Found 2 results
Open Access
Article
29 October 2025Material Analysis of CNT’s as Conductive Additive for NMC Lithium-Ion Polymer Batteries Cathode Electrode
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are promising conductive additives for lithium-ion polymer (LiPo) batteries. The performance of lithium metal oxide cathodes is highly dependent on the properties of the conductive carbon additive. This study investigates the advantages of CNTs over conventional carbon black for this application. Material properties, including hardness, tensile strength, thermal conductivity, and electrical resistivity, were analyzed and compared using Ansys Granta (CES EduPack 2024 R2) software. The results demonstrate that CNTs are superior in tensile strength (110 MPa), hardness (50 HV), and thermal conductivity (210 W/m·°C). These properties enhance the mechanical integrity of the CNT-based cathode composite, leading to improved battery performance. Furthermore, the electrochemical behavior of CNT/LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 composite cathodes was investigated, focusing on the carbon precursor (methane vs. natural gas) and CNT diameter. At a current rate of 3 °C, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) derived from methane delivered a specific capacity 20 mAh/g higher than those derived from natural gas. This indicates that methane-derived MWCNTs exhibit superior electrochemical performance, which is attributed to reduced polarization and a higher discharge potential. The study also revealed that MWCNTs with a smaller diameter (30–50 nm) performed better at high charge/discharge rates, owing to a higher number of primary particles per unit mass. This analysis aids in understanding material selection and its implications for battery design and lifecycle. The findings serve as a reference for future research exploring the use of CNTs in advanced battery materials.

Open Access
Review
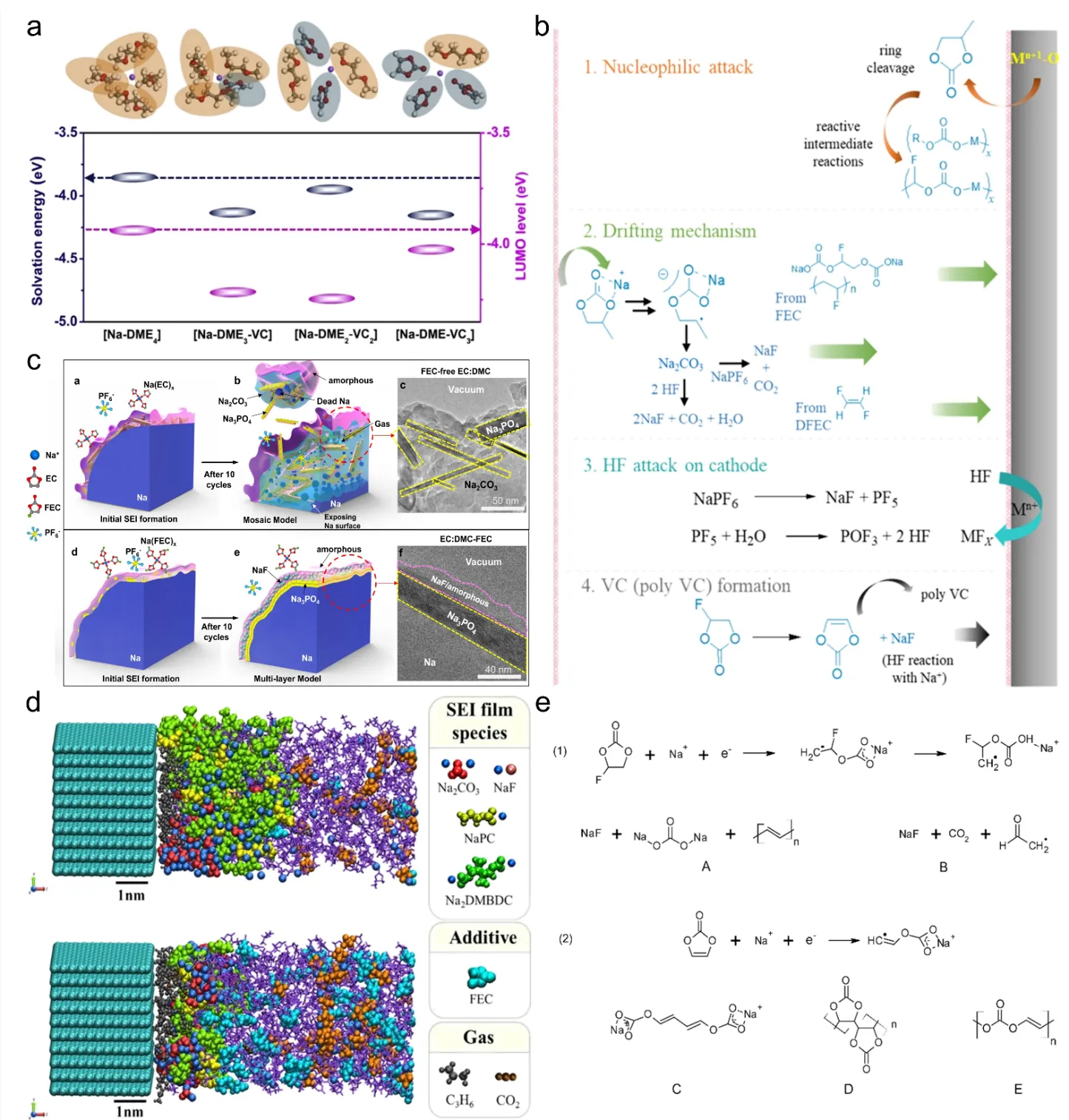
27 March 2024Research Progress on Electrolyte Additives for Sodium Ion Batteries
In view of the gradual depletion of lithium resources, sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) have emerged as a viable alternative to lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). This is primarily attributed to their comparable operational principles and abundant reserves of sodium resources. As an essential component of the secondary battery, the electrolyte is of paramount importance in the functioning of SIBs, and the electrode-electrolyte interface constructed by it affects the battery performance. Adding electrolyte additives in LIBs is a low-cost and efficient method that can enhance the performance of the electrolyte and the interface between the electrode and electrolyte. This method is also applicable to SIBs. Therefore, in this study, we provide a comprehensive overview of various electrolyte additives, including but not limited to carbonate additives, sulfur-containing additives, silicon-containing additives, phosphorus-containing additives and inorganic additives. We extensively analyze the impact of these additives on the electrode-electrolyte interface and the electrochemical performance of SIBs. The purpose of this review is to comprehensively evaluate the current status of electrolyte additives in SIBs, which serves as both a basic overview of the existing situation and a practical guide for selecting suitable additives for practical applications of SIBs.