Found 3 results
Open Access
Review
29 September 2025Robot Grinding: From Frontier Hotspots to Key Technologies and Applications
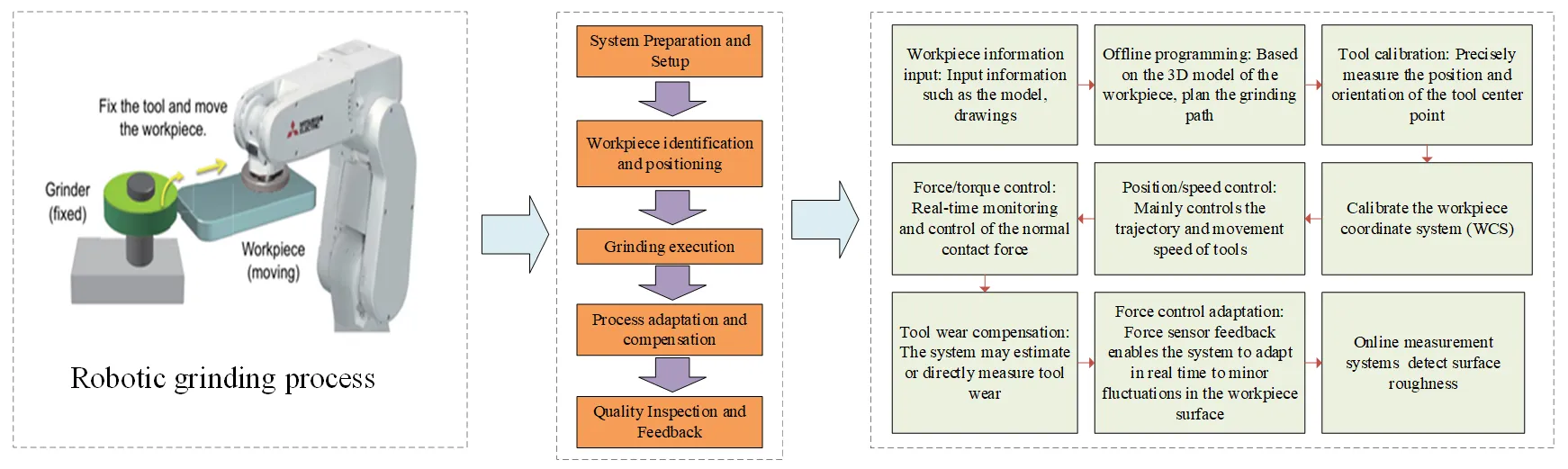
Robot grinding technology has shown broad application prospects in the field of machining complex curved parts due to its high flexibility, strong adaptability, and high automation. However, industrial robots are generally only suitable for rough machining, and for semi-finishing and finishing, improving the machining accuracy of robots and the surface quality of parts is a key issue. This paper summarizes the current research status of robot grinding and provides a reference for realizing robot precision grinding. At present, the research on robot grinding technology mainly focuses on robot pose control, force/position hybrid control strategy, intelligent machining path planning, vibration suppression technology, compliance control, and so on, aiming at solving the key bottleneck problems such as low machining accuracy, large grinding force fluctuation and poor surface quality consistency caused by insufficient robot stiffness. Firstly, the development history of the robot grinding system and the research status of process technology are summarized systematically. Secondly, the analysis focuses on grinding path planning, programming technology, and robot compliance force control technology. Finally, the current status of optimization research in robot grinding technology is summarized. The overarching purpose of this paper is to provide a systematic analysis and a comprehensive reference framework, aiming to address the core challenges hindering the achievement of high-precision, consistent surface quality in robotic grinding manufacturing. Based on the summarized state-of-the-art, robot grinding technology development trend is also predicted.
Open Access
Review
13 March 2025Review on Vibration Control of Wafer Handling Robot
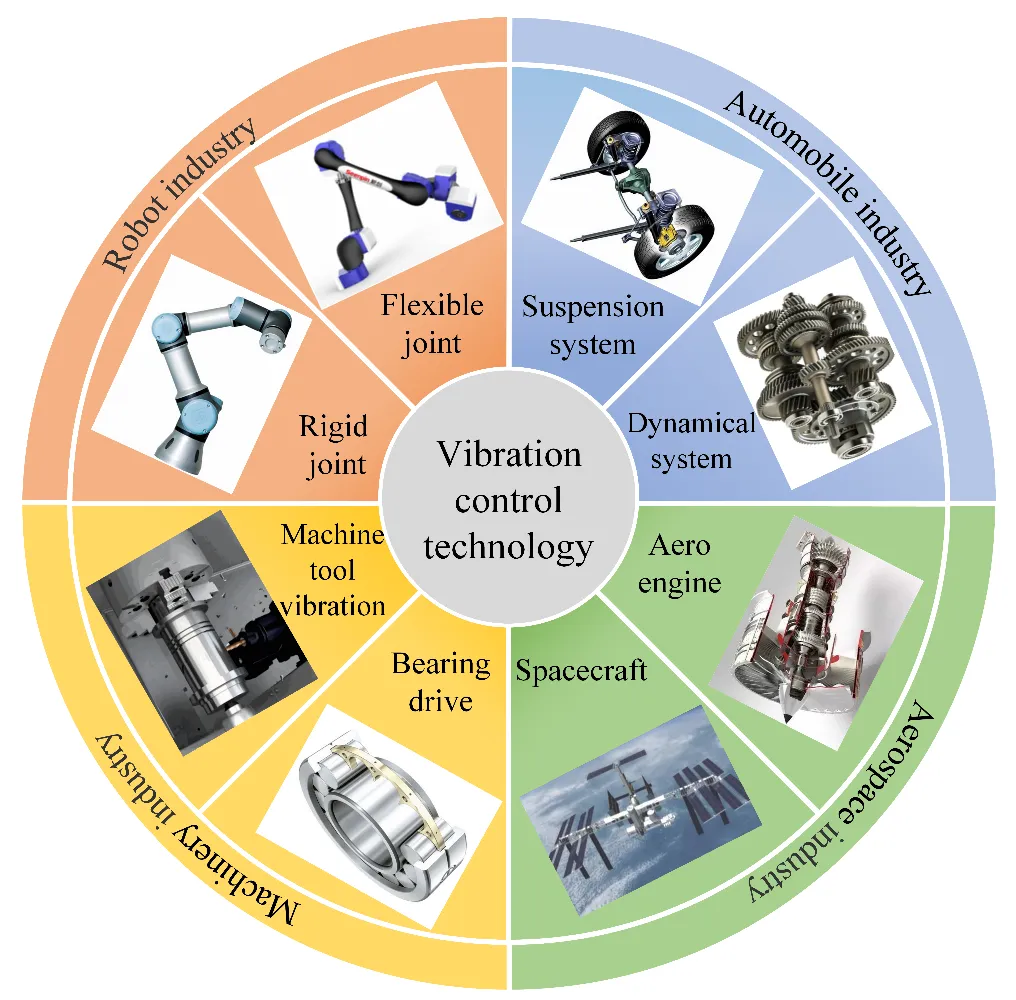
The wafer handling robot serves as the pivotal component of the wafer transfer system, wherein its operational speed and motion precision exert a direct influence on both the yield and productivity of wafer processing. With the semiconductor manufacturing process advancing towards nanoscale linewidths and heightened throughput, the time-varying stiffness characteristics of the flexible joints in wafer handling robots, along with the resultant end vibration issues, have emerged as critical challenges that constrain overall performance. A comprehensive understanding of the stiffness change mechanisms, coupled with enhancements in control methodologies, plays an indispensable role in the effective vibration control of wafer handling robots. To facilitate research in pertinent areas, this paper systematically reviews the cutting-edge methods for vibration suppression in variable stiffness flexible joint wafer handling robots, concentrating on the following core aspects: The impacts of diverse dynamic stiffness identification methodologies on the accuracy of stiffness identification are thoroughly examined; This paper also explores the potential of collaborative optimization strategies involving trajectory planning, control methodologies, and lightweight intelligent algorithms in enhancing real-time control. Furthermore, it evaluates the application scenarios and feasibility of passive vibration absorbers and semi-active adjustable dampers within the context of broadband vibration suppression technologies. In conclusion, this paper synthesizes and critically discusses the advantages and limitations inherent in various research findings, while also constructing a “model-control-vibration suppression” closed-loop optimization system aimed at facilitating ultra-precision vibration control of wafer handling robots under conditions of high dynamic operation. By elucidating the bottlenecks present in existing technologies alongside the trajectory for future interdisciplinary integration, this work provides theoretical support for the intelligent advancement of wafer handling robots and fosters the expedited and reliable development of wafer transfer systems.
Open Access
Review
02 April 2024Mapping the (in)Effective Enforcement of EU Environmental Law in Greece: Lessons from the EU and Domestic Courts
The effective implementation and enforcement of EU environmental law at national level constitutes a thorny issue with both legal and practical aspects. Greece is among the EU Member States which has historically faced difficulties in complying with the EU environmental acquis due to the poor functioning of the Greek administration, the limited manpower, expertise and resources (especially during the recent period of the economic crisis) for the competent authorities, the lack of political will, the low awareness of environmental problems. In this context, this paper aspires to unpack these enforcement challenges at the national level based on the case law of both the Greek Council of State and the Court of Justice of the European Union. Considering that waste management, nature protection, and water and air quality sectors are recognized as areas with the most significant deficiencies in implementation at the domestic level, the analysis will focus on these four key sectors. To this end, by reviewing the relevant EU and Greek jurisprudence, this paper aspires to identify the disparities between the formal requirements and the practical application of EU environmental regulations in Greece in light of the national political, economic, social, and cultural dynamics.
