Found 3 results
Review
20 January 2025Adsorption and High-Value Transformation of Volatile Fatty Acids from Microbial Fermentation Products: A Review
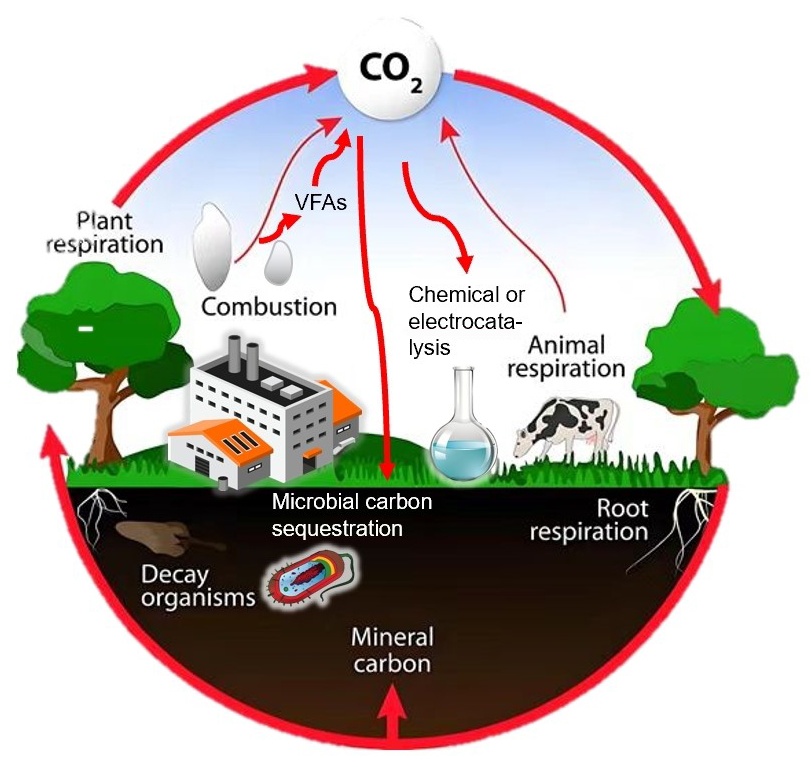
To mitigate the aforementioned global environmental issues, the concept of carbon capture and storage is crucial in addressing the necessity for carbon peaking and carbon neutrality. The buildup of volatile fatty acids during anaerobic fermentation is a primary factor contributing to the suboptimal performance or outright failure of anaerobic digestion systems. In response to the pressing demand for volatile organic acid recovery and high-value conversion, we primarily outlined the sources, recovery techniques, adsorption materials, and methods for high-value conversion of volatile fatty acids. The methods of adsorbing volatile acetic acid were presented, encompassing adsorption materials, mechanisms, and interfacial modifications of the adsorbent. Furthermore, drawing from recent research advancements, we have synthesized the high-value conversion techniques for volatile fatty acids and evaluated the research challenges and future prospects in this domain.
Review
21 February 2024One-pot Multi-enzyme Cascade Synthesis of Bifunctional Compounds from Vegetable Oils
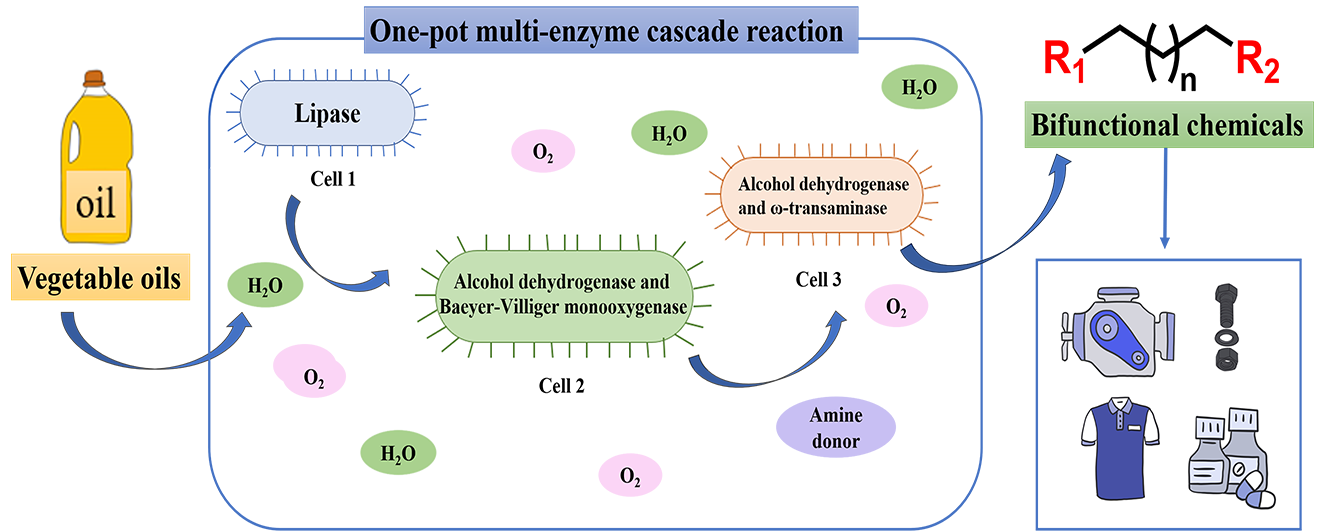
Green and efficient biocatalytic technology has become a complementary or alternative means of organic synthesis. Chemicals with two functional groups, such as α,ω-dicarboxylic acids, ω-amino fatty acids and ω-hydroxy fatty acids, are widely used in the synthesis of polymers such as polyesters and polyamides. In recent years, the production of biodegradable materials using renewable and abundant vegetable oils as green raw materials has attracted increasing attention, receiving an additional impetus from synthetic biology. This paper presents the recent research progress in the production of bifunctional chemicals with medium chain lengths of C8–C12 using multi-enzyme cascades. Recent studies have developed multilevel optimization strategies to improve the efficiency, economics, and sustainability of multi-enzyme cascades. Cofactor regeneration strategies were developed to avoid large additions of expensive coenzymes. Protein engineering strategies were applied to improve enzyme stability and catalytic performance. In addition, blocking the β-oxidation pathway, improving the efficiency of substrate transport across membranes and increasing cellular robustness are effective optimization strategies for whole-cell catalytic systems. In addition, we discuss the development prospects of producing high value-added fine chemicals from vegetable oils using one-pot multi-enzyme reaction systems.
Review
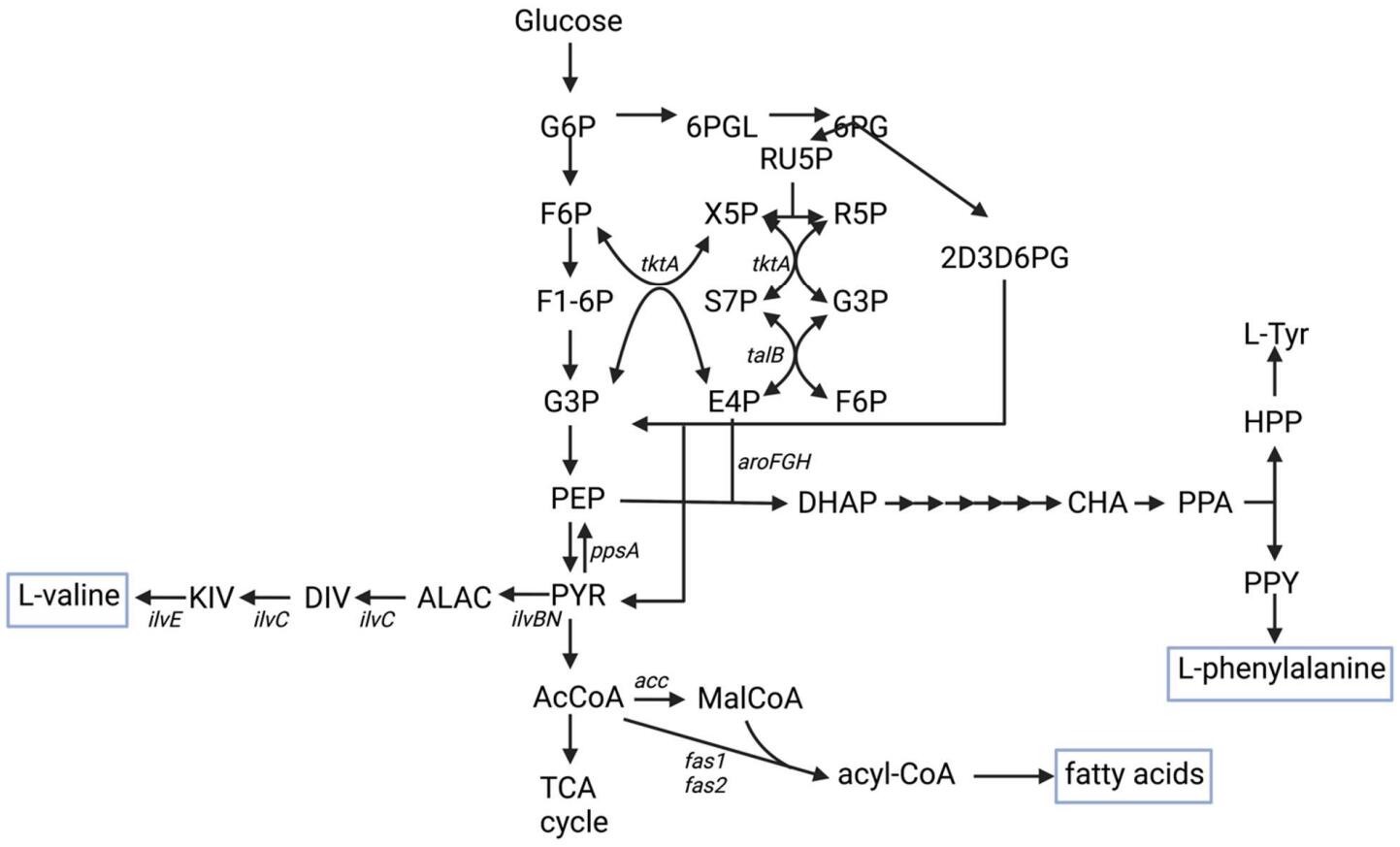
16 February 2023Increasing Nutritional Value of Cyanobacteria by Engineering Valine, Phenylalanine, and Fatty Acid Production
In 2020, the United Nations estimated that 2.37 billion people globally were without food or unable to eat a healthy balanced diet. The number of people with insufficient nutrition has increased in the short term due to COVID-19 pandemic and longer-term climate change is leading to shifts in arable land and water availability leading to a continued need to develop scalable sources of nutrition. One of the options that can yield high food mass per square foot of land use is the high-density culture of microalgae or other photosynthetic microorganisms. While photosynthetic microorganisms may provide high amounts of biomass with a small land footprint, the nutritional value of unmodified microorganisms may be limited. This mini-review presents the base nutritional value in terms of macro- and micronutrients of several cyanobacteria (Nostoc, Anabaena, Spirulina) in relation to established human nutritional requirements as a starting point for better utilization of cyanobacteria as nutritional supplements. It also discusses synthetic biology approaches that have been implemented in different organisms to increase the production of L-valine, L-phenylalanine, and fatty acids demonstrating some common genetic engineering design approaches and some approaches that are organism-specific.