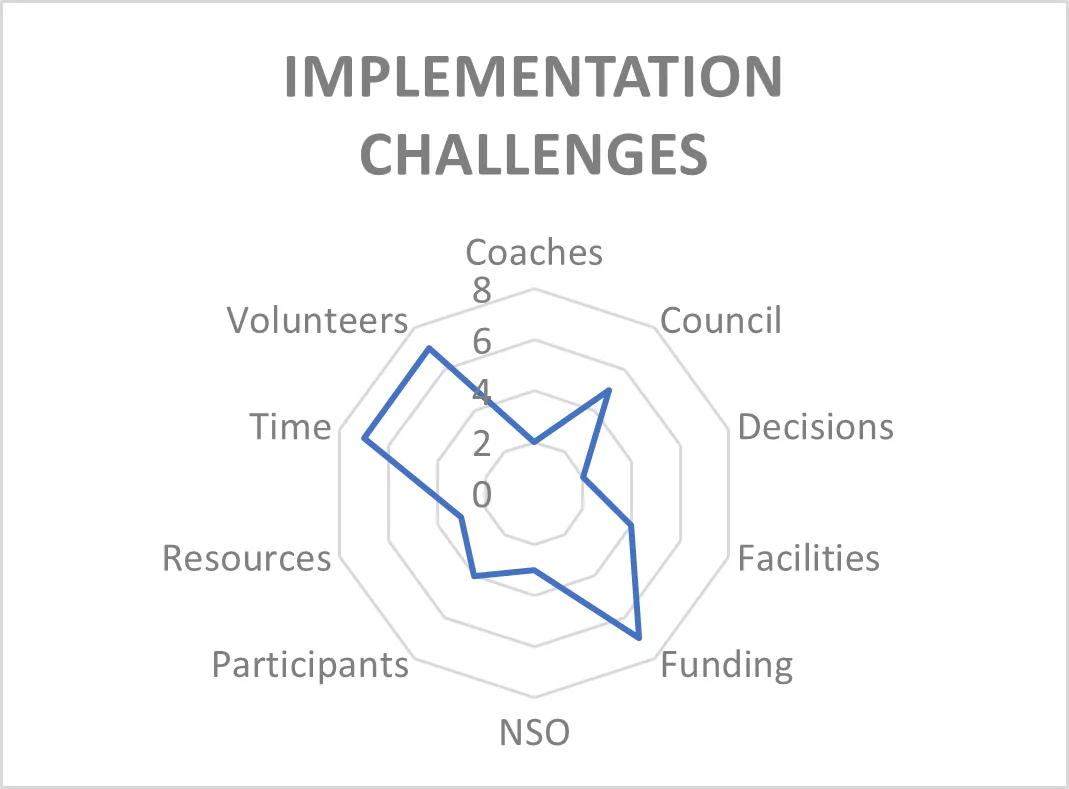
This article explored aspects of the community sport policy process in rural New South Wales, Australia, focusing on the views of community sport club (CSC) officials relating to policy matters. Community sport represents a complicated policy arena, and rural communities face a level of disparity compared with better-resourced urban CSCs, particularly concerning policy implementation and advocacy issues. Officials at CSCs from ten different sports (n = 10) in a rural setting participated in semi-structured interviews to pinpoint themes common in the community sport policy process. Further, the research identified aspects of the connections that impact CSCs, including those with government and National Sporting Organisations (NSOs). To highlight the beliefs and attitudes of the CSC officials, the interviews had two key thematic foci—implementation and advocacy—and the findings highlighted sub-themes relating to the fundamental interests of CSCs. Overall, the research accentuated the hierarchical nature—a power imbalance—of sport policy processes, the potential for CSCs to have a bottom-up role in policy creation, and the consideration of a policy analysis and evaluation structure such as the Advocacy Coalition Framework. Finally, the outcome points to enthusiasm for strengthening community sport by giving CSCs a voice through localized advocacy.
Open Access
Article
18 February 2024The Sustainable Development Concept in the Polish Legal Space from a Legal-Dogmatic Perspective
The sustainable development concept is of crucial importance for the socioeconomic development processes, not only at the international community level, but also—or, perhaps, particularly—at the national or even local levels. The aim of the article is to demonstrate, from a legal-dogmatic perspective, the place, role and significance of the sustainable development concept in the Polish legal space. This perspective applies to both the state policy intended to formulate a strategy which provides a basis for law-making processes and to find normative solutions making it possible to reconcile legally protected values which sometimes compete with one another, with account taken of the needs of future generations. The sustainable development concept has been very broadly followed in Poland not only in the legal doctrine, but also in the doctrine of economic and social sciences. This term has turned out to be such an effective political catchword that it has been commonly abused and, therefore, it has lost a good deal of its social importance; this makes it substantially more difficult to apply a normative approach to the issues related to the implementation of the concept in legislative practice. In the Polish legal space, the sustainable development concept has become the leading theme of many documents and legal acts, particularly those concerned with environmental protection, but also, although to a much more modest extent, those addressing the issues of socioeconomic development.

Open Access
Editorial
06 September 2022