Found 3 results
Open Access
Article
21 November 2024The Impact of Renewable Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, Globalization, and Financial Development on Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Evidence from Selected G7 Economies
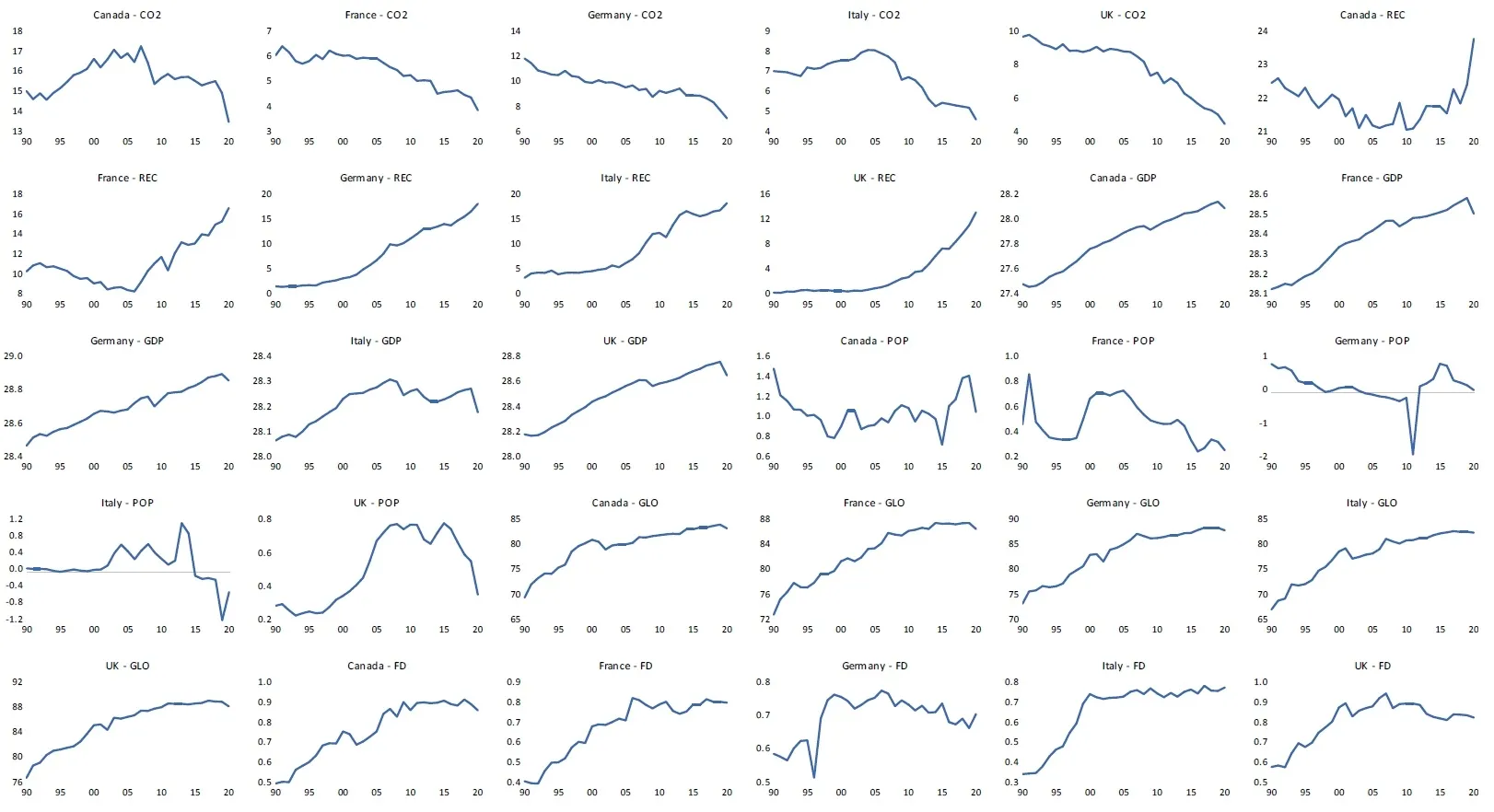
The aggregate upsurge in carbon dioxide emissions (CO2) witnessed through environmental degradation and global climate change is a call for great concern. This, therefore, calls for the enactment, utilization and implementation of provisions and policies geared towards curbing this global economic bad without impeding global economic growth rates. This study ascertains the extent to which renewable energy consumption (REC), economic growth (GDP), population growth (POP), globalization (GLO), and financial development (FD) affect carbon dioxide emissions (CO2) in selected G7 economies (France, Germany, Canada, Italy, and the United Kingdom) from 1990–2020. The Dynamic Fixed Effect Autoregressive Distributive Lag (DFE-ARDL) and the Pooled Mean Group ARDL (PMG-ARDL) methods were employed for analysis. The empirical findings for DFE-ARDL showed that REC, GDP, and POP have an adverse association with CO2 in the long-term. However, in the short-term, REC and FD improve the environment, while GDP and POP drive CO2. It is observed that the result for REC in the short and long-run is consistent. The PMG-ARDL results revealed that REC and GLO negatively affect CO2 in the long-run, and in the short-run, GDP spurs CO2, while FD reduces it. The result summary of both methods employed demonstrates that REC, GLO, and FD benefit the environment. At the same time, GDP and POP harm the environment in the short-run but reduce CO2 in the long-run. Conclusively, the research recommends increasing the utilization of renewable energy and policies that enable economic growth and CO2 to move in the opposite direction.
Open Access
Review
01 April 2024Desperately Seeking Sustainable Human Well-Being: A Review of Indicators, Concepts, and Methods
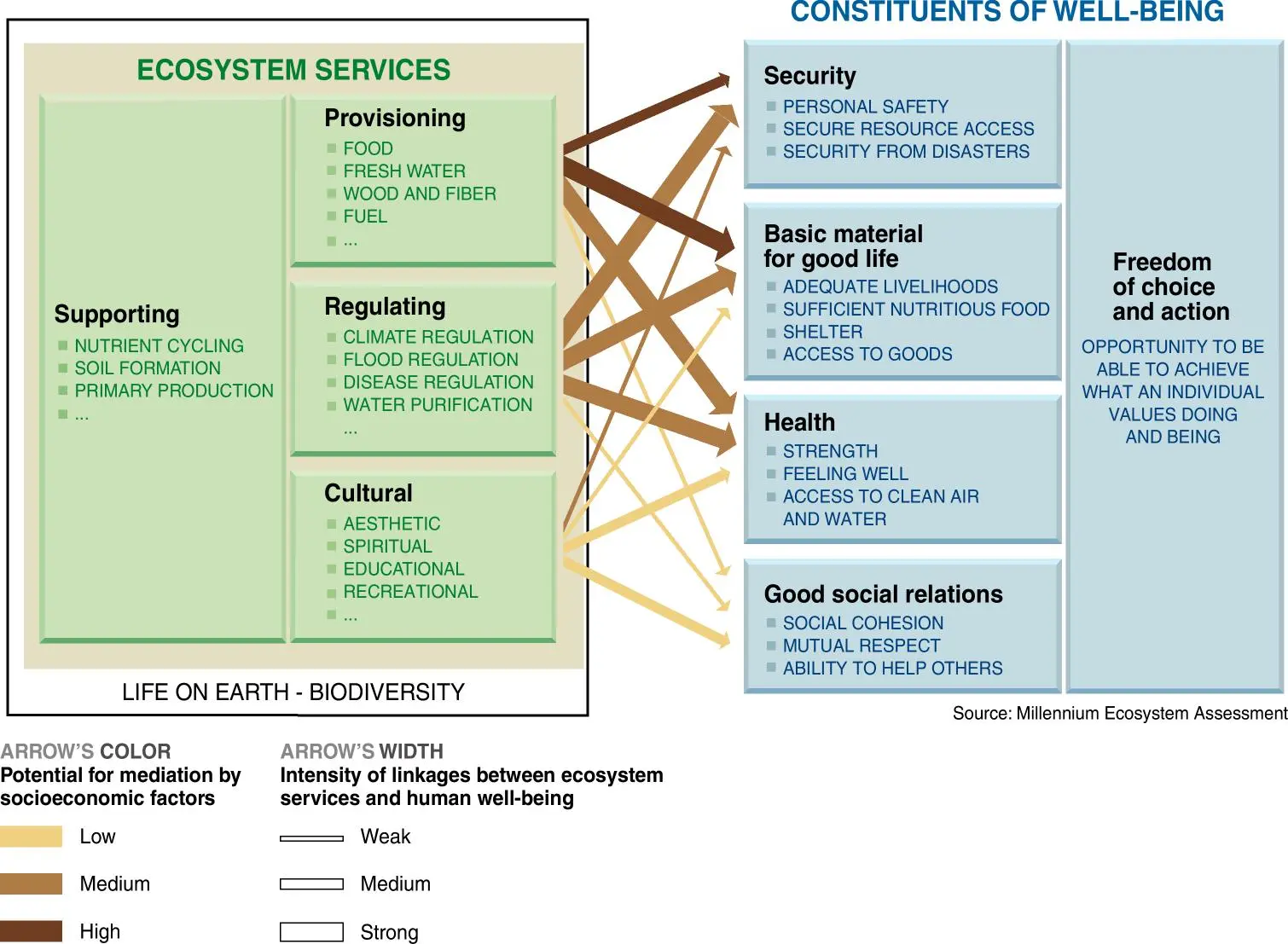
Evaluating progress in human development and well-being is imperative for policymakers to assess the impact of their policies. Traditional measurement methods focus mostly on economic growth and socio-economic objectives, often neglecting vital components of the natural environment, particularly the ecological determinants essential for the sustainability of human well-being. The tension between sustainability and development becomes apparent as the recognition of the dependence of human well-being on the natural environment and ecosystem services is crucial for safeguarding the environment for present and future generations. This highlights the necessity for indicators that capture the intricate relationship between human well-being and environmental changes while addressing the challenges posed by the tension between sustainable practices and traditional development models. This paper presents a literature review examining the domains, dimensions, and indicators related to the sustainability of human well-being regarding economic, social, and natural environments. Emphasizing the multidimensional nature, this paper highlights the drawbacks of relying solely on socioeconomic indicators for assessment. The review explores diverse concepts and methodologies proposed to evaluate the components and multidimensional factors influencing the sustainability of human well-being. Ultimately it offers a holistic understanding serving as a foundation for further research and policy development.
Open Access
Article
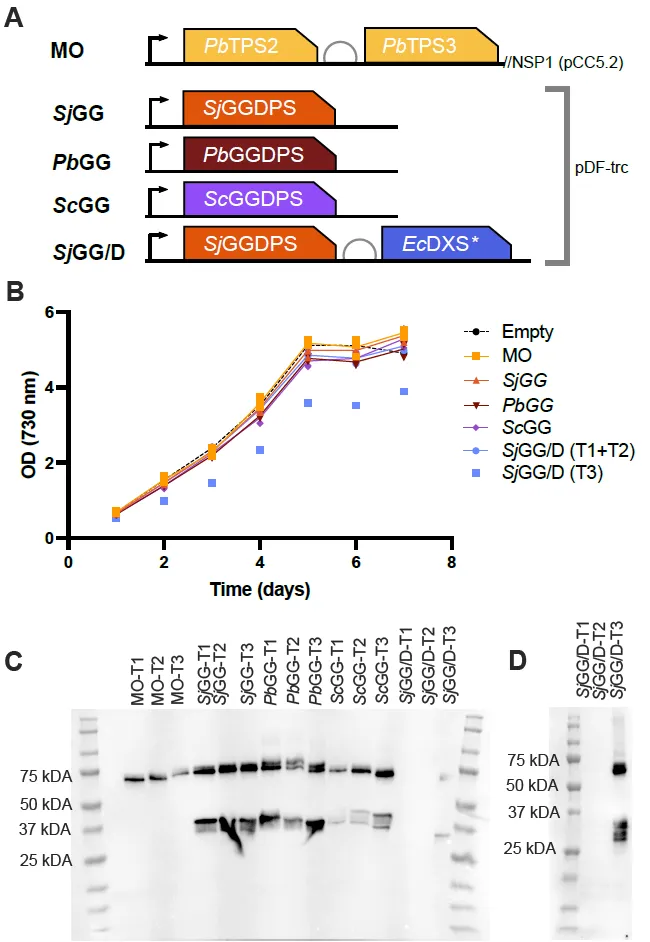
22 March 2024Modulation of the MEP Pathway for Overproduction of 13-R-manoyl Oxide in Cyanobacteria
The cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 has gained scientific interest for its potential to use solar energy and atmospheric CO2 for the production of high-value chemicals like pharmaceuticals, flavors, and fragrances. Forskolin is a diterpenoid found in the root cork of the plant Plectranthus barbatus and its biosynthetic pathway is initiated by two terpene synthases that convert geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGDP) into the precursor 13-R-manoyl oxide (13-R-MO). Using the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 as host, we expressed the two terpene synthases resulting in the synthesis of 0.83 mg/L 13-R-MO. Three different geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthases (GGDPSs) were selected for screening; a prokaryotic (Synechococcus sp. JA-3-3Ab (Sj)), a yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc)), and a plant (P. barbatus (Pb)) derived GGDPS. Strains containing the prokaryotic Sj- or the yeast ScGGDPS consistently yielded more 13-R-MO than the base strain. By overexpression of 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (DXS) positioned at the entry of the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway (MEP) together with the prokaryotic SjGGDPS, the 13-R-MO titer was increased 11-fold to reach 9.7 mg/L by boosting the synthesis of GGDP, the direct substrate for the diterpenoid synthases. We further show that application of a n-dodecane overlay to remove 13-R-MO from the culture medium provided a 2–3 fold increase of the 13-R-MO in a separate cultivation system.