Found 197 results
Review
14 October 2024Photocatalytic Antifouling Coating: From Fundamentals to Applications
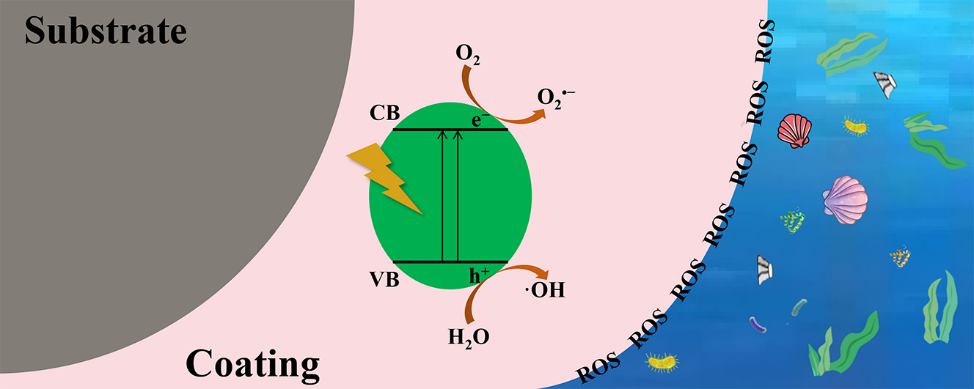
With the rapid development of shipping industry, marine vessels frequently suffer from biofouling caused by marine organisms, making the effective prevention of marine biofouling a critical issue. Traditional antifouling coatings, which utilize toxic and harmful substances, pose significant risks to marine ecosystems. Therefore, the development of environmentally sustainable antifouling coatings has become imperative. Photocatalytic antifouling coatings, as an eco-friendly alternative, present a promising solution to these economic, energy, and ecological challenges. This review compares the environmental benefits of photocatalytic antifouling coatings to traditional ones, highlighting the underlying mechanisms of marine biofouling. Additionally, it explores the preparation techniques employed in photocatalytic antifoulant, analyzing the advantages, disadvantages, and potential modifications for photocatalytic coatings. Based on these insights, the future development of photocatalytic antifouling coatings is discussed, aiming to provide valuable references for the exploration of more efficient, broad-spectrum, energy-saving, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective marine antifouling technologies.
Article
11 October 2024Surfactant Protein-C Regulates Alveolar Type 2 Epithelial Cell Lineages via the CD74 Receptor
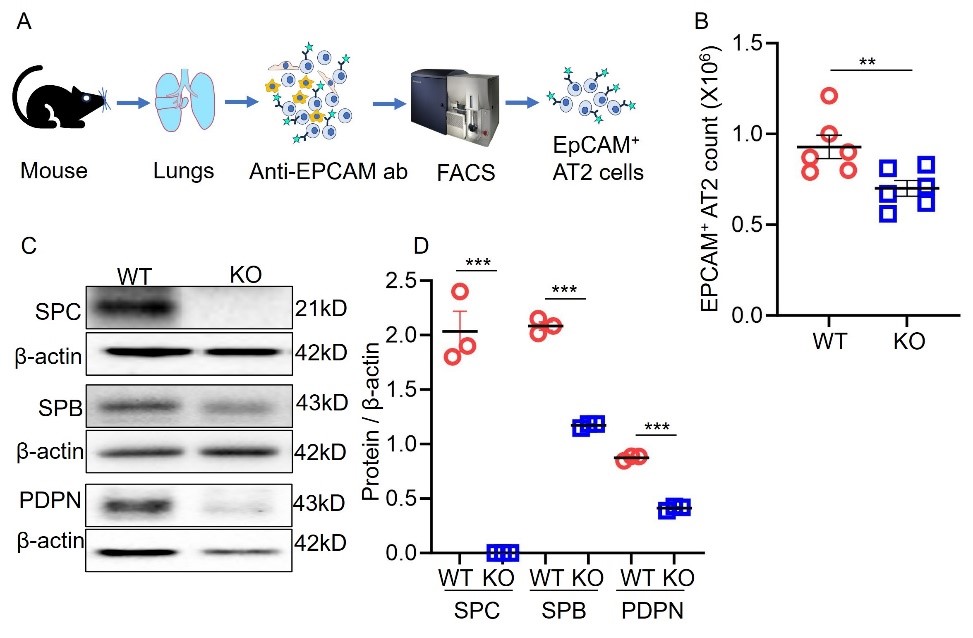
Deficiency of surfactant protein-C (SPC) increases susceptibility to lung infections and injury, and suppressed expression of SPC has been associated with the severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Alveolar type 2 epithelial cells (AT2) are critical for maintenance and repair of the lung. However, the role of the SPC in the regulation of AT2 cell lineage and the underlying mechanisms are not completely understood. This study aimed to investigate the mechanisms by which SPC regulates AT2 lineages. Sftpc−/− mice were used to model the SPC deficiency in ARDS patients. We utilized three-dimensional (3D) organoids to compare AT2 lineage characteristics between wild type (WT) and Sftpc−/− mice by analyzing AT2 proliferation, alveolar type 1 cells (AT1) differentiation and CD74 expression, using colony-formation assay, immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, and immunoblots. The results showed that Sftpc−/− mice demonstrated a reduced AT2 cell population. Influenza A virus subtype H1N1 (H1N1) infected Sftpc−/− mice demonstrated reduced AT2 proliferation and AT1 differentiation. Western blot indicated elevated levels of CD74 protein in AT2 cells of Sftpc−/− mice. Colony-forming efficiency was significantly attenuated in AT2 cells isolated from Sftpc−/− mice compared to the WT controls. Podoplanin (PDPN, a marker of AT1 cells) expression and transient cell count significantly increased in Sftpc−/− organoids. Moreover, siRNA-mediated gene silencing of CD74 in AT2 cells significantly increased AT2 proliferation and AT1 differentiation in Sftpc−/− organoids. This study suggests that SPC regulates AT2 lineage in vitro and in vivo. The SPC might influence AT2 lineage during the lung epithelium repair by activating signaling mechanism involving CD74 receptor.
Perspective
10 October 2024Conceptual Design of Aerostat-Based Autonomous Docking and Battery Swapping System for Extended Airborne Operation
In response to the ever-growing global demand for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, efficient battery solutions have become vital. This paper proposes a design and concept of an Autonomous Mid Air Battery Swapping System for Vertical Take-Off and Landing Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. The proposed design integrates Aerial Mechatronics, Lighter than Air Systems, and Digital Modelling by leveraging the innovative concept of aerostats for battery swapping. This adaptive and effective technology paves the way for the next generation of autonomous Vertical Take-Off and Landing, ensuring a longer flight time and range. Modern-day technologies have empowered Unmanned Aerial Vehicles to operate autonomously and be remotely controlled, expanding their utility across diverse industries. The enhanced Vertical Take-Off and Landing capabilities include the ability to dock on an aerostat-mounted system, facilitating seamless battery swapping without human intervention and ensuring extended flight duration and operational flexibility. These advancements promise to broaden the applications of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles across various industries.

Review
09 October 2024A Review of Multi-Domain Urban Energy Modelling Data
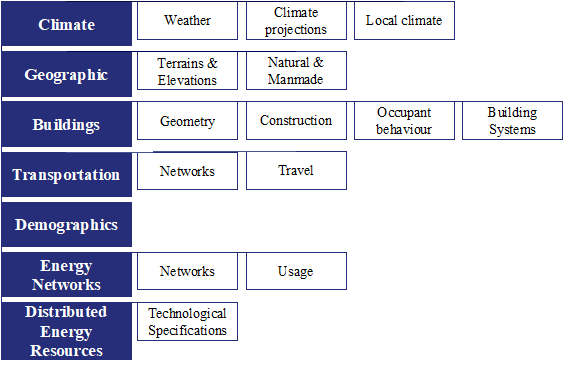
Urban energy models (UEMs) simulate energy use at the urban scale and are used to inform urban planning, policy development, infrastructure development, and digital twin monitoring and forecasting. Recent technological improvements have spurred interest in large, multi-domain UEMs, which analyse multiple interconnected parts of these energy systems, such as geography, transport, and buildings. Reviews have focussed on single domains or aspects of UEM data. However, multi-domain UEMs require detailed multi-domain data inputs to provide accurate results. This paper provides a comprehensive review of data requirements and a repository of data-specific information for researchers, including data formats, sources, acquisition methods, bridging methods, and challenges. The review was conducted using academic search engines and the authors’ direct research experience. Domains are characterised by Climate, Geographic, Building, Transportation, Demographics, Energy Networks and Consumption, and Distributed Energy Resources. Additionally, challenges common to multiple sectors are identified, and methods for addressing these are proposed. The paper concludes with a series of recommendations drawing from the general and sector-specific challenges. Overall, a large amount of data exists, but their use by urban energy modellers is limited due to lack of coordination and standardisation, and concerns over privacy and commercial interests. Coordinated public effort is required to overcome these limitations and improve the results of UEMs in the future.
Communication
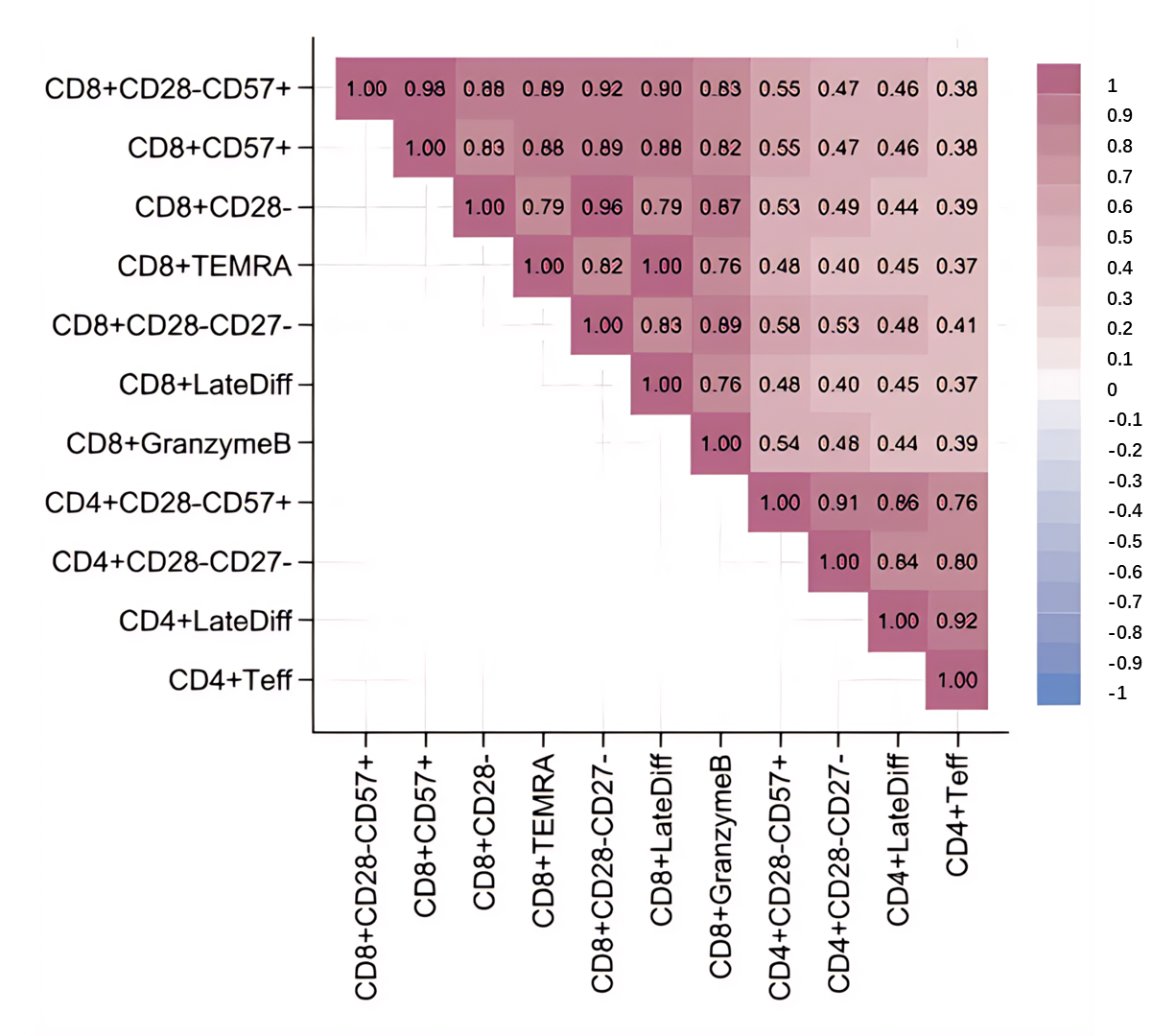
08 October 2024Alterations of T Cell Subsets Associated with Sickle Cell Trait
Sickle cell trait (SCT) has been associated with alterations in various immune-related laboratory parameters including lower circulating lymphocyte counts. To further characterize the impact of SCT on the immune system, we performed flow cytometry of monocyte and lymphocyte immune cell subsets from peripheral blood mononuclear cells collected in a large, community-based cohort of SCT-positive (n = 68) and SCT-negative (n = 959) Black adults. SCT was significantly associated with lower proportions of CD8+ and CD4+ T cell subsets that include senescent-like markers of repeated immune system challenges. These immune alterations could have potential implications for the susceptibility of individuals with SCT to various infectious diseases.
Review
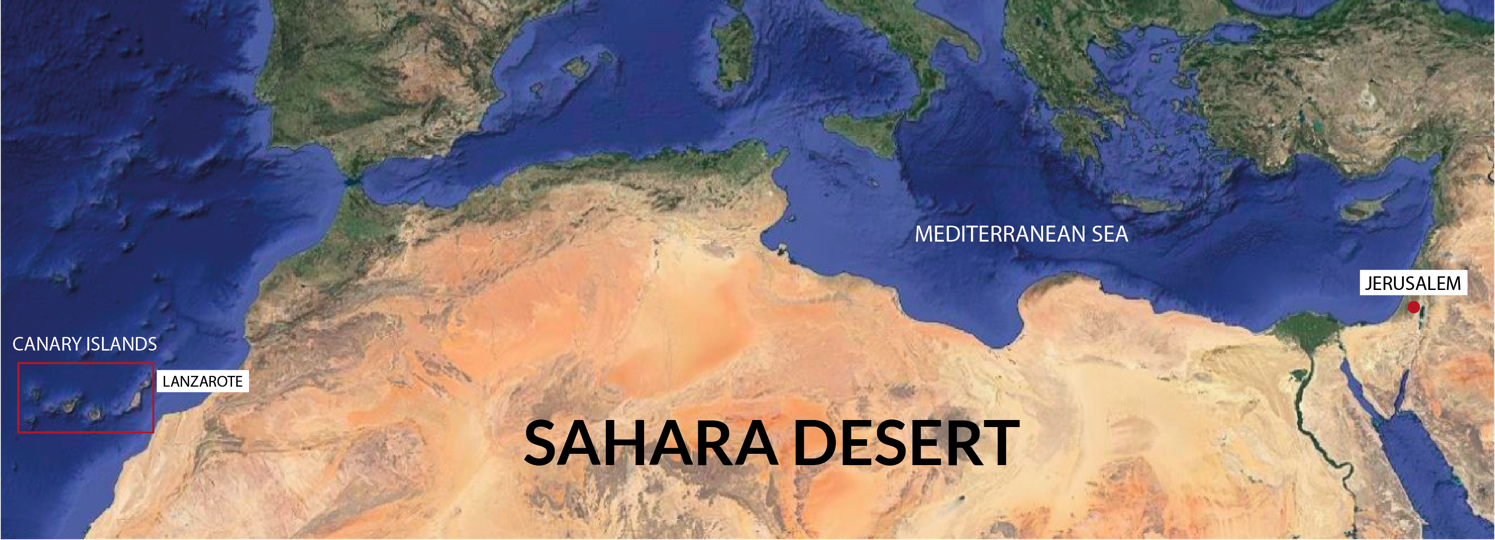
30 September 2024The Jerusalem Megalithic Rock Calendar Is an Identical Representation to That Found in Lanzarote Island (Canary Islands, Spain)
We have recently found that a megalithic basaltic rock lunisolar calendar in Lanzarote, Canary Islands (“Quesera or Cheeseboard” of Zonzamas) has almost a twin monument in Jerusalem (Al Quds in Arab). These two unique monuments are on the West and East sides of the Sahara Desert and support the hypothesis of a common “Green” Saharan culture and a later migration of people towards the Atlantic, Mediterranean, Middle East and other areas when desiccation started after 10,000 years BC, thus spreading culture and genes. Traces of this culture can still be found in Iberian rock inscriptions on the Canary Islands and in the Sahara Desert, particularly at Tim-Missaou in Algeria.This is concordant with Usko-Mediterranean languages (Basque and Berber are related and also with Iberian and Etruscan), genetics and other common anthropological traits. In this paper, we analyse the Al Quds-Jerusalem megalithic monument as representing a solar calendar of Egyptian-type (365 days in 1 year) and show how it could be identical to the Lanzarote megalithic calendar (“Quesera or Cheeseboard” of Zonzamas). Both monuments,each crest/channel, are coincidental in each solar month assignment in both Lanzarote and Jerusalem rock calendars representation. Jerusalem’s megalithic calendar was built at least 900 years BC, when it fell out of use. Therefore, it can be assumed that the Lanzarote megalithic calendar was constructed around a similar time, meaning an undetermined period over 2800 years ago.
Article
29 September 2024Reactions and Phase Transformations at Sintering of Cubic Boron Nitride Based Materials
Superhard cubic boron nitride (cBN) cutting materials with different contents of cBN were investigated. The compositions of cBN-based materials included ceramic and metallic binders. The sintering of materials was performed by high-temperature hot pressing (HPHT) six-anvil apparatus at pressure 4.5 GPa and temperatures 1400–1450 °C. The process of compaction and processing of superhard cBN materials is followed by numerous chemical reactions. The chemical reactions are very important in compaction and sintering. The volume transformations during chemical reactions affect the shrinkage of the materials and may also impact the residual porosity of the finished products. The adhesion between the grains also depends on these chemical reactions. The research analyzed the volume transformations of various reactions during HPHT sintering of cBN materials, which may play a significant role in forming their structure and properties.

Article
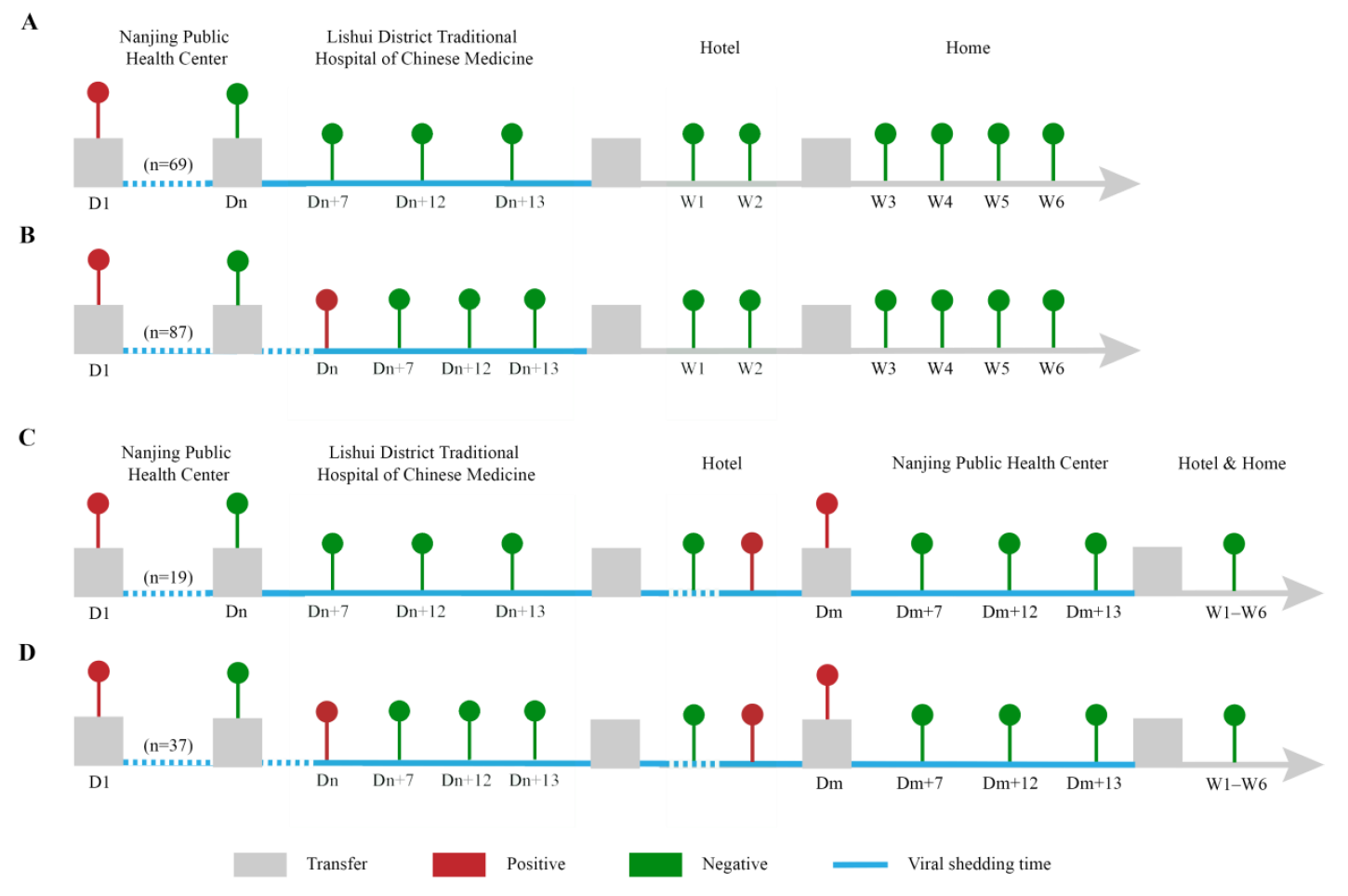
27 September 2024Evaluation of the Efficacy of Chinese Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccines against the Delta Variant in the Nanjing Outbreak: A Cohort Study
Background: The strains of COVID-19 are constantly mutating, and the effectiveness of Chinese inactivated vaccines against the COVID-19 Delta variant has not been described clearly. Methods: The clinical data of patients with the COVID-19 Delta variant in the 2021 Nanjing outbreak were retrospectively reviewed. Results: There were 212 patients with the COVID-19 Delta variant (unvaccinated, n = 56, 26.42%; vaccinated, n = 156, 73.58%) included in our cohort study. The median age was 45.5 (38, 53) years old. Eighty-seven subjects (41.04%) were airport staff, and 94 patients (44.34%) in 32 families were infected. There were 53 (25.00%) and 103 (48.58%) cases with one-dose and two-dose vaccination, respectively, and 55 (25.94%), 147 (69.34%) and 10 (4.72%) had mild, moderate and severe symptoms, respectively. The duration of viral shedding, or viral shedding time (VST), was significantly longer in unvaccinated individuals compared to vaccinated individuals (p = 0.0008). Moreover, the duration was significantly longer in patients who received one vaccine dose than those who received two doses (p < 0.0001). The mild patients had significantly shorter VSTs than the moderate subjects (p < 0.0001). Disease severity and vaccination dose were independent predictors for VST by Cox regression models. Conclusions: These results suggest that two-dose vaccination could reduce VST in patients with the COVID-19 Delta variant. Chinese inactivated vaccines may decrease the disease severity of cases with the COVID-19 Delta variant.
Article
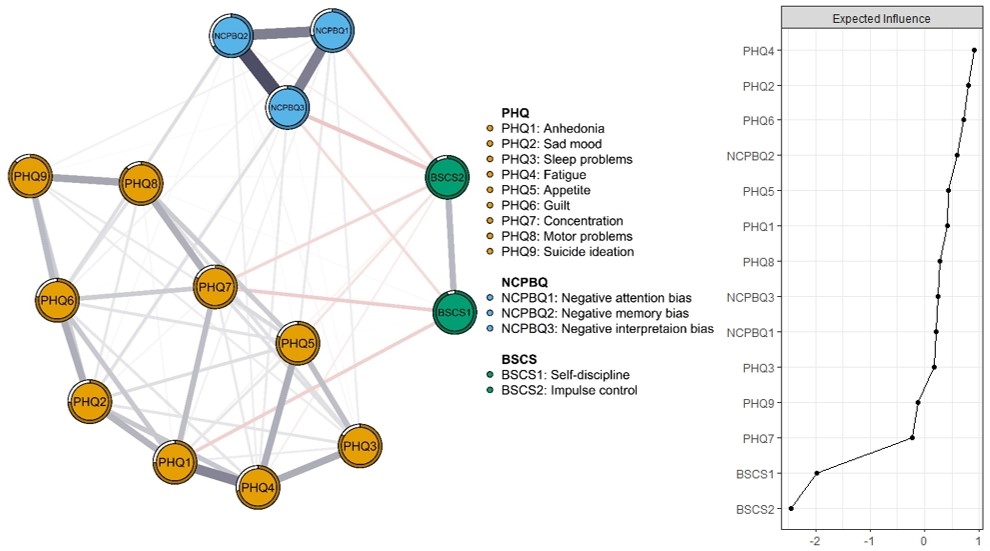
27 September 2024The Relationship between Negative Cognitive Processing Bias, Self-Control, and Depressive Symptoms among University Students: A Network Analysis
Depression is a heterogeneous disease, with individual symptoms uniquely associated with negative cognitive processing bias and self-control. However, studies on the relationships among them from a fine-grained level are lacking. The present study employed network analysis to explore the specific connections among the three constructs based on the dual-process model. Recruiting 1168 Chinese university students, the study estimated a regularized partial correlation network. Depression, negative cognitive processing bias, and self-control were assessed with the nine-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), the Negative Cognitive Processing Bias Questionnaire (NCPBQ), and the Brief Self-Control Scale (BSCS), respectively. Depression nodes fatigue, sad mood, and guilt were the most central symptoms. Negative memory bias, negative attention bias, and guilt were the bridge nodes. Network revealed distinct relations between different negative cognitive processing bias dimensions and depression symptoms, self-control and depression symptoms, and direct antagonistic effects between negative cognitive processing bias and self-control. The current study showed specific pathways between the three communities, and highlighted the role of dual-process model variables in depression development. Focusing on the identified critical depression nodes and related pathways could be effective for depression prevention and intervention.
Article
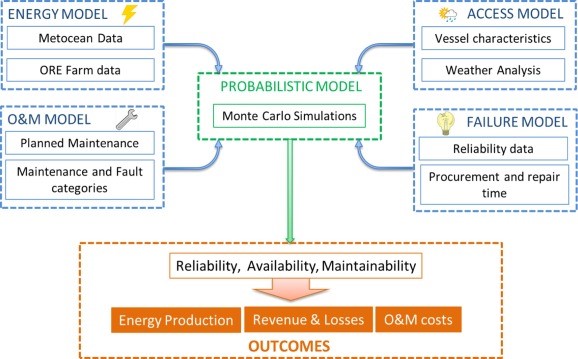
27 September 2024Strategic Deployment of Service Vessels for Improved Offshore Wind Farm Maintenance and Availability
This research explores the optimization of Operations and Maintenance (O&M) strategies for offshore wind farms using a sophisticated O&M simulator built on the Markov Chain Monte Carlo method. By integrating real-world constraints such as vessel availability and weather conditions, the study assesses O&M logistics’ impacts on wind farm availability, energy production, and overall costs across different scenarios in the Celtic Sea. Through comparative analysis of eight case studies involving various combinations of Crew Transfer Vessels (CTV) and Service Operation Vessels (SOV), the research highlights the critical role of strategic vessel deployment and the potential of permanent SOV stationing to enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and lower O&M costs. In this study, the permanent SOV can increase up to 20% availability of the whole wind farm. The findings underscore the importance of adaptive O&M planning in improving the sustainability and financial viability of offshore wind energy projects.