Found 1 results
Article
16 September 2023Hepatic Lysosomal Enzyme Activity in Primary Biliary Cholangitis
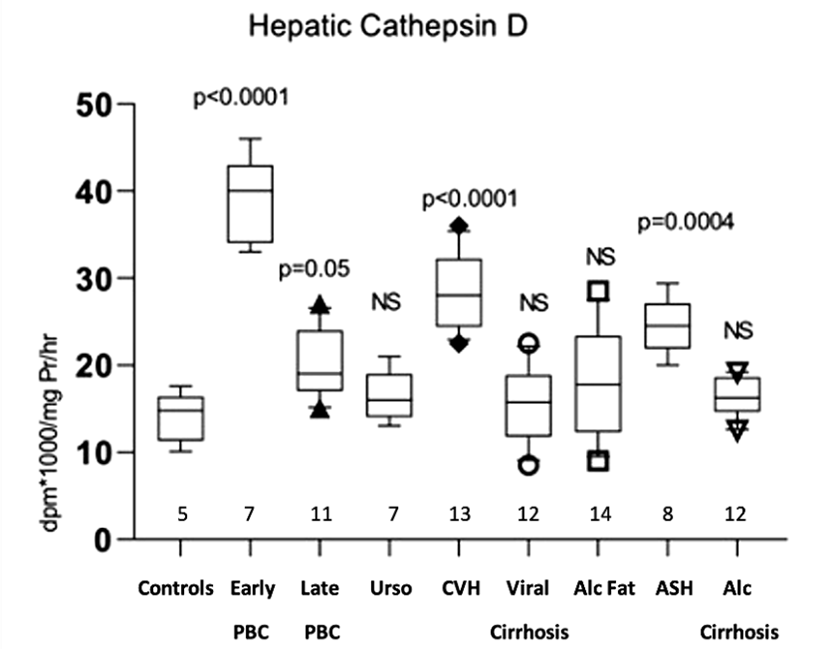
Lysosomal enzymes are implicated in autophagy and senescence. Hepatic lysosomal enzymes have not been studied in Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC). We therefore quantified the activities of lysosomal hydrolases in liver tissue of PBC patients. We compared enzyme activities in liver tissue from PBC patients with normal livers. Alcoholic liver disease and chronic viral disease served as disease controls. Cathepsin B1 was significantly increased in early PBC (225.1 ± 18.06 mean ± SD, p < 0.0001) and reduced in later stages (66.5 ± 9.7, p = 0.004, controls 130.4 ± 14.9). It was reduced in patients with extensive fibrosis such as alcoholic and viral cirrhosis (p < 0.01 and p = 0.004 respectively) but not in chronic hepatitis. Cathepsin D was increased in early PBC (39 × 103 ± 4.8 SD, p < 0.0001) and less so in later stages (20.1 × 103 ± 3.9, p = 0.05, controls 14.1 × 103 ± 2.9). It was also increased in the presence of histological necro-inflammation in hepatitis. Treatment with ursodeoxycholate (UDCA) restored the abnormal values of enzymes in PBC. Lipid hydrolases mostly paralleled the changes of Cathepsins. Sequential measurements in serum of patients with acute alcoholic hepatitis showed that cathepsin B1 gradually decreases, and esterases increase as aminotransferases improve. The increased activity of lysosomal enzymes in early PBC are possibly on line with increased senescence. Treatment with UDCA restores abnormal values. In chronic liver disease, Cathepsin B1 reduction is associated with fibrosis and increased cathepsin D with necro-inflammation. Abnormalities of lysosomal enzymes indicate impairment of the final stage of autophagy in chronic liver disease.