Found 4 results
Open Access
Review
17 November 2025Enzyme-Mediated Carbon Dioxide Fixation: Catalytic Mechanisms and Computational Insights
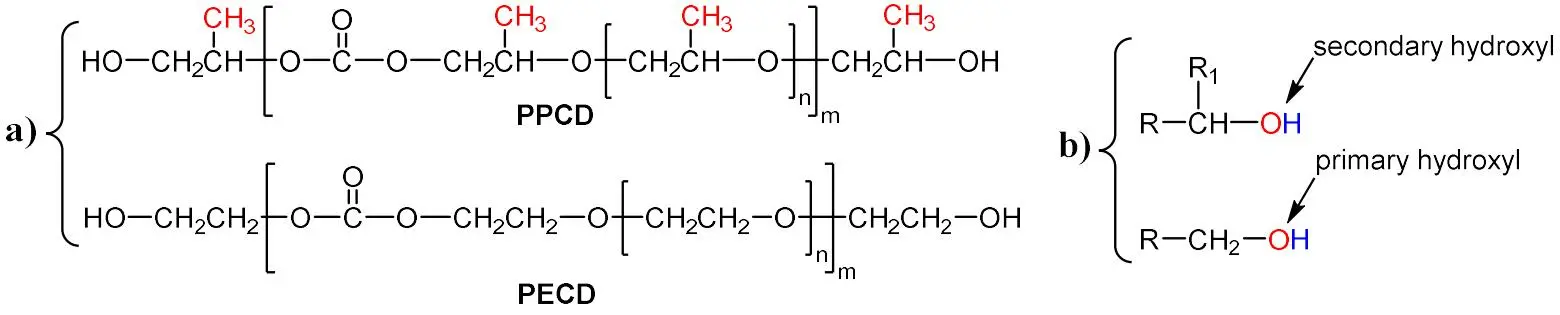
Carbon conversion technologies that transform carbon dioxide (CO2) into high-value chemicals are pivotal for achieving sustainability. Among these, enzyme-mediated CO2 fixation has recently gained increasing attention as a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chemical methods, which typically require harsh conditions and impose significant environmental costs. Recent advances in computer-aided techniques have greatly facilitated the mechanistic understanding of CO2-fixing enzymes and accelerated the development of enzyme-catalyzed carboxylation strategies. This review highlights recent progress in enzyme-mediated CO2 fixation by categorizing key enzymes into four classes based on their cofactor or metal ion requirements: cofactor-independent enzymes, metal-dependent enzymes, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAD(P)H)-dependent enzymes, and prenylated flavin mononucleotide (prFMN)-dependent enzymes. We outline the basic principles and applications of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and quantum mechanical (QM) calculations, which serve as essential tools for investigating enzyme conformational dynamics and reaction mechanisms. Through representative case studies, we demonstrate how computational analyses uncover catalytic features that enhance CO2 conversion efficiency. These insights underscore the critical role of computer-aided approaches in guiding the rational design and optimization of biocatalysts, thereby advancing the application of enzyme-based systems for CO2 fixation.
Open Access
Article
21 November 2024The Impact of Renewable Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, Globalization, and Financial Development on Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Evidence from Selected G7 Economies
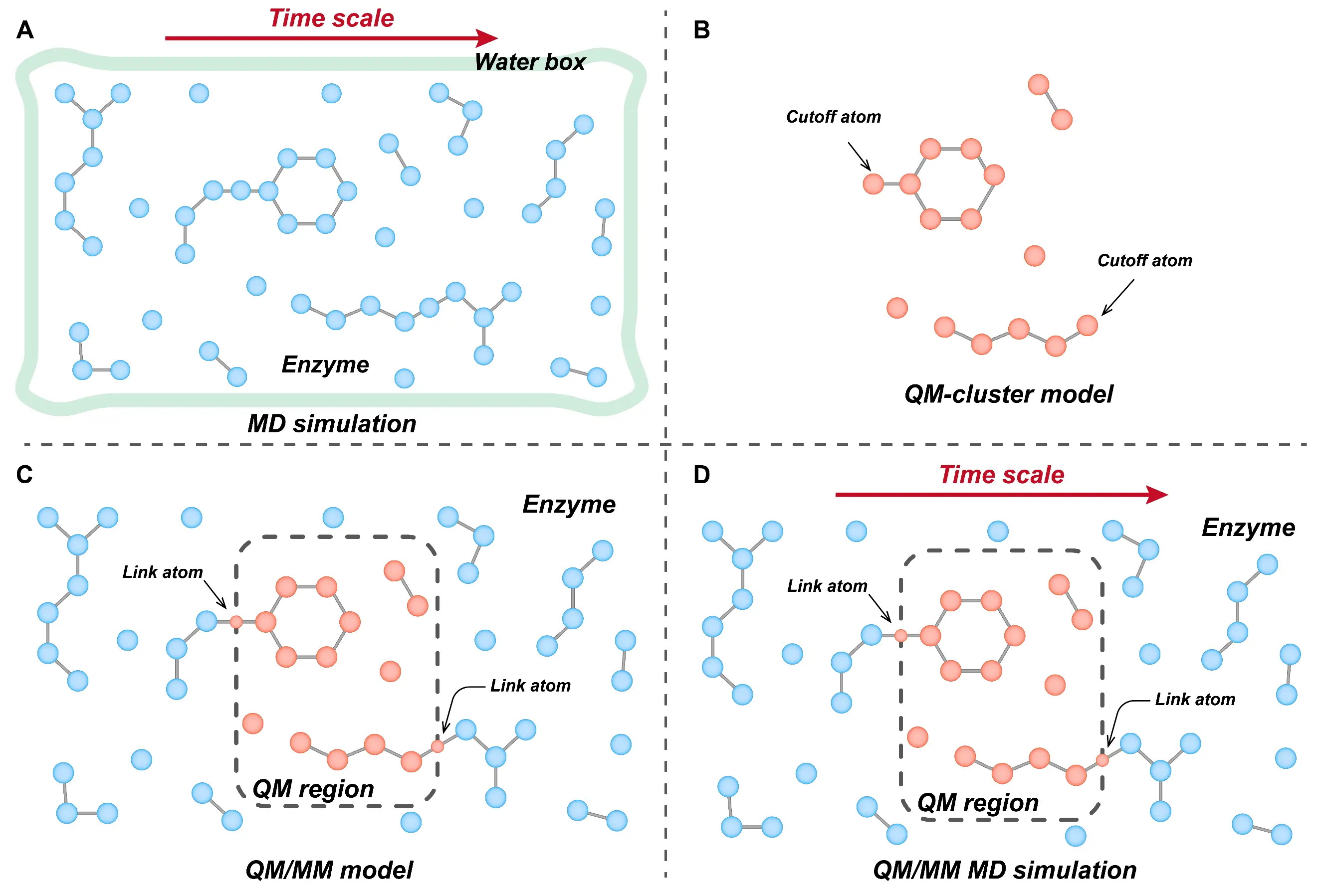
The aggregate upsurge in carbon dioxide emissions (CO2) witnessed through environmental degradation and global climate change is a call for great concern. This, therefore, calls for the enactment, utilization and implementation of provisions and policies geared towards curbing this global economic bad without impeding global economic growth rates. This study ascertains the extent to which renewable energy consumption (REC), economic growth (GDP), population growth (POP), globalization (GLO), and financial development (FD) affect carbon dioxide emissions (CO2) in selected G7 economies (France, Germany, Canada, Italy, and the United Kingdom) from 1990–2020. The Dynamic Fixed Effect Autoregressive Distributive Lag (DFE-ARDL) and the Pooled Mean Group ARDL (PMG-ARDL) methods were employed for analysis. The empirical findings for DFE-ARDL showed that REC, GDP, and POP have an adverse association with CO2 in the long-term. However, in the short-term, REC and FD improve the environment, while GDP and POP drive CO2. It is observed that the result for REC in the short and long-run is consistent. The PMG-ARDL results revealed that REC and GLO negatively affect CO2 in the long-run, and in the short-run, GDP spurs CO2, while FD reduces it. The result summary of both methods employed demonstrates that REC, GLO, and FD benefit the environment. At the same time, GDP and POP harm the environment in the short-run but reduce CO2 in the long-run. Conclusively, the research recommends increasing the utilization of renewable energy and policies that enable economic growth and CO2 to move in the opposite direction.
Open Access
Communication
22 August 2024Mixed Matrix Membranes Produced from a Fluorinated MOF and Pebax for CO2/H2 Separation
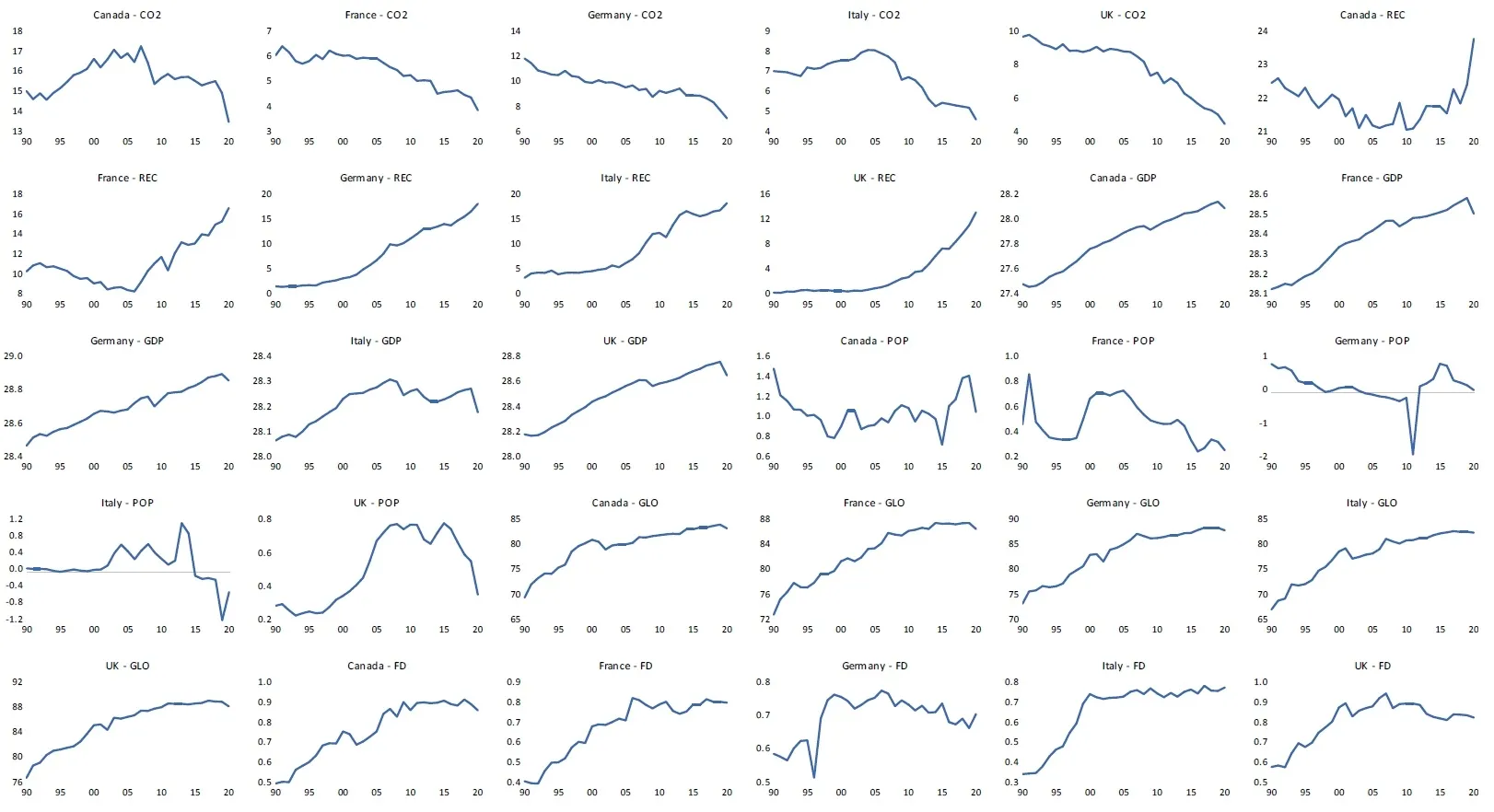
Hydrogen (H2) emerges as a promising clean energy source, but its efficient purification from various sources needs advanced separation technologies. This study explores the use of CO2-selective membranes, especially mixed matrix membranes (MMM) incorporating KAUST-7 metal-organic framework (MOF), for hydrogen purification. The MMM was fabricated with various KAUST-7 content in a polymer matrix (Pebax 1657) and characterized via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and gas permeation tests. The XRD analysis confirms the incorporation of KAUST-7 into the MMM, while SEM reveals a homogeneous particle distribution at low content (below 10%) but agglomeration at higher ones (above 10%). FTIR confirms good interfacial interactions between the MOF and polymer matrix. TGA results show that the MMM thermal stability slightly decreases with increasing MOF content. Gas permeation results reveal improved CO2 permeability (79%) and CO2/H2 selectivity (19%) for MMM compared to neat Pebax membranes, with an optimal performance observed at 10 wt.% KAUST-7. Beyond this threshold, the performance deteriorates, possibly due to polymer rigidity and MOF agglomeration. Overall, the study highlights the potential of KAUST-7/Pebax MMM for enhanced hydrogen purification.
Open Access
Article
21 March 2023Waterborne Polyurethane Dispersion Synthesized from CO2 Based Poly (Ethylene Carbonate) Diol with High Performance
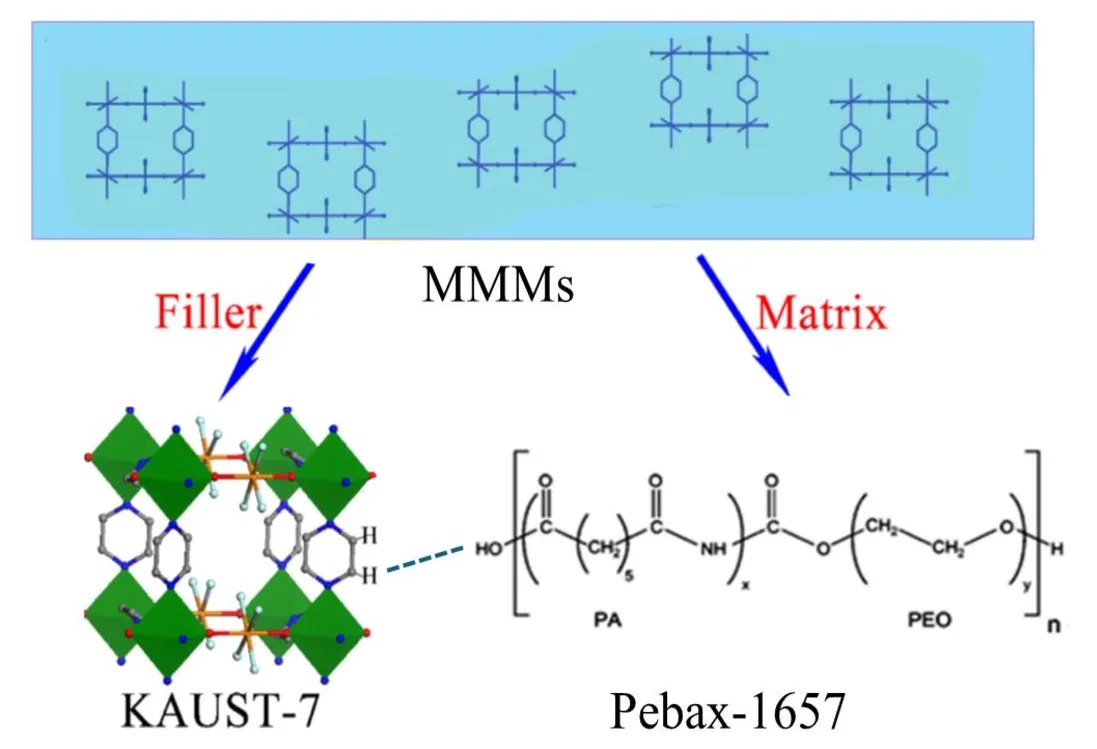
CO2-based aliphatic polycarbonates (APCs) are not widely commercialized due to the poor performance and high cost, compared to the traditional synthetic materials. In this paper, poly(ethylene carbonate) diol (PECD) was synthesized from CO2 and ethylene oxide (EO), and the comprehensive properties were characterized. Furthermore, the preparation and properties of waterborne polyurethane dispersion (WPU) derived from PECD were studied. The result showed that PECD had high reactivity, narrow molecular weight distribution index and excellent thermal stability. The obtained WPU exhibited superior tensile performance, adhesion properties and surface hardness. Due to the low cost of EO and CO2, PECD is expected to be widely used in the preparation of polyurethanes.