Found 2 results
Article
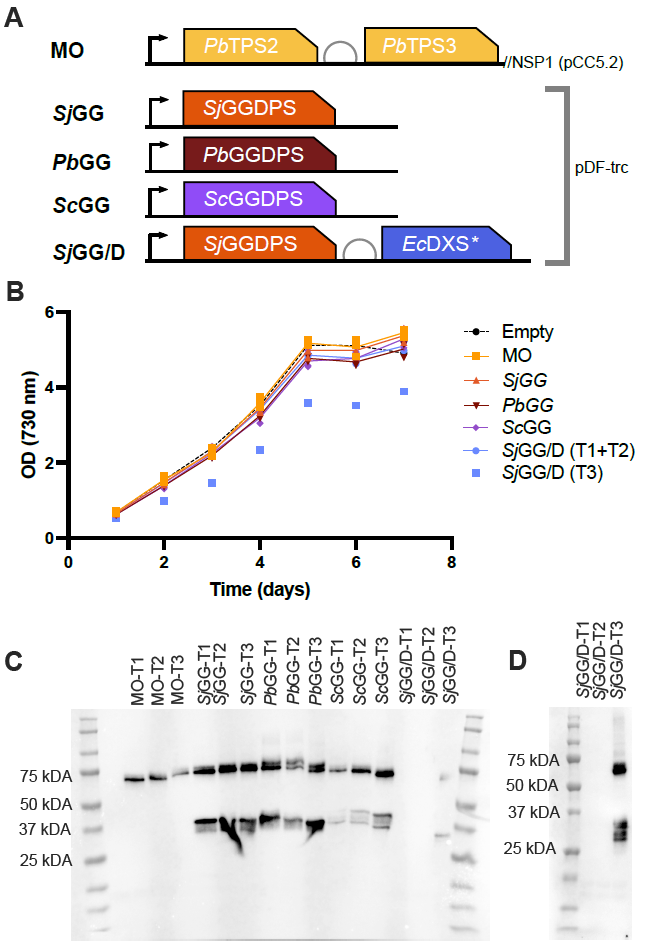
22 March 2024Modulation of the MEP Pathway for Overproduction of 13-R-manoyl Oxide in Cyanobacteria
The cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 has gained scientific interest for its potential to use solar energy and atmospheric CO2 for the production of high-value chemicals like pharmaceuticals, flavors, and fragrances. Forskolin is a diterpenoid found in the root cork of the plant Plectranthus barbatus and its biosynthetic pathway is initiated by two terpene synthases that convert geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGDP) into the precursor 13-R-manoyl oxide (13-R-MO). Using the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 as host, we expressed the two terpene synthases resulting in the synthesis of 0.83 mg/L 13-R-MO. Three different geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthases (GGDPSs) were selected for screening; a prokaryotic (Synechococcus sp. JA-3-3Ab (Sj)), a yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc)), and a plant (P. barbatus (Pb)) derived GGDPS. Strains containing the prokaryotic Sj- or the yeast ScGGDPS consistently yielded more 13-R-MO than the base strain. By overexpression of 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (DXS) positioned at the entry of the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway (MEP) together with the prokaryotic SjGGDPS, the 13-R-MO titer was increased 11-fold to reach 9.7 mg/L by boosting the synthesis of GGDP, the direct substrate for the diterpenoid synthases. We further show that application of a n-dodecane overlay to remove 13-R-MO from the culture medium provided a 2–3 fold increase of the 13-R-MO in a separate cultivation system.
Review
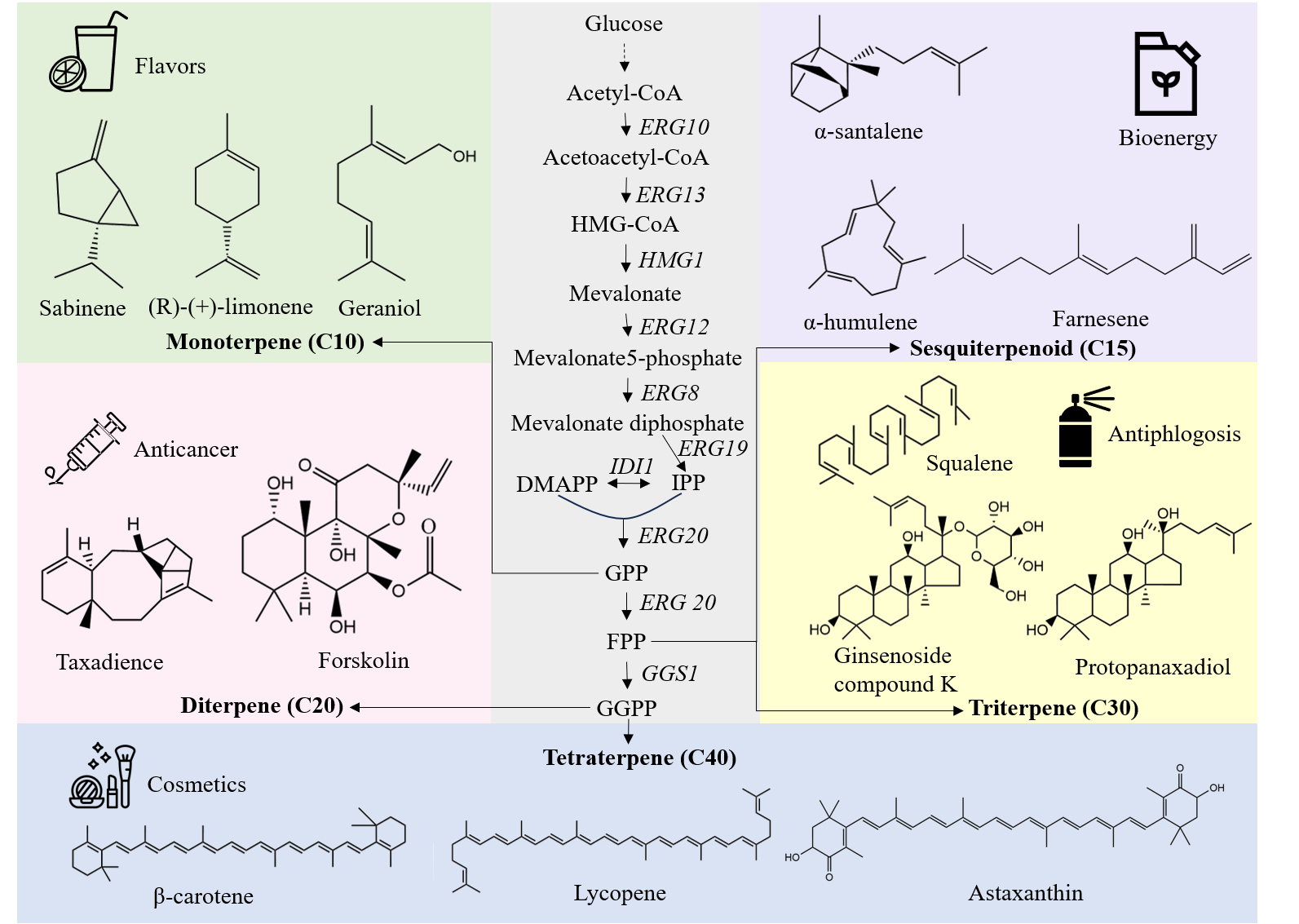
13 February 2024Development and Perspective of Production of Terpenoids in Yeast
Terpenoids are a large class of secondary metabolites known for their remarkable diverse biological activities, making them widely utilized in the pharmaceutical, food, cosmetic, biofuel and agricultural fields. However, the current production of terpenoids heavily relies on plant extraction and chemical synthesis, which brings about concerns regarding infield, environmental and ecological issues. With the advancements in metabolic engineering and emerging synthetic biology tools, it is now possible to sustainably produce these high value-added terpenoids using microbial chassis. Among them, yeast has emerged as a promising candidate for the heterologous biosynthesis of terpenoids due to its inherent advantages, including robustness, safety, and the availability of sufficient precursor. This review focuses on the diverse strategies employed to enable terpenoids production in yeasts. These strategies encompass metabolic engineering approaches to optimize the mevalonate pathway, protein engineering techniques to improve terpenoid biosynthesis, the applications of organelles compartmentalization, high throughput screening and global approaches for the development of efficient cell factories. Furthermore, this review discusses the future prospects and challenges associated with yeast-based terpenoid production, while also emphasizing guidelines for future studies in this field.