Found 8 results
Open Access
Article
29 December 2025Vertical Axis Tidal Turbine Behaviour under Sheared Flow Effects
Tidal turbines are often subjected to complex flow conditions that can affect their power output and the risk of failure. In this article, an experimental study on a vertical axis tidal turbine with twin counter-rotating rotors is carried out at 1/20 scale, submitted to a sheared turbulent (ST) flow and a sheared weakly turbulent (SWT) flow. The performance and wake development comparison indicates that the turbine behaves differently depending on the shear rate considered. A 7% decrease in performance is observed at the turbine’s nominal operating point between uniform and ST conditions. The asymmetry of the flow along the vertical axis is reflected in the angular and frequency distributions of the rotor torque, indicating a production asymmetry between the lower and the upper rotors. Analysis of wake development reveals that transport terms constitute the main mechanism of wake dissipation. In the case of SWT and uniform flow, vertical advection largely dominates the other terms, whereas in ST flow, transverse advection is initially predominant. This results in a higher average wake height and a lower average wake width in the ST case compared to the other flow conditions, and a faster wake recovery.
Open Access
Article
15 August 2025Integrating DNA and Chemical Profiling to Trace Illicit Drug Manufacture and Distribution
Illicit drug materials represent a valuable but underutilized source of forensic intelligence. While chemical profiling is routinely used to trace drug composition and origin, the recovery of trace DNA offers the potential to link these substances directly to individuals involved in their manufacture and distribution. This study evaluates the forensic utility of integrating DNA profiling with chemical analysis to improve source attribution across different drug formulations. Pharmaceutical-grade simulants in the form of capsules, tablets, and powders were handled by volunteers under controlled deposition scenarios. DNA was recovered using moistened cotton swabs, extracted via automated silica-based workflows, and analyzed using STR profiling. In parallel, chemical fingerprints were generated through GC-MS and LC-MS, with sample classification based on retention time and mass spectral data. Capsules yielded the highest DNA recovery (median: 310 pg), followed by tablets (230 pg) and powders (18 pg), with single-source STR profiles obtained in over 85% of capsule and tablet cases. Chemical profiling achieved 85% accuracy for capsules, 78% for tablets, and 65% for powders. When integrated, the combined approach significantly outperformed individual methods, achieving classification accuracies of 97% for capsules, 85% for tablets, and 72% for powders (p < 0.01). These findings demonstrate the enhanced evidentiary value of dual profiling, particularly in cases involving degraded or limited DNA. The proposed framework supports a more comprehensive forensic strategy, enabling biological and chemical linkage of drug materials to persons of interest and manufacturing sources. This integrative approach offers critical advantages for law enforcement and prosecution in disrupting drug trafficking networks.
Open Access
Article
28 July 2025Investigating Touch DNA Success Rates in Vehicle Sites for Hit-and-Run Casework
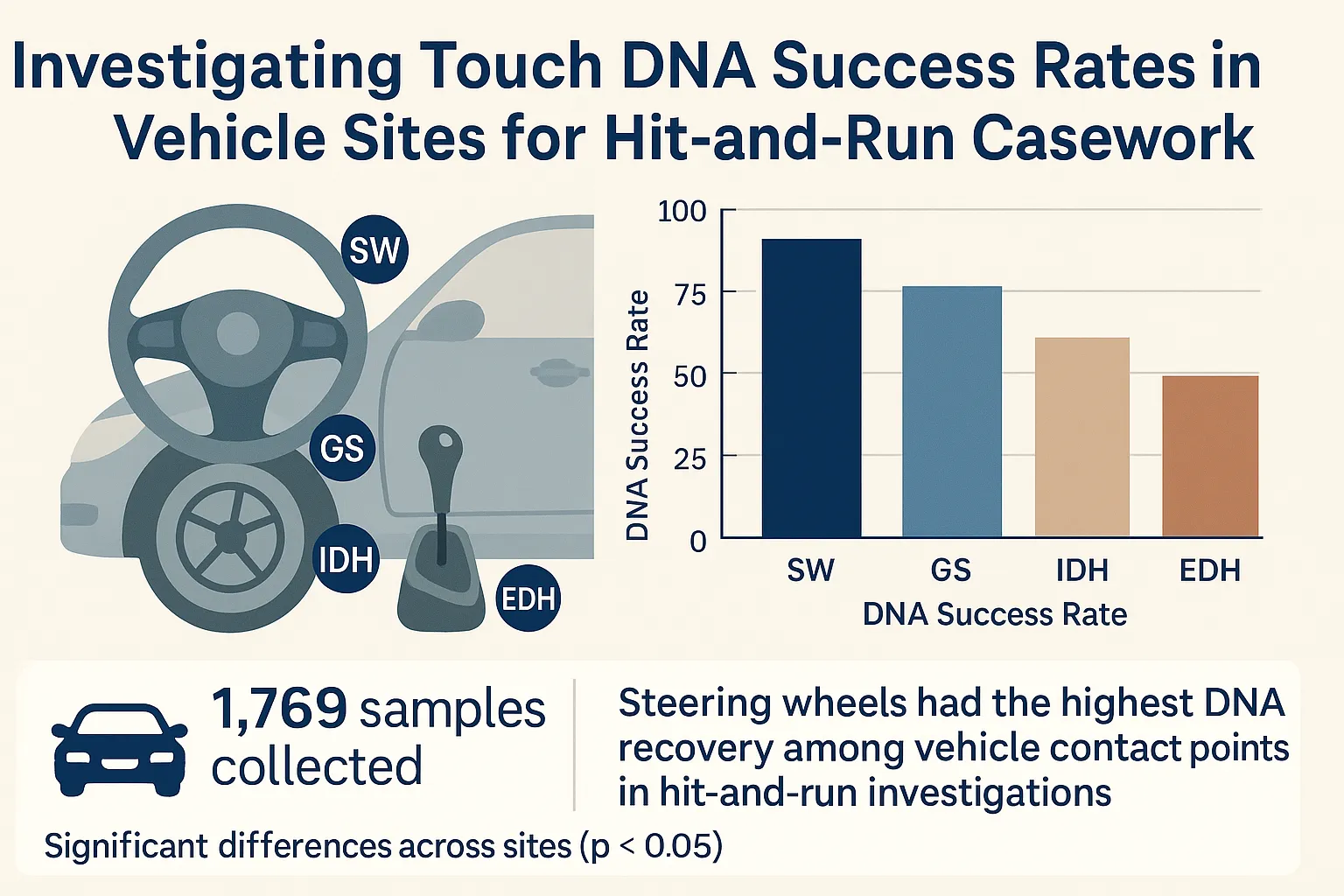
This study evaluated the effectiveness of Touch DNA recovery from four key vehicle contact points—steering wheel (SW), gear shift (GS), interior door handle (IDH), and exterior door handle (EDH)—in the context of hit-and-run forensic casework. 1769 samples were collected from 359 vehicles processed between 2020 and 2023. Statistically significant differences were observed in the quantity and quality of DNA recovered across these sites (p < 0.05). The steering wheel yielded the highest DNA success rates, followed by the gear shift, whereas the exterior and interior door handles demonstrated substantially lower recovery efficiency. These findings underscore the critical role of strategic sampling site selection in maximizing evidentiary outcomes. The results support prioritizing the steering wheel and gear shift as primary targets for DNA collection in vehicle-based investigations. The study highlights the practical utility of Touch DNA in linking individuals to vehicular crimes and calls for further research into alternative sampling techniques and contamination control measures to optimize forensic DNA recovery protocols in real-world hit-and-run scenarios.
Open Access
Opinion
10 February 2025Depletion and Recovery of Soil Organic Matter: Ecological, Economic and Social Implications
Over the past decades, urbanization, industrialization and unsustainable management have impaired soil fertility and ecosystem functioning, thereby affecting ecological stability and economic development. The mechanistic coupling between pressures and effects lies in the loss of soil organic matter (SOM), which directly and indirectly controls the vast majority of soil properties and the functioning of the soil ecosystem. From the functions SOM exerts in the soil ecosystem, to the consequences of its depletion and the possibilities it offers for ecological restoration, this concise opinion offers a perspective on the multifaceted roles of SOM in sustaining ecosystem functioning and the services it generates. Indeed, SOM plays crucial roles in supporting soil long-term fertility and the provision of ecosystem services, such as food, water, genetic, medical and biochemical resources, religious, cultural and recreational values, as well as sequestration of carbon and regulation of climate. These roles foster the view of SOM as an ideal proxy for soil quality and health, and justify the interest in acting on SOM as a mean of enhancing the sustainability and effectiveness of ecological restoration projects. The improvement of SOM to favor the onset of proper ecological dynamics in heavily degraded ecosystems, such as urban, industrial and agricultural soils, can be also coupled to the recovery of useful organic matter from wastes, integrating ecosystem restoration within waste management and sustainable circular economy strategies. Since, ultimately, the sustainability of our civilization depends upon proper ecological dynamics, soil quality rises to a topic of public concern and this opinion aims at providing a reference point of view on the intertwined implications of its preservation on the ecological, economic and social spheres.

Open Access
Article
07 January 2025Trace DNA Recovery: Insights from Dubai Police Casework
Trace DNA represents a critical form of forensic evidence, frequently recovered from a wide variety of touched or used items. Despite its evidentiary value, trace DNA analysis poses significant challenges due to the minute quantities of DNA involved, as well as the influence of factors such as surface type, collection methods, and environmental exposure. This study systematically examines the success rates and characteristics of trace DNA profiles recovered from six-item categories—tools, stolen items, wearable items, packaging materials, vehicles, and touched items—processed between 2021 and 2023 by the Biology and DNA Section of the Dubai Police Force. A total of 6277 cases were analyzed, encompassing a range of crimes, including homicide, suicide, missing persons, paternity disputes, and burglary. The results demonstrated an overall trace DNA success rate of 64%, with wearable items yielding the highest success rate at 76% and packaging materials yielding the lowest at 54%. Detailed analysis of positive DNA trace samples revealed significant variability in DNA profile types across item categories. Wearable items and touched items predominantly yielded full single (FS) DNA profiles, reflecting their reliability as sources of singular and high-quality DNA. Conversely, stolen items and packaging materials showed a greater prevalence of full mixed (FM) DNA profiles, highlighting their association with complex mixtures due to handling by multiple contributors. Tools and vehicles, meanwhile, exhibited higher rates of partial profiles, presenting unique challenges related to surface irregularities and environmental factors. This study emphasizes the importance of tailoring forensic strategies to item-specific characteristics, as well as the need for systematic mechanisms to categorize trace samples. Addressing operational challenges such as manual sorting and leveraging automation or AI-based systems can further streamline trace DNA analysis. The findings also underscore the importance of data sharing and standardization across forensic laboratories to enhance trace DNA recovery protocols and improve reliability in forensic investigations. Future research should focus on the effects of material properties, environmental exposure, and collection techniques on DNA retention, advancing the field of trace DNA profiling and its applications in forensic science.
Open Access
Article
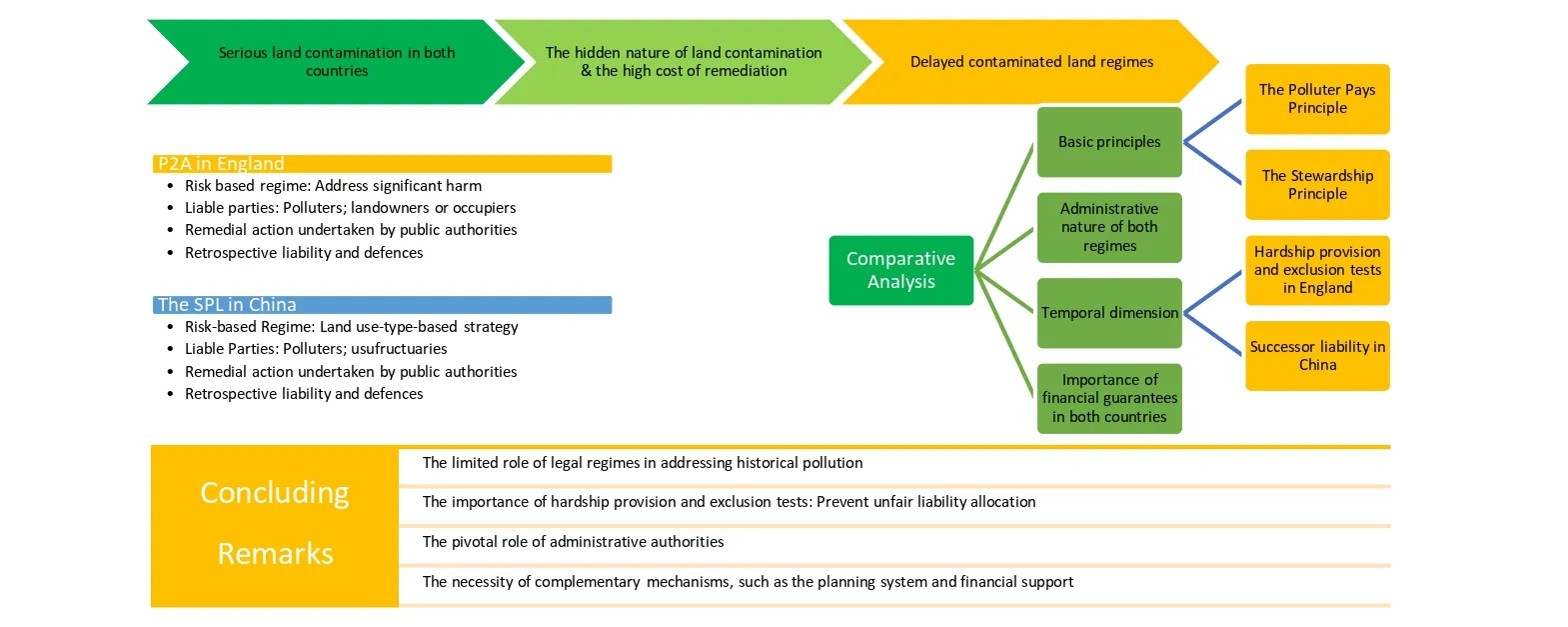
15 December 2023The Role of Liability Regime in Addressing Historical Contaminated Land Problems: A Comparative Perspective from England and China
This article conducts a comparative analysis of contaminated land regimes in China and England, focusing on their development, liability attribution, key principles, administrative nature, and financial guarantees. Both regimes are risk-based and are supported by the Polluter Pays Principle and the Stewardship Principle. They have similar liability arrangements: attributing the liability firstly to the polluter and then to landowners/occupiers or the usufructuaries. Administrative authorities under both regimes hold pivotal roles in remediating land on certain occasions. However, the cost recovery mechanisms vary due to the different constitutional roles among enforcing authorities, courts, and liable parties in the two countries. Both regimes impose retrospective liability, yet England provides detailed rules regarding the hardship provision and exclusion tests, preventing the unfair allocation of liability more effectively. Experience from England highlights the limited role of legal regimes in managing historical pollution, emphasising the need for supplementary mechanisms. This is why financial support is critical for effective land remediation in both countries.
Open Access
Perspective
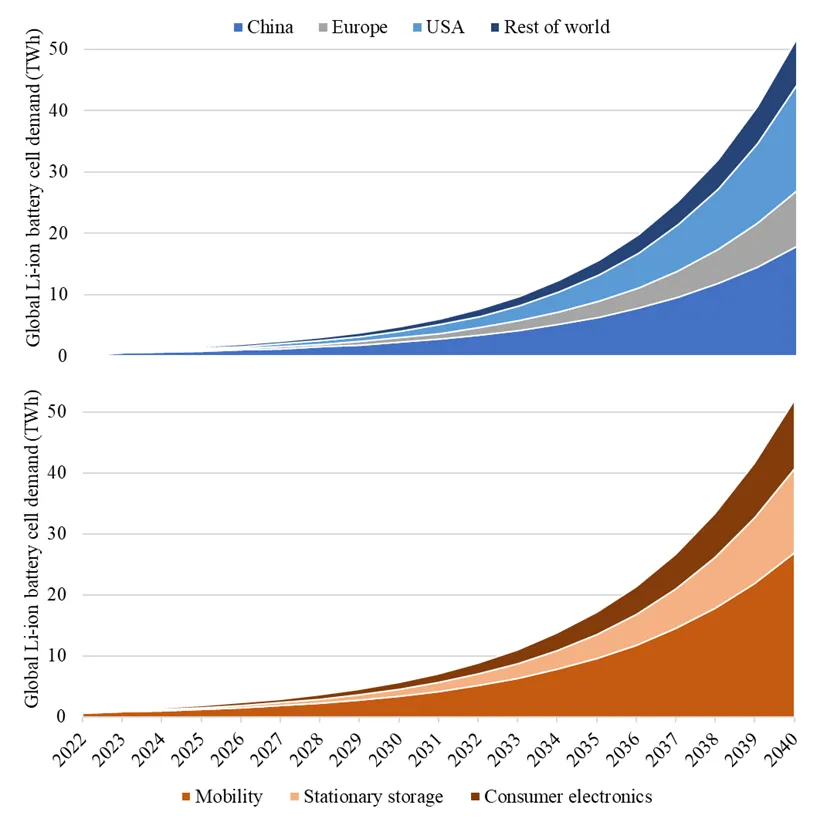
13 September 2023Estimate of Economic Impact of EVs Li-ion Batteries Recovery
Nowadays, increasing attention is directed towards the sustainable use of raw materials. For a circular economy, recovery from spent devices represents a fundamental practice. With the transition to electric mobility, an increasing number of devices powered by lithium batteries are produced. Indeed, this is the fastest growing sector producing spent batteries, which are an important secondary source of critical raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, graphite, and nickel. Therefore, this work aims to quantify the economic impact of recovering raw materials from lithium batteries used in the electric vehicles sector. Based on the chemical composition of the various lithium batteries and their market diffusion, the intrinsic economic value of this waste has been estimated to be around 6500 €/ton. Starting from the literature data on the global energy demand from lithium batteries and deriving the trend of their specific energy over time, the mass of material introduced into the market annually is estimated to reach 60 Mton/year by 2040. The annual amount of end-of-life lithium batteries was calculated by applying the Weibull distribution to describe the probability of failure, yielding 10 Mton/year by 2040. Finally, based on these results, the economic impact of the recovery market was assessed for two different scenarios.
Open Access
Article
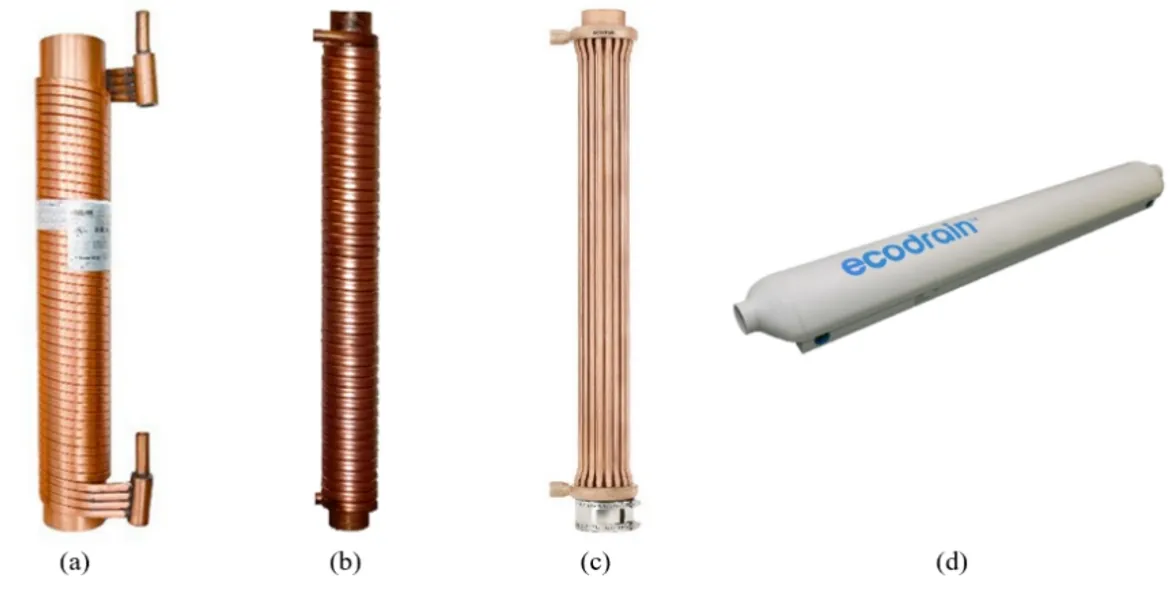
15 August 2023Thermal and Economic Evaluations of a Drain Water Heat Recovery Device under Transient Conditions
This study explores the transient characteristics of a drain water heat recovery (DWHR) device employed for heat recovery from warm grey water in buildings. Experimental measurements were conducted to investigate the response time of the DWHR device under various flow conditions. The thermal performance of the system was assessed using both transient and steady-state effectiveness analyses. The findings reveal that the response time is influenced by the water volume within the system, with an increase observed, and by the water flow rate, which leads to a decrease in response time. Additionally, a decrease in effectiveness is noted when hot water is used in short and frequent intervals. Furthermore, an economic analysis demonstrates that considering the transient behavior of the device results in a significant overall decrease of 37% in annual savings. Specifically, the usage of sinks exhibits a reduction in annual savings by 56%, while showers show a decrease of 13% in annual savings.