Found 25 results
Open Access
Article
28 February 2026Photocatalyzed Thiocarbamylation of Alkenyl Radicals via Thiophene Salts
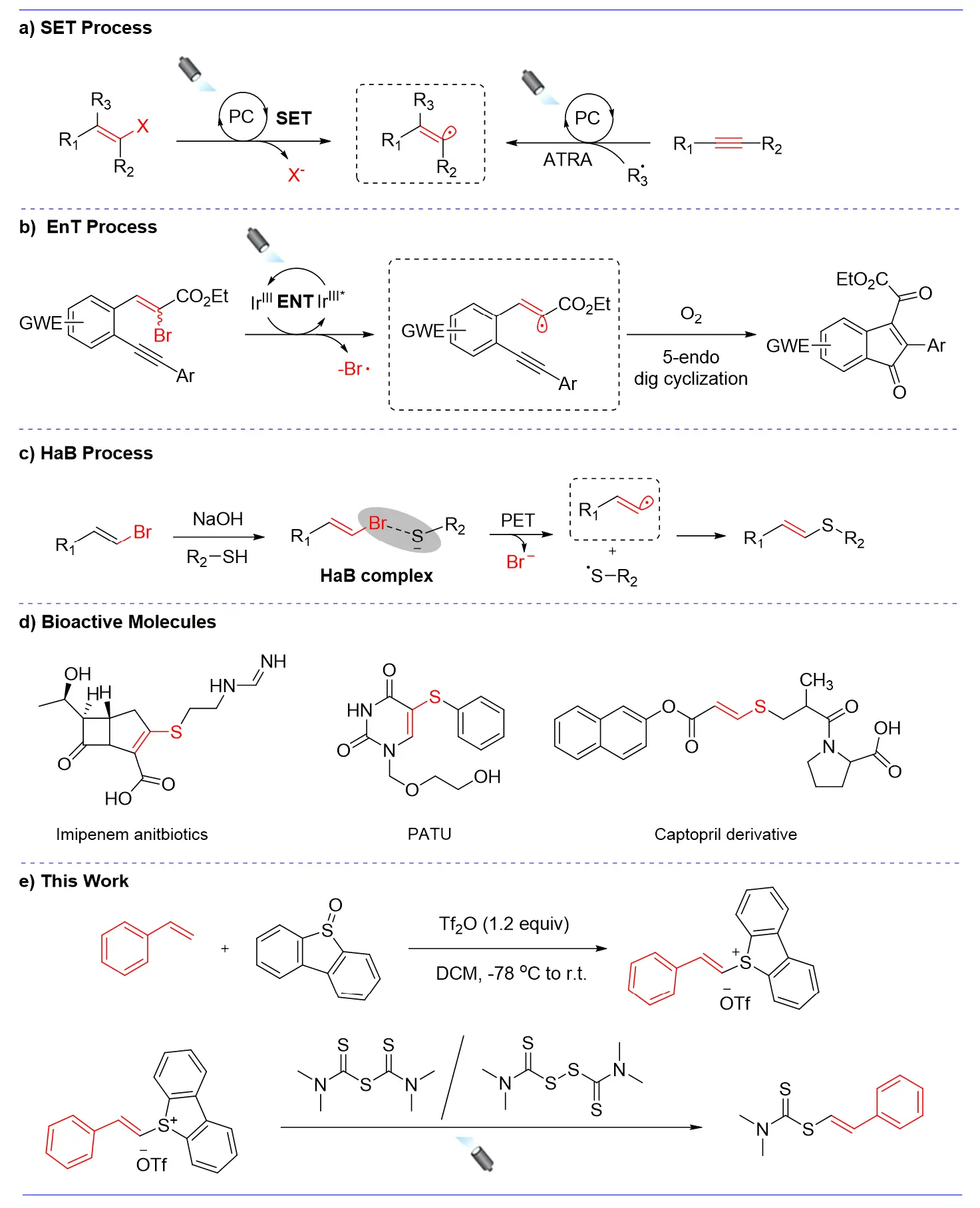
In recent years, visible-light-induced transformations have taken a central role in driving forward the progress of modern organic synthesis. Despite the abundance of synthetic strategies enabling access to aryl- and alkyl-centered radicals, the exploitation of photochemistry to generate highly reactive alkenyl radicals has remained notably underdeveloped. Herein, we report a sustainable strategy for generating alkenyl radicals based on a photocatalytic single-electron transfer process. Through systematic optimization of conditions such as photocatalysts, light sources, and additives, we confirmed that radical reactions can efficiently occur under metal-free conditions using styrenylthiophene salt as radical donors, thiuram derivatives as radical acceptors, and 4CzIPN (1,2,3,5-tetrakis(carbazol-9-yl)-4,6-dicyanobenzene) as the photocatalyst. This method is operationally simple, environmentally friendly, and does not require the addition of precious metal reagents, providing a novel strategy for the methodology of alkenyl radical generation.
Open Access
Article
16 December 2025Toluene or Formaldehyde Removal by Photocatalysis and Adsorption Using Hybrid Optical Fiber Textiles Containing Activated Carbon and/or TiO2
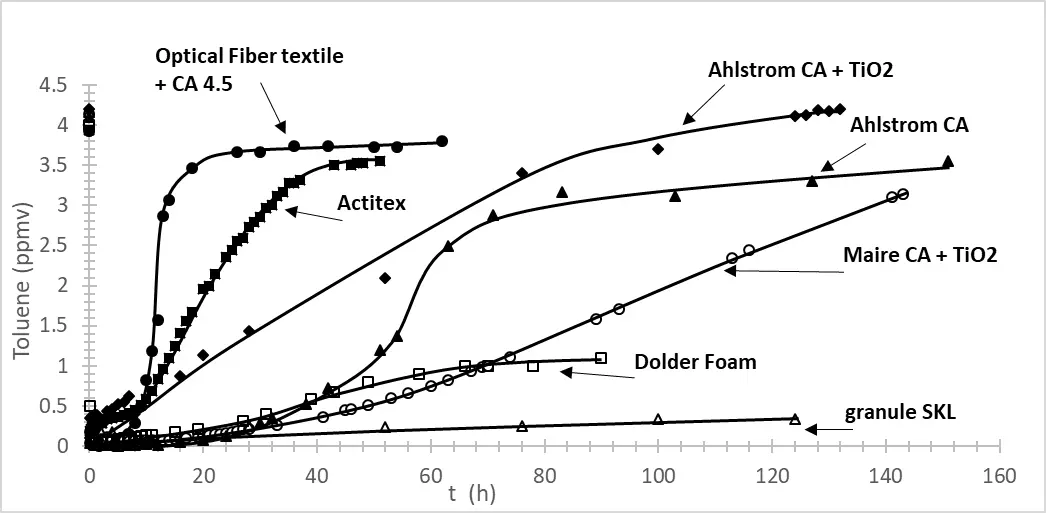
Indoor air treatment has become a significant concern in recent years. The aim of this study is to investigate the effectiveness of coupling adsorption and photocatalysis for the removal of toluene and formaldehyde, especially in the presence of optical fiber textile. First, we examine the adsorption properties of various commercial activated carbon (AC) filters, as well as different amounts of AC deposited on optical fiber textiles, and assess the impact of titanium dioxide (TiO2) on the adsorption performance. In the second phase, we compare the photocatalytic degradation of toluene and formaldehyde under different irradiance levels. Finally, we analyze the impact of three AC-TiO2 combinations: separate filters, TiO2 deposited on AC-impregnated fiber optic textiles, and TiO2 partially deposited on AC filters. The results led us to test a new photocatalytic and adsorbent material, including heating wires and optical fibers.
Open Access
Perspective
07 November 2025A Critical Analysis of Kinetic Models in Photocatalysis and Some Necessary Improvements
A brief critical analysis of kinetic models is presented, particularly the quadratic model (QM), highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. A generalized quadratic model (GQM) is proposed that can accommodate the experimental observation that the degradation rate is non-zero in the limit of zero substrate concentration. The limits of this model are outlined by comparison with a more extended kinetic scheme.

Open Access
Article
24 October 2025N-TiO2 Photonic and Quantum Photocatalytic Efficiency Determined by Monte Carlo Simulation
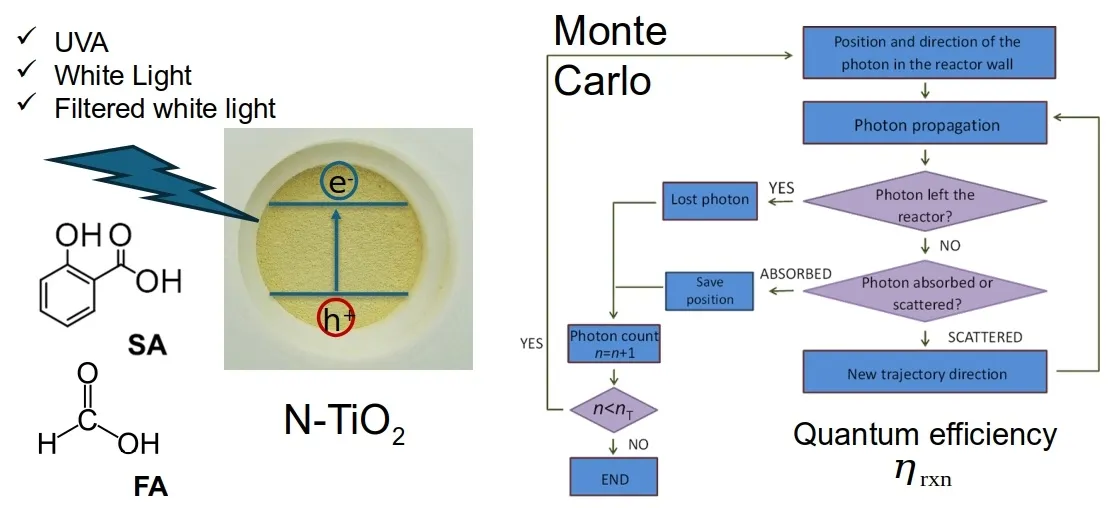
Nitrogen-modified titanium dioxide (N-TiO2) is proposed as an alternative to improve solar light absorption in photocatalytic applications. Due to its high chemical stability and low toxicity, various synthesis methods have been developed, yielding materials with different properties. Evaluating its performance compared to other photocatalysts requires calculating the quantum efficiency, which involves appropriate mathematical models to interpret experimental data. This study used a Monte Carlo approach to determine the local volumetric rate of photon absorption (LVRPA). TiO2 and N-TiO2 were synthesized via the sol-gel method using urea as the nitrogen source, and commercial TiO2 P-25 was used as a reference. Formic acid and salicylic acid were chosen as model pollutants due to their differing adsorption behavior on TiO2. Three light sources were used: UVA, white, and blue light. Nitrogen doping increased quantum efficiency for formic acid degradation under UVA from 2.4 to 3.5 (46% increase) and salicylic acid from 1.0 to 2.1 (110% increase). P-25 showed the highest efficiencies under UVA, with 6.2 for formic acid and 5.2 for salicylic acid. Under white light, salicylic acid degradation efficiency doubled from 0.4 to 0.8 after nitrogen doping. No activity was observed for formic acid with undoped TiO2 under white light, but N-TiO2 achieved 1.1. Under blue light, no activity was detected for formic acid, while salicylic acid degradation showed efficiencies of 0.3 (N-TiO2) and 0.2 (P-25). Quantum efficiency was highest under UVA, indicating that nitrogen doping improves visible light response but does not surpass UVA performance.
Open Access
Article
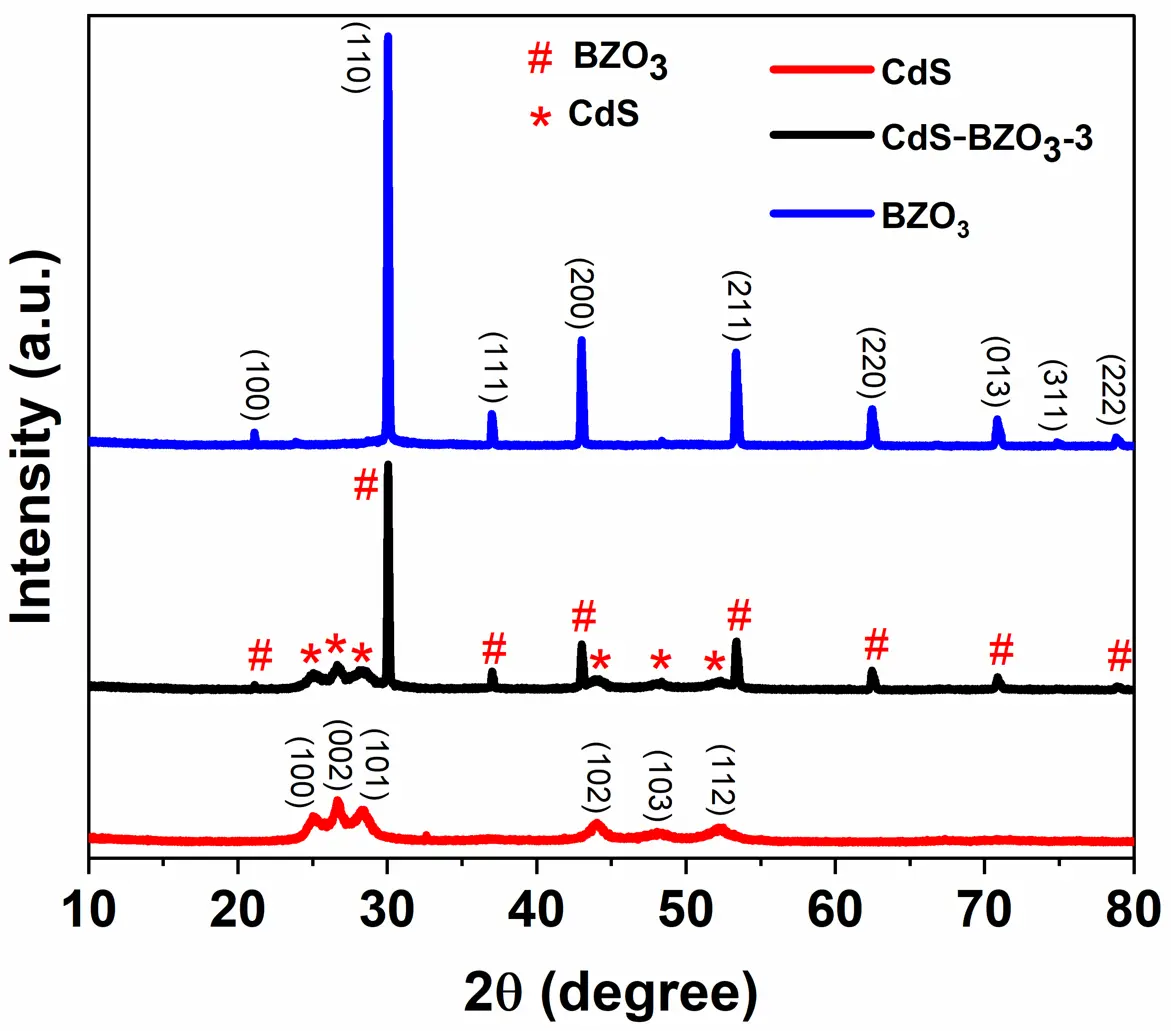
09 October 2025Preparation of CdS-BaZrO3 Heterojunction for Enhanced Photocatalytic Water-Splitting Hydrogen Production
Photocatalytic water splitting using solar light, a promising technical approach for hydrogen production. However, the slow charge transfer and rapid recombination of photogenerated charge carriers in photocatalysis limit their practical application. To address these issues, in this work, we successfully prepared a novel CdS-BaZrO3 (CdS-BZO3) heterojunction via a simple chemical-bath deposition method. The as-prepared heterojunctions facilitate the separation and transportation of photogenerated charges, while also maintaining the high redox-oxid ation ability of the photocatalysts. As a result, CdS-BZO3 heterojunctions show enhanced photocatalytic water-splitting hydrogen production ability without a co-catalyst. Especially, the optimized CdS-BZO3 sample exhibits high photocatalytic activity with a hydrogen production rate of 44.77 μmol/h, which is 4.4 and 2.9 times higher than that of BZO3 and CdS, respectively. At the same time, the CdS-BZO3 heterojunction exhibits good stability in the photocatalytic hydrogen production cycle test. This work provides a reference for the heterostructure construction of perovskite-based photocatalysts to improve photocatalytic performance.
Open Access
Article
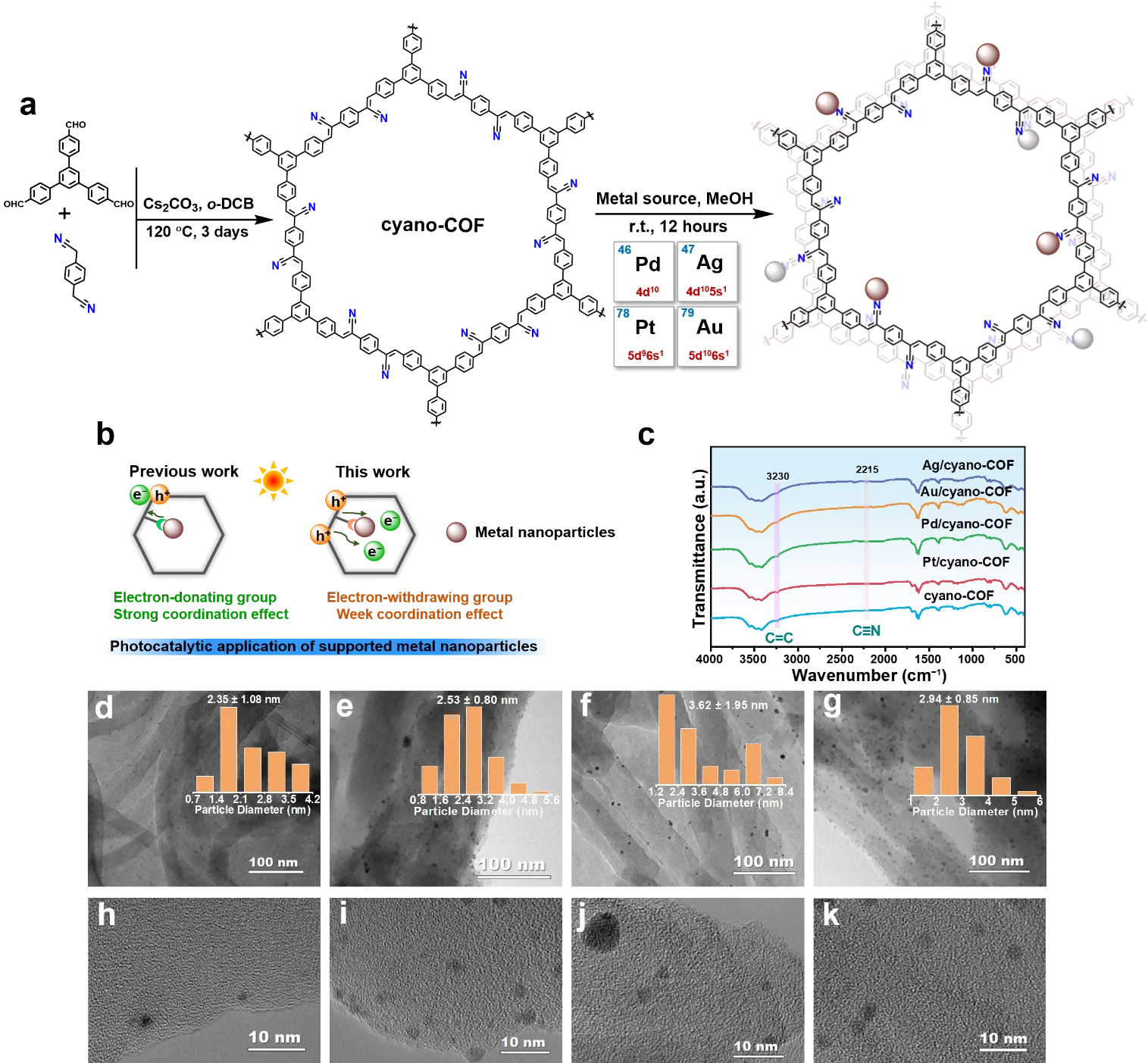
11 August 2025Noble Metal Sites Modulated Cyano-COF for Boosted Photocatalytic O2 to H2O2 Production
Photocatalytic O2 reduction to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a promising chemical synthesis pathway with green property. However, the development of efficient and stable photocatalysts that enable high selectivity and activity remains an urgent scientific challenge. Herein, cyano-based covalent organic framework (cyano-COF) photocatalysts modulated by noble metal sites (i.e., Pt, Pd, Au, and Ag), denoted as Pt/cyano-COF, Pd/cyano-COF, Au/cyano-COF, and Ag/cyano-COF, are designed and synthesized. The cyano-group (-C≡N), acting as a strong electron acceptor, interacts with the noble metal sites to establish an efficient electron transfer pathway, which facilitates the separation of photogenerated charges, optimizes the reaction pathway, and thus enables boosted generation of H2O2 via the two-step single electron oxygen reduction reaction (O2→·O2−→H2O2). Under visible irradiation, Pt/cyano-COF, Pd/cyano-COF, Au/cyano-COF, and Ag/cyano-COF deliver superior H2O2 production rates of 903 ± 24, 1073 ± 35, 963 ± 9, and 851 ± 56 μmol·g−1·h−1, respectively, much higher than that of pristine cyano-COF (577 ± 69 μmol·h−1·g−1). This study offers profound insights into the mechanism of noble metal sites in the solar-driven selective reduction of O2 to H2O2 synthesis.
Open Access
Article
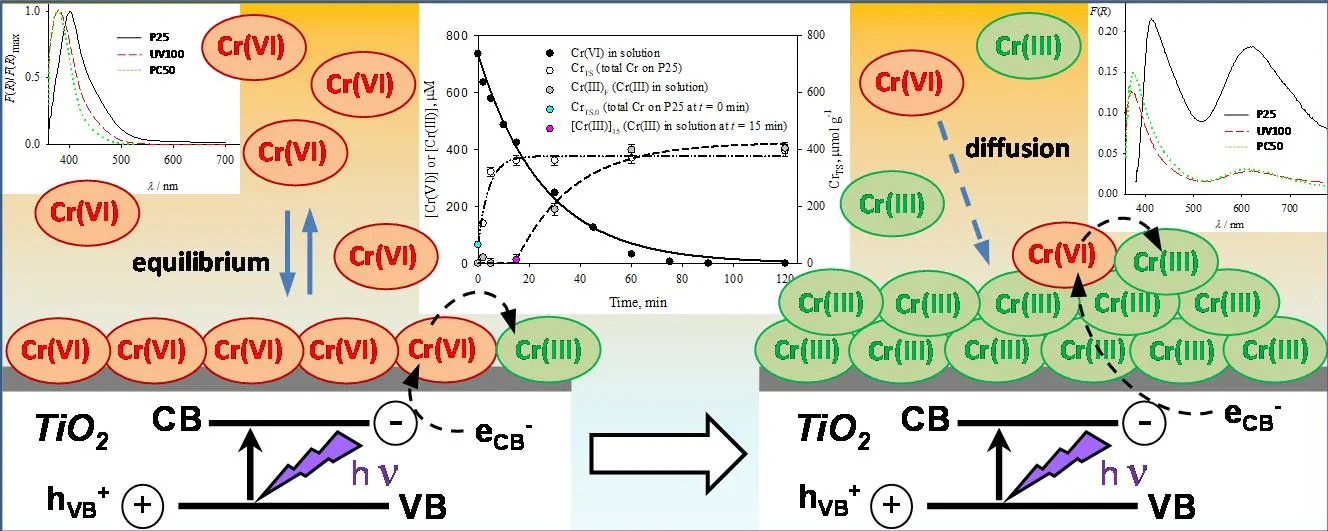
14 July 2025Correlation between Adsorption and Photocatalysis in the Aqueous System Cr(VI)-TiO2
The photocatalytic removal of Cr(VI) (0.80 mM, pH 2) using various commercially available photocatalysts (P25, UV100, PC50) was revisited, with particular attention given to Cr(VI) adsorption (as a Cr(VI)-TiO2 surface complex) and the formation of a Cr(III) hydroxide layer during the photocatalytic reduction. Cr(VI) adsorption followed a quasi-Langmuir-type isotherm, and the spectra of the Cr(VI)-TiO2 surface complex were deconvoluted into two Gaussian peaks, red-shifted when a rutile phase was present. Cr(VI) photoreduction exhibited nearly pseudo first-order kinetics, with P25 showing the highest reaction rate. Adsorbed Cr(VI) was reduced by eCB−, and the formed Cr(III) was retained over the TiO2 surface under non-equilibrium conditions, acting as a new adsorption site for Cr(VI). At longer reaction times, partial dissolution of the Cr(III) layer was observed. These findings suggest that the photoreduction kinetics are primarily governed by the slow adsorption of Cr(VI) onto the Cr(III) deposition layer. As an important conclusion, three consecutive processes never mentioned before take place: (1) reduction of adsorbed Cr(VI), (2) formation of Cr(III) over the photocatalyst and (3) adsorption of Cr(VI) over the deposited Cr(III) layer, together with partial Cr(III) redissolution. This insight provides a deeper understanding of the underlying photocatalytic mechanism.
Open Access
Opinion
11 June 2025Reflections on Photocatalysis Progress Since the Inspiration of Prof. David Ollis in 1992
Why has photocatalysis not gained the wide-ranging commercial applications in environmental purification of air and water that seemed promising 30+ years ago since the first international conference on TiO2 photocatalytic purification and treatment of water in 1992? The primary reason lies in its low intrinsic efficiency. The progress of R&D to enhance this efficiency has been slow, possibly due to an incomplete understanding of the underlying mechanisms of photocatalysis. There is also the possibility that certain factors, with effects comparable to those of the band gap, significantly influence photocatalytic performance but remain underexplored. Additionally, challenges such as mass transfer limitations and surface contamination hinder the industrial application of photocatalysts. It may be time for scientists to reconsider and address the limitations and practical application scenarios of photocatalysis.

Open Access
Article
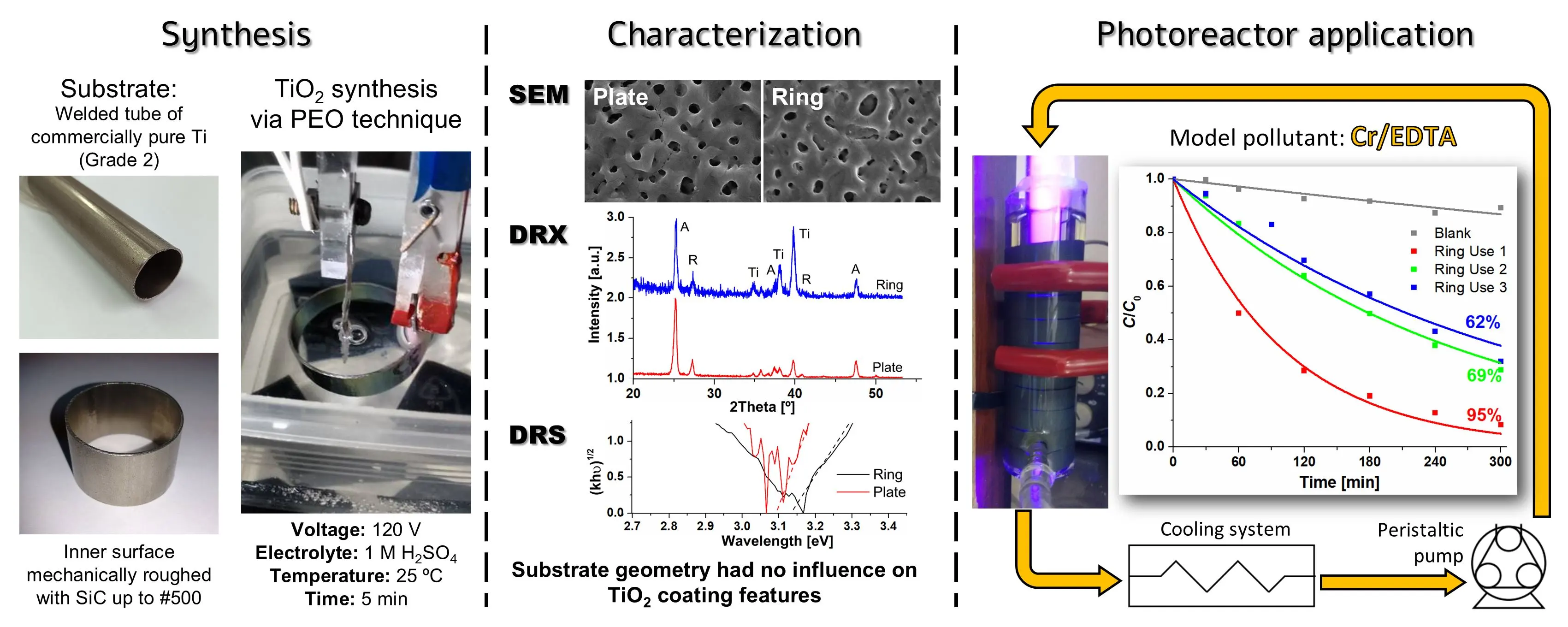
03 April 2025Design, Building and Performance of a New Photocatalytic Reactor Using TiO2-Coated Rings Synthesized by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation
An annular UV photocatalytic reactor with recirculation in batch was designed and built. The design considered low construction, simple operation and maintenance costs, availability and durability of the materials used, easy cleaning, and high standards of hygiene and safety. The TiO2 photocatalysts were synthesized by plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) on commercial Ti rings were compared with coatings obtained on Ti plates as a reference, and no influence of the substrate geometry on the morphology, crystallinity, or bandgap of the coatings was observed. The efficiency of the photocatalytic reactor using 10 TiO2-coated rings was tested by Cr(VI) transformation in the presence of EDTA. The Cr(VI) transformation after 5 h irradiation attained 95%; a rather high photocatalytic activity (62%) was maintained after the third use of the rings without reactivation of the photocatalyst. These coatings synthesized by PEO have not been applied in modular photocatalytic reactors until now.
Open Access
Article
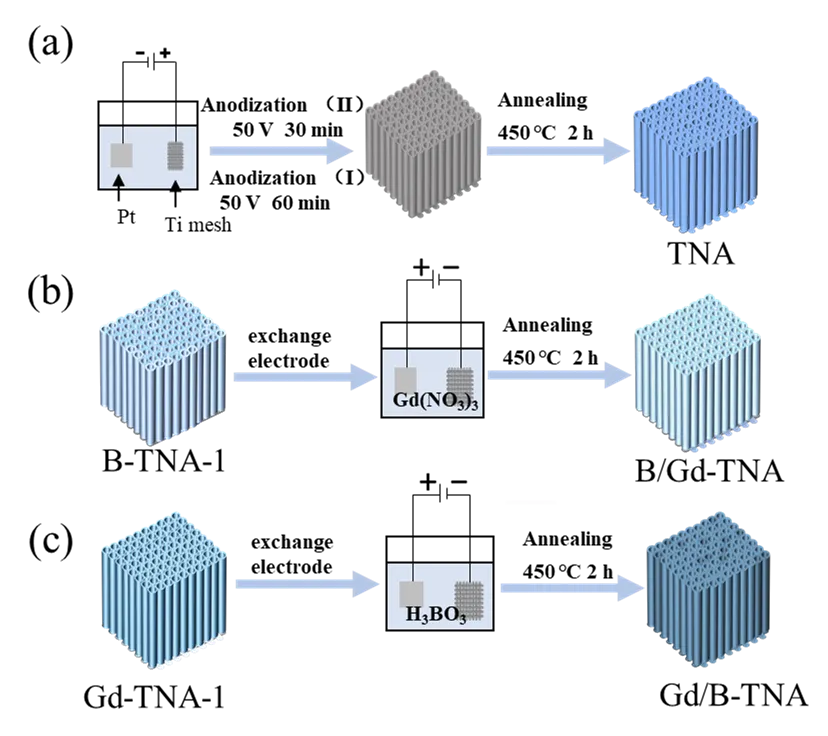
01 April 2025B, Gd Co-Doped TiO2 Nanotube Arrays for Efficient Degradation of Gaseous Toluene under Visible Light Irradiation
Although photocatalytic degradation of VOCs has attracted widespread attention, the efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation performance remains a challenge. This work presents the visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of gaseous toluene over B, Gd co-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays prepared via a controllable electrochemistry method. It was found that B and Gd co-doping strategy not only enhances the visible light responsiveness of TiO2 nanotube arrays but also introduces moderate oxygen vacancies on the surface of TiO2, which is beneficial to the formation of free hydroxyl radicals and their attack on toluene molecules. The doping order also affects the photocatalytic performance. The optimized sample achieves an enhanced degradation efficiency for toluene under visible light irradiation and exhibits considerable stability. This work may provide an efficient TiO2-based photocatalyst for the removal of volatile organic compounds for air purification and give an understanding of the mechanism of photocatalytic degradation of toluene over co-doping TiO2.