Found 2 results
Open Access
Review
09 December 2024Synthesize and Applications of Biodegradable Plastics as a Solution for Environmental Pollution Due to Non-Biodegradable Plastics, a Review
Biodegradable plastics are a potential sustainable alternative to conventional petrochemical-based non-degradable plastics. Due to their lightweight, flexibility, durability, versatile applications, chemical inertness, electrical and heat insulation, and conductivity, plastics have become an essential material for many industries, with annual production currently exceeding 450 million tons. However, these materials are non-biodegradable, leading to detrimental consequences such as the formation of microplastics from improper disposal and the generation of toxic gases, including furans, dioxins, mercury, and polychlorinated biphenyls, from burning plastic waste. This results in environmental pollution, affecting land, water bodies, and the atmosphere. In response, studies where the focus has been on creating bio-degradable polymers such as polylactic acid, polyhydroxy alkanoates, Polycaprolactone, Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate), and Polybutylene succinate, which were extracted from renewable resources or chemically modified as biodegradable polymers. Biodegradable polymers exhibit a wide range of properties and can now be modified to be used in various applications suitable for substituting some conventional plastic products. Thus, the article highlights the critical issue of environmental pollution caused by non-biodegradable plastics and provides a comprehensive overview of the synthesis processes, properties, novel applications, and challenges associated with the use of biodegradable plastics.
Open Access
Review
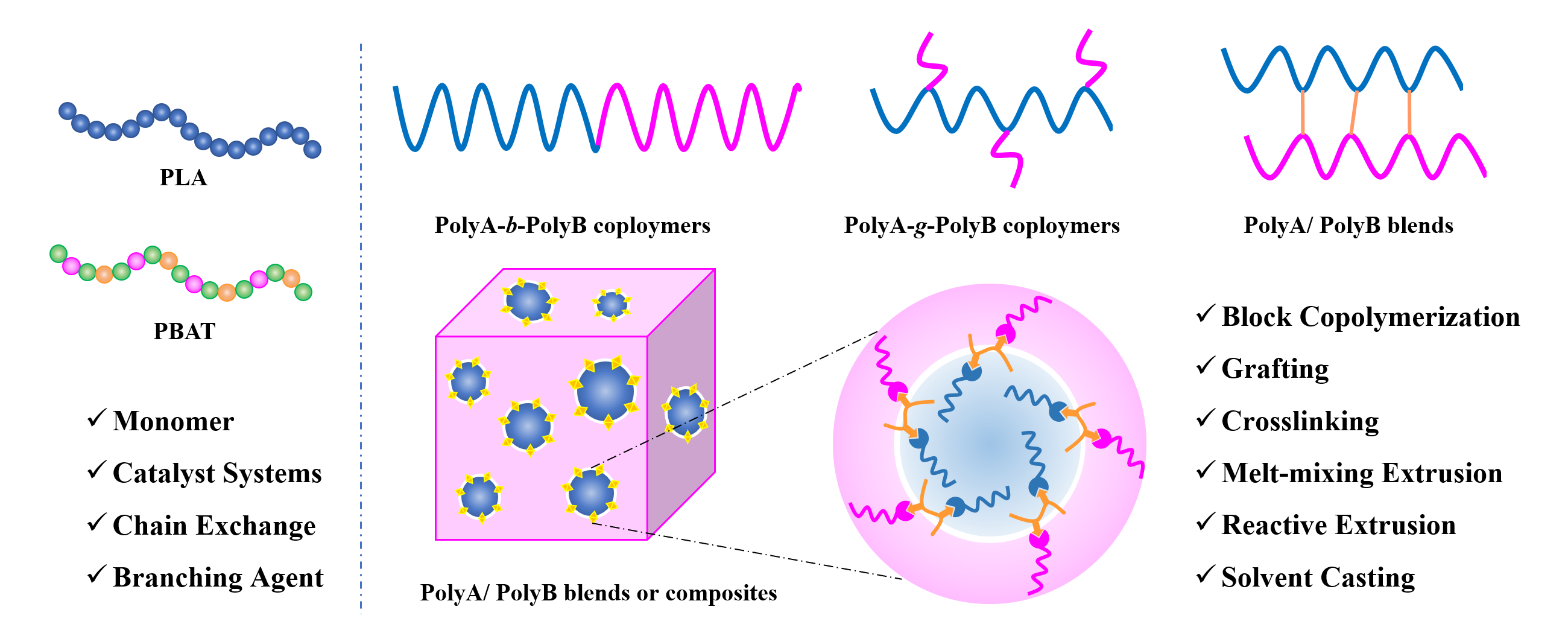
12 April 2023Recent Progress in Modification and Preparations of the Promising Biodegradable Plastics: Polylactide and Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)
The acquisition of high-performance biodegradable plastics is of great significance in addressing the problem of environmental pollution of plastics. Polylactide (PLA) and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) are the most promising biodegradable polymers and have excellent functional properties. However, low elongation at break and impact strength of PLA and low tensile modulus and flexural strength of PBAT hinder their application. A large number of studies focus on improving the performance of PLA and PBAT and broadening their applications. In terms of polymer modification, this paper summarized recent progresses in both chemical and physical modification methods for PLA and PBAT, respectively. The properties of PLA can be improved by co-polymerization, grafting, cross-linking and blending. The properties of PBAT can be improved mainly through blending with other degradable polymers, natural macromolecules and inorganic materials. This review can provide the reference and ideas for the modification of biomass-based biodegradable plastics like PLA and fossil-based biodegradable plastics like PBAT.