Found 3 results
Article
14 April 2025Efficient Extracellular Production of Phospholipase D in Escherichia coli via Genetic and Process Engineering Modification
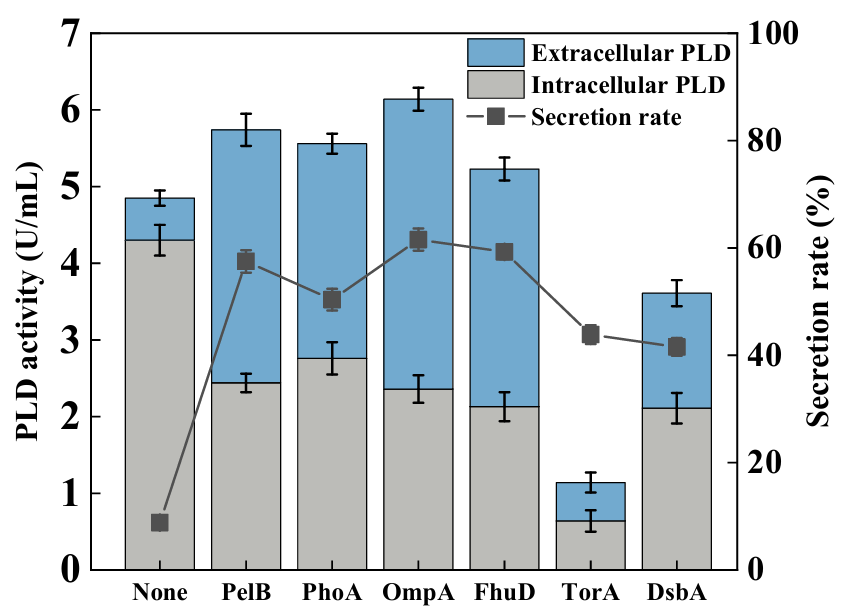
Phospholipase D (PLD) is the key enzyme in the catalytic production of rare phospholipids including phosphatidylserine. It was considered a promising method via genetic manipulation for the heterologous production of PLD in the model chassis. Few works focused on the extracellular production of PLD in engineered microbes. Herein, genetic and process engineering modification strategies were developed to achieve secretory production of PLD in Escherichia coli. The N-terminal fusion secretion signal peptide OmpA and the plasmid pBAD-gⅢC with pBAD promoter were proven to be the most effective in promoting the secretory production of PLD. Given the limitation of the cell membrane, the regulation of the key protein expression in the cell membrane as well as the addition of surfactants, were explored to accelerate the secretory production of PLD further. It was indicated that adding 0.5% (w/v) Triton X-100 was more conducive to producing PLD. Finally, fed-batch fermentation was conducted, and the maximum extracellular PLD activity achieved was 33.25 U/mL, which was the highest level reported so far. Our work demonstrated the effectiveness of genetic and process engineering strategies for the secretory production of PLD in E. coli, which provided an alternative platform for the industrial production of PLD.
Article
19 February 2025The Effect of Polyethylene Glycol on Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared Using Sonochemical Synthesis
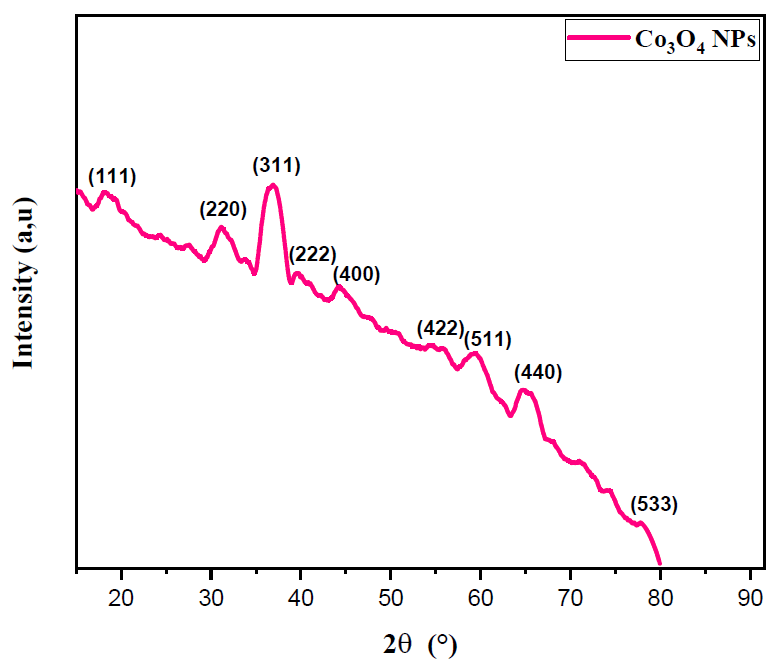
In this work, Cobalt oxide nanoparticles (Co3O4·NPs) were synthesized via a simple sonochemical reaction by using polyethylene glycol (PEG) as a surfactant. Structural, morphological and spectroscopic analysis of obtained powder (Co3O4·NPs) was investigated by X-ray diffraction, FTIR spectroscopy and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The nanocrystalline nature of the sample was confirmed by XRD, which exhibits the cubic face-centered normal spinel structure of (Co3O4·NPs) and the space group of Fd-3m with the average crystallite size around 15 nm. FTIR spectrum shows two strong absorption bands of (Co+2–O) and (Co+3–O) which confirm the spinel structure of Co3O4·NPs. Moreover, SEM micrographs showed that the agglomeration of the nanoparticles was reduced by the addition of (PEG) surfactant and UV-Vis was used to study the synthesized material’s optical properties. The Co3O4 band gap ranged around 2.2 and 3.5 eV.
Article
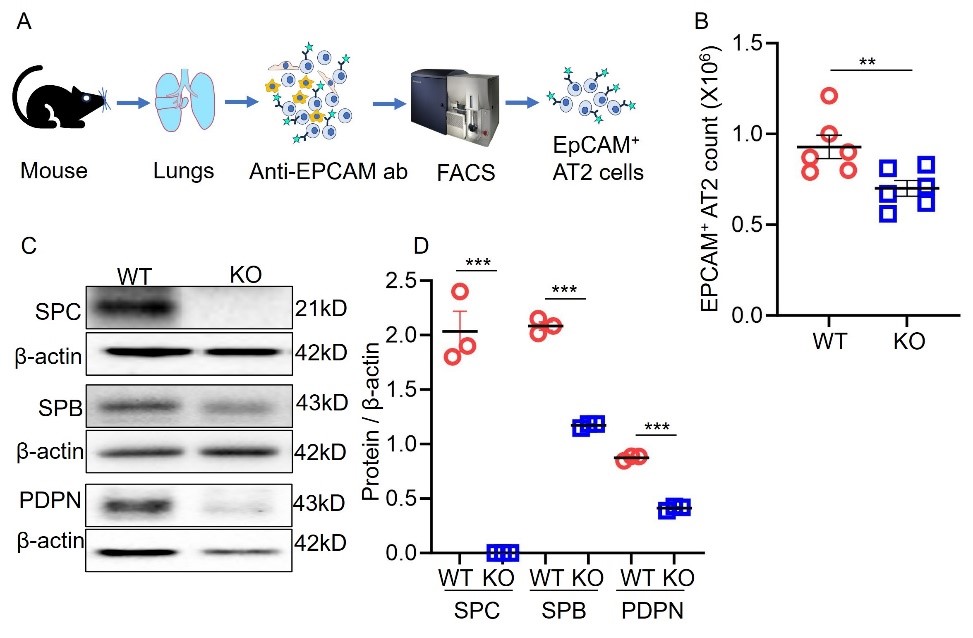
11 October 2024Surfactant Protein-C Regulates Alveolar Type 2 Epithelial Cell Lineages via the CD74 Receptor
Deficiency of surfactant protein-C (SPC) increases susceptibility to lung infections and injury, and suppressed expression of SPC has been associated with the severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Alveolar type 2 epithelial cells (AT2) are critical for maintenance and repair of the lung. However, the role of the SPC in the regulation of AT2 cell lineage and the underlying mechanisms are not completely understood. This study aimed to investigate the mechanisms by which SPC regulates AT2 lineages. Sftpc−/− mice were used to model the SPC deficiency in ARDS patients. We utilized three-dimensional (3D) organoids to compare AT2 lineage characteristics between wild type (WT) and Sftpc−/− mice by analyzing AT2 proliferation, alveolar type 1 cells (AT1) differentiation and CD74 expression, using colony-formation assay, immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, and immunoblots. The results showed that Sftpc−/− mice demonstrated a reduced AT2 cell population. Influenza A virus subtype H1N1 (H1N1) infected Sftpc−/− mice demonstrated reduced AT2 proliferation and AT1 differentiation. Western blot indicated elevated levels of CD74 protein in AT2 cells of Sftpc−/− mice. Colony-forming efficiency was significantly attenuated in AT2 cells isolated from Sftpc−/− mice compared to the WT controls. Podoplanin (PDPN, a marker of AT1 cells) expression and transient cell count significantly increased in Sftpc−/− organoids. Moreover, siRNA-mediated gene silencing of CD74 in AT2 cells significantly increased AT2 proliferation and AT1 differentiation in Sftpc−/− organoids. This study suggests that SPC regulates AT2 lineage in vitro and in vivo. The SPC might influence AT2 lineage during the lung epithelium repair by activating signaling mechanism involving CD74 receptor.