Found 1 results
Open Access
Article
17 October 2025Bioenergy Technology and Carbon Intensity in U.S. and China: Threshold Roles of Capital Accumulation, Education and Inequality
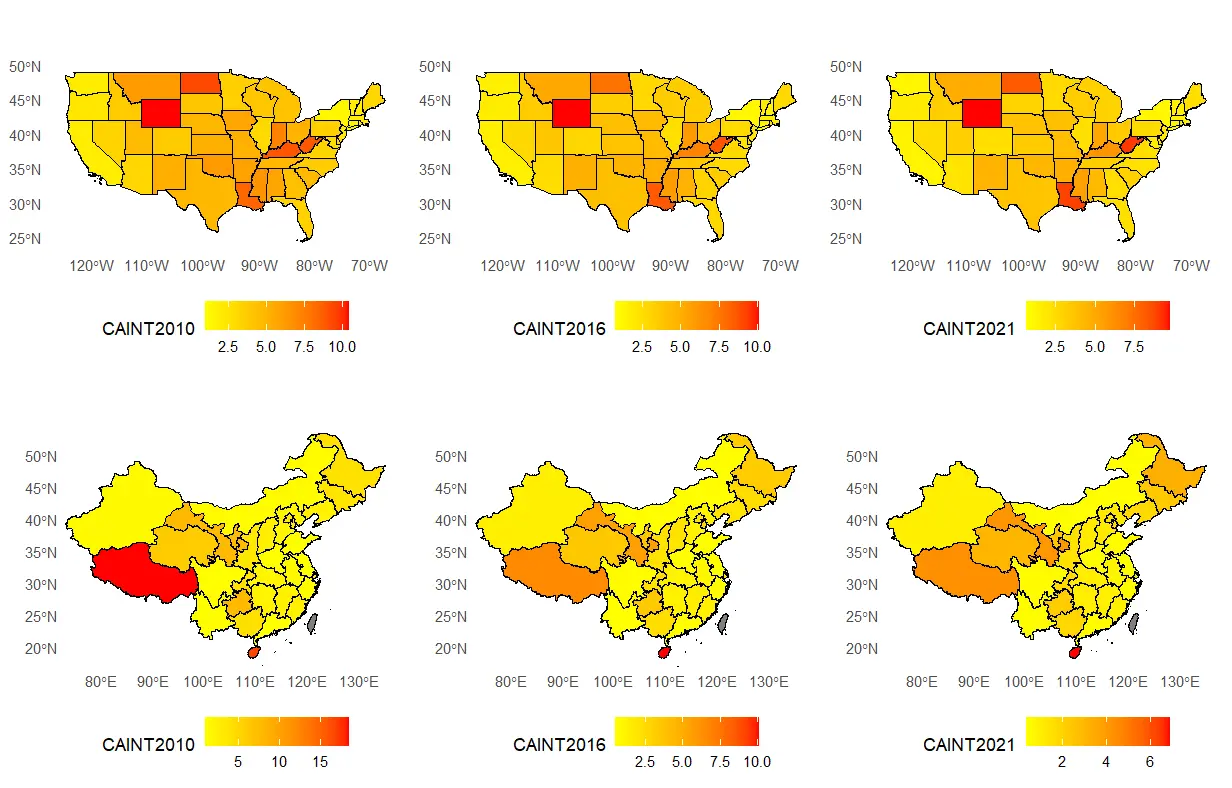
Bioenergy technology holds significant promise for reducing carbon intensity and fostering sustainable development, yet its impact remains unclear. This article employs both a panel threshold model and a random forest model, analyzing data from the primary administrative regions in the United States and China to explore the threshold effects and regional heterogeneity of bioenergy technology on carbon intensity, where the bioenergy technology is measured using patent data. In the United States, the impact of bioenergy technology on carbon intensity initially shows a positive effect, which later turns negative as per capita capital stock increases. The technology’s inhibitory effect strengthens with higher levels of education but becomes insignificant as the Gini coefficient rises. In China, increasing per capita capital stock shifts the impact of bioenergy technology from negative to insignificant, while higher education levels enhance its inhibitory effect. The Gini coefficient, however, does not significantly affect the impact of technology. Additionally, these threshold effects exhibit notable regional variations. The study provides cross-country evidence of how institutional and structural conditions shape the carbon mitigation effects of bioenergy technology, offering practical insights for policies that combine trade facilitation, education, and inequality reduction with low-carbon energy transitions.