Found 52 results
Open Access
Article
03 April 2025Design, Building and Performance of a New Photocatalytic Reactor Using TiO2-Coated Rings Synthesized by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation
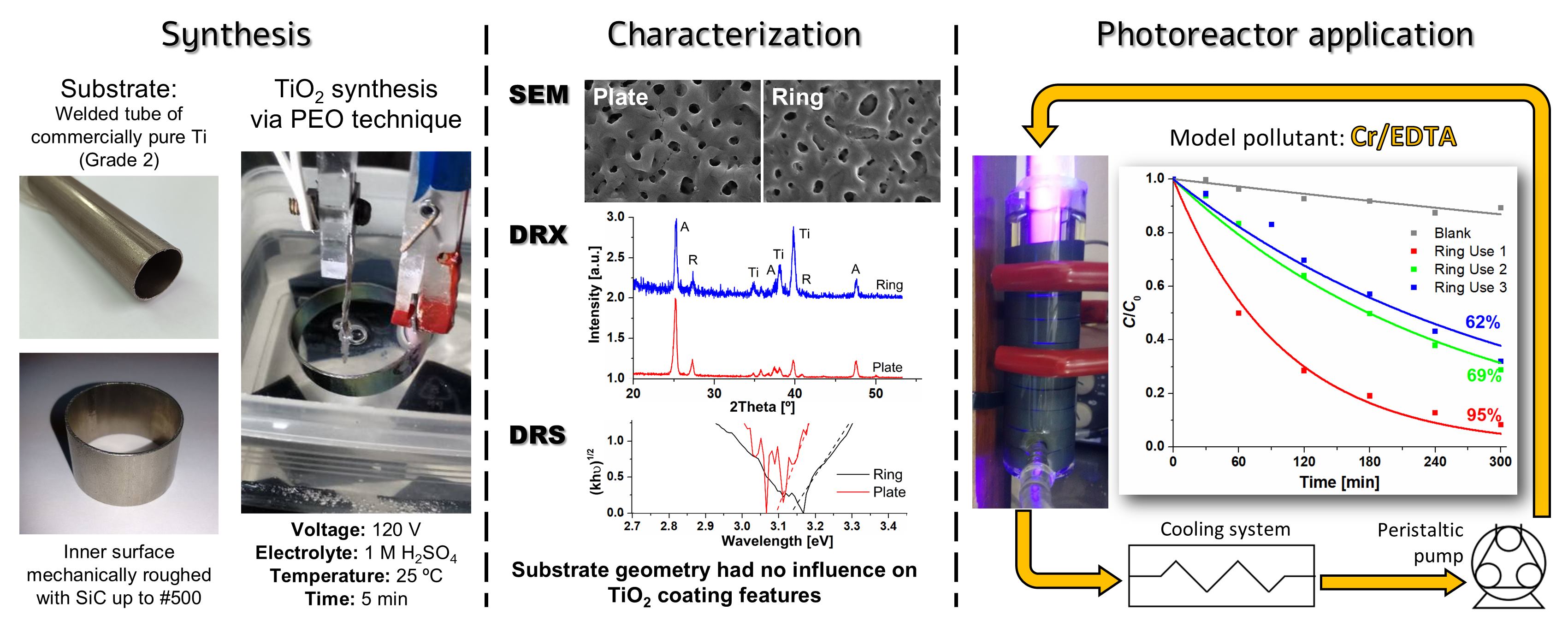
An annular UV photocatalytic reactor with recirculation in batch was designed and built. The design considered low construction, simple operation and maintenance costs, availability and durability of the materials used, easy cleaning, and high standards of hygiene and safety. The TiO2 photocatalysts were synthesized by plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) on commercial Ti rings were compared with coatings obtained on Ti plates as a reference, and no influence of the substrate geometry on the morphology, crystallinity, or bandgap of the coatings was observed. The efficiency of the photocatalytic reactor using 10 TiO2-coated rings was tested by Cr(VI) transformation in the presence of EDTA. The Cr(VI) transformation after 5 h irradiation attained 95%; a rather high photocatalytic activity (62%) was maintained after the third use of the rings without reactivation of the photocatalyst. These coatings synthesized by PEO have not been applied in modular photocatalytic reactors until now.
Open Access
Review
02 April 2025Wide-Bandgap Semiconductors: A Critical Analysis of GaN, SiC, AlGaN, Diamond, and Ga2O3 Synthesis Methods, Challenges, and Prospective Technological Innovations
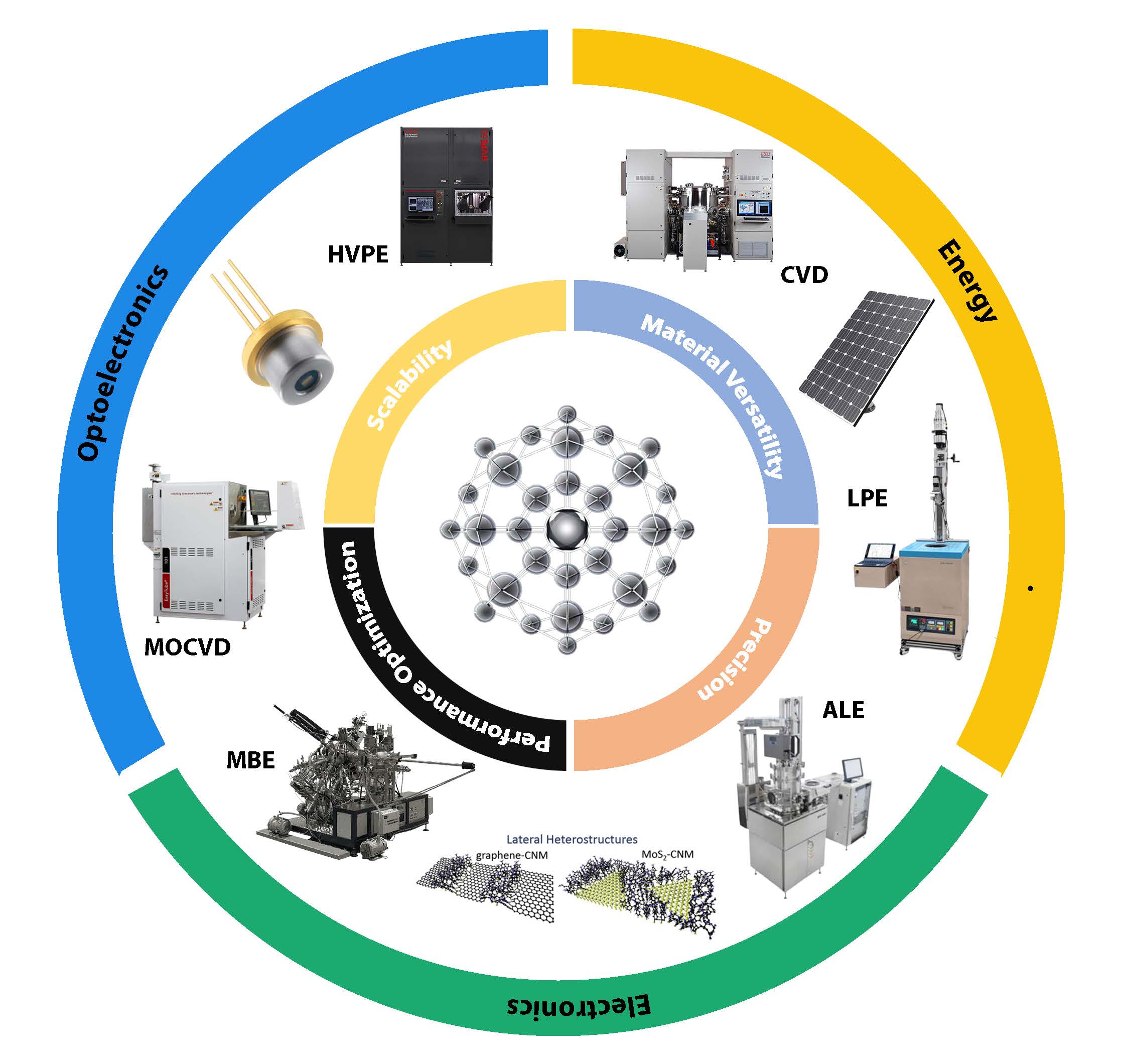
The increasing demand for high-performance Wide-Bandgap (WBG) semiconductors, including GaN, SiC, and emerging Ultrawide-Bandgap (UWBG) materials such as Ga2O3 and diamond, has driven significant advancements in epitaxial growth techniques. However, achieving scalability, defect-free growth, and sustainability remains a major challenge. This review systematically evaluates Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE), Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD), Hydride Vapor Phase Epitaxy (HVPE), and other novel growth and hybrid growth techniques, emphasizing energy efficiency, defect control, and environmental impact. Industry 4.0-driven AI-based process optimization and closed-loop recycling have emerged as transformative strategies, reducing waste and improving manufacturing efficiency. Key findings reveal that HVPE enables rapid defect-free GaN fabrication, Hot-Filament CVD enhances SiC growth with superior thermal properties, and Atomic Layer Epitaxy (ALE) achieves sub-nanometer precision crucial for next-generation quantum and RF applications. Despite these advancements, p-type doping in UWBG materials, substrate compatibility, and thermal management remain unresolved challenges. Future research must focus on scalable eco-friendly epitaxy, novel doping mechanisms, and policy-driven sustainability efforts. This review provides a comprehensive roadmap for sustainable WBG semiconductor manufacturing, bridging materials innovation, energy efficiency, and industrial adoption to support the next generation of power electronics and optoelectronics.
Open Access
Review
01 April 2025Sustainable Manufacturing and Applications of Wide-Bandgap Semiconductors—A Review
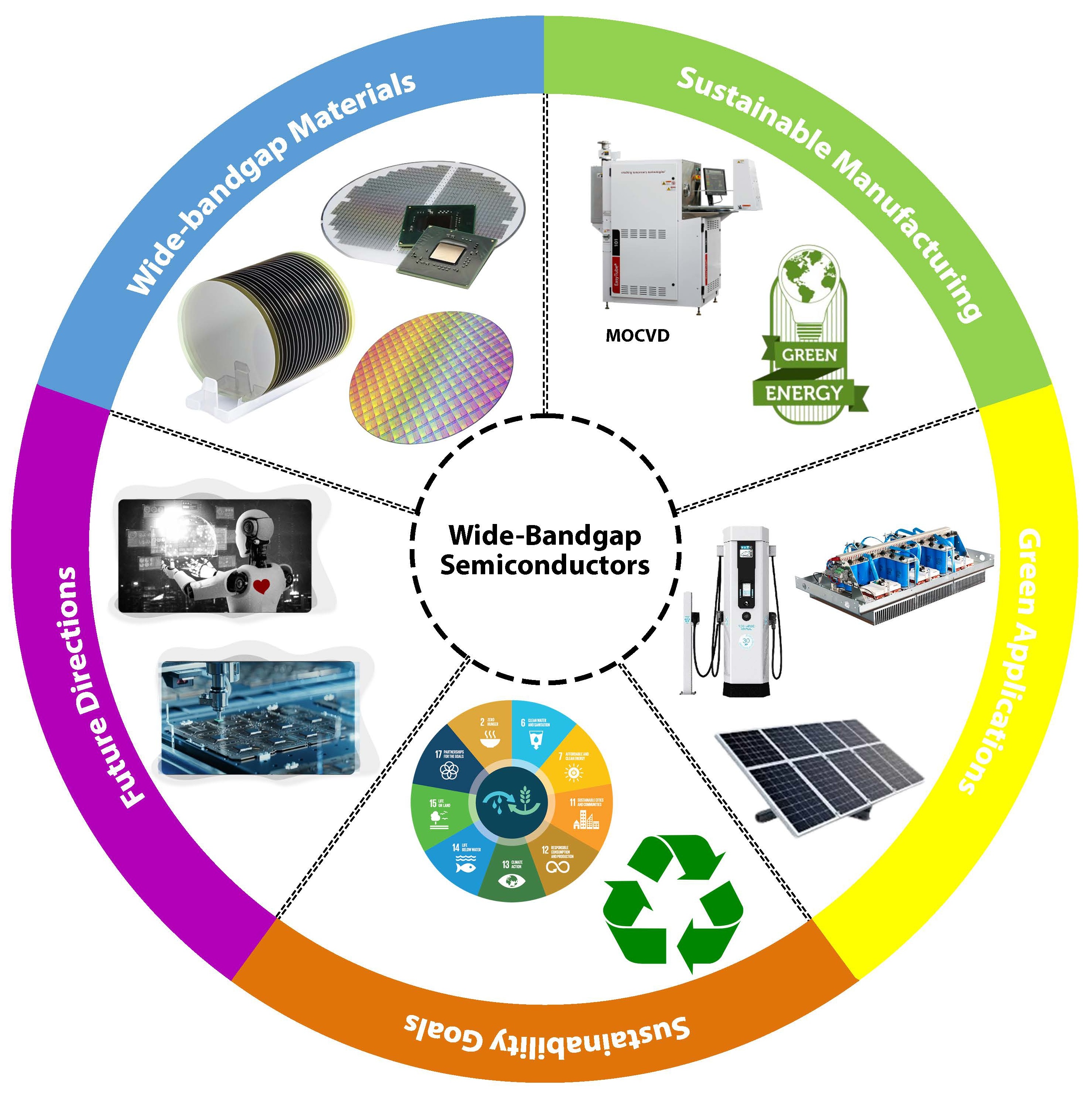
Wide-bandgap (WBG) semiconductors such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) are revolutionizing high-power electronics due to their superior thermal conductivity, breakdown voltage, and energy efficiency. These materials are critical in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and high-frequency applications like 5G infrastructure. However, their production processes are resource-intensive and present significant environmental challenges. This review evaluates recent advancements in sustainable WBG semiconductor manufacturing, focusing on low-energy epitaxial growth, closed-loop recycling, and the mitigation of toxic by-products. Additionally, it highlights the role of Industry 4.0 innovations, such as AI-driven process optimization and IoT-based resource management, in enhancing sustainability. The review identifies research gaps in cost reduction, alternative WBG materials like Gallium Oxide (Ga2O3) and Diamond, and scalable green manufacturing solutions. It underscores the necessity for industry-wide collaboration and regulatory frameworks to drive the adoption of eco-friendly semiconductor fabrication. The findings of this study provide a roadmap for advancing sustainability in WBG semiconductor production, ensuring their long-term viability in the transition toward energy-efficient technologies.
Open Access
Article
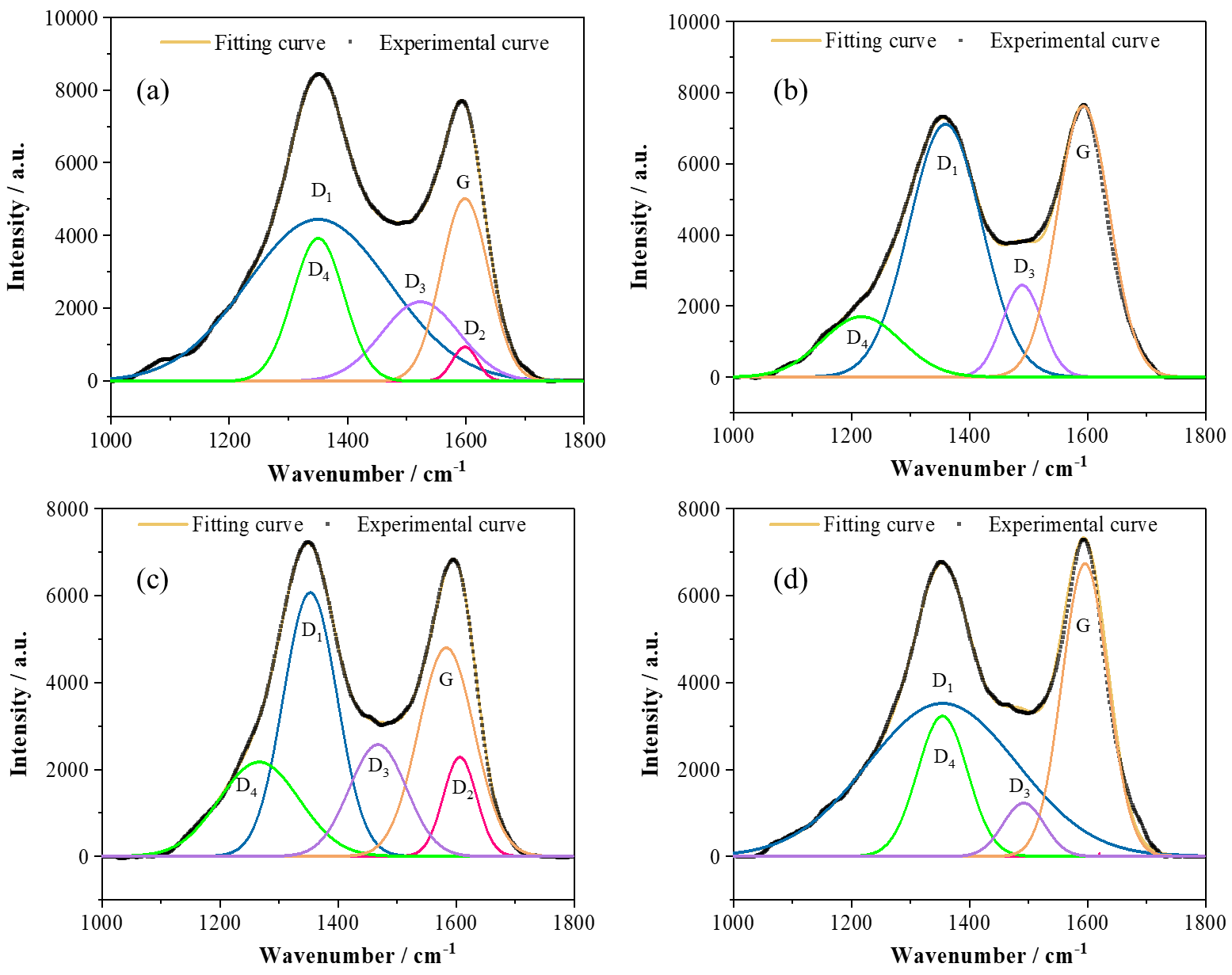
25 March 2025Kinetic and Experimental Analysis of the Effect of Heating Rate on Combustion Performance of Cokes
Under the continuous advancement of the dual-carbon strategy, enhancing the efficient utilization of coke as the primary fuel in sintering processes holds significant importance. This study employed multiscale techniques (XRD, Raman, TG-DTG, DSC, and kinetics) to investigate four types of coke (JY, JH, MJ, WG), establishing a structure-activity relationship between microstructure, heating rate, and combustion behavior for sintering optimization. With high graphitization and ordered structure, JH coke shows rising activation energy under increasing heating rates, which is ideal for stable low-temperature combustion and SO2 reduction. In contrast, WG coke exhibits a defective structure and declining activation energy, enabling rapid high-temperature combustion (>800 °C) with minimal CO emissions via staged combustion. JY coke displays erratic activation energy due to high ash and structural disorder, necessitating pre-screening and blending for controllability. MJ coke achieves stable activation energy through compositional homogeneity and moderate structure, balancing dynamic temperature gradients but requiring ash distribution control to limit liquid phase formation. Heating rate critically modulates combustion: elevating from 5 to 15 °C/min broadens combustion intervals, shifts exothermic peaks from narrow-sharp to broad-high profiles, and enhances reactivity. WG excels at high rates with peak combustion rates and optimal performance. These findings reveal structure-dependent activation energy trends: ordered structures (e.g., JH) resist thermal activation at higher rates, while defective configurations (e.g., WG) promote reactivity. Strategically, JH and WG suit complementary thermal zones. This work provides a structure-activity framework for coke selection and technical pathways to achieve energy-efficient, low-emission sintering, advancing the industry’s low-carbon transition.
Open Access
Article
17 March 2025A Strategy for Resisting the Vested Interests Driving the Collapse of the Biosphere and Civilisation
The biosphere and civilisation are facing existential and other major threats: climate change, biodiversity loss, nuclear war, social inequality/injustice, loss of human rights, and autocracy. These threats are driven by politically powerful vested interests supported by an economic system based on the exploitation of the environment and most people for the benefit of a wealthy minority. This article proposes a strategy to resist and weaken state capture, i.e., the influence of the vested interests driving the principal threats, while simultaneously facilitating the transition to a sustainable society. Despite the achievements of diverse community-based non-government organisations (CNGOs) campaigning on specific issues, scientists are now warning of the potential collapse of civilisation. As the threats are linked together in several ways, I propose a strategy to address them together to yield multiple benefits, supplementing campaigns on individual issues. A broad social movement—comprising an alliance between CNGOs devoted to the environment, social justice, human rights, and peace—could exert sufficient political power to expose and defeat the methods of state capture. Simultaneously, the movement could gain widespread community support by campaigning for a well-being economy, including universal basic services and a job guarantee, thus facilitating the transition to an ecologically sustainable, more socially just, and more peaceful civilisation.

Open Access
Review
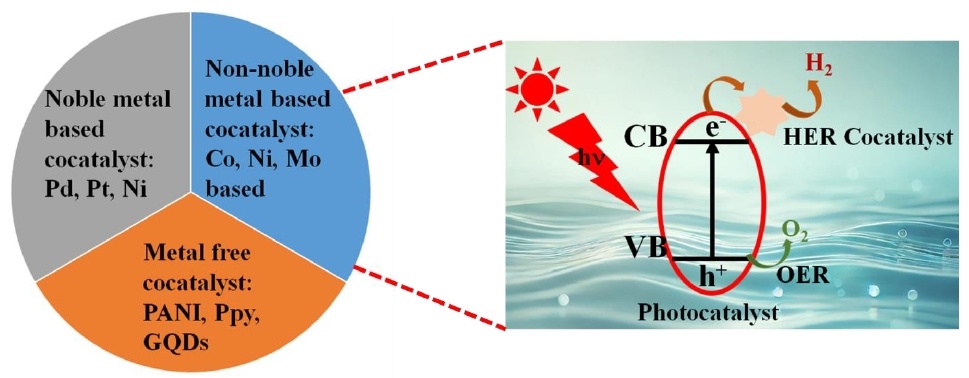
07 March 2025Unravelling the Role of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Co-Catalysts in Photocatalytic Water Splitting: Mechanistic Insights and Material Strategies
The reliance on fossil fuels has led to a substantial increase in greenhouse gas emissions, presenting a critical environmental challenge. Addressing this issue necessitates the adoption of alternative renewable energy sources, with green hydrogen emerging as a promising candidate due to its high gravimetric energy density and absence of harmful emissions. Among the various hydrogen production techniques, photocatalytic technology has garnered significant attention for its dual potential to produce green hydrogen and degrade pollutants, thereby addressing both energy and climate crises. Efforts to scale photocatalytic technology for industrial applications have identified cocatalyst integration as a pivotal strategy, as it enhances reaction kinetics by lowering the activation energy and mitigating charge carrier recombination. This review comprehensively examines the hydrogen economy, the underlying principles of photocatalysis, recent technological advancements, key factors influencing photocatalytic reactions, the role of catalysts in hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) surface mechanisms, strategies for cocatalyst optimization, and future directions for the field.
Open Access
Article
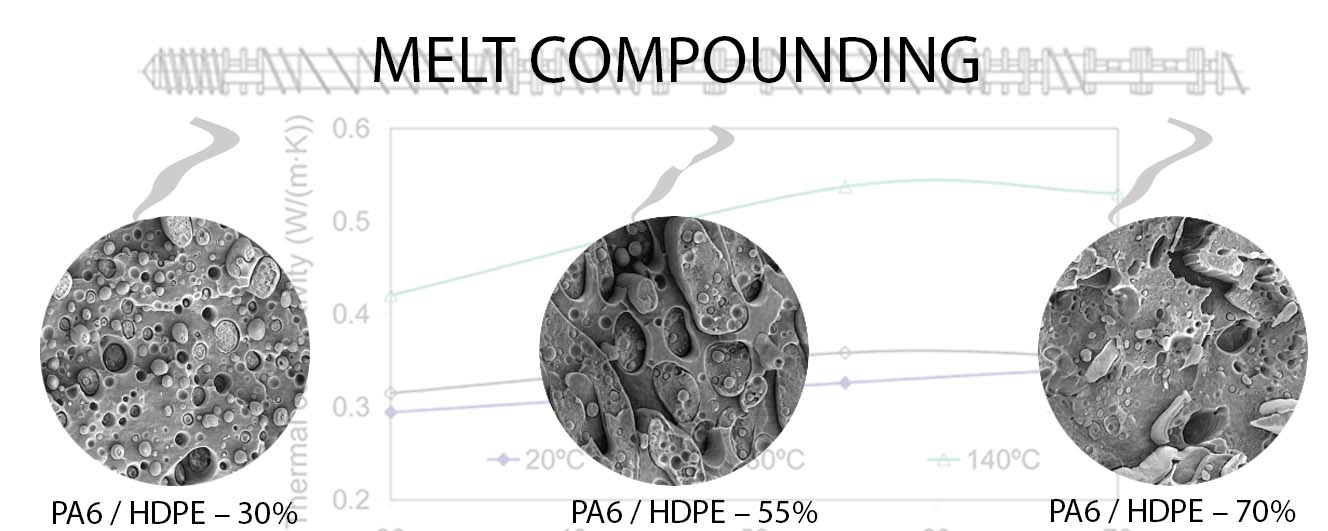
27 February 2025Thermophysical Properties of Polyamide 6 and High-Density Polyethylene Blends (Part 1. Without Compatibilization)
The structure and thermophysical properties of polymer blends polyamide 6/high-density polyethylene with component ratios of 70:30, 45:55 and 30:70, which not only provide phase inversion of the blended polymers, but also the formation of an interpenetrating network, have been investigated by differential scanning calorimetry, scanning electron microscopy and light flash method. The data on the influence of blends composition on their mechanical properties, density, structure, temperature, as well as melting and crystallization heats of polymer components have been obtained. The regularities of changes in thermal diffusion, heat capacities and thermal conductivity coefficients of polyamide 6 and high-density polyethylene individually and as part of the blends in dependence on their composition and temperature have been established. A nonlinear increase of the thermal conductivity coefficient from temperature was revealed when melting a more easily melting component of the blend. It was found that the maximum increase in thermal conductivity occurs in the blend forming an interpenetrating network. A possible way of creating composites with adaptive thermal conductivity by melting one of the components of the blend is proposed.
Open Access
Review
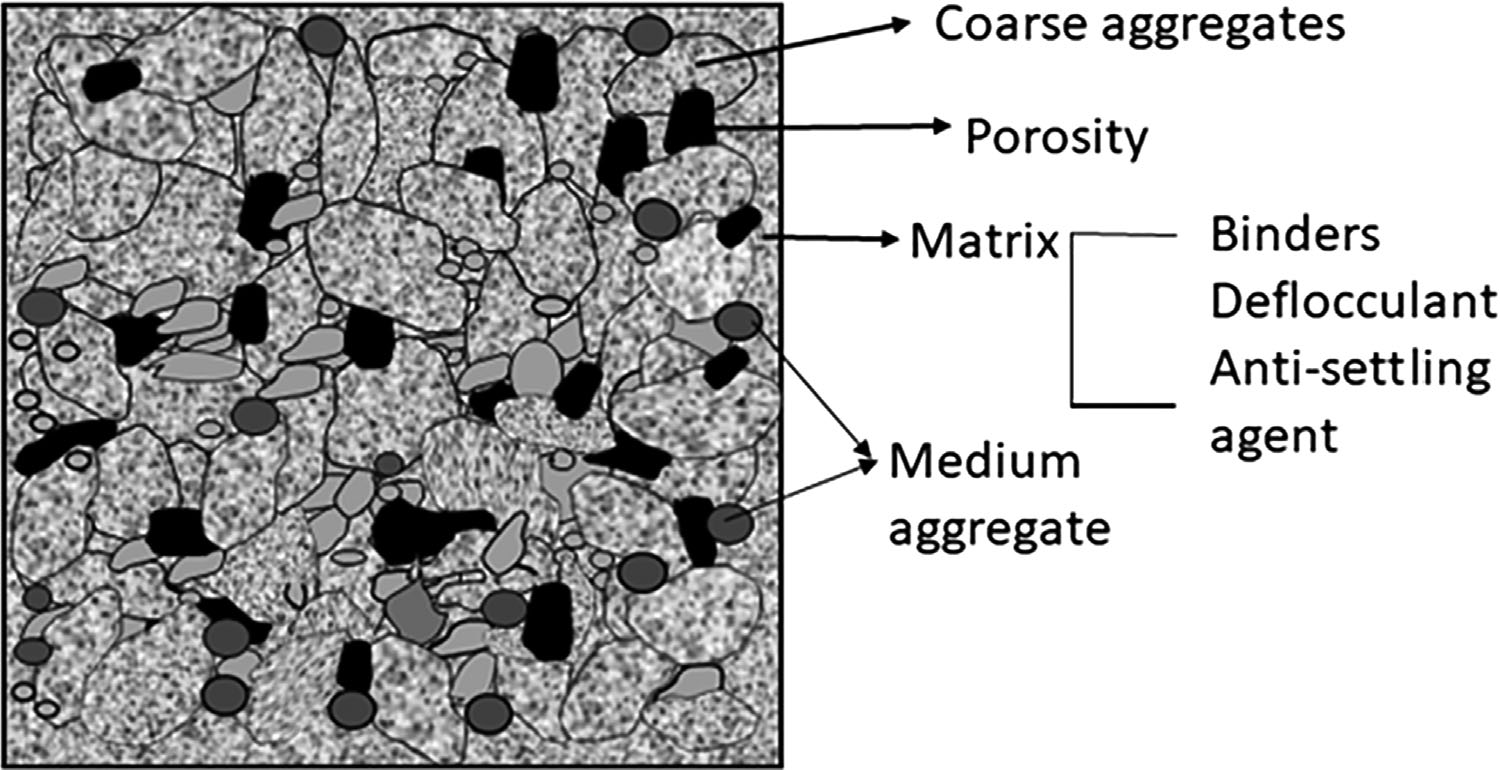
21 February 2025Cement-Free Binders in Alumina-Magnesia Refractory Castables—A Review
To solve the problem of the accelerated deterioration of calcium aluminate (CAC)-bonded alumina-magnesia refractory castables during the secondary refining process, the development of cement-free binders has emerged as one significant research field of castables. The hydration behavior, curing mechanism, and properties of the most recent research on cement-free binders are compared in this paper. The problems and the modification of each binder of recent research are summarized. High-temperature performance of the castables bonded by traditional hydraulic cement-free binders (ρ-Al2O3 and activated MgO) is outstanding, explosive spalling resistance of the castables bonded by sol binders (silica sol, alumina sol) is good, and the properties of the castables bonded by novel organic hydratable binder (hydratable magnesium citrate) combine the advantages of these two binders above, but the mid-temperature mechanical strength is low. Furthermore, alumina-magnesia castables bonded by organic-composited inorganic cement-free binders are expected to be a future domain.
Open Access
Article
19 February 2025The Effect of Polyethylene Glycol on Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared Using Sonochemical Synthesis
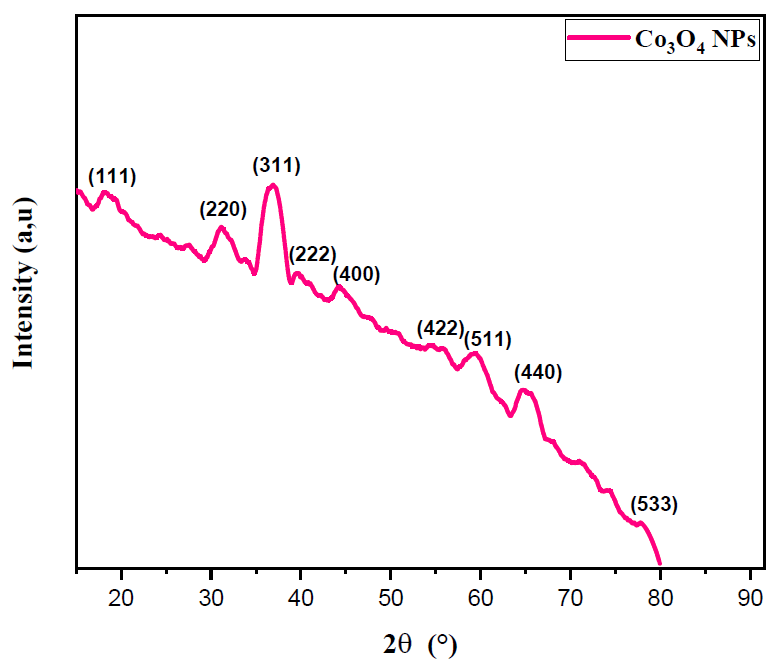
In this work, Cobalt oxide nanoparticles (Co3O4·NPs) were synthesized via a simple sonochemical reaction by using polyethylene glycol (PEG) as a surfactant. Structural, morphological and spectroscopic analysis of obtained powder (Co3O4·NPs) was investigated by X-ray diffraction, FTIR spectroscopy and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The nanocrystalline nature of the sample was confirmed by XRD, which exhibits the cubic face-centered normal spinel structure of (Co3O4·NPs) and the space group of Fd-3m with the average crystallite size around 15 nm. FTIR spectrum shows two strong absorption bands of (Co+2–O) and (Co+3–O) which confirm the spinel structure of Co3O4·NPs. Moreover, SEM micrographs showed that the agglomeration of the nanoparticles was reduced by the addition of (PEG) surfactant and UV-Vis was used to study the synthesized material’s optical properties. The Co3O4 band gap ranged around 2.2 and 3.5 eV.
Open Access
Article
06 February 2025Performance Impacts of Rainwater Tanks on Stormwater Drainage Systems
This article explores the impact of using rainwater tanks on the performance of a stormwater drainage system and the possible challenges posed by climate change and future rainfall projections. This project examines a residential development in Aldinga, South Australia. The study sets clear research objectives that include the creation and simulation of drainage systems with different conditions (e.g., with and without rainwater tanks, historical data, and projected data). The aim is to analyze performance changes in the drainage network after the inclusion of rainwater tanks. Furthermore, the incorporation of projected rainfall data is considered to study possible implications of climate change on the system performance. The methodology follows a quantitative approach, with data collection, creating different models with the use of software, and simulating various conditions such as storms with different annual exceedance probabilities and varying proportions of roof area connected to rainwater tanks. Several findings are identified in this project. When roof areas of all residential allotments are connected to rainwater tanks, substantial benefits are observed in reducing peak flows within the network and runoff volumes. This proportion of connected roof area is directly correlated with reductions in peak flow. Also, while the use of projected rainfall data slightly affects benefits in peak flow and volume reduction, they will remain relatively high at least until 2050. Other performance features, such as hydraulic gradient line, long sections, and time to peak, are also explored. Study validates the hypothesis that rainwater tanks have a significant impact on runoff reductions and flood management, particularly when 100% of roof area is connected with rainwater tanks. Also, there is an impact when projected data is used, but it remains manageable and should be considered under specific contexts to decide whether these impacts are significant. Several opportunities for future research are suggested. These include the examination of larger areas, projections to a more distant future, the use of different rainfall patterns, and the consideration of extreme rainfall events.