Found 2 results
Open Access
Review
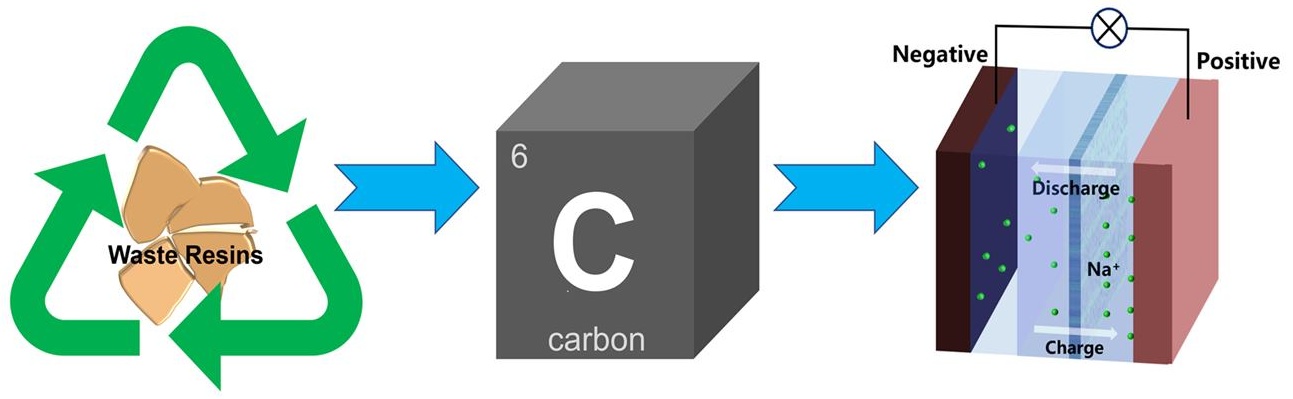
01 November 2024Waste Resin Derived Carbon Materials for Sodium-Ion Batteries
As the environmental issues caused by waste resin become increasingly severe, there is an urgent need to develop ways to handle it in a high-value and harmless manner. Turning waste resin into functional carbon materials is a realizable and promising scheme, which could be a trigger to carry forward emerging sustainable battery technologies and applications. However, there are few review articles about the basics and research progress of the waste resin derived carbon materials for sodium-ion batteries. This review article provides a brief overview mainly about resin recycling and the potential usage of the resultant carbon materials for sodium-ion batteries. Specifically, we show the potential improvements in existing research, focusing on utilization of the waste as well as the significance of new routes for resin recycling. This work offers insights for the design of sustainable carbon materials for battery systems.
Open Access
Review
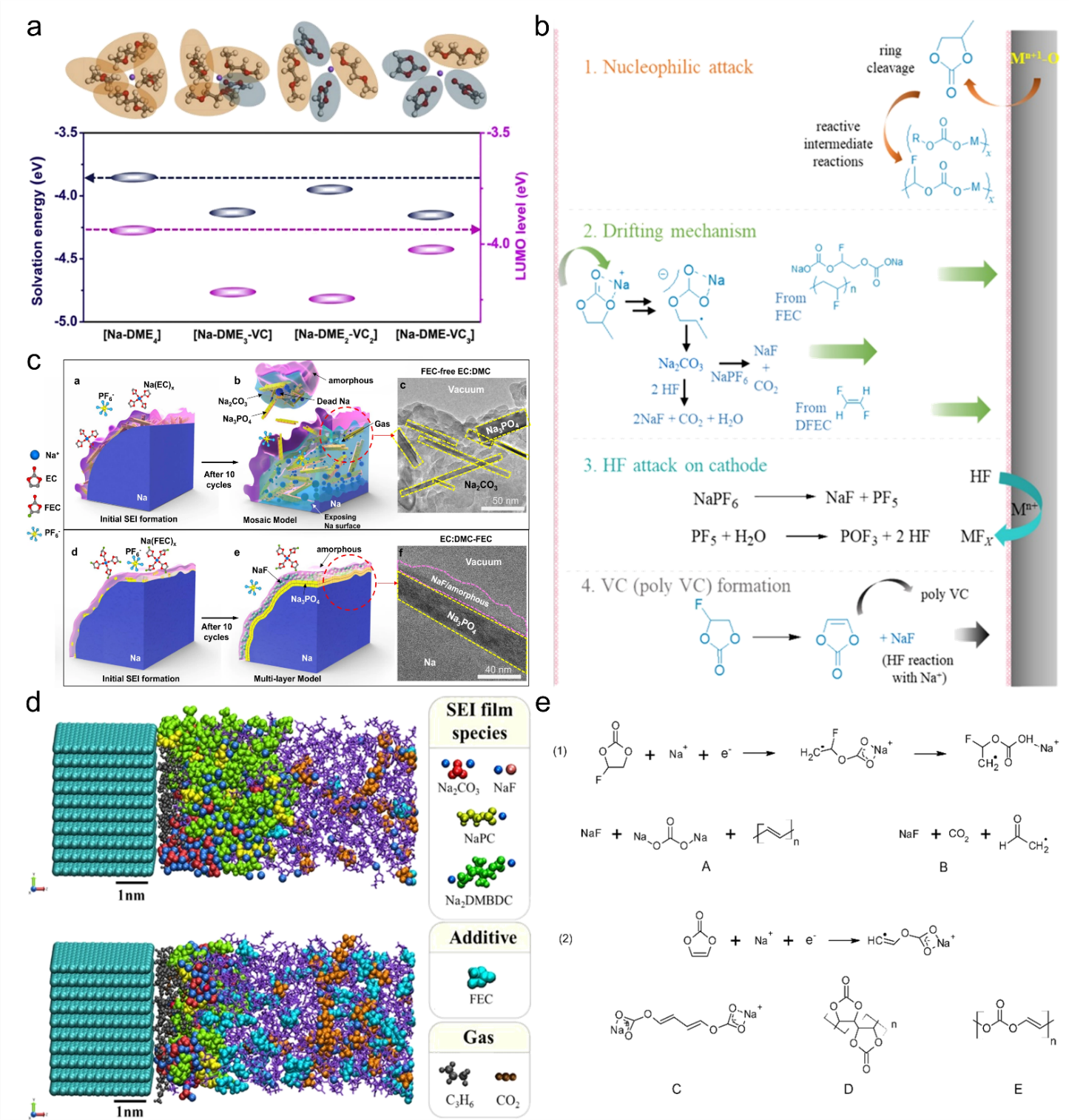
27 March 2024Research Progress on Electrolyte Additives for Sodium Ion Batteries
In view of the gradual depletion of lithium resources, sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) have emerged as a viable alternative to lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). This is primarily attributed to their comparable operational principles and abundant reserves of sodium resources. As an essential component of the secondary battery, the electrolyte is of paramount importance in the functioning of SIBs, and the electrode-electrolyte interface constructed by it affects the battery performance. Adding electrolyte additives in LIBs is a low-cost and efficient method that can enhance the performance of the electrolyte and the interface between the electrode and electrolyte. This method is also applicable to SIBs. Therefore, in this study, we provide a comprehensive overview of various electrolyte additives, including but not limited to carbonate additives, sulfur-containing additives, silicon-containing additives, phosphorus-containing additives and inorganic additives. We extensively analyze the impact of these additives on the electrode-electrolyte interface and the electrochemical performance of SIBs. The purpose of this review is to comprehensively evaluate the current status of electrolyte additives in SIBs, which serves as both a basic overview of the existing situation and a practical guide for selecting suitable additives for practical applications of SIBs.