Found 1 results
Open Access
Review
15 December 2025Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization Techniques, and Functional Applications of Selenium Heterocycles
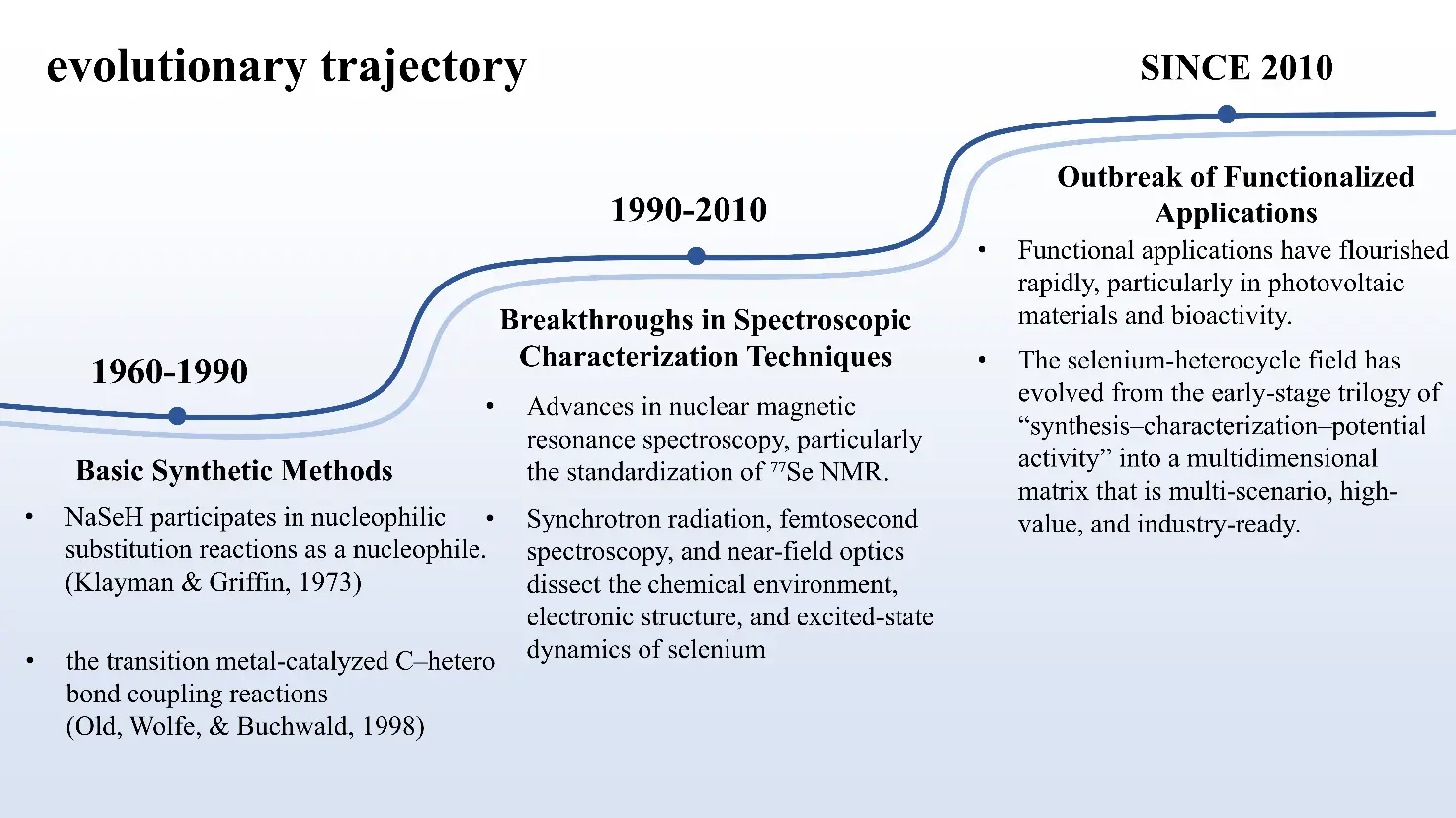
The paper reviews the unique chemical properties of selenium, focusing on selenium-containing heterocycles and organoselenium chemistry. The present study undertakes a critical examination of synthetic strategies, ranging from classical nucleophilic selenation and transition-metal catalysis to emerging photo-redox and electrochemical approaches. The text goes on to highlight advanced characterisation techniques, with particular reference to the combination of 77Se NMR spectroscopy with DFT calculations and single-crystal X-ray diffraction for structural elucidation. The functional applications of these compounds are the subject of extensive discussion, including their role in enhancing the performance of sustainable organic photovoltaic (OPV) materials for renewable energy conversion, and their potential in biomedicine as TrxR inhibitors for cancer therapy and as photosensitizers in antibacterial applications. The present study places particular emphasis on the contribution of selenium-containing heterocycles to improving the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of solar devices. Finally, the review outlines future research directions and common challenges in this field, such as enhancing the sustainability of catalytic processes and addressing biosafety concerns associated with selenium-based reagents.