Found 8 results
Open Access
Article
21 March 2025Additive Manufacturing of Tungsten-Alloyed Tantalum from Polyhedral Shaped Powder Blends
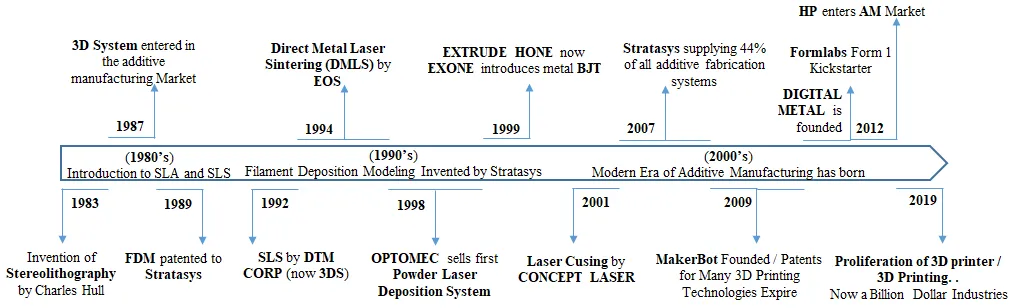
Tantalum and tungsten are completely soluble in each other and are used in applications in the combined form of so-called tantaloys. They provide high melting points (Ta: 3017 °C, W: 3410 °C) and excellent corrosion resistance while maintaining high ductility for W contents up to 7.5 wt%. Providing good resistance to hydrogen embrittlement, Ta-W alloys are attractive candidates for applications in fusion reactors. This study demonstrated the feasibility of producing chemically homogeneous bulk material with fine grained microstructure from non-spherical powder blends with up to 7.5% tungsten using laser powder bed fusion (PBF-L/M). It is observed that cracking remains a challenge, especially with the increase in tungsten content. The effect of rapid solidification on the microhardness of up to 385 HV0.1 for 7.5% W is discussed. It provides initial indications of the possibility of achieving higher strengths and paves the way for further alloy development with regard to the additive manufacturing of this alloy family.
Open Access
Communication
10 March 2025Design Effect of a Mini Channels Heat Sink Using Additive Manufacturing
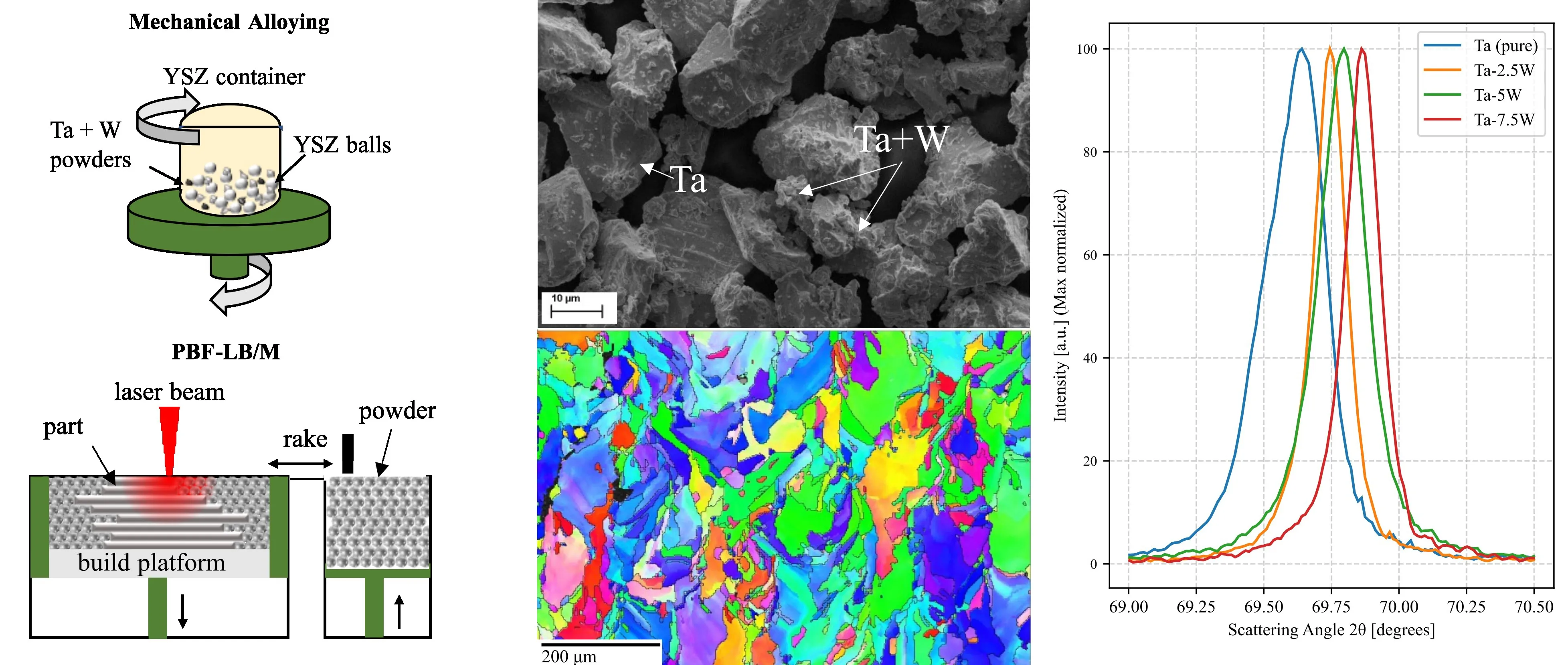
The present work aims to examine the influence of designing mini channel heat sinks using Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing. Stereolithography (SLA) is a common additive manufacturing technique. The internal mini channels of the heat sink are made of aluminium materials and the outer cover is made of commercial polymer. Three models of the mini channel heat sinks are considered. A constant heat flow is applied to the bottom wall of the heat sink, and water is used as a coolant. The flow and heat transfer were studied for different cooling speeds. The physical properties of the fluid provided good thermal performance for the heat sink, especially at increased flow rates. The acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) copolymer resin has shown its good insulator for the heat sink and has improved the performance of the heat sink. This study demonstrates that the ABS copolymer resin enhances the cooling of electronic components.
Open Access
Article
26 February 2025Life Cycle Assessment of Tensile Specimens of Stainless Steel Obtained by Additive Manufacturing versus Conventional Manufacturing
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of additive manufacturing (AM) evaluates the environmental impacts associated with each stage of the process, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. Unlike conventional manufacturing, AM offers significant advantages, such as reduced material waste, optimized designs for lightweight structures, and localized production, which can decrease transportation emissions. However, its environmental benefits are context-dependent, as energy-intensive processes like laser powder bed fusion or high reliance on specific materials can offset these gains. LCA provides a comprehensive framework to assess these trade-offs, guiding sustainable decision-making by identifying hotspots in energy use, material efficiency, and recyclability, ultimately driving innovation towards greener AM practices. This research conducted a cradle-to-gate study of a cylindrical dog-bone tensile specimen. The life-cycle inventory data were obtained from Ecoinvent for conventional manufacturing, while data from the literature review and our research were employed for laser-based powder bed fusion. The results obtained show that the additive manufacturing process is more environmentally friendly. Although the environmental impact is minor, this process consumes a large amount of energy, mainly due to the atomization process and the high laser power. Regarding the mechanical response, AM reduced the ductility but increased the yield strength and achieved the same fracture strength.
Open Access
Review
25 February 2025Innovations in IN939: From Cast Alloy to Additive Manufacturing
Nickel-based superalloys are the most reliable material choice for the hot sections of turbines. These superalloys are mainly employed in aircraft engines, particularly in the combustor and turbine sections. In this scenario, the growing need for materials that can endure high temperatures while retaining their strength has driven the development of IN939. Although IN939 holds these significant important properties and applications, it has received less attention in recent literature than other superalloys. This review aims to comprehensively analyze the main research on IN939 over the past 50 years. From 1970 to 1980, research primarily focused on the development of IN939 through casting methods. Between 1980 and 1990, the emphasis shifted to studying its oxidation resistance and microstructural stability during service. The period from 1990 to 2000 focused on repairing components after long service time at high temperatures. In recent decades, advances in additive manufacturing techniques have led to growing interest in developing IN939 using methods like laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). Research in the area has demonstrated that the LPBF technique offers a promising approach to manufacturing high-performance IN939 components.
Open Access
Article
15 October 2024Binder Jetting 3D Printing Utilizing Waste Algae Powder: A Feasibility Study
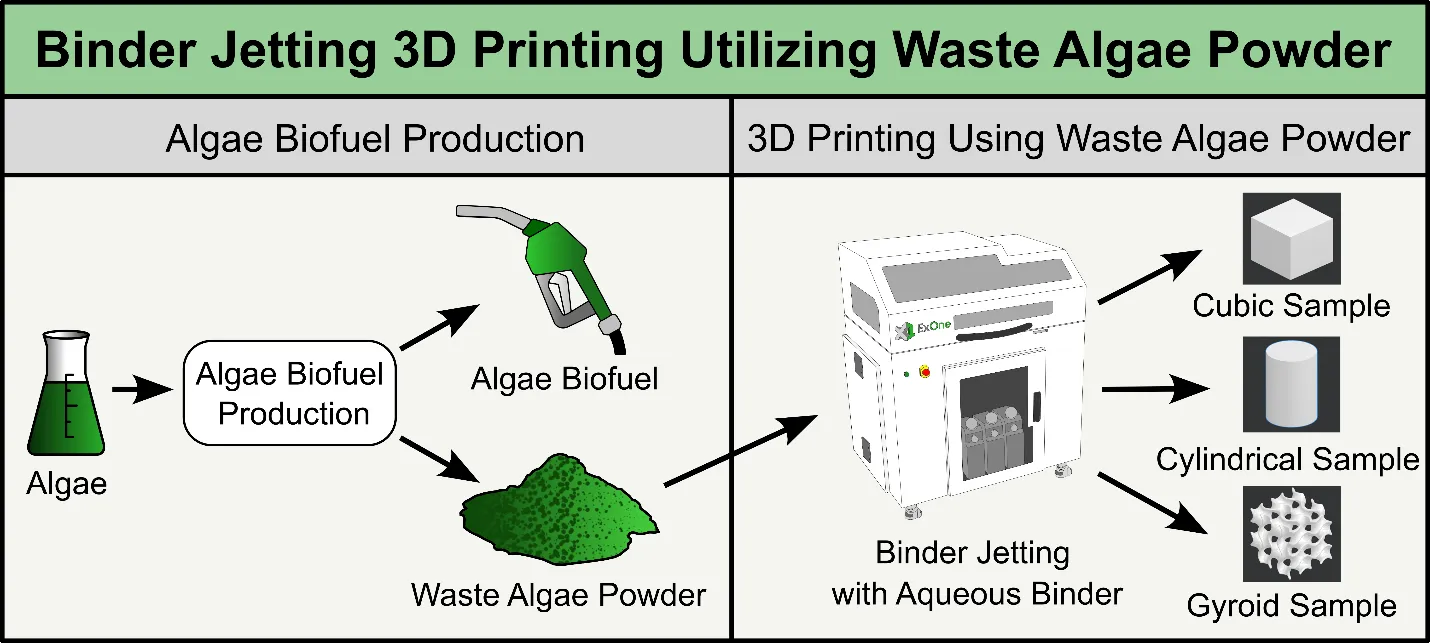
This paper reports, for the first time in the literature, a preliminary study to investigate the feasibility of utilizing waste algae powder (byproducts of biofuel manufacturing from algae) in binder jetting 3D printing to produce environmentally friendly products. In this study, the algae powder’s morphology and particle size distribution were characterized using scanning electron microscopy and particle size analyzer, respectively, and the flowability was assessed through apparent density and repose angle. The algae powder successfully printed the cylindrical, cubic, and gyroid parts on a binder jetting 3D printer. Results show that it is feasible to print parts with binder jetting 3D printing utilizing waste algae powder. The use of waste algae powder in additive manufacturing offers a novel approach to upcycling waste algae powder into valuable products for various applications such as packaging and construction.
Open Access
Article
28 August 2024Metallurgical Characteristics of 316L Stainless Steel by Laser Additive Manufacturing
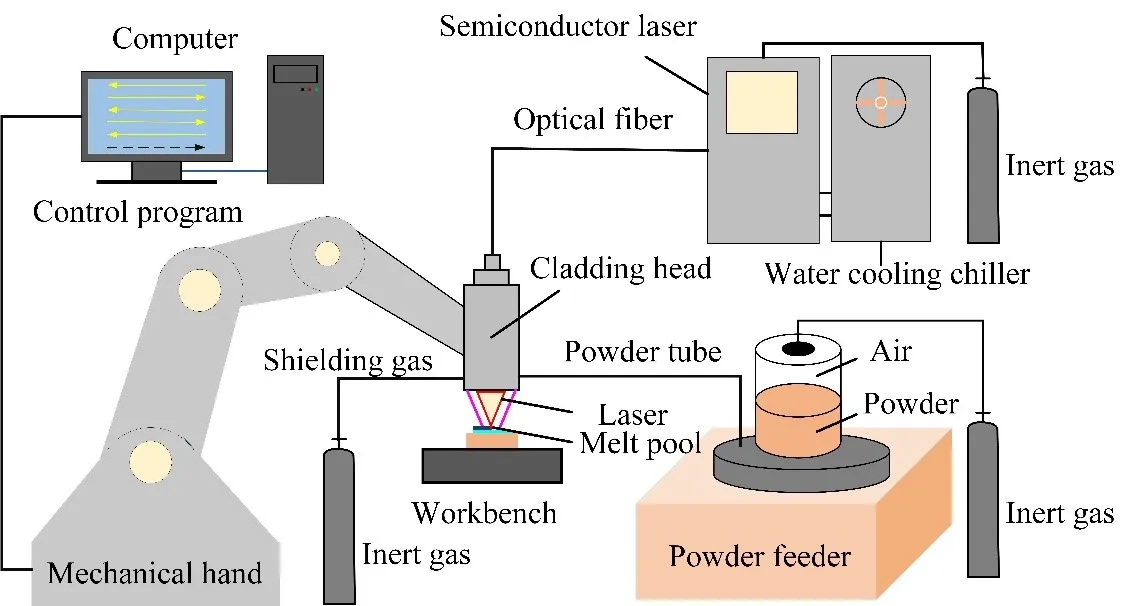
Laser Additive Manufacturing (LAM), an avant-garde technology in manufacturing, harnesses the precision of laser energy to fabricate intricate parts through the meticulous process of melting and subsequently depositing layers of metal powders. Among the esteemed materials employed, 316L stainless steel (316L SS) stands out for its unparalleled corrosion resistance, exceptional high-temperature tolerance, and remarkable creep strength, making it a ubiquitous choice in the aerospace, medical, and nuclear power sectors. LAM has distinguished itself in the fabrication of intricate 316L SS components, yet enhancing the metallurgical bonding strength within these structures remains a pivotal area of ongoing research. This research endeavor delves into the intricate microstructure and mechanical properties that characterize the interface between the LAM-produced 316L SS cladding layer and its substrate, further investigating how varying laser energy densities (E) subtly influence these properties within the additive manufactured components. Remarkably, the interface region exhibits a tensile strength of 615.1 MPa, surpassing that of both the deposited layer and the substrate by 5.4% and 7.4% respectively, underscoring a robust bond between the two layers. This investigation not only sheds light on the unique process capabilities and performance merits of LAM in crafting 316L SS cladding layers but also pioneers novel approaches and conceptual frameworks for bolstering the metallurgical bonding strength of this esteemed material. As such, it constitutes a treasure trove of insights for subsequent research endeavors and practical applications across related disciplines.
Open Access
Review
13 February 20243D Printing Technology for Rapid Response to Climate Change: Challenges and Emergency Needs
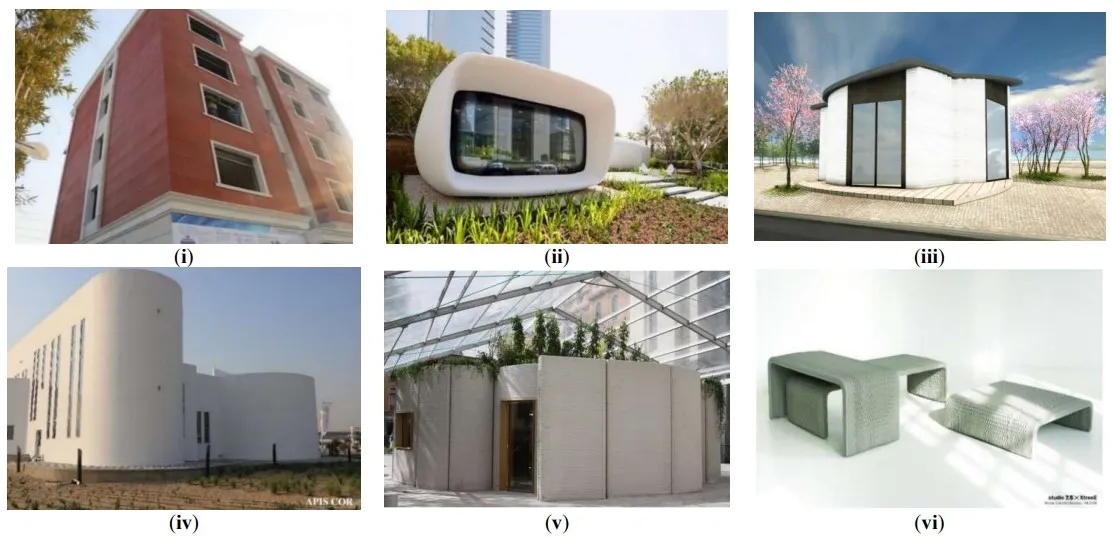
Providing rapid, efficient, inexpensive, and resilient solutions is an eminent and urgent need for emergency relief conditions, mainly and increasingly driven by the impacts of climate change. Under such disastrous circumstances, the current practice involves preparation, dispatching and managing significant amounts of materials, resources, manpower, and transportation of basic needs, which can be hindered remarkably by infrastructure damage and massive loss of lives. However, an emerging technology known as 3D printing (3DP) can play a significant role and rapidly bring unlimited innovative solutions in such conditions with much lesser resources to meet the necessities of large populations affected. Considering the recent progress of 3DP technology and applications in different industrial and consumer sectors, this study aims to provide an analysis of the status and current progress of 3DP technology in various fields to understand and present its potential for readiness and response to disasters, emergency and relief need driven by climate change. Secondly, this study also presents a sustainability assessment of 3DP technology for such cases to evaluate economic, environmental, and social impacts. Finally, policies and strategies are suggested to adapt 3DP technology in different sectors to prepare for large-scale emergencies.
Open Access
Review
17 January 2024A Review on Significant Role of Additive Manufacturing in Biomedical Applications
The rapid development of manufacturing sector has created a platform for implementing novel technologies such as additive manufacturing (AM). AM or 3D printing, has generated a lot of interests in biomedical applications during the last decade with a variety of novel printed polymeric materials. 3D printing fabricates 3D object with layer-by-layer processing through computer-controlled programming software. It has innumerable applications including electronics, aerospace engineering, automobile industry, architecture and medical sectors. One of the most demanding sectors of 3D printing is biomedical engineering applications such as medicines, drug delivery system, surgical instruments, orthopedics, scaffolds, implants etc. The clinical ramifications of AM-made healthcare goods are being catalyzed by recent developments in biomaterials. This review paper aims to explain the concept of 3D printing and its significance in developing polymeric materials for biomedical applications. An inclusive survey has been conducted on the various techniques involved in printing the biomedical devices. The proper selection of polymeric materials is important for biomedical applications, especially from 3D printing point of view and this vital parameter has been considered in this review paper. According to our findings, more breakthroughs in biomaterials, are required for the success and expansion of AM technology in the biomedical applications.