Found 2 results
Article
21 February 2025Porous Cu(Mn)-Doped ZnO-MgO Nanocomposites for Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Applications
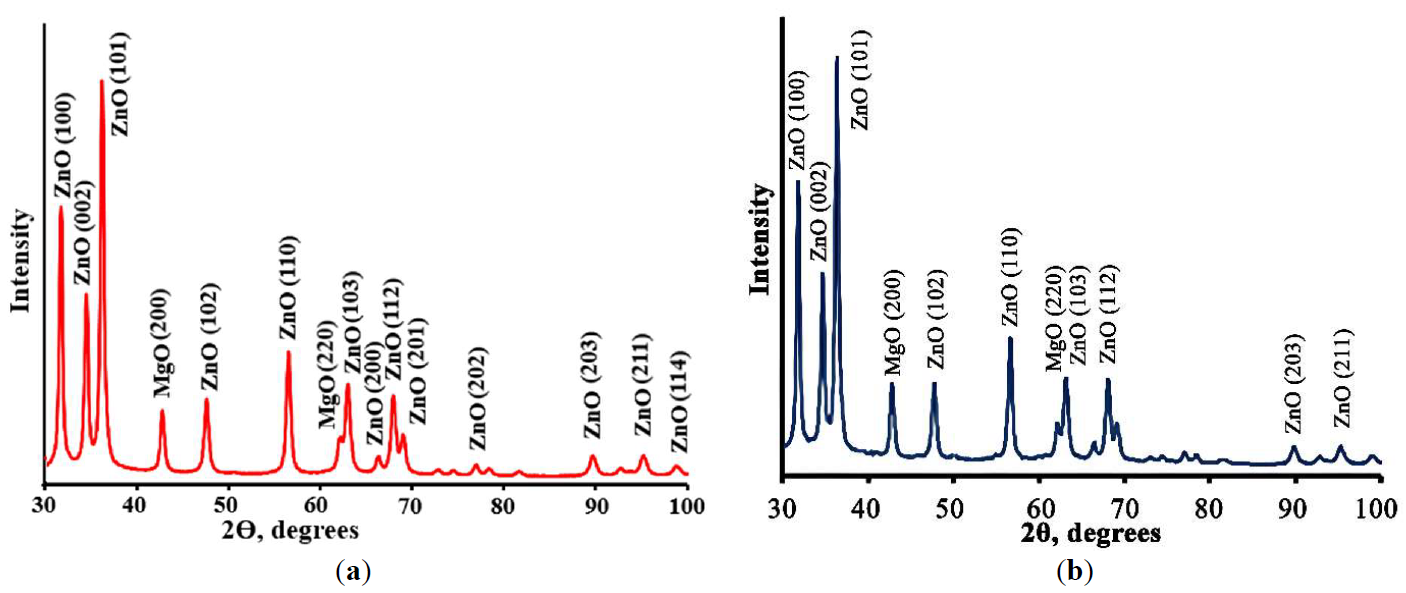
Porous Cu(Mn):ZnO-MgO composites synthesized by polymeric sol-gel method were characterized. The crystal structure, morphology, spectral properties, the ability of the photogeneration of chemically active singlet oxygen under external visible irradiation, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties of porous composites were studied. Obtained composites consist of small ZnO and MgO crystals having size less than 20 nm. It was found that Cu2+ and Mn2+ ions are embedded into the lattices of ZnO and MgO crystals, altering their crystal cell parameters. The band gap values of obtained composites are 3.41 ÷ 3.42 eV which are slightly higher than the band gap of pure ZnO. Prepared materials demonstrate a high ability of photogeneration of chemically active singlet oxygen under blue light (λ = 405 nm) irradiation. It was found that dependencies of the intensity of singlet oxygen photogeneration from the power density of visible irradiation are linear. Photocatalytic decomposition of the diazo dye Chicago Sky Blue in solutions under UV and blue light irradiation proceeds rapidly in the presence of the prepared composites (constants rate of photocatalytic dye decomposition under UV irradiation are 0.024 min−1 and 0.025 min−1 for ZnO-MgO composites doped with Cu and Mn, correspondingly). Porous composites demonstrate superior antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria. These materials are promising for practical application in medicine and photocatalytic technologies of air and water cleaning.
Article
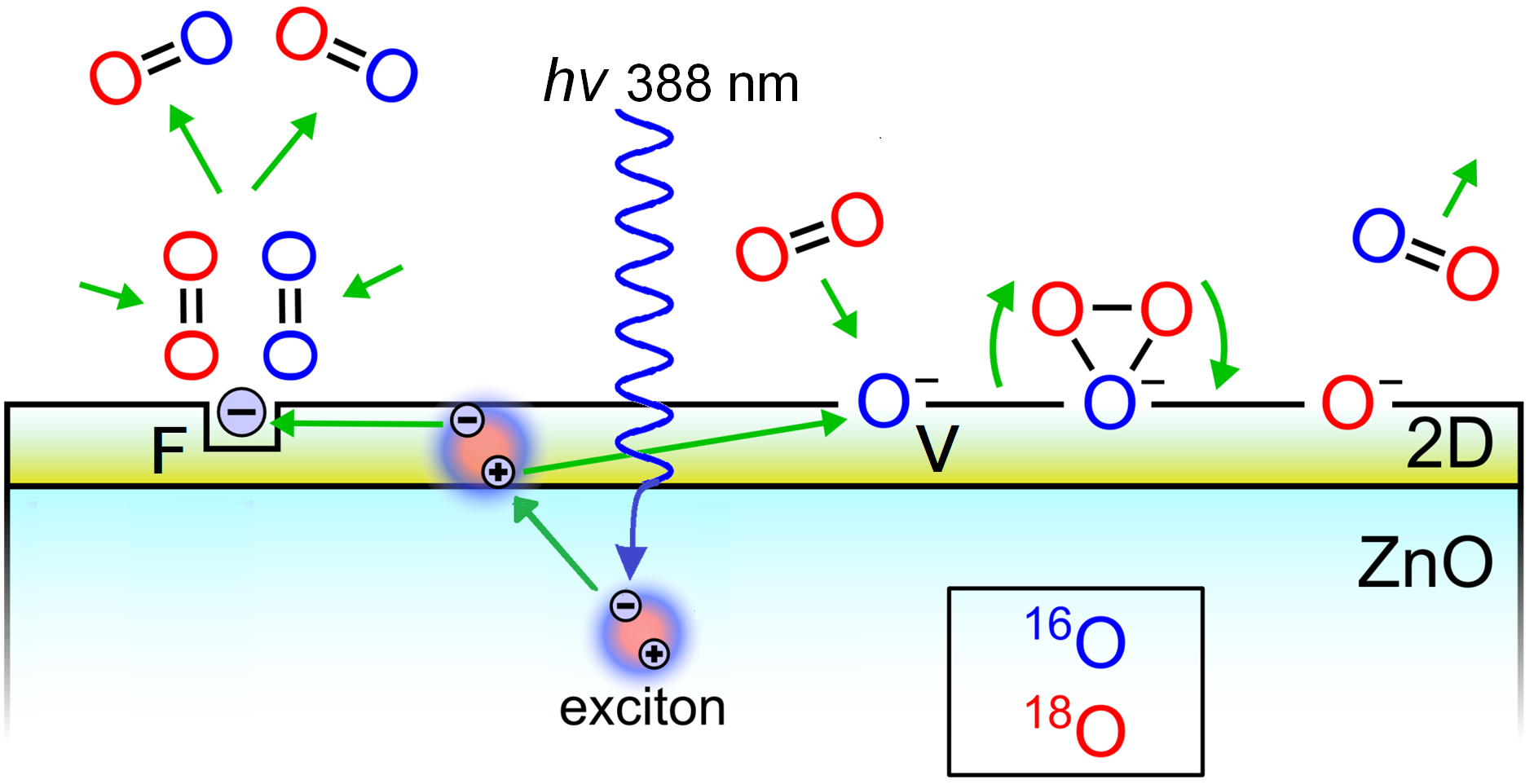
31 August 2023Potential Role of Exciton in Photocatalysis
This article commemorates the outstanding Russian scientists E.F. Gross and A.N. Terenin. It revisits their successors’ efforts to develop Terenin’s idea of using excitons, discovered by Gross, for photocatalytic redox reactions on wide-gap semiconductors. Terenin proposed ZnO as the subject of study. To explore the possibility of replacing photogenerated electrons and holes in a redox reaction by an exciton being a quasi-neutral particle, the test reaction of the photoactivated oxygen isotope exchange (POIE) was studied. It was found that many years of initial unsuccessful attempts were due to the fact that the exciton energy is spent on luminescence. In our experiments, the excitons decayed non-radiatively, and the long-lived electron-donor F-type and hole V-type active centers were formed by creating the 2D surface nanostructure ZnO/ZnO1−x/O−. These centers allowed to obtain the reaction efficiency 5–8 times higher than with the interband transitions. Thus, the developed 2D surface nanostructure ZnO/ZnO1−x/O− resolved the problem of using an exciton in photocatalysis and demonstrated the perspective of this nanostructure as an efficient photocatalyst.