Found 14 results
Review
27 August 2024Strongly Correlated Electrons and High Temperature Superconductivity
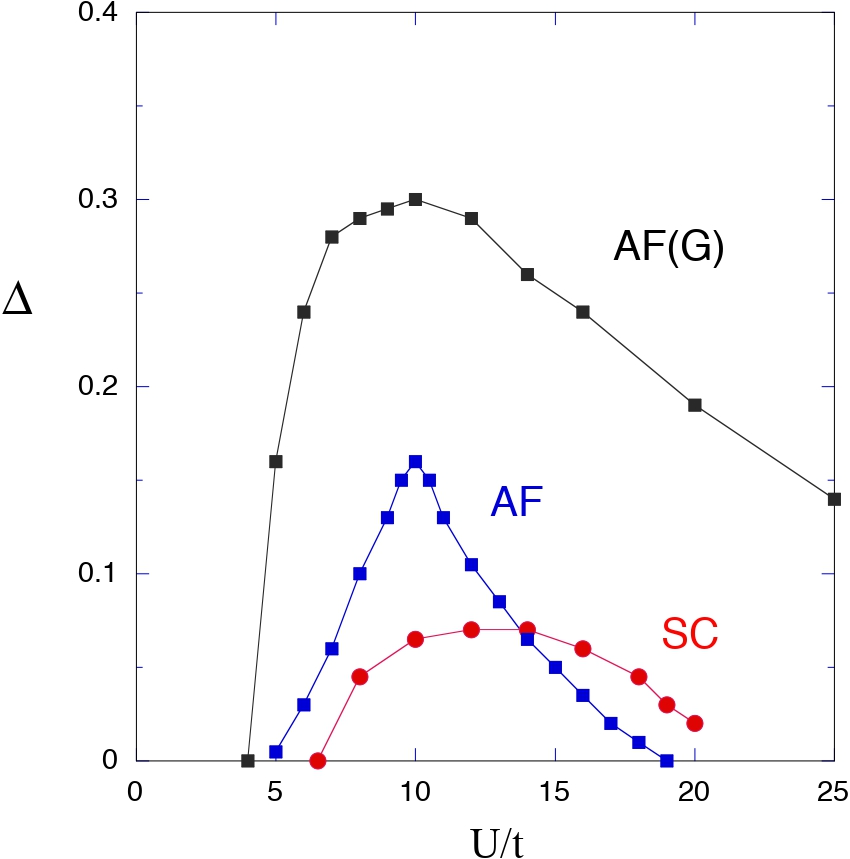
It is very important to clarify the mechanism of high-temperature superconductivity in strongly correlated electron systems. The mechanism of superconductivity in high temperature cuprate superconductors has been studied extensively since their discovery. We investigate the properties of correlated electron systems and mechanism of superconductivity by using the optimization quantum variational Monte Carlo method. The many-body wave function is constructed by multiplying by correlation operators of exponential type. We show that d-wave superconducting phase exists in the strongly correlated region where the on-site repulsive interaction is as large as the bandwidth or more than the bandwidth. The d-wave pairing correlation function is shown as a function of lattice sites, showing that the long-range order indeed exists.
Article
17 April 2024Thermogravimetric Study of the Oxidation Behavior of the Cantor’s Alloy at 1000 °C and Beyond
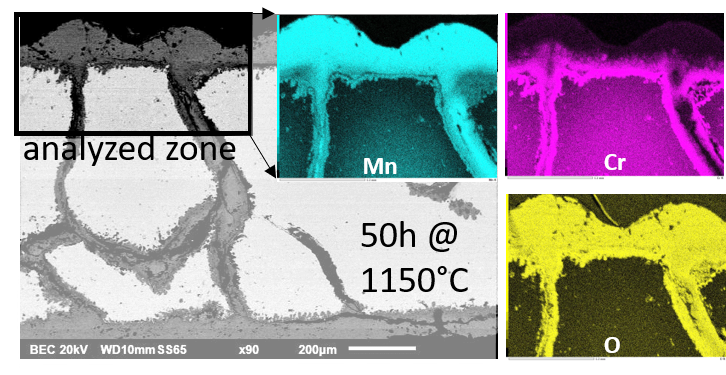
A polycrystalline Cantor alloy, equimolar in Co, Cr, Fe, Mn and Ni, was cast. It was subjected to oxidation in a thermo-balance in a flow of synthetic dry air, at 1000, 1050, 1100 and 1150 °C. The mass gain was globally parabolic but rather irregular. The parabolic constants, ranging from 55 to 700 × 10−12·g2·cm−4·s−1, are much higher than for a chromia-forming alloy. They obey an Arrhenius law with an activation energy equal to 270 kJ/mol. The external oxide scales formed are composed of an outer part made of manganese oxide and an inner part made of (Cr, Mn) oxide containing a thin internal layer of chromia. The Mn and Cr-depleted depths and the Mn and Cr masses lost by the alloy increase with the oxidation temperature. Cr-rich acicular particles precipitated in subsurface at 1100 °C and internal oxidation along the grain boundaries are present in the whole thickness of the sample oxidized at 1150 °C. Oxide spallation occurred during the cooling, at temperatures in the 200–350 °C range, only for the alloys oxidized at 1050 and 1100 °C. Not too thick scale (1000 °C) or deep internal oxidation (1150 °C) may be favorable for scale adherence.
Editorial
17 April 2024
Article
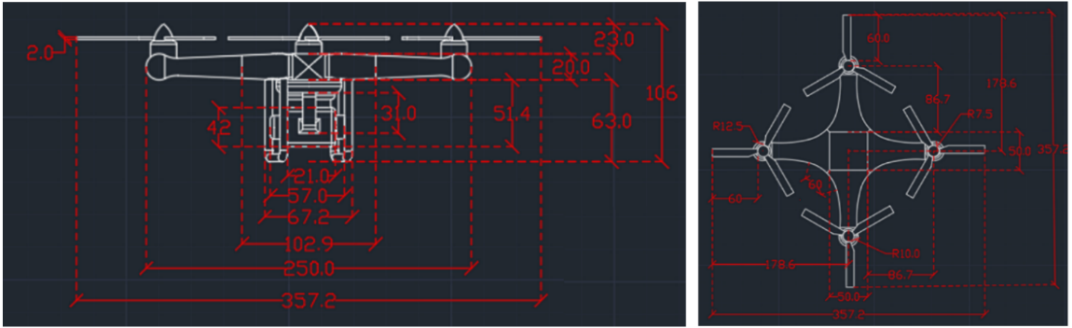
19 March 2024Designing a Quadcopter for Fire and Temperature Detection with an Infrared Camera and PIR Sensor
In agriculture, medicine, and engineering, sudden fire outbreaks are prevalent. During such events, the ensuing fire spread is extensive and unpredictable, necessitating crucial data for effective response and control. To address this need, the current initiative focuses on utilizing an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) with an Infrared (IR) sensor. This sensor detects and analyses temperature variations, accompanied by additional camera footage capturing thermal images to pinpoint the locations of the incidents precisely. The UAV’s programming is executed using Arduino-Nano and mission planner software, interfacing with the Pixhawk flight controller operating in a guided mode for autonomous navigation. The UAV configuration includes a radio module interfacing with Arduino-Nano, a flight controller, and remote-control functionality. The flight duration is approximately 10–15 min, contingent upon flight dynamics and environmental temperature. Throughout its airborne operation, the UAV transmits live telemetry and log feeds to the connected computer, displaying critical parameters such as altitude, temperature, battery status, vertical speed, and distance from the operator. The Pixhawk flight controller is specifically programmed to govern the UAV’s behavior, issuing warnings to the pilot in case of low voltage, prompting a timely landing to avert potential crashes. In case of in-flight instability or a crash, the mission planner can trace the UAV’s location, facilitating efficient recovery and minimizing costs and component availability losses. This integrated approach enhances situational awareness and mitigation strategies, offering a comprehensive solution for managing fire incidents in diverse fields.