Found 301 results
Open Access
Opinion
11 June 2025Reflections on Photocatalysis Progress Since the Inspiration of Prof. David Ollis in 1992
Why has photocatalysis not gained the wide-ranging commercial applications in environmental purification of air and water that seemed promising 30+ years ago since the first international conference on TiO2 photocatalytic purification and treatment of water in 1992? The primary reason lies in its low intrinsic efficiency. The progress of R&D to enhance this efficiency has been slow, possibly due to an incomplete understanding of the underlying mechanisms of photocatalysis. There is also the possibility that certain factors, with effects comparable to those of the band gap, significantly influence photocatalytic performance but remain underexplored. Additionally, challenges such as mass transfer limitations and surface contamination hinder the industrial application of photocatalysts. It may be time for scientists to reconsider and address the limitations and practical application scenarios of photocatalysis.

Open Access
Case Report
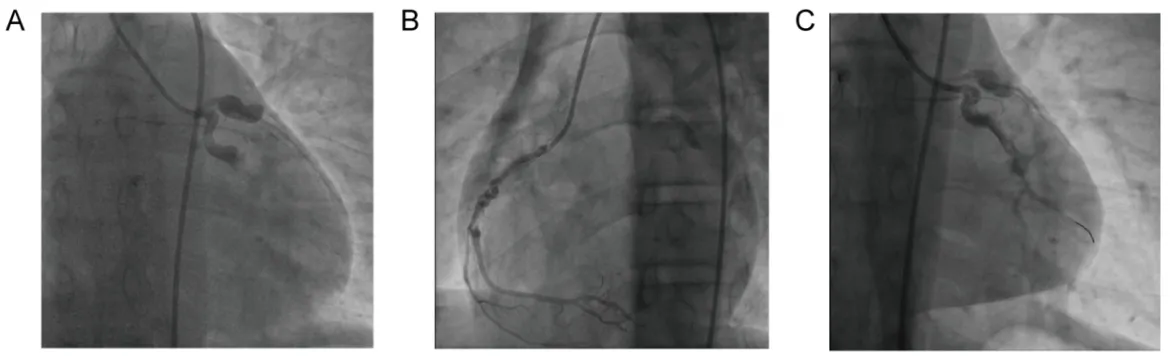
09 June 2025Acute Myocardial Infarction with Multiple Giant Coronary Artery Aneurysms in a Juvenile with Kawasaki Disease
Coronary artery aneurysm (CAA), the most risky late complication of Kawasaki disease (KD), is associated with severe adverse cardiac events, such as acute myocardial infarction (AMI), in young patients. Herein, we describe a 16-year-old boy who suffered from occasional angina attack after a recent myocardial infarction due to multiple giant CAAs during the asymptomatic period of KD. Coronary angiography (CAG) revealed multiple large CAAs of about 9 mm in diameter at the left anterior descending artery (LAD) and more than 12 mm at the left circumflex coronary artery (LCX). To optimize the management and reduce the morbidity and mortality of giant CAAs, it is imperative to consider antecedent KD at the earliest possible stage, particularly in young patients with angina pectoris or AMI but lacking traditional risk factors for atherosclerosis. Long-term follow-up with an electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, or coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) is essential and should not be overlooked. In addition, this case highlights the great significance of working out a more comprehensive and effective management strategy for such KD juveniles, including drugs, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or even surgery.
Open Access
Article
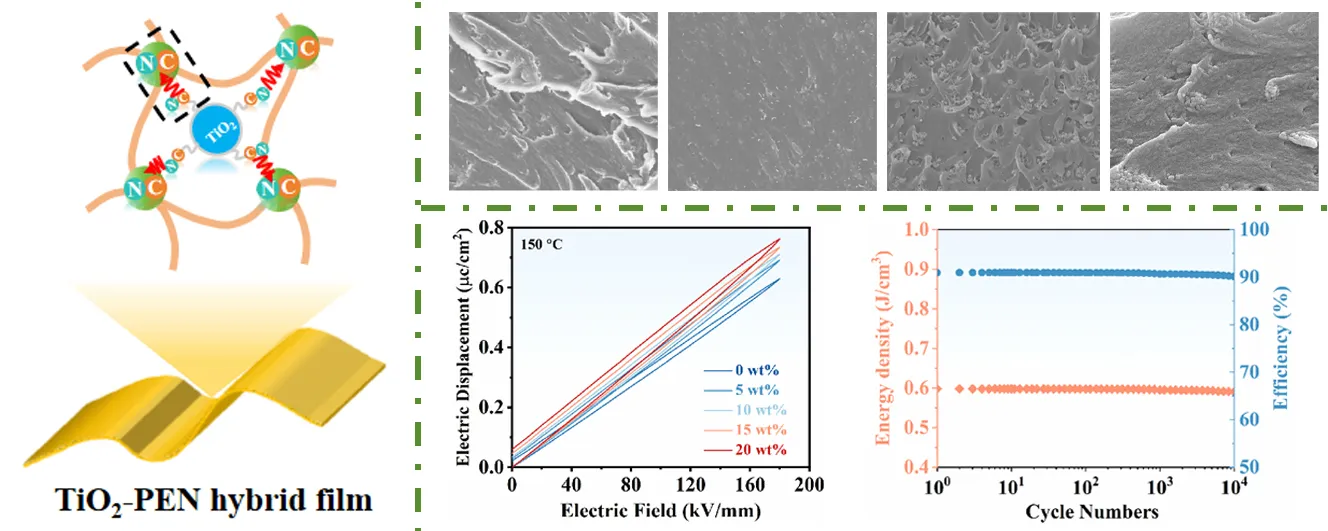
09 June 2025High-Temperature Dielectric Energy Storage Materials Fabricated by Crosslinking Titanium Dioxide and Polyarylene Ether Nitrile
Dielectric materials have broad application prospects in the field of high-temperature electronic power systems. Up to now, high-temperature dielectric materials are mainly prepared by using high glass transition temperature (Tg) polymers. However, the incompatibility between polymers and fillers, which are incorporated for high energy density, leads to soaring dielectric losses at high temperatures, resulting in a nosedive of discharged energy density (Ud) and efficiency (η). In this paper, we report the fabrication of high-temperature dielectric materials via the self-crosslinking of phthalonitriles from phthalonitriles modified titanium dioxide (TiO2-2CN) and phthalonitriles terminated polyarylene ether nitrile (PEN-2CN). TiO2-2CN is firstly synthesized and characterized, then incorporated into PEN-2CN to prepare TiO2/PEN nanocomposites, which transform into TiO2-PEN hybrids afterwards. The fabricated TiO2-PEN hybrids are confirmed by the change of SEM sectional morphology, as well as the increase of their Tg and thermal decomposition temperature (Td). With the addition of TiO2-2CN, both the Tg, Td, and Ud of TiO2/PEN nanocomposites are improved. In addition, due to the formation of covalent bonds within TiO2-PEN, the hybrids exhibit excellent high-temperature dielectric energy storage performance. Specifically, at 150 °C, the Ud of 10 wt% TiO2-PEN is 0.60 J/cm−3, which is over 95% of that at RT. Moreover, η is greater than 90% and remains unchanged after 10,000 charge and discharge cycles. This method used for preparing TiO2-PEN hybrids through a self-crosslinking reaction of phthalonitriles provides a new approach for preparing high-temperature dielectric materials.
Open Access
Article
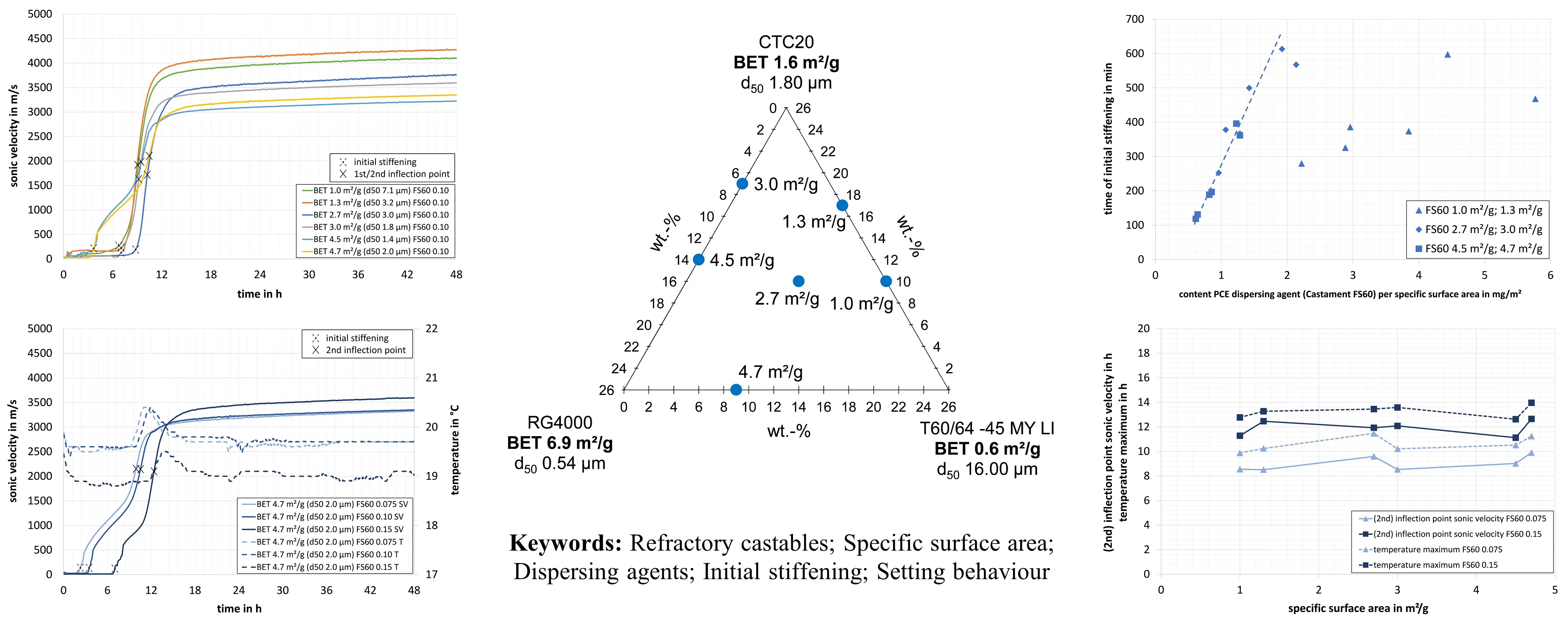
06 June 2025Effects of Changing the Specific Surface Area in the Ceramic Matrix of CAC-Containing Refractory Castables on the Initial Stiffening and Setting Behaviour
Besides the coarse and medium grain size distribution, the matrix components play a central role in the performance of refractory castables. Practical experience shows that the particle size distribution (PSD) and the specific surface area of the ceramic matrix significantly influence processing, setting, and sintering behaviour. However, there is a lack of systematic studies on how PSD or specific surface area changes affect castable properties. This study aims to address this gap by varying ceramic matrices to create refractory model castables with different matrix surface areas. Three dispersing agents with different mechanisms (electrosteric and steric) were used at graded concentrations. Results show that castables with higher specific surface areas (using (very) finely ground and highly sintered alumina raw materials with high specific surface areas) and different dispersing agents and their concentrations show substantial differences in the initial stiffening and setting behaviour. Higher specific surface areas of the matrix result in an earlier first stiffening, while adding more dispersing agents leads to delayed stiffening. The refractory model castables’ first stiffening and hydration range (with a simultaneous temperature maximum) vary considerably depending on the dispersing agent used and its concentration, caused by completely different mechanisms.
Open Access
Article
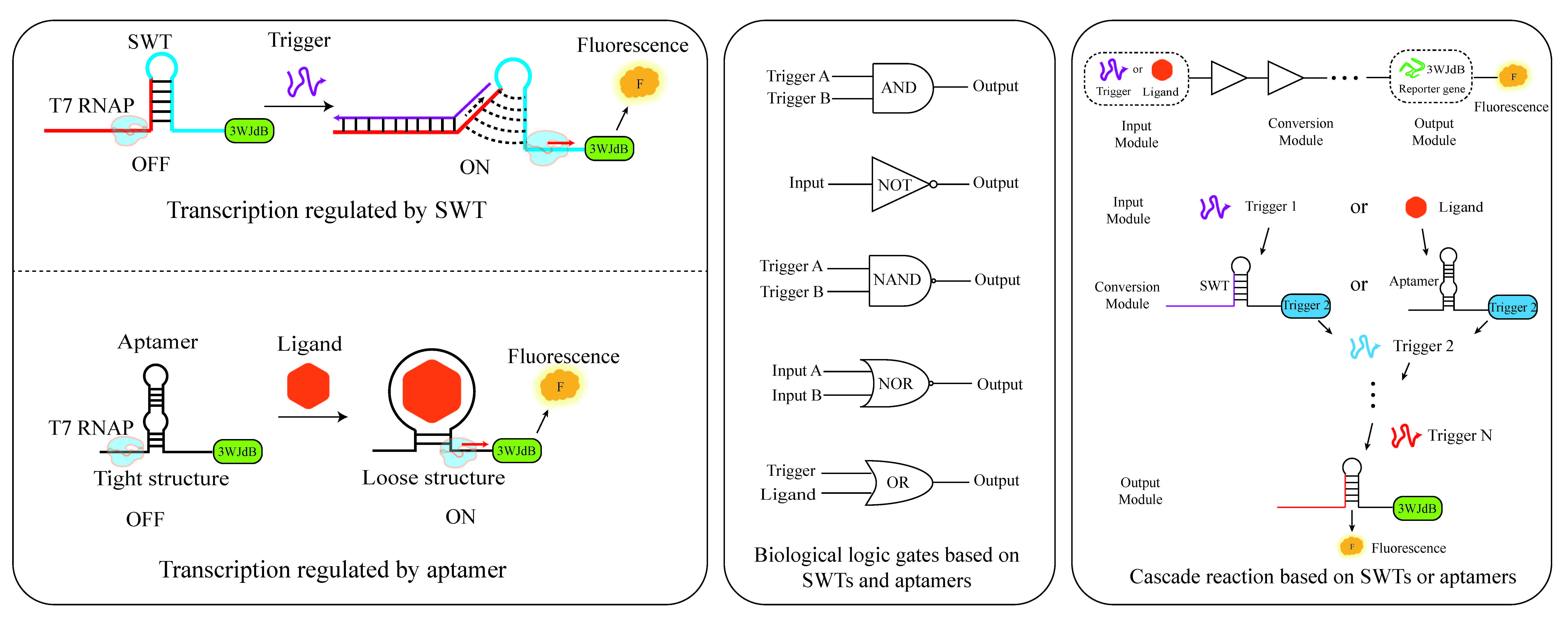
04 June 2025Modular Transcriptional Regulation Using Switchable Transcription Terminators and Aptamers: Design and Optimization in Synthetic Biology
Transcriptional regulation is a key step in gene expression control. While transcription factor-based regulation has been widely used and offers robust control over gene expression, it can sometimes face challenges such as achieving high specificity, rapid dynamic responses, and fine-tuned regulatory precision, which have motivated the exploration of alternative regulatory strategies. With the development of synthetic biology, novel genetic elements such as Switchable Transcription Terminators (SWT) and aptamers provide more flexible and programmable strategies for transcriptional regulation. However, the independent regulatory capabilities of these two types of elements and their combined regulatory mechanisms still require further investigation. In this study, based on an in vitro transcription system, we systematically explored the transcriptional regulation potential of SWT and aptamers. We innovatively combined these two elements to construct a modular gene expression regulation system. First, we screened and optimized a series of SWTs, obtaining high-performance SWTs with low leakage expression and high ON/OFF ratios. These were further validated for reproducibility of their regulatory performance in E. coli. Next, we constructed multi-level cascading circuits using SWTs, successfully extending the system to six levels and building four types of biological logic gates based on SWT in vitro: AND gate, NOT gate, NAND gate, and NOR gate. Furthermore, based on a previously identified thrombin aptamer capable of transcriptional regulation, we confirmed that ligand binding significantly promoted gene transcription. Finally, we integrate switchable transcription terminators (SWTs) and aptamers to create a modular, ligand-responsive system. We combined aptamers with SWTs to construct heterologous input logic gates, successfully improving the precision and dynamic range of regulation. Compared to the individual regulation of SWT and aptamer, the Aptamer-SWT synergistic regulation enhanced transcription activation by up to 3.3-fold and 7.84-fold, respectively. Additionally, we co-utilized these two genetic elements to construct heterologous input AND and OR gates in vitro. This study expands the strategies for gene expression regulation and provides new elements and theoretical support for efficient, programmable transcriptional regulation in synthetic biology. This system holds potential for biosensing, gene circuit design, and nucleic acid therapy applications.
Open Access
Article
03 June 2025Ecosystem Service Importance, Contributions, and Trends: Perspectives from Farmers in the Mountains of Nepal
Understanding farmers’ perceptions of local ecosystem services is crucial for developing effective ecosystem management strategies and policy interventions to improve the overall welfare of residents. Although there is widespread recognition of the linkages between ecosystem services and human well-being, empirical studies examining farmers’ perceptions and contributions to local ecosystem services, particularly at the micro level in mountainous regions, remain limited. To address these knowledge gaps, we conducted an empirical study employing focus group discussions (n = 6), key informant interviews (n = 12), and household surveys (n = 370) in Mid-Marsyangdi watershed, Lamjung, Nepal. The study revealed that farmers perceive high dependency on regulating followed by provisioning, supporting, and cultural ecosystem services such as freshwater, nutrient cycling, water regulation and purification, timber production, livestock fodder, and natural hazard regulation. Their contributions are notably high in managing freshwater, nutrient cycling, and timber production. Farmers’ practices like forest conservation, agroforestry, inter-cropping, terracing, terrace improvement, multi-year cropping, and organic composting enhance ecosystem services. A significant discrepancy exists between perceived importance and actual contribution, particularly in water regulation, purification, and wild edible food, highlighting areas needing greater attention. The study showed a significant difference (p < 0.001) between perceived importance and contribution across all ecosystem services, with perceived importance consistently higher. Further, a study showed the influence of socio-demographic variables on the farmers’ perception. These findings can inform more effective policy-making for farmer welfare, mountain development, and environmental management.

Open Access
Article
26 May 2025Towards Circular Sustainable Cities: Thoughts and Recommendations for Qatar
Despite the ambitious national visions, Qatar is facing many challenges regarding the notion of sustainability. In this context, a considerable emphasis has been placed on the notion of Circular Economy (CE) to address suitability issues. Despite such an emphasis, the actual implementation of CE notions is still facing several obstacles present in, but not limited to, the Qatari context, such as heavy reliance on landfilling, water scarcity, and a heavy reliance on the oil and gas sectors. Our contention is that CE is an important factor in the sustainability equation and works towards meeting Qatar’s vision of becoming an environmentally sustainable country. by using a qualitative approach, predominantly adopting case study, document and content analysis, this paper explores the notion of CE and its implementation in light of the Qatar National Vision 2030. the challenges facing CE implementation, such as resources, qualified personnel, access to technology, and coordination between different areas of the economy, should be of prime importance for policymakers in Qatar. in order to ensure a sustainable circular city model in Qatar, the challenges related to CE implementation must be addressed accordingly. To this end, the paper suggests several policy recommendations, including the provision of adequate resources and personnel, the use of clean technology to improve the environmental quality of economic activities, in addition to the provision of adequate support and funding for the development of sustainable economic practices. These solutions will help to ensure sustainable economic development based on the concept of CE.

Open Access
Article
26 May 2025Electric Vehicles, Artificial Intelligence, and Climate Policy
This article explores the environmental implications of electrification and artificial intelligence (AI) infrastructure, emphasizing the importance of aligning technological development with climate goals. There is a lack of academic literature that explains and analyses such issues. Section 1 assesses the climate efficacy of promoting electric vehicles (EVs) and electric heating in regions where electricity is primarily coal-based. While electrification offers substantial climate benefits when powered by clean energy, lifecycle analyses reveal that EVs in coal-reliant grids may emit more greenhouse gases than internal combustion engine vehicles. Similarly, the climate performance of electric heat pumps depends on the carbon intensity of electricity sources. The section advocates for integrated policies that simultaneously promote electrification and grid decarbonization, enhancing emissions reductions and public health while mitigating the negative impacts of increased demand on polluting power plants. Section 2 uses Saudi Arabia as a case study and examines the environmental impact of AI data centers in the context of Saudi Arabia’s energy and climate policies. It highlights AI infrastructure’s energy and water intensity and its potential to strain environmental resources. To align AI development with national sustainability goals, the article recommends policies such as siting data centers near renewable energy sources, enforcing environmental efficiency standards, fostering R&D partnerships, mandating sustainability reporting, and expanding power purchase agreements and demand response participation. These measures aim to ensure responsible AI growth within climate-aligned frameworks. The implications of this study are that electrification and AI infrastructure can significantly reduce emissions and improve efficiency if powered by clean energy, but they also risk increasing environmental strain unless technological growth is carefully aligned with climate and sustainability goals.
Open Access
Article
19 May 2025Research on Thermal Fault Detection and Location of Photovoltaic Connectors Based on Multiple Model Estimator
Offshore photovoltaic (PV) systems encounter challenges due to high humidity and salt spray environments. The PV connectors on the DC input side of inverters are particularly susceptible to increased contact resistance and local overheating caused by environmental corrosion. This paper introduces a novel thermal fault location method utilizing a multiple model estimator (MME). The approach develops a lumped thermal model and an abnormal overheating disturbance model for the PV connectors. By combining a Kalman filter with a probability fusion algorithm, the method effectively detects thermal faults. Simulation and experimental results demonstrate that this approach can accurately locate faults while requiring only a minimal number of thermal sensors, thereby enhancing the reliability of offshore PV systems.

Open Access
Perspective
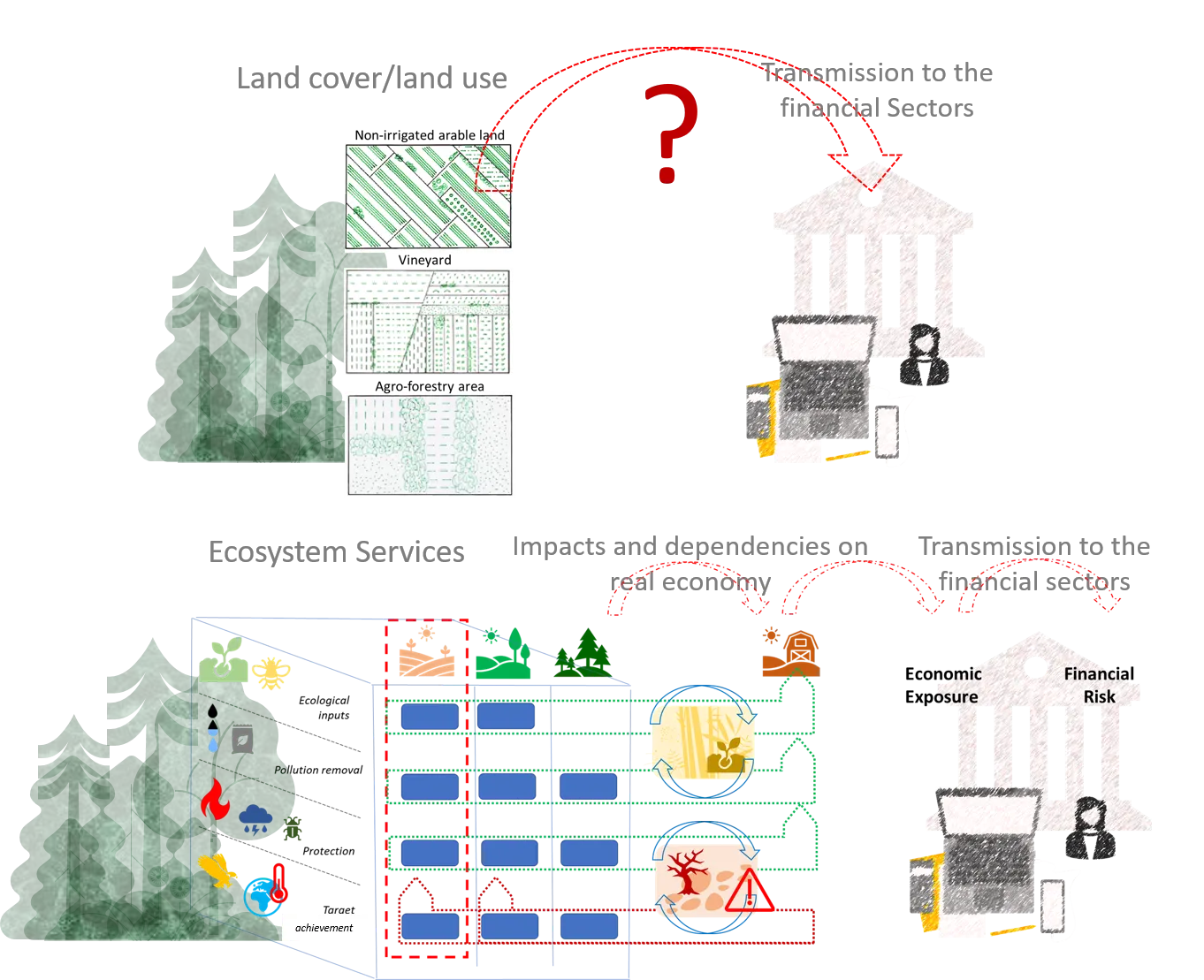
16 May 2025From “Land” to “Ecosystems”—Paving the Way for Ecosystem Services in Sustainable Finance
Although biodiversity loss is acknowledged as one of the main drivers of financial risk, there is still no clear understanding of how impacts and dependencies on biodiversity affect the financial sector. In fact, nature degradation does not manifest itself as a systemic risk because it does not threaten the very nature of the financial system. There are transmission channels between nature and finance that need to be investigated: the many intermediate cause-and-effect relationships should be identified and assessed. Such a process involves multiple disciplinary domains, ranging from ecology and economics to finance. An Ecosystem Services-based approach may represent a comprehensive framework to (i) reconcile coherently different environmental issues such as climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution and sustainable use of resources, and (ii) connect ecosystems and socio-economic systems. Not only can ecosystem services be assessed, but also ecosystem vulnerabilities which are at the origin of nature-related financial risks. Adopting an ecosystem services-based perspective can be the first step toward building ecologically meaningful and economically useful transmission channels for financial risks.