Found 1 results
Open Access
Article
08 September 2025Open Water in Winter: An Influential but Underestimated Ecosystem in Northern Boreal Mountain Regions
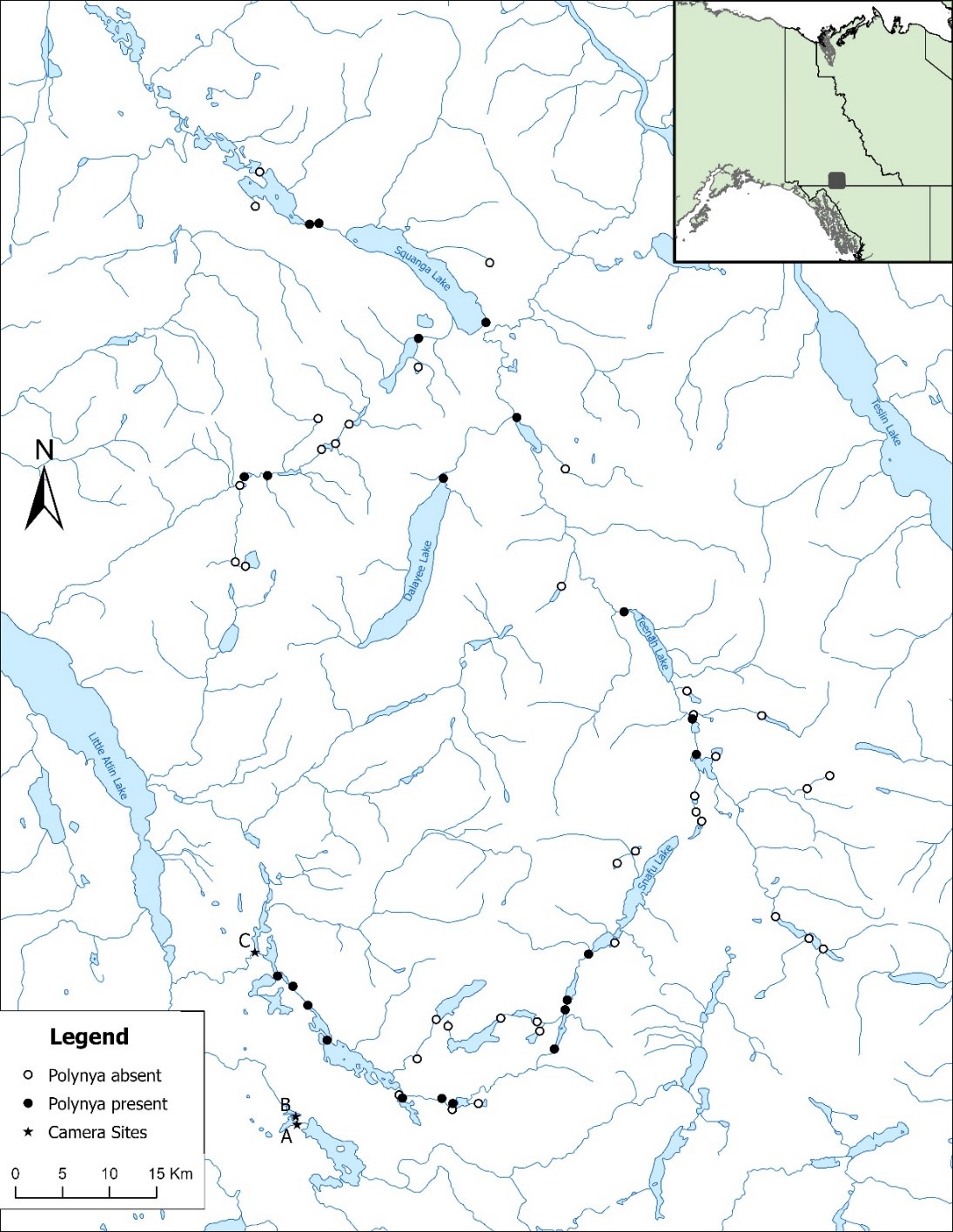
Patches of open water (polynyas) persist throughout six-month winters on many ice-covered lakes in boreal mountain ecoregions of northwestern North America. We explored their distribution, hydrological correlates, and the diversity of species using them from freeze-up to break-up. In headwater drainages, lakes with outflow polynyas were significantly larger than those without, but many small lakes also had polynyas. There was a consistent threshold in upstream catchment size below which outflow polynyas were absent and above which they persistently occurred in downstream lakes. Outflow polynyas depend on winter-long through-flow of water, likely maintained by the hydraulic head of higher elevation ground water in perched water tables in this region of very limited permafrost. Based on camera trapping, two species, the American dipper and river otter, used polynyas heavily throughout winter foraging. Polynyas likely provided crucial forage for at least 9 species of migratory waterfowl (Anatidae) to complete their spring migration or to prepare for reproduction on local lakes. Cameras recorded additional 5 bird and 11 mammal species, as foragers, scavengers, or incidentally. We report previously undocumented significance of these spatially-limited and seasonal polynya ecosystems in expanding the diversity of winter ecological opportunity for numerous species on small to medium-sized lakes.