Found 56 results
Article
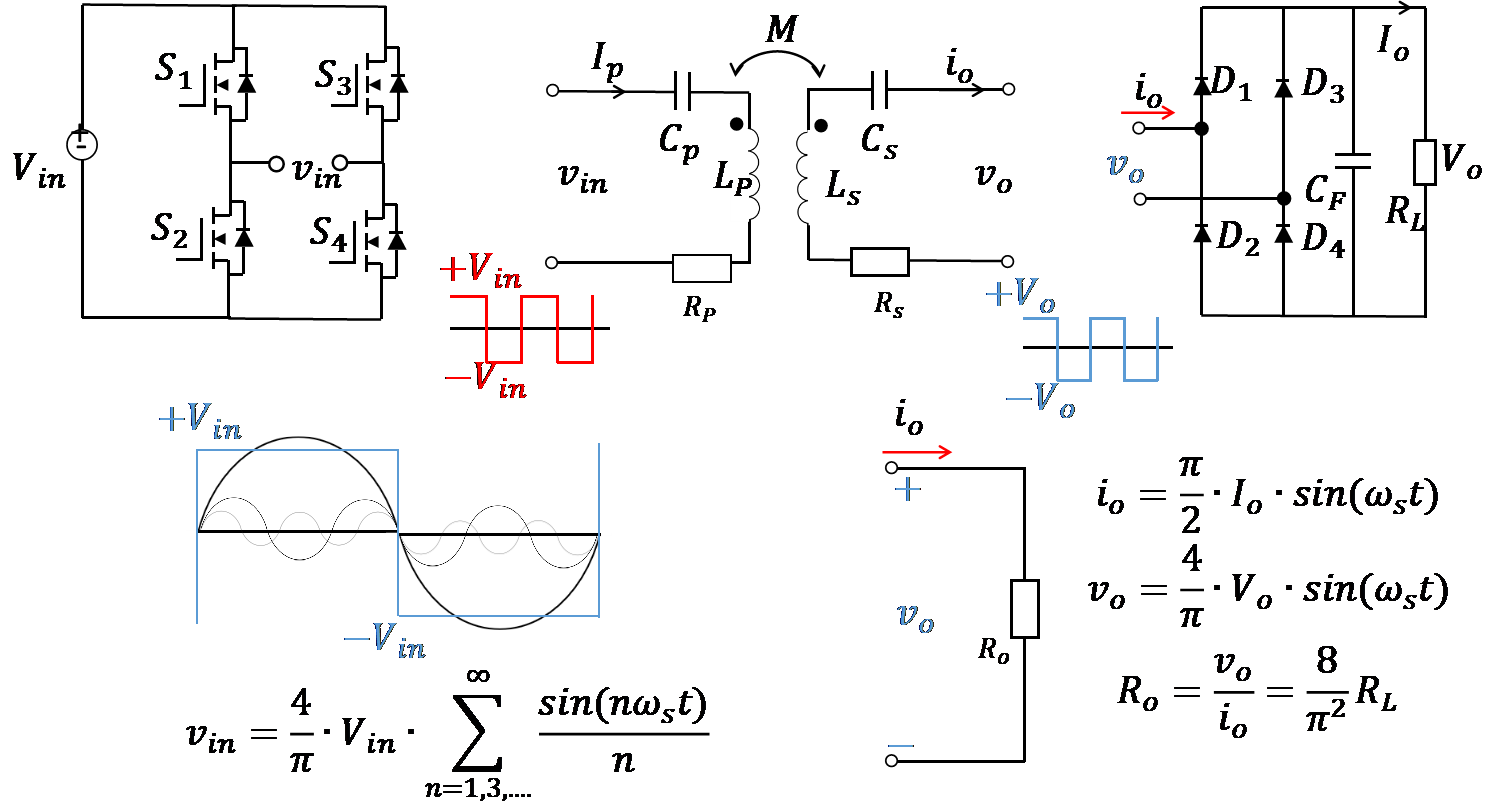
06 May 2025High-Efficiency Wireless Charging System for UAVs Based on PT-Symmetric Principle
To address the limited endurance of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and the efficiency degradation and instability in traditional wireless charging systems, this study proposes a high-efficiency UAV wireless charging system based on the parity-time (PT) symmetric principle. A non-Hermitian coupled resonator model is established, incorporating a dynamic gain-loss balancing mechanism and real-time parameter feedback control to adaptively compensate for coupling coefficient fluctuations caused by UAV positional deviations, thereby maintaining PT-symmetric phase stability. The receiver coil adopts a planar air-core spiral structure and is integrated beneath the UAV landing gear to minimize interference with aircraft operations. Experimental results show a transmission efficiency of 90.2% at 65 W output power, with both power and efficiency remaining stable in the strong coupling region. The system demonstrates strong robustness against horizontal misalignment and eliminates the need for complex relay structures or high-precision alignment. This work not only provides a theoretical foundation for the application of PT-symmetry in wireless power transfer but also offers a novel technical pathway for enhancing UAV endurance.
Article
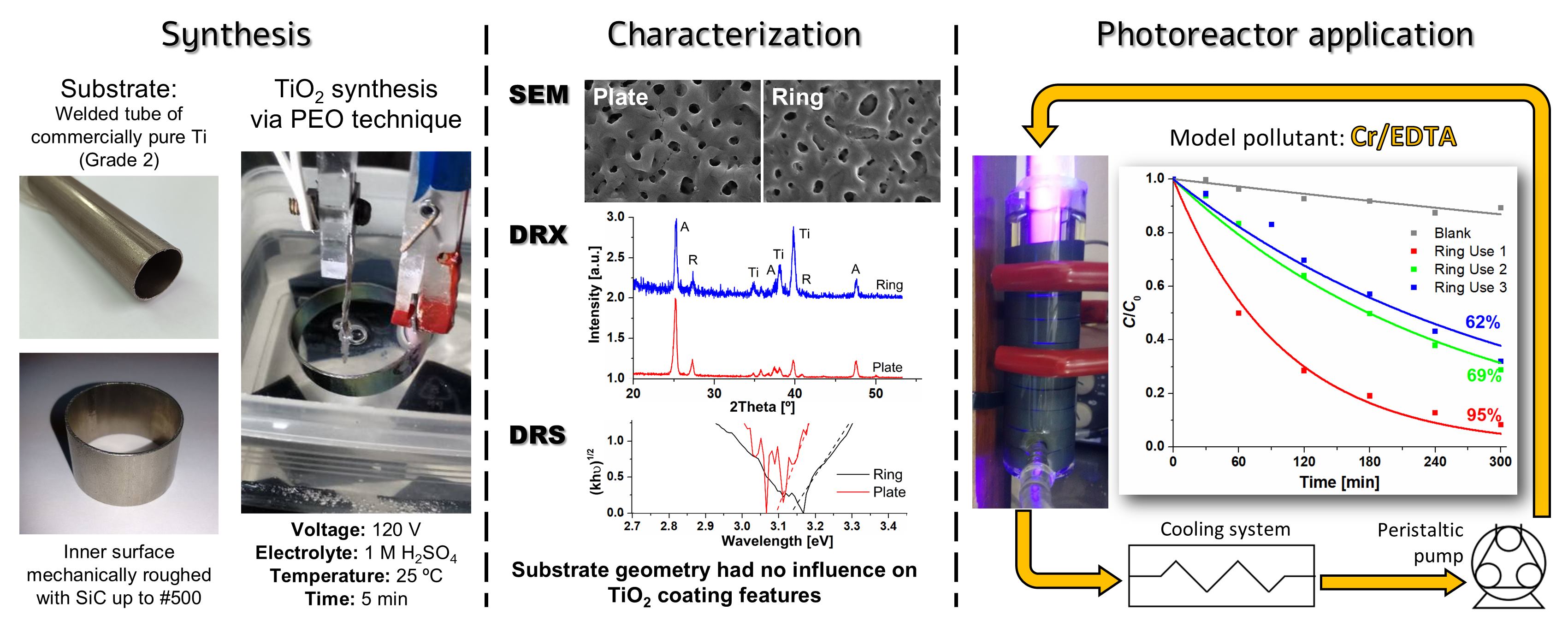
03 April 2025Design, Building and Performance of a New Photocatalytic Reactor Using TiO2-Coated Rings Synthesized by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation
An annular UV photocatalytic reactor with recirculation in batch was designed and built. The design considered low construction, simple operation and maintenance costs, availability and durability of the materials used, easy cleaning, and high standards of hygiene and safety. The TiO2 photocatalysts were synthesized by plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) on commercial Ti rings were compared with coatings obtained on Ti plates as a reference, and no influence of the substrate geometry on the morphology, crystallinity, or bandgap of the coatings was observed. The efficiency of the photocatalytic reactor using 10 TiO2-coated rings was tested by Cr(VI) transformation in the presence of EDTA. The Cr(VI) transformation after 5 h irradiation attained 95%; a rather high photocatalytic activity (62%) was maintained after the third use of the rings without reactivation of the photocatalyst. These coatings synthesized by PEO have not been applied in modular photocatalytic reactors until now.
Article
02 April 2025On Hidden Mathematics in the Artwork of the Indigenous People of Brazil
Using examples from indigenous art in Brazil, this paper demonstrates that these works contain “hidden mathematics” (such as symmetry, striped ornaments, rows, etc.), which challenges the traditional notion of “primitive art”.

Article
20 March 2025Fluctuations in Internal Water Footprint of Major Crops in Egypt: Implications for Sustainable Water Management
The scarcity of water represents a significant obstacle to the advancement of agriculture in Egypt, requiring the implementation of inventive water policies and effective resource management practices. The notion of virtual water, which considers the water contained within things, is a possible remedy to mitigate the strain on water resources. This study examines the changes over time in the amount of water used internally and the amount of virtual water exported by rice, maize, and wheat crops in Egypt between 2000 and 2018. The assessment evaluates the impact of climate variables, crop productivity, and renewable water sources on the internal water footprint. The study uses data from several sources and applies a Nonlinear Autoregressive Distributed Lag (NARDL) model to analyse how productivity, renewable water supplies, temperature, and precipitation affect the internal water footprint. The EVIEWS software is utilised for conducting statistical analysis. The results demonstrate that the internal water footprint and productivity of the crops studied vary over time, and climate conditions and the availability of water control this variation. The maximum internal water footprint values for rice, maize, and wheat were recorded in 2008, 2011, and 2017, respectively, aligning with the highest temperatures and available renewable water resources. The analysis reveals complex connections between the independent factors and the internal water footprint of each crop. Precipitation has an inverse correlation with the internal water footprint of rice, but renewable water resources have a favourable impact on the internal water footprint of wheat. The study emphasizes improving crop choices to minimize water usage and boost water output. Given Egypt’s expected water scarcity by 2025 and its reliance on Nile water for irrigation, implementing sustainable solutions for water resource management in agriculture is crucial. These findings give useful insights for policymakers and stakeholders in creating efficient water management policies and promoting food security in Egypt.
Editorial
17 March 2025The Roots of Rights—Special Issue: “Transformative Practices: Rights of Nature and the Good Life”
This special issue focuses on the social practices of Rights of Nature (RoN), specifically exploring the transformative competencies and skills involved. The research investigates both individual competencies, such as resilience, mindfulness, and creativity, and collective skills, like relationship building and sustainable forms of interaction with the social and the ecological environment. The central question is if RoN does include “best practice” examples of cultivating non-instrumental relationships with the self, the social other, and the natural other.

Communication
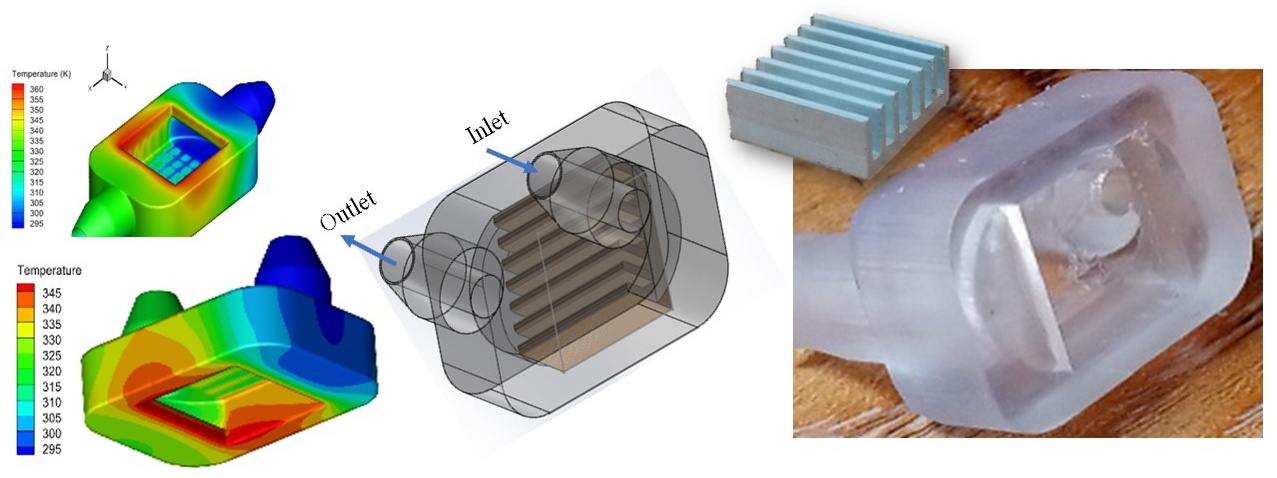
10 March 2025Design Effect of a Mini Channels Heat Sink Using Additive Manufacturing
The present work aims to examine the influence of designing mini channel heat sinks using Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing. Stereolithography (SLA) is a common additive manufacturing technique. The internal mini channels of the heat sink are made of aluminium materials and the outer cover is made of commercial polymer. Three models of the mini channel heat sinks are considered. A constant heat flow is applied to the bottom wall of the heat sink, and water is used as a coolant. The flow and heat transfer were studied for different cooling speeds. The physical properties of the fluid provided good thermal performance for the heat sink, especially at increased flow rates. The acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) copolymer resin has shown its good insulator for the heat sink and has improved the performance of the heat sink. This study demonstrates that the ABS copolymer resin enhances the cooling of electronic components.
Article
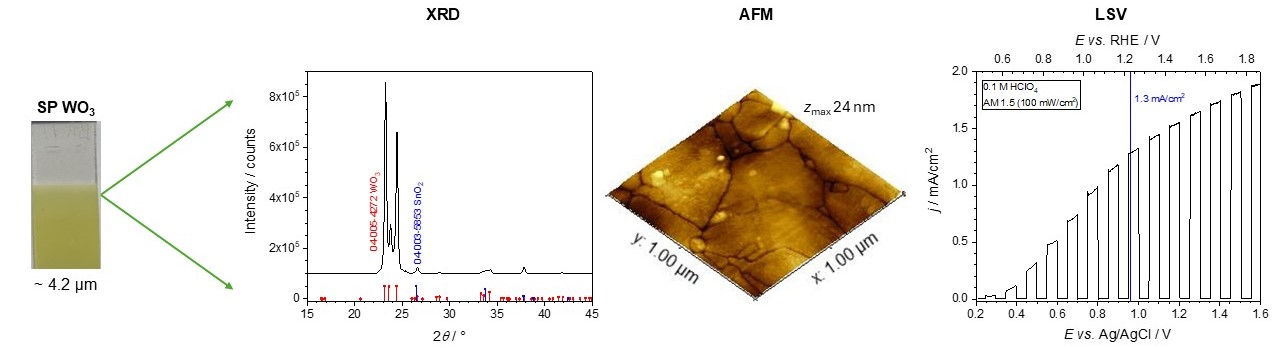
07 March 2025WO3 Photoanodes for Photoelectrochemical Applications
WO3 layers were prepared by spray pyrolysis of a peroxotungstic acid solution on FTO/glass substrates. Investigated parameters were layer thickness and influence of post-annealing in air. Films deposited at 250 °C were amorphous. Post-annealing at 550 °C for 2 h resulted in the formation of monoclinic crystalline structure. A comprehensive account of electrochemical efficiency in terms of IPCE for WO3 films as a function of the three parameters (wavelength, thickness and direction of light incidence) fully characterizing the photoelectrodes is presented here for the first time. The highest improvement in crystallinity and also the highest photocurrent response was found for WO3 layers deposited at 250 °C and post-annealed at 550 °C, namely 1.9 mA/cm2 (in 0.1 M HClO4 at 1.6 V vs. Ag/AgCl) under irradiation with a solar simulator (AM 1.5, 100 mW/cm2) and IPCE = 0.5 at 369 nm (front side irradiation), which is comparable with values obtained by other deposition techniques (e.g., hydrothermal or sol gel). Spray pyrolysis as a method of fabricating WO3 electrodes has the advantage of being able to produce large electrodes for use in practical applications.
Article
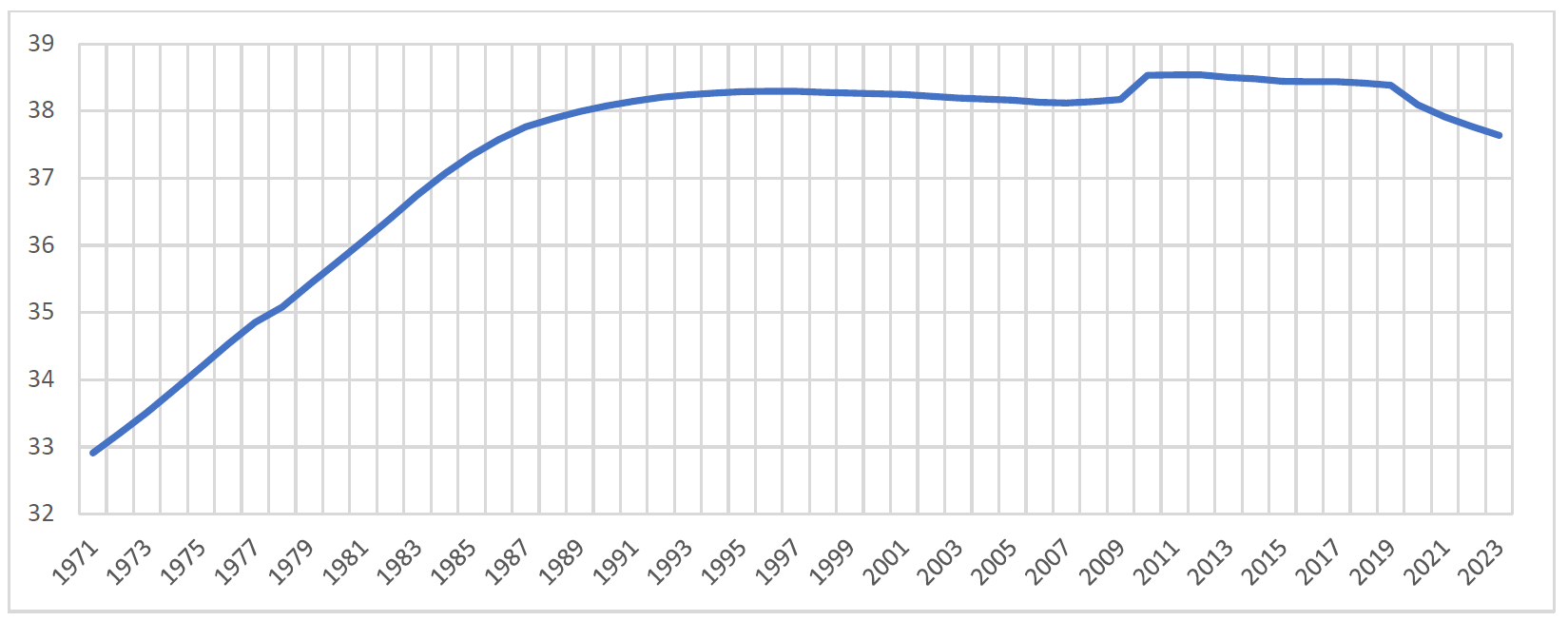
26 February 2025Autopsies in Poland 1971–2023
Autopsies, depending on their purpose, can be described as forensic or clinical. Both types are intended to determine the cause of death, but their goal is different. For forensic autopsies, this goal is to provide expertise with evidential value in various legal proceedings. For clinical autopsies, they have historically been seen as a tool in the development and investigation of disease processes. The aim of the study was to determine how the percentage of autopsies changed in Poland in the years 1971–2023. Research material was data obtained from the Polish Central Statistical Office. On the basis of this data, we showed changes in the population number, the number of deaths, and the number of autopsies in the indicated period. It was shown that in Poland, the percentage of autopsies in relation to all deaths in the period from 1971 to 2023 (53 years) fell about 4-fold from the initial level of approximately 16% to only approximately 4% now. This downward trend is consistent with the trends in other EU countries.
Article
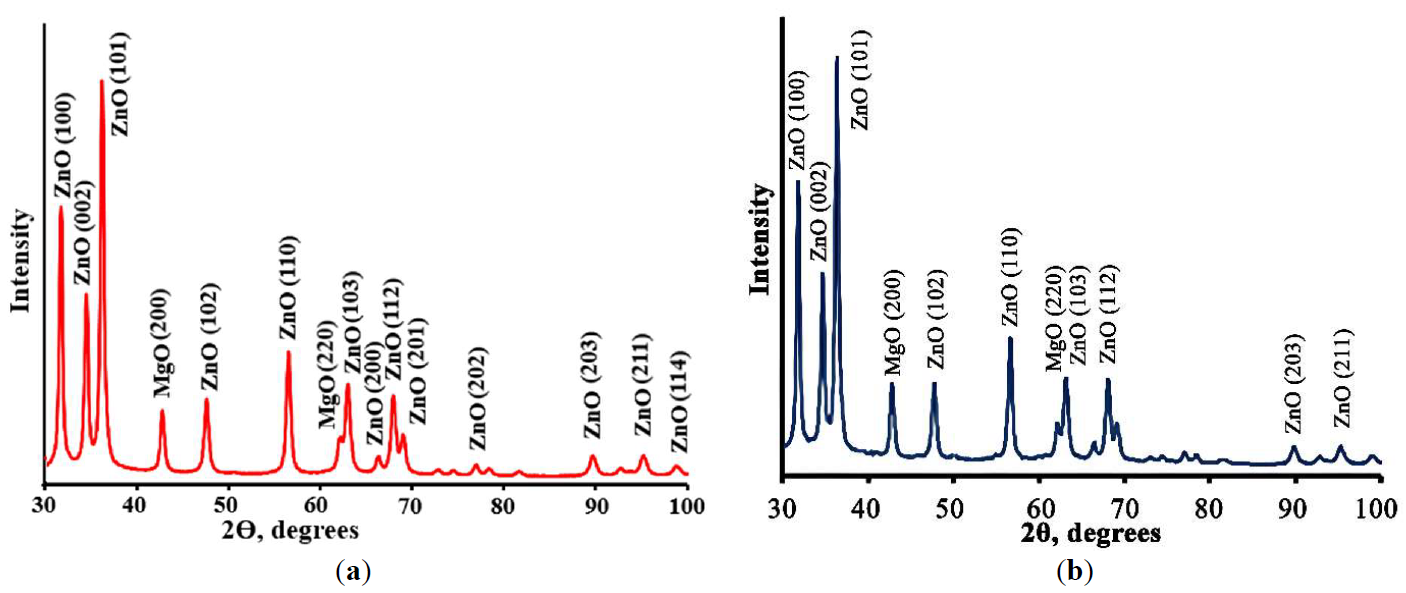
21 February 2025Porous Cu(Mn)-Doped ZnO-MgO Nanocomposites for Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Applications
Porous Cu(Mn):ZnO-MgO composites synthesized by polymeric sol-gel method were characterized. The crystal structure, morphology, spectral properties, the ability of the photogeneration of chemically active singlet oxygen under external visible irradiation, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties of porous composites were studied. Obtained composites consist of small ZnO and MgO crystals having size less than 20 nm. It was found that Cu2+ and Mn2+ ions are embedded into the lattices of ZnO and MgO crystals, altering their crystal cell parameters. The band gap values of obtained composites are 3.41 ÷ 3.42 eV which are slightly higher than the band gap of pure ZnO. Prepared materials demonstrate a high ability of photogeneration of chemically active singlet oxygen under blue light (λ = 405 nm) irradiation. It was found that dependencies of the intensity of singlet oxygen photogeneration from the power density of visible irradiation are linear. Photocatalytic decomposition of the diazo dye Chicago Sky Blue in solutions under UV and blue light irradiation proceeds rapidly in the presence of the prepared composites (constants rate of photocatalytic dye decomposition under UV irradiation are 0.024 min−1 and 0.025 min−1 for ZnO-MgO composites doped with Cu and Mn, correspondingly). Porous composites demonstrate superior antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria. These materials are promising for practical application in medicine and photocatalytic technologies of air and water cleaning.
Article
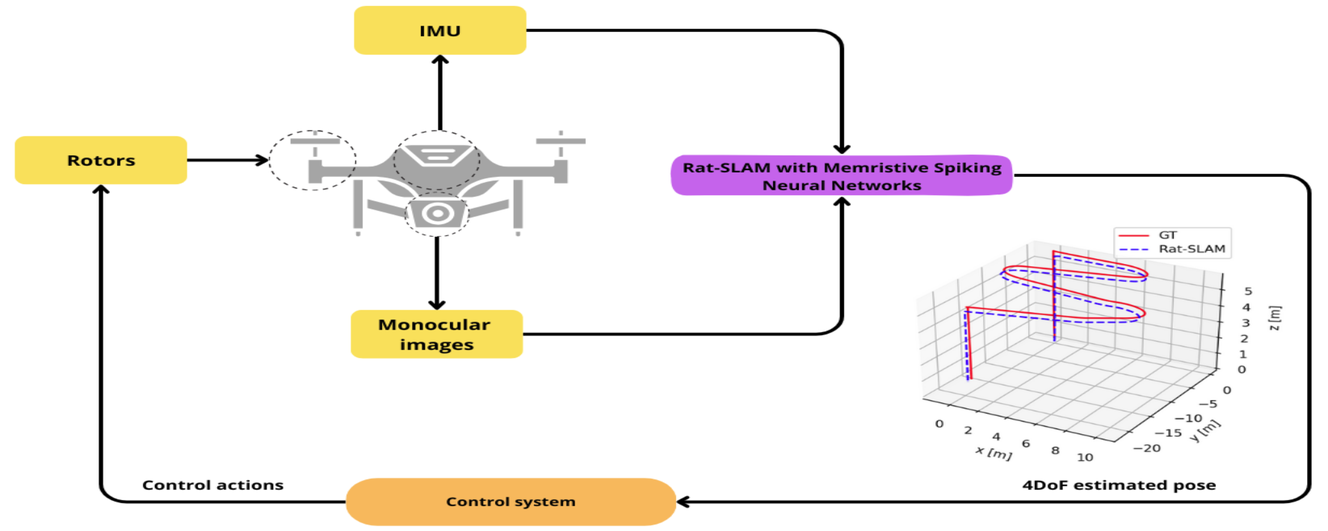
18 February 20254DoF Rat-SLAM with Memristive Spiking Neural Networks for UAVs Navigation System
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are versatile platforms with potential applications in precision agriculture, disaster management, and more. A core need across these applications is a navigation system that accurately estimates location based on environmental perception. Commercial UAVs use multiple onboard sensors whose fused data improves localization accuracy. The bioinspired Rat-Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (Rat-SLAM) system, is a promising alternative to be explored to tackle the localization and mapping problem of UAVs. Its cognitive capabilities, semi-metric map construction, and loop closure make it attractive for localization in complex environments. This work presents an improved Rat-SLAM algorithm for UAVs, focusing on three innovations. First, Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) are incorporated into Rat-SLAM’s core modules to emulate biological processing with greater efficiency. Second, Neuromorphic Computing models the neurons of the SNNs, assessing the feasibility of implementing SNNs on specialized hardware to reduce software processing, a key advantage for UAVs with limited onboard resources. Third, SNNs are developed based on the Memristive Leaky Integrate-and-Fire model, integrating memristors into artificial neurons to leverage their low power and memory properties. Our approach was evaluated through trajectory simulations using the Hector Quadrotor UAV in the Gazebo environment within the Robot Operating System, yielding valuable insights and guiding future research directions.