Found 469 results
Open Access
Review
25 February 2025Innovations in IN939: From Cast Alloy to Additive Manufacturing
Nickel-based superalloys are the most reliable material choice for the hot sections of turbines. These superalloys are mainly employed in aircraft engines, particularly in the combustor and turbine sections. In this scenario, the growing need for materials that can endure high temperatures while retaining their strength has driven the development of IN939. Although IN939 holds these significant important properties and applications, it has received less attention in recent literature than other superalloys. This review aims to comprehensively analyze the main research on IN939 over the past 50 years. From 1970 to 1980, research primarily focused on the development of IN939 through casting methods. Between 1980 and 1990, the emphasis shifted to studying its oxidation resistance and microstructural stability during service. The period from 1990 to 2000 focused on repairing components after long service time at high temperatures. In recent decades, advances in additive manufacturing techniques have led to growing interest in developing IN939 using methods like laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). Research in the area has demonstrated that the LPBF technique offers a promising approach to manufacturing high-performance IN939 components.
Open Access
Article
21 February 2025Porous Cu(Mn)-Doped ZnO-MgO Nanocomposites for Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Applications
Porous Cu(Mn):ZnO-MgO composites synthesized by polymeric sol-gel method were characterized. The crystal structure, morphology, spectral properties, the ability of the photogeneration of chemically active singlet oxygen under external visible irradiation, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties of porous composites were studied. Obtained composites consist of small ZnO and MgO crystals having size less than 20 nm. It was found that Cu2+ and Mn2+ ions are embedded into the lattices of ZnO and MgO crystals, altering their crystal cell parameters. The band gap values of obtained composites are 3.41 ÷ 3.42 eV which are slightly higher than the band gap of pure ZnO. Prepared materials demonstrate a high ability of photogeneration of chemically active singlet oxygen under blue light (λ = 405 nm) irradiation. It was found that dependencies of the intensity of singlet oxygen photogeneration from the power density of visible irradiation are linear. Photocatalytic decomposition of the diazo dye Chicago Sky Blue in solutions under UV and blue light irradiation proceeds rapidly in the presence of the prepared composites (constants rate of photocatalytic dye decomposition under UV irradiation are 0.024 min−1 and 0.025 min−1 for ZnO-MgO composites doped with Cu and Mn, correspondingly). Porous composites demonstrate superior antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria. These materials are promising for practical application in medicine and photocatalytic technologies of air and water cleaning.
Open Access
Article
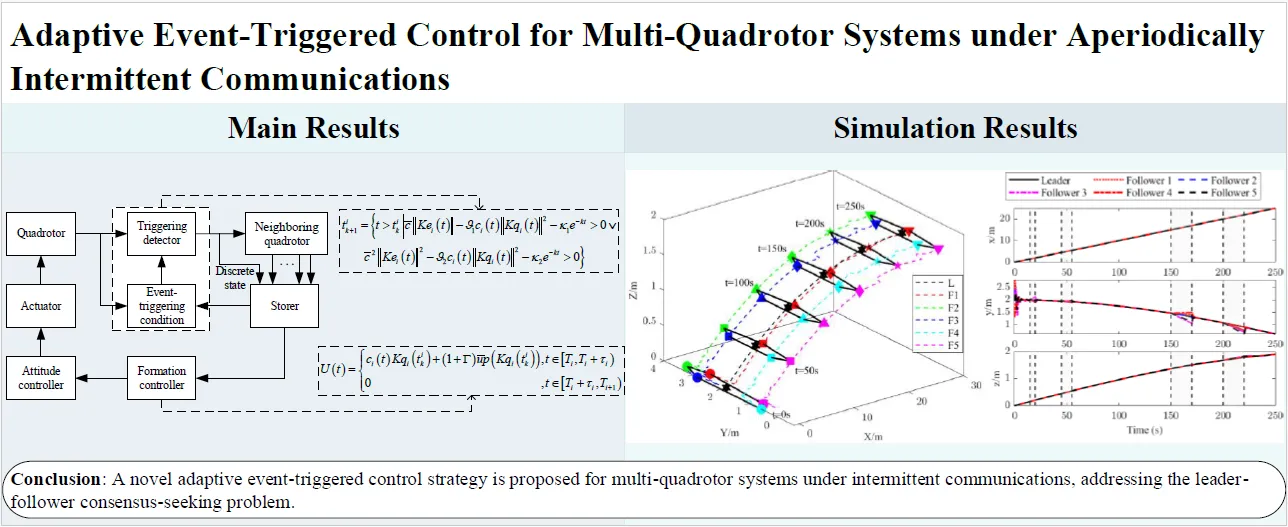
19 February 2025Adaptive Event-Triggered Control for Multi-Quadrotor Systems under Aperiodically Intermittent Communications
A novel adaptive event-triggered control strategy is proposed for multi-quadrotor systems under intermittent communications, addressing the leader-follower consensus-seeking problem where the leader has an unknown bounded input. Firstly, an activation time ratio condition is proposed, eliminating the reliance on the maximum time interval of intermittent communication. Secondly, a compensation term related to the leader’s unknown bounded input is designed in the controller to compensate for the error caused by intermittent communication in each period. Meanwhile, a prediction method is developed to eliminate the dependence on continuous information of neighboring quadrotors. Zeno behavior is strictly excluded, and communication among quadrotors is efficiently reduced with the designed event-triggering condition. Finally, numerical simulations verify the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed control strategy.
Open Access
Article
19 February 2025The Effect of Polyethylene Glycol on Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared Using Sonochemical Synthesis
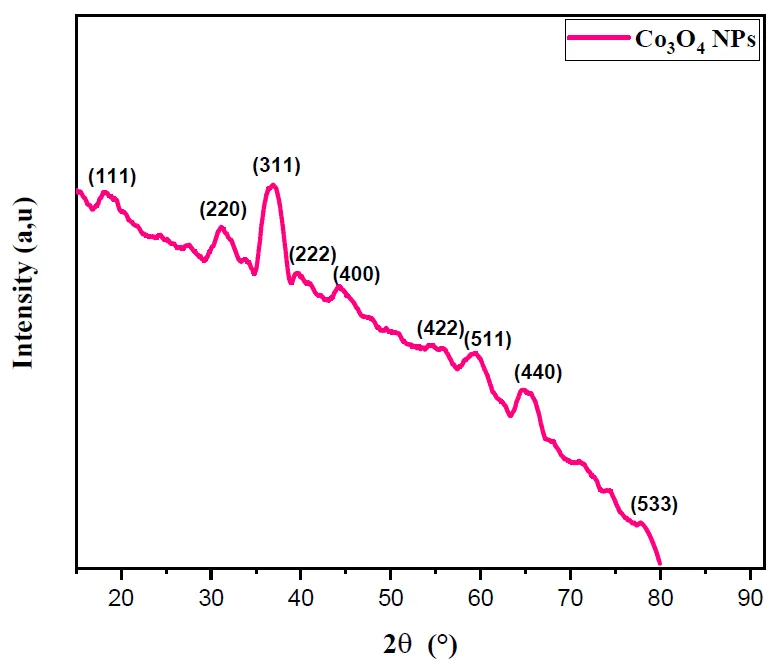
In this work, Cobalt oxide nanoparticles (Co3O4·NPs) were synthesized via a simple sonochemical reaction by using polyethylene glycol (PEG) as a surfactant. Structural, morphological and spectroscopic analysis of obtained powder (Co3O4·NPs) was investigated by X-ray diffraction, FTIR spectroscopy and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The nanocrystalline nature of the sample was confirmed by XRD, which exhibits the cubic face-centered normal spinel structure of (Co3O4·NPs) and the space group of Fd-3m with the average crystallite size around 15 nm. FTIR spectrum shows two strong absorption bands of (Co+2–O) and (Co+3–O) which confirm the spinel structure of Co3O4·NPs. Moreover, SEM micrographs showed that the agglomeration of the nanoparticles was reduced by the addition of (PEG) surfactant and UV-Vis was used to study the synthesized material’s optical properties. The Co3O4 band gap ranged around 2.2 and 3.5 eV.
Open Access
Article
18 February 20254DoF Rat-SLAM with Memristive Spiking Neural Networks for UAVs Navigation System
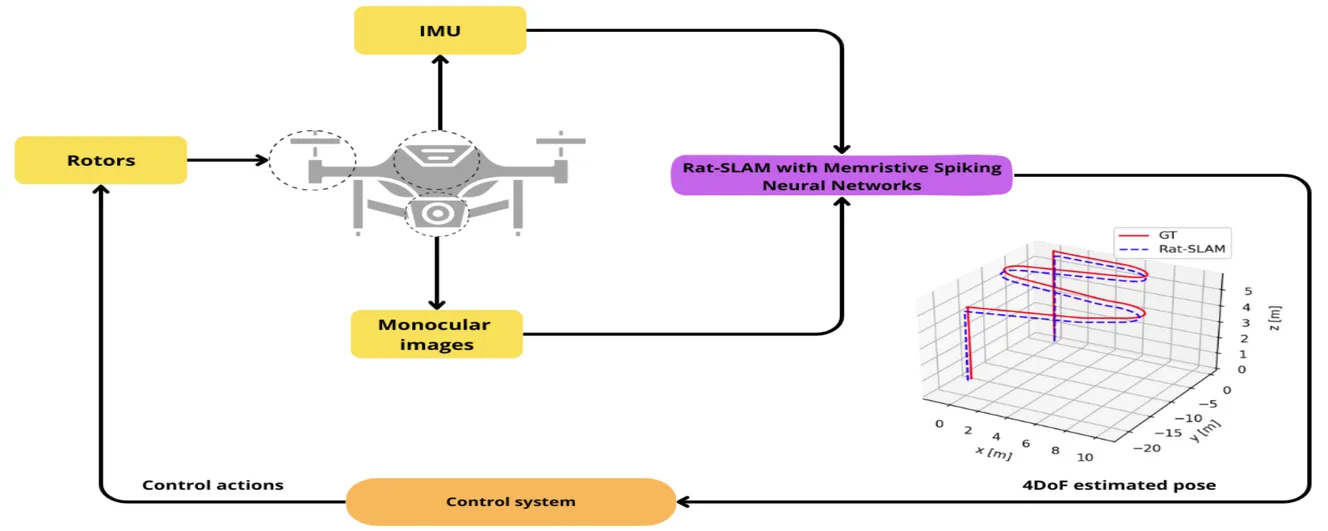
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are versatile platforms with potential applications in precision agriculture, disaster management, and more. A core need across these applications is a navigation system that accurately estimates location based on environmental perception. Commercial UAVs use multiple onboard sensors whose fused data improves localization accuracy. The bioinspired Rat-Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (Rat-SLAM) system, is a promising alternative to be explored to tackle the localization and mapping problem of UAVs. Its cognitive capabilities, semi-metric map construction, and loop closure make it attractive for localization in complex environments. This work presents an improved Rat-SLAM algorithm for UAVs, focusing on three innovations. First, Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) are incorporated into Rat-SLAM’s core modules to emulate biological processing with greater efficiency. Second, Neuromorphic Computing models the neurons of the SNNs, assessing the feasibility of implementing SNNs on specialized hardware to reduce software processing, a key advantage for UAVs with limited onboard resources. Third, SNNs are developed based on the Memristive Leaky Integrate-and-Fire model, integrating memristors into artificial neurons to leverage their low power and memory properties. Our approach was evaluated through trajectory simulations using the Hector Quadrotor UAV in the Gazebo environment within the Robot Operating System, yielding valuable insights and guiding future research directions.
Open Access
Review
18 February 2025The Intersection between Immune System and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis—A Concise Review
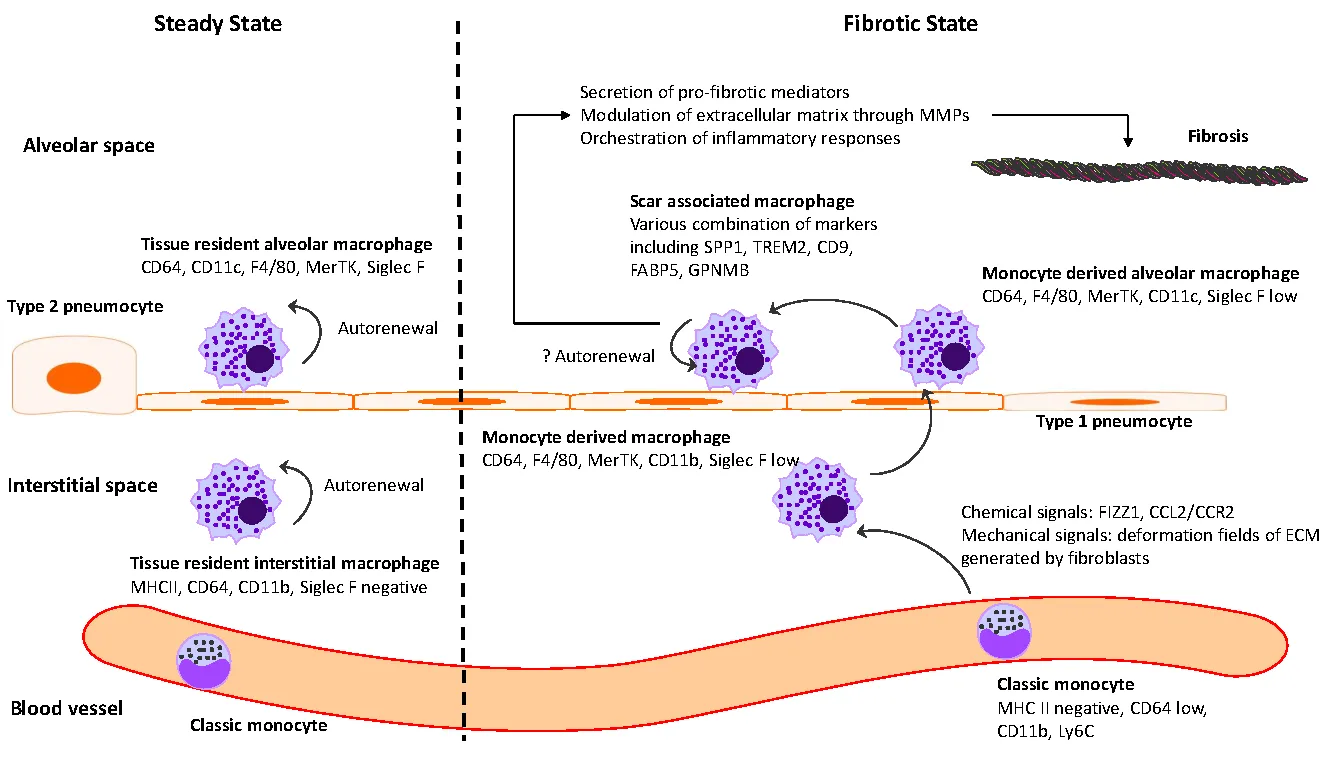
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is marked by progressive alveolar destruction, impaired tissue regeneration, and relentless fibrogenesis, culminating in respiratory failure and death. A diverse array of resident and non-resident cells within the lung contribute to disease pathogenesis. Notably, immune cells, both resident and recruited, respond to cues from sites of lung injury by undergoing phenotypic transitions and producing a wide range of mediators that influence, initiate, or dictate the function, or dysfunction, of key effector cells in IPF pathology, such as alveolar epithelial cells, lung fibroblasts, and capillary endothelial cells. The role of the immune system in IPF has undergone an interesting evolution, oscillating from initial enthusiasm to skepticism, and now to a renewed focus. This shift reflects both the past failures of immune-targeting therapies for IPF and the unprecedented insights into immune cell heterogeneity provided by emerging technologies. In this article, we review the historical evolution of perspectives on the immune system’s role in IPF pathogenesis and examine the lessons learned from previous therapeutic failures targeting immune responses. We discuss the major immune cell types implicated in IPF progression, highlighting their phenotypic transitions and mechanisms of action. Finally, we identify key knowledge gaps and propose future directions for research on the immune system in IPF.
Open Access
Perspective
18 February 2025The Reconfiguration of Social Bonds in the Digital Age: Virtual Connections vs. Face-to-Face Relationships
The article examines how smartphones and social media are transforming human interactions, challenging traditional concepts of friendship, intimacy, and belonging. Phenomena such as “phubbing” and constant connectivity are explored, highlighting the negative impacts of hyperconnectivity on the quality of face-to-face interactions and emotional well-being. While these technologies expand the reach of connections, they often lead to more superficial relationships, altering family, educational, and professional dynamics. Anthropological analysis is emphasized as essential for understanding these changes, revealing how digital practices vary across different cultural and social contexts. Ethnographic studies and innovative methodologies are suggested to investigate how digital technologies reshape identities, communities, and social hierarchies. The importance of an interdisciplinary approach, combining anthropology, psychology, and data science, is underscored to address the emerging challenges of the digital era and foster more authentic and healthy human relationships.

Open Access
Article
18 February 2025Unemployment, Inequality, and Occupational Stress: Mental Health Outcomes in Brazil (2012–2022)
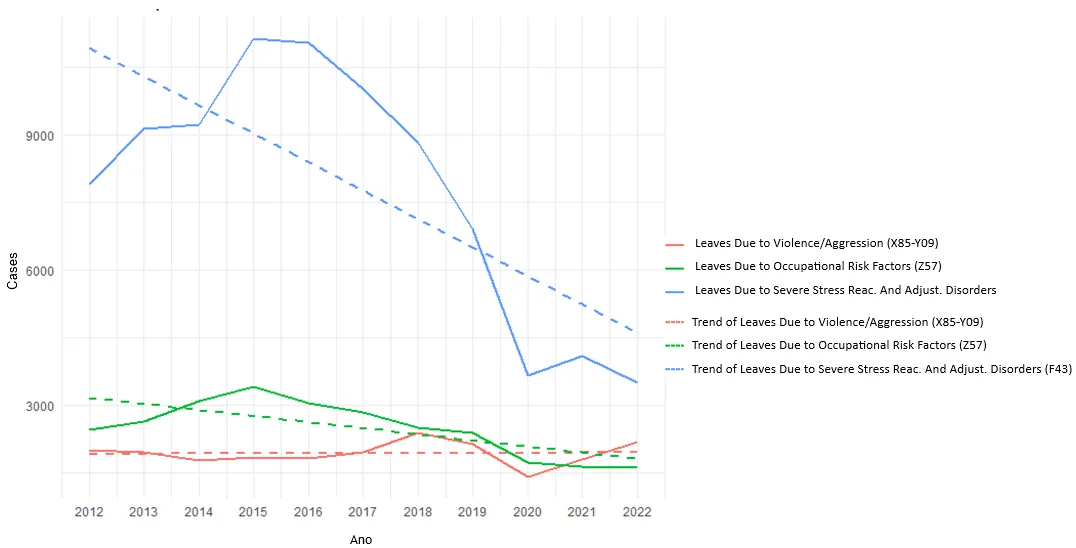
This study examines the relationship between occupational stress-related leaves, classified under International Classification of Diseases code F43, and socioeconomic factors such as unemployment, income inequality, and worker income in Brazil from 2012 to 2022. Work-related stress disorders, especially those involving severe stress reactions and adjustment disorders, are big problems for occupational health. Bad working conditions and differences in income can make these problems worse. This research utilized secondary data from official Brazilian databases to perform time-series analyses and structural equation modeling. Results revealed a decline in stress-related leaves during the COVID-19 pandemic, likely influenced by remote work adoption and reduced exposure to workplace hazards. Structural modeling identified key relationships: unemployment rates and occupational risk exposure were positively associated with stress-related leaves, while higher income levels were protective. Unexpectedly, income inequality influenced aggression-related leaves but had no significant direct impact on stress-related leaves. These findings underscore the multifaceted impact of socioeconomic and workplace factors on occupational health, highlighting the need for policies addressing mental health at work and fostering equitable labor conditions. The study also identifies limitations, including potential underreporting and the exclusion of demographic nuances. Future research should adopt a multidisciplinary approach and consider disaggregated data to enhance understanding and intervention strategies.
Open Access
Article
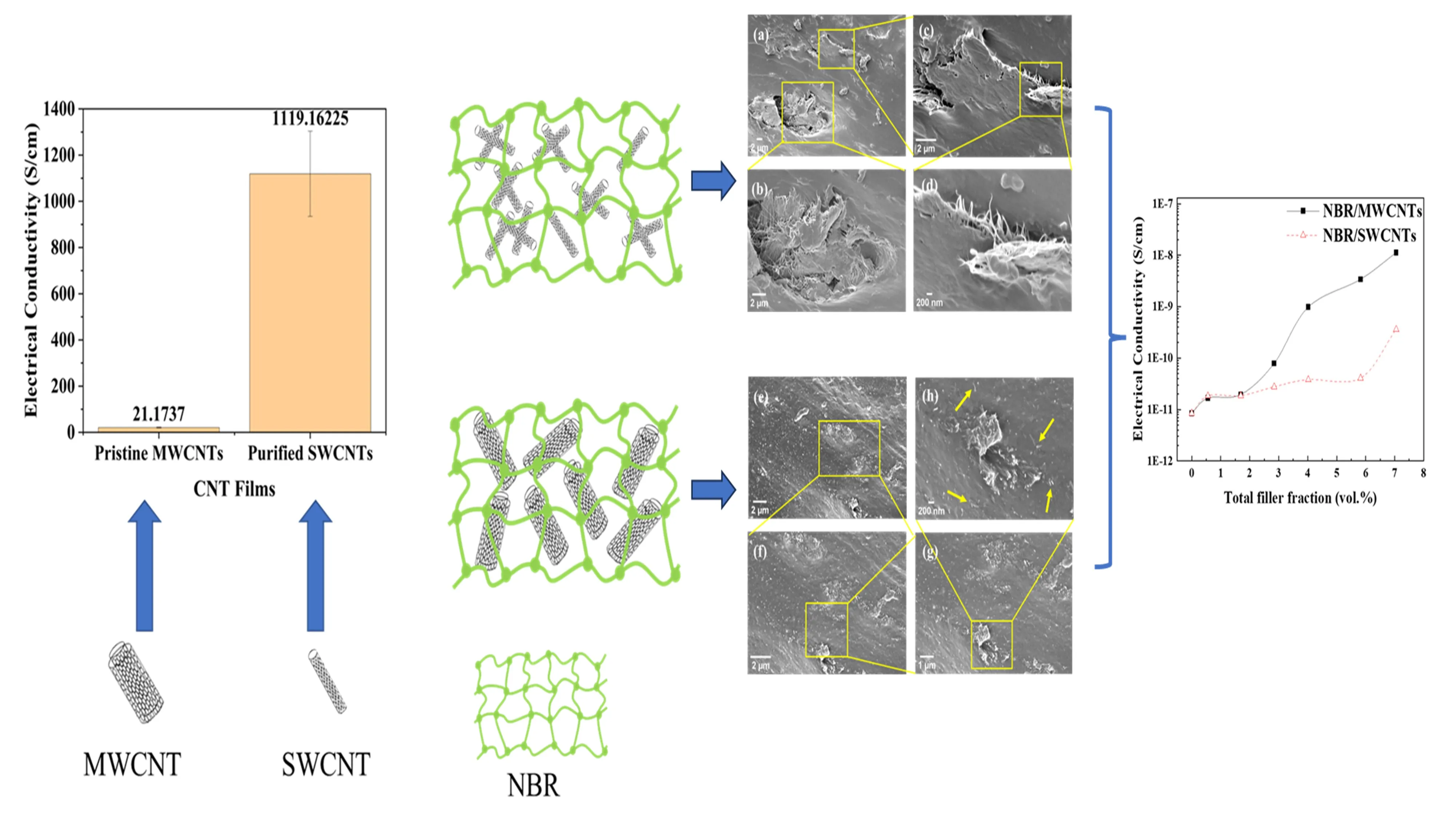
17 February 2025Comparative Study of Elastomer Nanocomposites Respectively Containing SWCNTs and MWCNTs
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are essential for providing polymers with mechanical reinforcement and multifunctional properties. This study investigated two groups of nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) nanocomposites containing single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), respectively. SWCNTs were purified to remove appro-ximately 20 wt.% of impurities, and both CNTs were modified with polyethylene glycol tert-octylphenyl ether (Triton X-100) before emulsion compounding and 2-roll milling with NBR. MWCNTs were found to disperse in the elastomer matrix relatively uniformly, while SWCNTs formed aggregates. Consequently, NBR/MWCNT nanocomposites exhibited superior mechanical properties, e.g. a tensile strength of 10.8 MPa at 4.02 vol.% MWCNTs, compared to 5.6 MPa for NBR/SWCNT nanocomposites. Additionally, NBR/MWCNT nanocomposites exhibited more remarkable electrical conductivity and swelling resistance to toluene. The diameter of elastomer macromolecules (0.2–0.5 nm) is close to that of SWCNTs (1–2 nm), and their single graphene wall with a hollow structure makes SWCNTs almost as flexible as elastomer macromolecules. This similarity suggests that SWCNTs should be treated as a special type of polymer. SWCNTs cannot disperse as uniformly as MWCNTs in the elastomer matrix, likely due to their smaller size and lower sensitivity to mechanical shearing during the emulsion compounding and 2-roll milling process.
Open Access
Book Review
14 February 2025