Found 6 results
Article
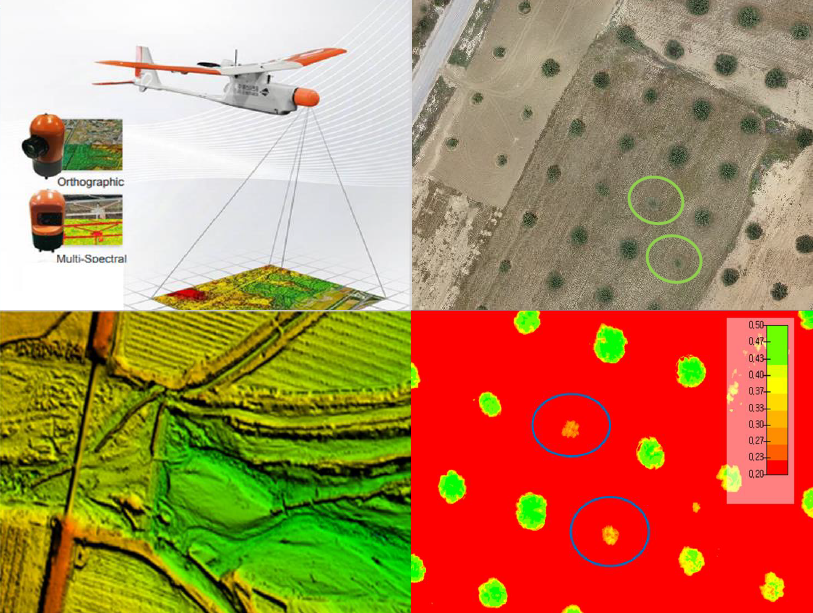
10 March 2025Leveraging Drone Technology for Precision Agriculture: A Comprehensive Case Study in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia
The integration of drone technology in precision agriculture offers promising solutions for enhancing crop monitoring, optimizing resource management, and improving sustainability. This study investigates the application of UAV-based remote sensing in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia, focusing on olive tree cultivation in a semi-arid environment. REMO-M professional drones equipped with RGB and multispectral sensors were deployed to collect high-resolution imagery, enabling advanced geospatial analysis. A comprehensive methodology was implemented, including precise flight planning, image processing, GIS-based mapping, and NDVI assessments to evaluate vegetation health. The results demonstrate the significant contribution of UAV imagery in generating accurate land use classifications, detecting plant health variations, and optimizing water resource distribution. NDVI analysis revealed clear distinctions in vegetation vigor, highlighting areas affected by water stress and nutrient deficiencies. Compared to traditional monitoring methods, drone-based assessments provided high spatial resolution and real-time data, facilitating early detection of agronomic issues. These findings underscore the pivotal role of UAV technology in advancing precision agriculture, particularly in semi-arid regions where climate variability poses challenges to sustainable farming. The study provides a replicable framework for integrating drone-based monitoring into agricultural decision-making, offering strategies to improve productivity, water efficiency, and environmental resilience. The research contributes to the growing body of knowledge on agricultural technology adoption in Tunisia and similar contexts, supporting data-driven approaches to climate-smart agriculture.

Review
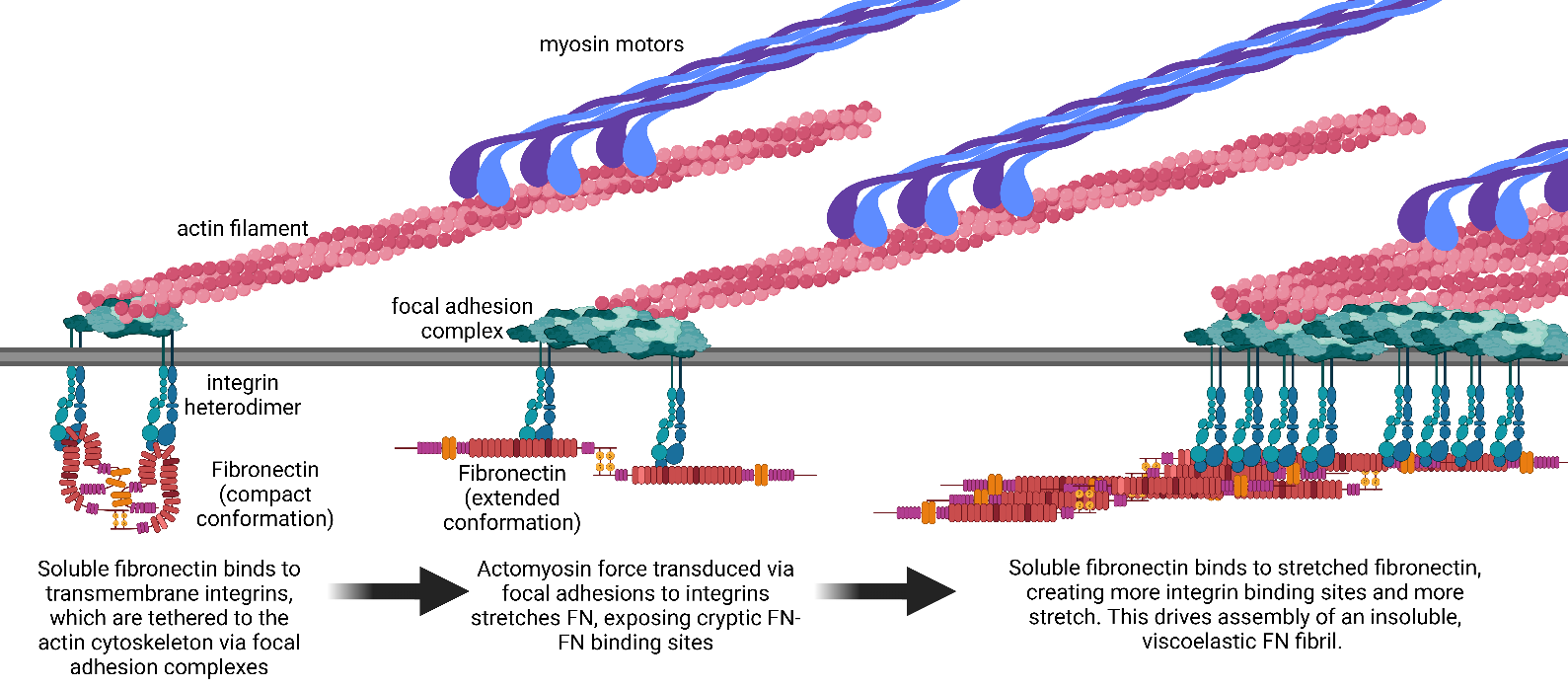
08 February 2025Mechanics and Synergistic Signaling of Fibronectin, Integrins, and TGF-β Isoforms
Fibrotic diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis, hepatic fibrosis, chronic kidney disease, and cancer are marked by an excess accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM). This process involves the assembly of the ECM protein fibronectin (FN) into insoluble fibrils. FN fibril assembly is highly linked with integrin signaling, TGF-β1 signaling, and cellular contractility. This linkage consists of four stages: (i) Integrin binding and contractile forces facilitate the assembly of FN into insoluble fibrils; (ii) assembled FN fibrils bind the large latent complex of TGF-β1; (iii) activation of TGF-β1 from the latent complex requires integrin binding and contractile forces; and (iv) active TGF-β1 increases contractility, integrin expression, and FN assembly. The significance of integrin signaling and TGF-β1 signaling in fibrotic diseases is well-appreciated, as numerous clinical trials targeting integrins or TGF-β1 have been reported. However, despite a clear effort to target integrins and TGF-β1 clinically, the vast majority of these trials have failed or have been terminated. These suggest a potentially incomplete understanding of the synergistic effects of these pathways. Here we present a review of both FN fibrillogenesis and TGF-β1 signaling, as well as current opinions of under-explored areas of crosstalk related to these pathways that may explain why these have not been successfully targeted in many disease states including fibrosis.
Article
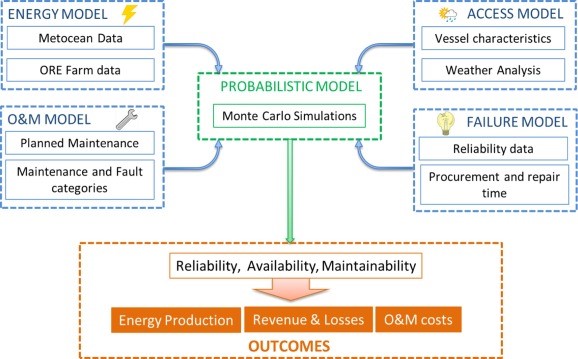
27 September 2024Strategic Deployment of Service Vessels for Improved Offshore Wind Farm Maintenance and Availability
This research explores the optimization of Operations and Maintenance (O&M) strategies for offshore wind farms using a sophisticated O&M simulator built on the Markov Chain Monte Carlo method. By integrating real-world constraints such as vessel availability and weather conditions, the study assesses O&M logistics’ impacts on wind farm availability, energy production, and overall costs across different scenarios in the Celtic Sea. Through comparative analysis of eight case studies involving various combinations of Crew Transfer Vessels (CTV) and Service Operation Vessels (SOV), the research highlights the critical role of strategic vessel deployment and the potential of permanent SOV stationing to enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and lower O&M costs. In this study, the permanent SOV can increase up to 20% availability of the whole wind farm. The findings underscore the importance of adaptive O&M planning in improving the sustainability and financial viability of offshore wind energy projects.
Review
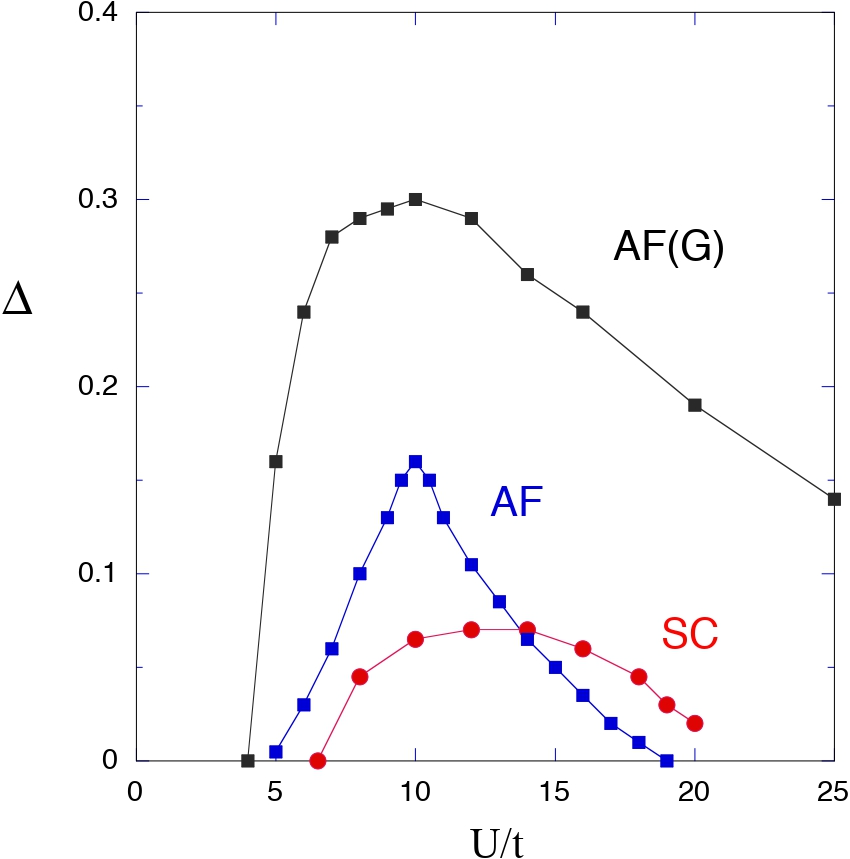
27 August 2024Strongly Correlated Electrons and High Temperature Superconductivity
It is very important to clarify the mechanism of high-temperature superconductivity in strongly correlated electron systems. The mechanism of superconductivity in high temperature cuprate superconductors has been studied extensively since their discovery. We investigate the properties of correlated electron systems and mechanism of superconductivity by using the optimization quantum variational Monte Carlo method. The many-body wave function is constructed by multiplying by correlation operators of exponential type. We show that d-wave superconducting phase exists in the strongly correlated region where the on-site repulsive interaction is as large as the bandwidth or more than the bandwidth. The d-wave pairing correlation function is shown as a function of lattice sites, showing that the long-range order indeed exists.
Article
08 August 2024Rural Nonfarm Enterprise and Its Impact on Household Livelihood in Ethiopia: Evidence from Gurage Zone
In Ethiopia, until recently, less attention has been given to rural entrepreneurship, while the rural economy has accounted for the lion’s share of employment, export earnings, and national income. This study scrutinized the factors influencing rural household participation in nonfarm enterprise and its impact on household livelihood in the Gurage zone. Data was collected from 352 households using questionnaires, and Key-Informant Interviews and Focus Group Discussions were used. The factors influencing household participation in nonfarm enterprises were estimated using a logit model, while Propensity Score Matching (PSM) was employed to assess the impact on household livelihoods. Women, single-headed households, households with larger family sizes, and households with secondary and primary education are more likely to participate in nonfarm enterprises. In addition, access to extension services, training, market, transport, credit, and being a member of cooperatives have increased the probability of household participation in nonfarm enterprise. Participation in nonfarm enterprises improved the livelihood of rural households. Rural nonfarm enterprises should be integrated into national policy as a means of economic empowerment, focusing on creating employment opportunities for women and youth and reducing poverty. Rural infrastructure expansion, access to credit, and entrepreneurship training should be prioritized and the sector should be enhanced as an alternative livelihood strategy.

Article
12 October 2023Risk Analysis of Crisis Management on the Example of Rural Areas in Poland
The aim of this article is to analyze and assess the risk of crisis hazards and to introduce possible improvements on the example of the Municipality of Branice. The types of threats and the consequences associated with their occurrence are also described. The quality management method (FMEA) was used to develop the risk assessment, as well as an indication of the risk values presented by the risk matrix made. Thanks to the research part of the study, the most probable possible risks and their consequences were detected, and improvements were proposed to prevent the occurrence of such situations in the future. The main conclusions of the study are: (1) a properly prepared crisis management plan is the most important and effective method to deal with emergencies that threaten the life and health of citizens; (2) hazards have been, are, and will continue to accompany people, so adequate preparation is needed to minimize their effects or even eliminate them altogether; (3) during the occurrence of an emergency, the sphere of logistical action is very broad and determines the methods and actions of the relevant services in order to reduce the effects of the threats that occur; (4) the conducted analysis of threats possible to occur in the area of Branice Commune indicates that the highest probability of occurrence of a threat is floods and waterlogging as well as hurricanes and strong winds; (5) the conducted FMEA analysis indicates that a very important factor preventing the creation of the threats discussed in the point above are periodical inspections and cleaning or modernization works of the given threat areas. In summary, the FMEA analysis showed that in the analysed municipality, the most serious risks were flooding and flooding, as well as hurricanes and high winds. The following remedial actions are proposed in the analysis and to improve these areas in the rural areas: water surge in the riverbed (cleaning of the riverbed; repair of dikes; securing roads and communication bridges against possible damage; securing drinking water reservoirs against pollution; securing sewage treatment plants against possible leakage of faecal matter into flood waters); obstruction of field drainage (regular mowing and cleaning of ditches; checking the patency of ditches; roofs of residential and commercial buildings and fallen trees in villages close to houses (inspections and pruning of dangerous tree branches and possible removal of trees threatening danger of falling; inspection of roof structures by building supervision) and fallen trees in riverbeds (cleaning of banks and riverbeds; inspection of tree stands near rivers). The policy implications of this study may be far-reaching, not least because it may determine rural managers to change their management and attention to and response to crisis threats that may occur in such areas. Regarding the limitations of the study, it is important to remember that it was conducted on the author’s chosen terrain. In most cases, changes in the terrain, the population or its management have a determining influence on the shaping of emergency response principles. Therefore, the study conducted should provide an overview of the research issue undertaken. In the future, it is planned to extend the study area to equal rural areas occurring in the world, and it is also planned to verify the existing hazards on the ground on a continuous basis. In addition, it is intended to extend the deeper cooperation with both the rural authorities and the rescue units in order to imply the research results in the actual territorial units.
