Found 6 results
Open Access
Article
26 December 2025Leveraging Productivity Analysis for Smallholders’ Sustainable Development: Dairy Efficiency in Central Madagascar’s Crop-Livestock Family Farms
Milk production in developing African countries is a viable path for smallholders’ sustainable development. Supporting interventions should be shaped by evidence from comprehensive, context-specific analyses. Using survey data, this study contributes to the development-oriented literature on dairy productivity in African smallholder systems by conducting the first stochastic frontier analysis in the Malagasy context. Focusing on milk producers in central Madagascar’s crop-livestock family farms, a stochastic frontier production function with inefficiency effects is developed. The fitted frontier comprises the number of cows, annual purchased feed expenditure, farmer’s labor, and total household assets owned. Distance from the frontier is explained by the use of improved breeds, integration in the regional milk zone, farmer years of experience, the presence of off-farm income, and the number of oxen owned. Technical efficiency ranged from 4.6% to 90.8% around a mean of 55.5%. Results revealed how, in this context, cows are embedded in diversified family farming systems where resources are allocated across production activities and household needs. The study’s multidisciplinary stochastic frontier analysis provides a more complete picture to guide research and policy for smallholders’ sustainable rural development.
Open Access
Article
12 September 2025Polymer Composites Based on Natural Minerals with Different Compositions and Their Strength Indicators
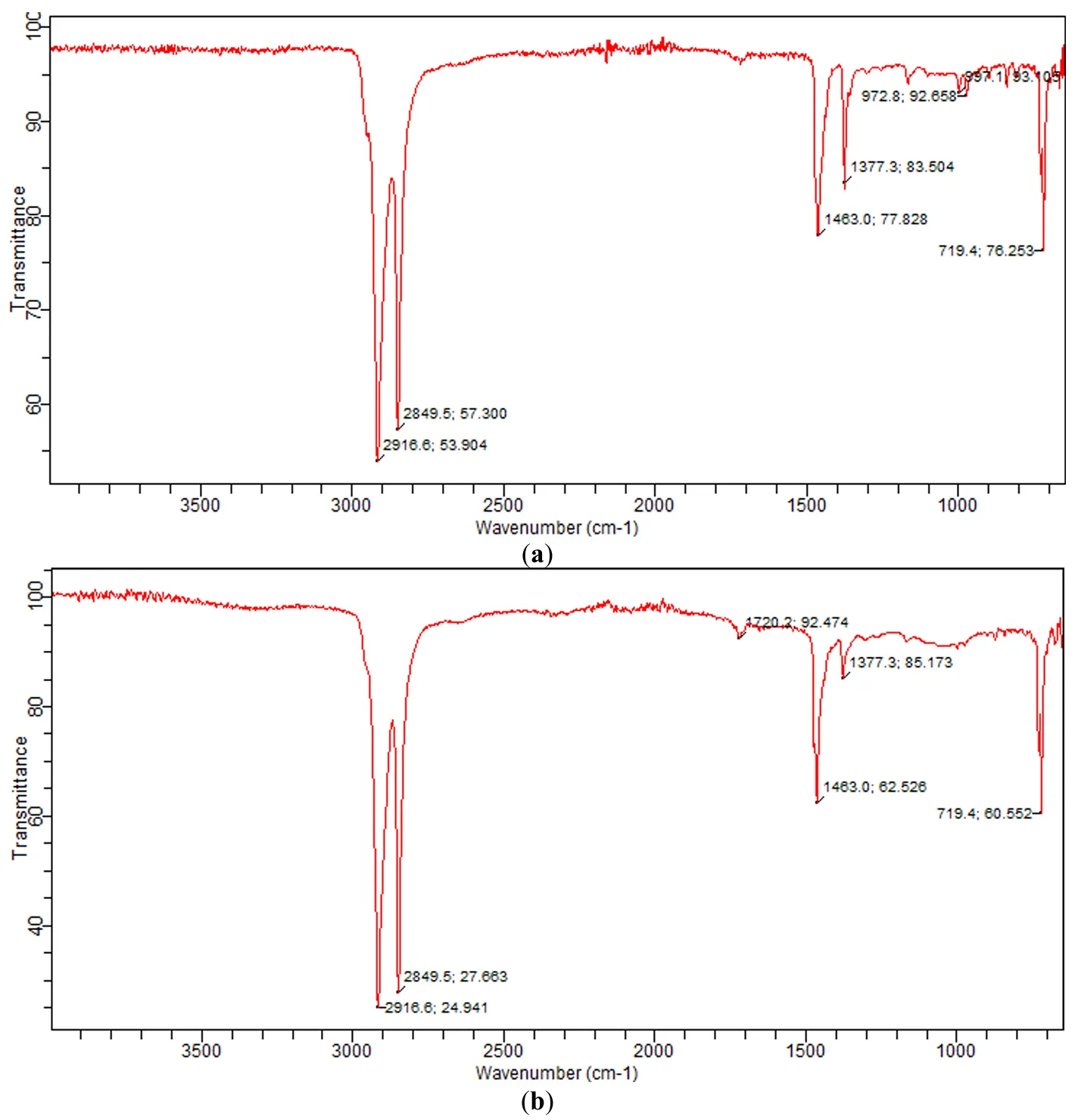
The presented scientific research work is dedicated to solving the problem of obtaining polymer composite materials with various superior operational properties based on polyolefins and a number of natural mineral rocks characterized by their corresponding characteristics, and investigating the application possibilities of the created materials. In this regard, local natural mineral resources are prepared for research in laboratory conditions through technological processes and mixed with a polymer matrix using a physical-mechanical method. The resulting mixture is brought to a ready state for research and is introduced into the process. Composite samples created on the basis of polyolefin and mineral rock are sent for research in accordance with different ratios of the components that make up the composite. The goal is to find the optimal ratio and determine the material that reflects higher quality criteria. Research conducted in this direction has yielded positive results. Research work that meets the requirements of modern chemical science can be considered satisfactory from an ecological and economic perspective.
Open Access
Article
19 August 2025Inventory of Ant Fauna in the Influence Area of a Small Hydropower Plant in the State of Paraná, Brazil
The construction of hydroelectric dams for power generation causes environmental alterations and ecosystem restructuring in directly and indirectly affected areas. This study aimed to survey the ant fauna in the indirect area of influence of a small hydroelectric plant located in Mangueirinha, Paraná State, Brazil. Seven sampling campaigns were conducted, two before and five during the project’s implementation, using pitfall traps as the sampling method. A total of 72 ant species were recorded, belonging to 26 genera and six subfamilies. Species richness and abundance did not differ significantly between the pre-implementation and implementation phases. The Chao1 estimator indicated that actual species richness may be approximately 7.6% higher than observed. These findings contribute to understanding ant biodiversity in areas subject to land-use change in Paraná State. The results highlight the value of using insect species richness and abundance, particularly of bioindicator groups such as ants, for environmental impact monitoring.

Open Access
Article
19 May 2025Database of Ecological Indicators of Freshwater Algae and Cyanobacteria
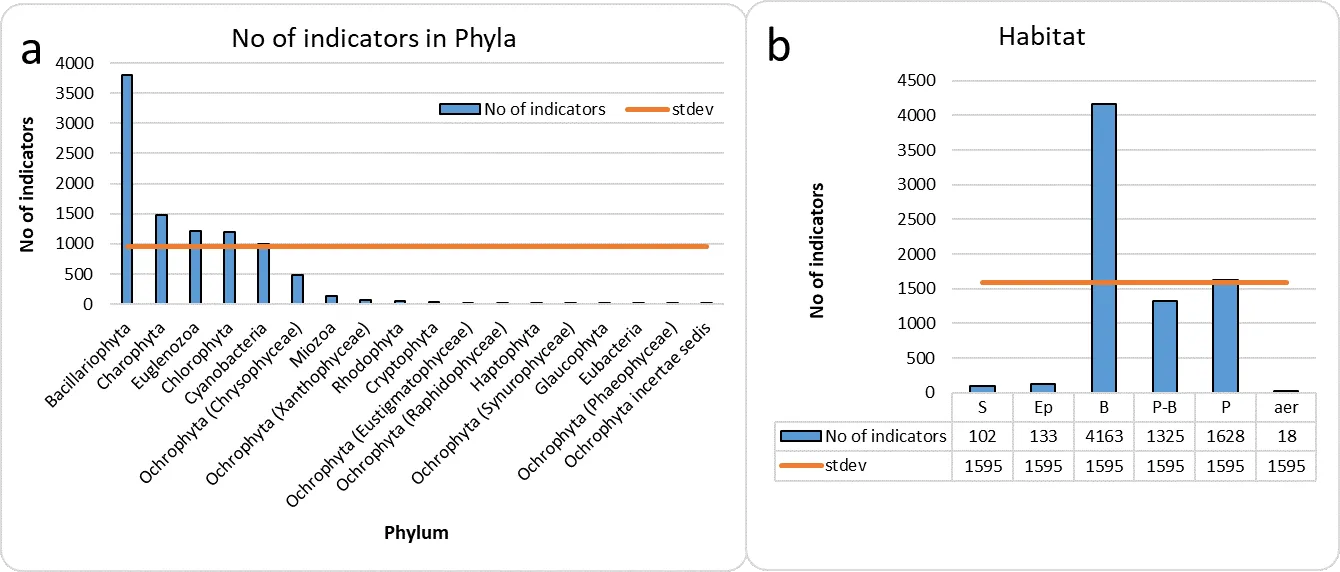
Accumulation of ecological data on species of algae and cyanobacteria represents 9531 taxa-indicators from 18 taxonomic phyla. The most represented among the indicators is the taxonomic group of diatoms. The indicators are grouped into twelve ecological groups, which can be indicators of nine environmental parameters. The environmental characteristics for each of the indicator systems and the relationship between some of them are given. Individual abbreviations of ecological indicator groups that have been established as a result of long-term use are given. References are given to examples of the application of analysis of specific water bodies using bioindication methods, and prospects for use in monitoring and assessing water quality are shown. A specific example of using the database is given. The table of indicator taxa contains cumulative ecological data and is easy to use. This table is a living tool that can be supplemented and transformed when new information about indicator species comes.
Open Access
Article
02 July 2024Early Risk Indicators for DSM-IV Diagnoses in Adolescents and Young Adults with Intellectual Disabilities
To identify risk indicators at ages 6–18 years that are associated with DSM-IV diagnoses in adolescents and young adults with intellectual disabilities five years later. To assess the potential health gain and efficiency of preventive interventions targeting these risk indicators. Parents reported on potential child, parental, and environmental risk indicators. Five years later, parents were interviewed using a standardised psychiatric interview schedule (DISC-IV) to assess DSM-IV diagnoses in children with ID (N = 614) at the age of 11 to 24 years. Logistic regression and linear probability models were used to test the contribution of risk indicators to the prediction of DSM-IV diagnoses. Deviant levels of internalising and externalising problems, inadequate adaptive behaviour, and parental psychopathology predicted psychiatric disorder. Children/adolescents exposed to multiple risk indicators were at greater risk of developing DSM-IV disorders. Strategies aiming for the risk reduction of psychiatric disorders in children/adolescents with ID should focus on intervening at an early age, improving psychopathology and adaptive behaviour skills of the children/adolescents, and supporting their parents.

Open Access
Review
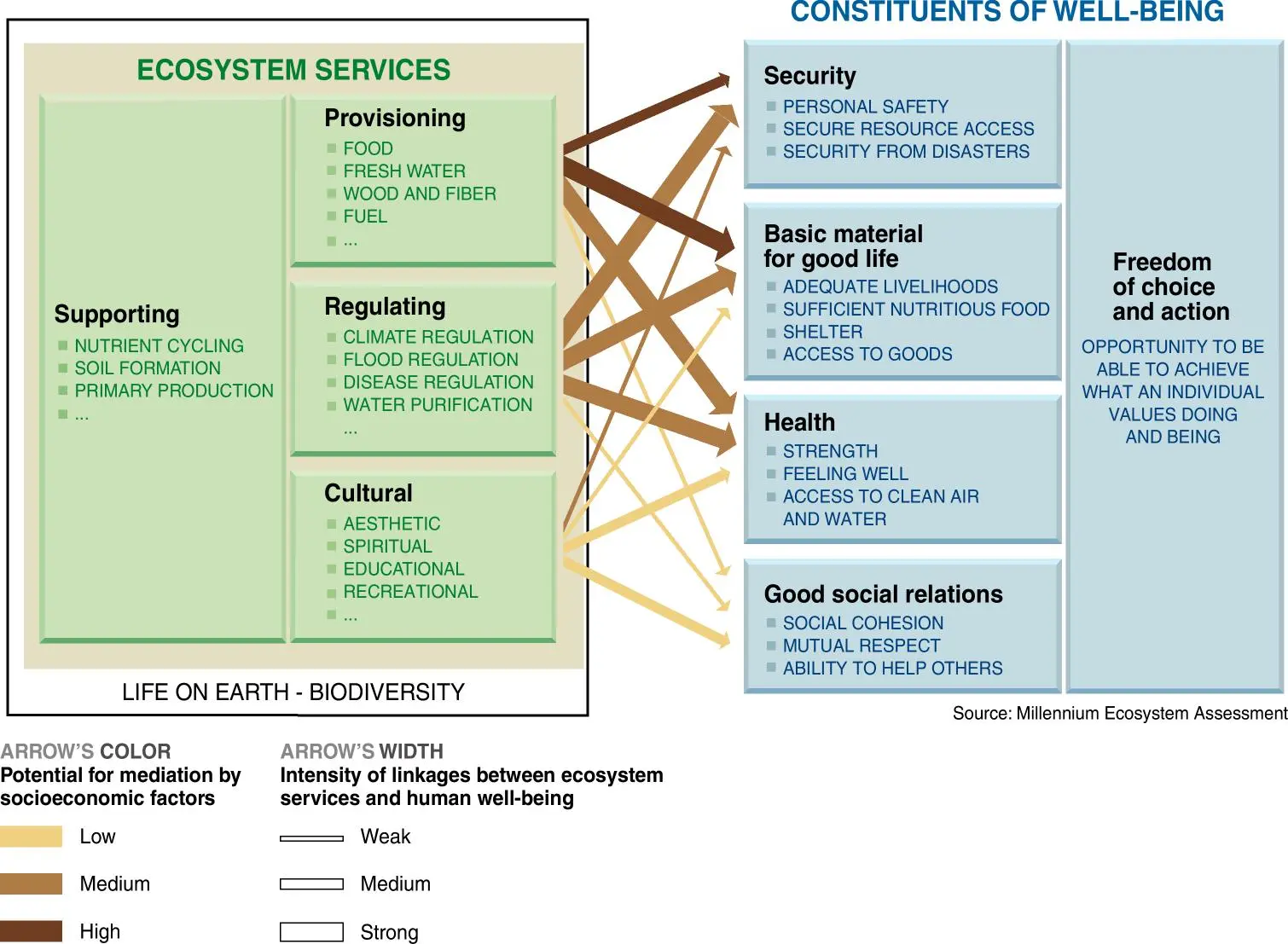
01 April 2024Desperately Seeking Sustainable Human Well-Being: A Review of Indicators, Concepts, and Methods
Evaluating progress in human development and well-being is imperative for policymakers to assess the impact of their policies. Traditional measurement methods focus mostly on economic growth and socio-economic objectives, often neglecting vital components of the natural environment, particularly the ecological determinants essential for the sustainability of human well-being. The tension between sustainability and development becomes apparent as the recognition of the dependence of human well-being on the natural environment and ecosystem services is crucial for safeguarding the environment for present and future generations. This highlights the necessity for indicators that capture the intricate relationship between human well-being and environmental changes while addressing the challenges posed by the tension between sustainable practices and traditional development models. This paper presents a literature review examining the domains, dimensions, and indicators related to the sustainability of human well-being regarding economic, social, and natural environments. Emphasizing the multidimensional nature, this paper highlights the drawbacks of relying solely on socioeconomic indicators for assessment. The review explores diverse concepts and methodologies proposed to evaluate the components and multidimensional factors influencing the sustainability of human well-being. Ultimately it offers a holistic understanding serving as a foundation for further research and policy development.