Study on the Alleviative Effect of Diethyl Aminoethyl Hexanoate (DA-6) on Pepper Seed Germination under Salt Stress
Received: 23 September 2025 Revised: 05 December 2025 Accepted: 19 January 2026 Published: 21 January 2026
© 2026 The authors. This is an open access article under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
1. Introduction
Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) is an annual or limited perennial herbaceous or shrub plant in the Capsicum genus of the Solanaceae family [1]. Chili peppers are mainly fed as fruits, in addition to fresh consumption, the fruits, roots, stems, and leaves of chili peppers can be used as traditional Chinese medicinal materials [2]. DA-6 (Diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate) is a broad-spectrum and efficient plant growth regulator that can significantly promote plant growth, enhance stress resistance, and increase yield. It works by increasing chlorophyll content, enhancing photosynthesis, and regulating endogenous hormone balance, making it suitable for various crops and non-toxic with high safety [3]. Research on crops such as corn, rice, peanuts, flowers, and vegetables has shown that it can increase the activity of plant peroxidase and nitrate reductase, promote plant cell division and elongation, and facilitate seed germination and seedling growth [4]. At the same time, DA-6 naturally degrades in the environment, without toxicity, residues, or hormones. It has the characteristics of safety, high efficiency, low cost, and easy use, and has broad application prospects and market value [5,6,7].
Salinized soil is widely distributed in China. According to statistics from the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China, saline alkali land occupies an important position in China’s agricultural land. The area of saline alkali land in China is approximately 150 million hectares, accounting for about 10% of the total land area. It is mainly distributed in provinces and regions such as Inner Mongolia, Xinjiang, Gansu, Ningxia, Shaanxi, Hebei, and Shandong [8,9]. The effects of salt stress on plants include ion toxicity, osmotic stress, and oxidative stress, which directly hinder plant growth and development and reduce crop yield. Crops that are sensitive to the environment in saline alkali land may experience delayed growth and development [10], growth obstruction, and decreased yield [11,12]. On a global scale, under the mutual influence of human irrational activities and ecosystem degradation, soil salinization areas continue to expand, posing a serious threat to global food production [13]. The restoration of saline soil is urgently needed. Promoting comprehensive management and sustainable development can not only increase arable land resources but also ensure the continuity of land productivity [12]. It is of great significance for maintaining national food security and ecological security, and is an extremely critical systematic project [14].
At present, DA-6 has been applied in crop seed germination. For example, Hua et al. [15] studied the effect of different concentrations of DA-6 on the germination of quinoa seeds. The results showed that DA-6 within the appropriate concentration range had a significant promoting effect on the germination speed and seed vitality of quinoa seeds. Wang et al. [16] investigated the effect of soaking white clover seeds in DA-6 on chromium tolerance during germination rate and germination period under chromium stress. The results showed that DA-6 treatment significantly improved the chromium tolerance of white clover seeds; Yang [17] applied substances such as brassinolide and DA-6 to corn seeds to study their effects on seed germination and salt resistance. The results showed that all substances could improve the salt resistance of rice seeds, and the combination of brassinolide and DA-6 had the best effect on promoting corn hypocotyl growth.
This experiment soaked pepper seeds with different concentrations of DA-6 to study its effect on the germination characteristics of pepper seeds, in order to select the appropriate concentration range of DA-6 and provide technical theoretical reference for high-yield cultivation of pepper. By treating pepper seeds with different concentrations of DA-6 under the same concentration of salt stress, the germination rate, germination potential, root length, and some physiological indicators, including catalase (CAT) activity, peroxidase (POD) activity, and malondialdehyde (MDA) content, were observed [18]. Exploring the regulatory effect of soaking chili seeds in DA-6 on salt tolerance. At the same time, Furthermore, investigate whether DA-6 soaking can alleviate the germination of chili seeds under salt stress.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Treatments
The experimental material was the chili Pepper variety “Changxian Tianxia”, which was selected and bred by Anhui Foster Seed Co., Ltd. (Hefei, China) and produced in Anhui Province. The experiment was conducted from 10 March to 20 April 2025, at Huaibei Normal University, Huaibei, China. Diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate (DA-6) and other analytical drugs were provided by the laboratory of the School of Life Sciences, Huaibei Normal University.
The same variety of chili seeds was selected to ensure their purity and vitality. The DA-6 used in the experiment was a commercially available product with clear active ingredients. Selected chili seeds with plump and pest free particles for the experiment, rinsed with clean water for 30 min, and then soaked the seeds in warm water for 3 h to promote germination. The soaked seeds were taken out, drain of water, and set aside for later use.
This experiment consisted of 5 treatments (T1 (CK), T2, T3, T4, T5), with 3 biological replicates per treatment and 25 seeds per treatment (Table 1). The reason for selecting DA-6 concentrations of 0.1, 0.5, 1, and 5 mmol/L for treatment was that these concentrations form a gradient from low to high, aimed at systematically evaluating the dose-response relationship of DA-6. Low concentrations (such as 0.1 mmol/L) typically promote germination and growth, while high concentrations (such as 5 mmol/L) may inhibit or produce toxic side effects, thereby helping to determine the optimal treatment concentration. After completely dissolving and stirring with 1000 g of purified water, each group should be treated accordingly. 15 culture dishes were used; 2 layers of moist filter paper were placed in each dish, 20 seeds were evenly placed, and the procedure was repeated 3 times per group. After selecting the optimal concentration of amine ester, four treatments were set up (Table 2): C (100 mL distilled water treatment + germination bed using 100 mL distilled water), C + DA-6 (1 mmol/L DA-6 solution 100 mL seed soaking + germination bed using 100 mL distilled water), S (100 mL distilled water seed soaking + germination bed using 200 mmol/L NaCl 100 mL solution), S + DA-6 (1 mmol/L DA-6 solution 100 mL seed soaking + germination bed using 200 mmol/L NaCl solution) [11]. Recorded the number of seed sprouts every day. The observation period for the chili seed germination experiment was 7 days, and the observation time for the seedling stage was 15 days.
Table 1. Experimental Treatment.
|
Treatment |
Diethyl Aminoethyl Hexanoate Concentration (mmol/L) |
|---|---|
|
T1 (CK) |
0 |
|
T2 |
0.1 |
|
T3 |
0.5 |
|
T4 |
1 |
|
T5 |
5 |
Table 2. Experimental Treatment.
|
Treatment |
Seed Soaking |
Germination Bed |
|---|---|---|
|
C |
distilled water |
distilled water |
|
C + DA-6 |
1 mmol/L DA-6 |
distilled water |
|
S |
100 mL distilled water |
200 mmol/L NaCl |
|
S + DA-6 |
1 mmol/L DA-6 |
200 mmol/L NaCl |
2.2. Determination of the Physiological Index
2.2.1. Determination of Seed Germination Index and Fresh Dry Weight
During the seven day process of seed germination, count the number of seeds germinated daily and observe the germination situation. On the 5th day of germination, measure the germination vigor (GV), and on the 7th day, measure the germination percentage (GP). The relevant formula is as follows:
GV = (Number of germinated seeds on the fifth day/Total number of sample seeds) × 100%.
GP = (Number of germinated seeds on the seventh day/Total number of sample seeds) × 100%.
And calculate the germination index (GI) and mean germination time (MGT). The formula is as follows:
| ```latex\mathrm{G}\mathrm{I}=\sum \frac{\mathrm{G}\mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{D}\mathrm{t}}``` | |
| ```latex\mathrm{M}\mathrm{G}\mathrm{T}=\frac{\sum \left(\mathrm{D}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{ }×\mathrm{G}\mathrm{t}\right)}{\sum \mathrm{G}\mathrm{t}}``` |
Among them, Gt is the number of germination days after soaking treatment, and Dt is the number of days used for germination [19].
2.2.2. Determination of Malondialdehyde Content, Antioxidant Enzyme Activity, and Oxidative Damage
Three samples were randomly selected, and the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) was determined using the thiobarbituric acid method. The activity of catalase (CAT) was detected by absorbance at 240 nm, and the activity of peroxidase (POD) was detected by absorbance at 470 nm [20].
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
Data statistics and analysis were conducted using SPSS 26.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA), and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed at the p < 0.05 level. The data was plotted using Origin 2024 software 10.1.
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of Different Concentrations of DA-6 Solution on Seed Germination
From Figure 1 and Table 3, it can be seen that the germination rate, germination potential, average germination time, and germination index varied under different concentrations of DA-6 solution soaking. Among them, soaking seeds at a concentration of 1.0 mmol/L showed the most significant improvement. When the concentration of DA-6 is within a certain range, it can effectively improve the germination rate, germination vigor, and germination index of chili seeds, and significantly reduce the average germination time of seeds. But when the concentration of DA-6 exceeds a certain limit, it inhibits the germination of chili seeds.
Table 3. Germination status of different treated seed germination under salt stress.
|
DA-6 Concentration/mmol/L |
Number of Seeds/Piece |
Number of Sprouts/Piece |
Germination Potential/% |
Germination Rate/% |
Germination Index |
Average Germination Time/d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
20 |
11 |
15% |
55% |
5.664 |
6.00 |
|
0.1 |
20 |
12 |
10% |
60% |
6.093 |
6.08 |
|
0.5 |
20 |
14 |
15% |
70% |
7.692 |
5.78 |
|
1.0 |
20 |
17 |
20% |
85% |
9.54 |
5.64 |
|
5.0 |
20 |
10 |
5% |
50% |
5.064 |
6.10 |
3.2. The Effect of Different Experimental Treatments on Seed Germination under Salt Stress
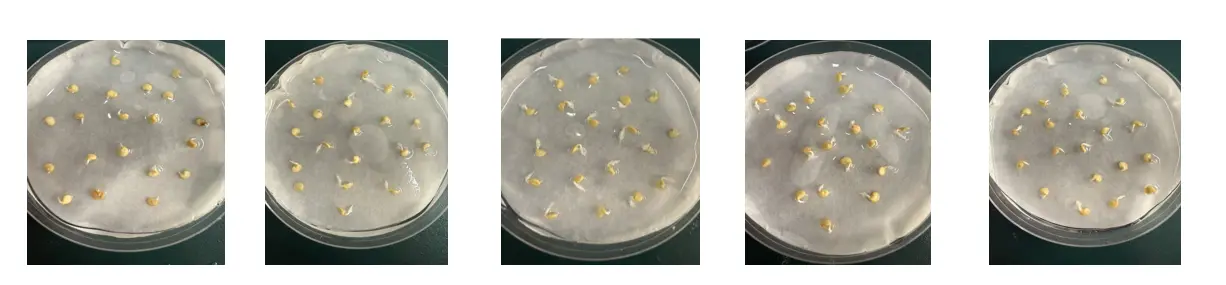
As shown in Figure 2 and Table 4, there are significant differences in the germination of chili seeds treated differently. Under salt stress, the germination potential, germination rate, and germination index of chili seeds significantly decreased, but the average germination time significantly increased. Salt stress significantly inhibited chili seed germination. The germination rate, germination vigor, and germination index of seeds soaked in DA-6 under salt stress were significantly higher than those of chili seeds soaked in water under salt stress. Overall, treatment with 200 mmol/L NaCl significantly inhibited the germination of pepper seeds. Compared with the control group, the germination rate and vigor of pepper seeds under salt stress decreased by 20% and 10%, respectively (p < 0.05). Soaking pepper seeds in DA-6 can effectively alleviate the inhibitory effect of salt stress on pepper seed germination. Whether treated with distilled water or NaCl, the germination potential of pepper seeds soaked in DA-6 increased by 10% and 15%, respectively. However, there was no significant change in germination rate in either treatment group.
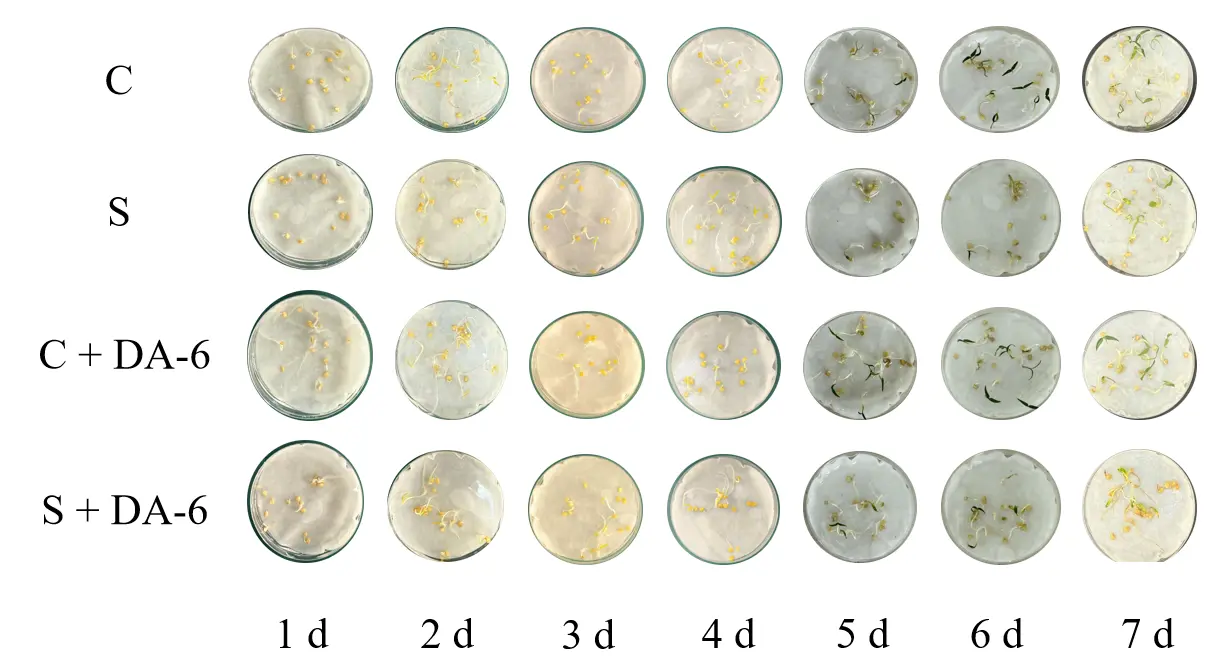
Figure 2. Significant conditions of pepper seed germination under different treatments. C: 100 mL distilled water treatment + 100 mL distilled water for germination bed. S: 100 mL distilled water seed soaking + 200 mmol/L NaCl 100 ml solution for germination bed.
Table 4. Seed germination status of different treatments.
|
Treatment |
Number of Seeds/Piece |
Number of Sprouts/Piece |
Germination Potential/% |
Germination Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
C |
20 |
18 |
75% |
90% |
|
C + DA-6 |
20 |
18 |
85% |
90% |
|
S |
20 |
14 |
65% |
70% |
|
S + DA-6 |
20 |
18 |
90% |
90% |
3.3. The Effect of Different Experimental Treatments on the Growth of Chili Seeds under Salt Stress
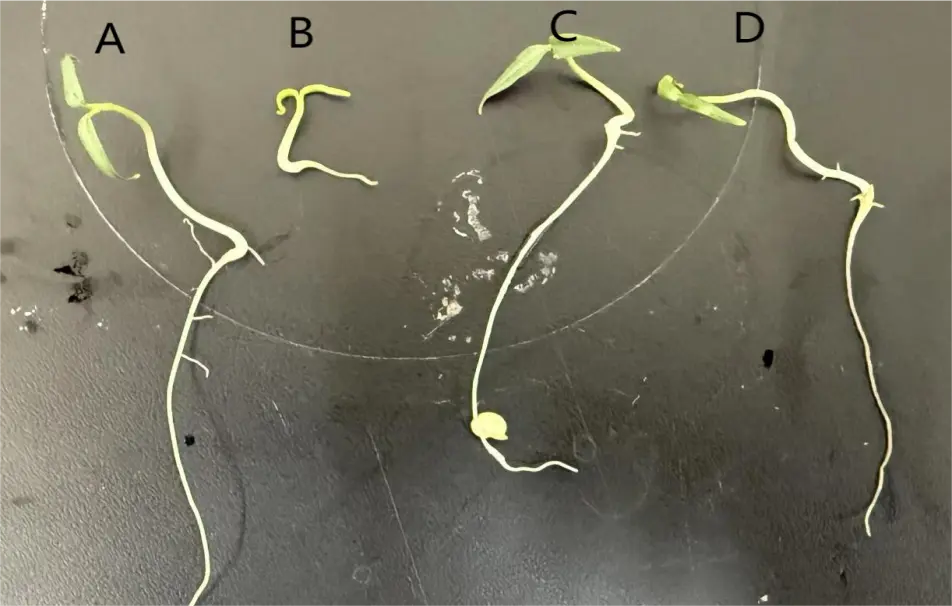
According to Table 5 and Figure 3, under the same environmental factors, the growth of pepper seeds soaked in DA-6 was better. In distilled water treatment and NaCl treatment, the root length and stem length of pepper seeds were significantly increased. Overall, salt stress significantly inhibited the growth of roots and stems of chili seeds, resulting in significantly lower root and stem lengths in the S group and S + DA-6 group compared to the C group and C + DA-6 group under the same environmental factors. Under distilled water treatment, the root length of pepper seeds soaked in DA-6 increased by 19.7%, while there was no significant difference in stem length. Under NaCl treatment, pepper seeds soaked in DA-6 increased by 18.7% and stem length increased by 35.9%. This indicates that under the same treatment conditions, DA-6, as a plant growth regulator, can effectively alleviate the inhibitory effect of salt stress on pepper seed growth and promote the growth of pepper roots and stems.
Table 5. Growth and development of different tissue culture materials.
|
Treatment |
Root Length/cm |
Stem Length/cm |
|---|---|---|
|
C |
3.10 ± 1.38 a |
0.105 ± 0.006 a |
|
C + DA-6 |
3.86 ± 1.92 a |
0.116 ± 0.008 a |
|
S |
2.17 ± 0.93 b |
0.043 ± 0.002 c |
|
S + DA-6 |
2.67 ± 1.41 c |
0.067 ± 0.004 b |
a,b,c: Different letters meant significant difference among different treatments at 0. 05 level.
3.4. The Effects of Different Experimental Treatments on Enzyme Activity and MDA Content in Chili Pepper under Salt Stress
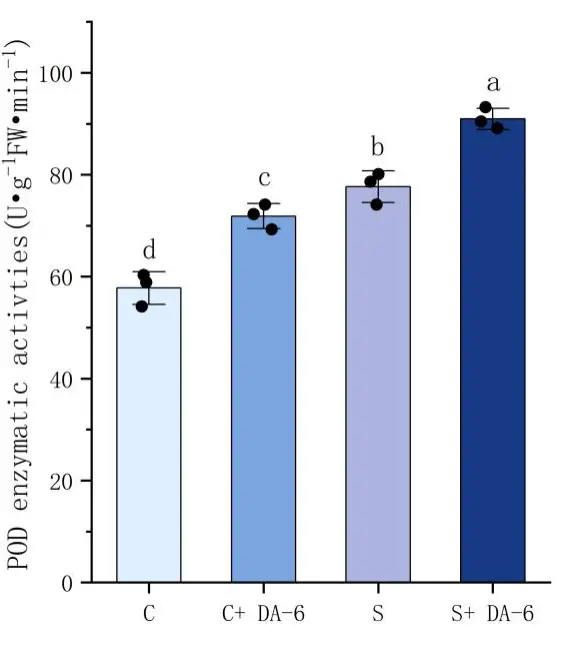
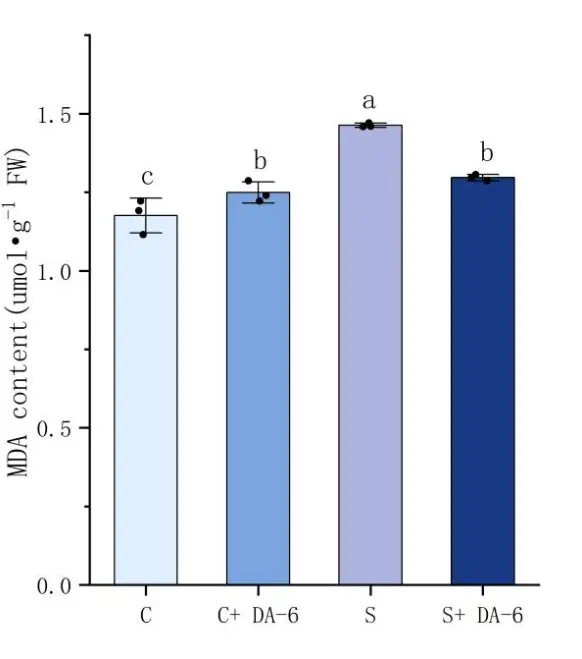
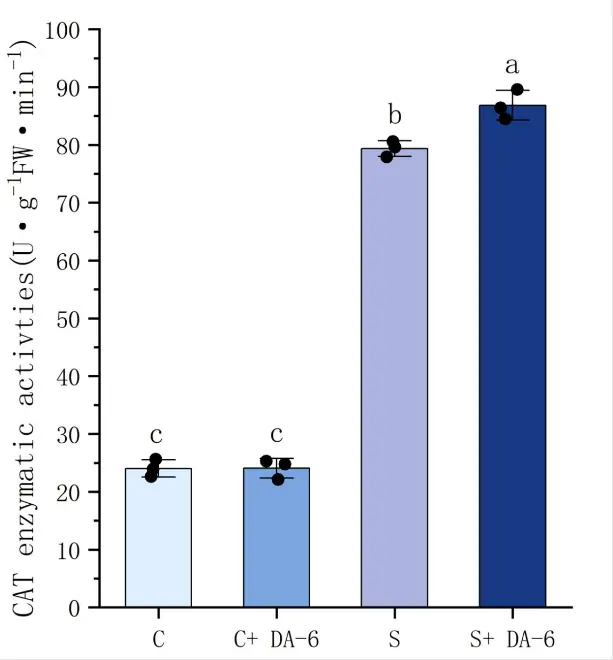
As shown in Figure 4, salt stress induces the accumulation of MDA. In the comparison between distilled water treatment and NaCl treatment, it can be found that the MDA content in seeds under salt stress increased by 19.6% compared to seeds treated with distilled water. The use of DA-6 soaking treatment can significantly reduce the MDA content of seeds, with a decrease of 11.4% in NaCl treatment. In terms of antioxidant enzymes, salt stress stimulates the activity of antioxidant enzymes in the body, leading to a significant increase in CAT and POD activity under salt stress treatment. Through analysis, it can be concluded that under distilled water treatment conditions, soaking chili seeds in DA-6 can enhance the antioxidant enzyme activity, with CAT and POD activities increasing by 1.5% and 19.6%, respectively. Although the activity of the CAT enzyme did not significantly increase, under NaCl treatment, the activities of CAT and POD increased by 8.6% and 14.6%, respectively. The results showed that the DA-6 seed soaking treatment can effectively improve the antioxidant capacity of pepper seeds under salt stress, stimulate the body to produce more antioxidant enzymes, and thus resist the harm of salt stress to seed germination and growth.
 |
 |
|
(A) |
(B) |
 |
|
|
(C) |
Figure 4. Effects of water soaking or DA-6 soaking on seed physiological indicators. Note: (A) shows the POD enzyme activity of pepper seeds under different treatments, (B) shows the MDA content of pepper seeds under different treatments, and (C) shows the CAT enzyme activity of pepper seeds under different treatments. a,b,c,d: Different letters meant significant difference among different treatments at 0. 05 level.
3.5. The Correlation Between Physiological and Biochemical Indicators of Chili Seeds under Salt Stress and Other Factors under Different Treatments
According to Table 6, different soaking treatments significantly regulate the oxidative stress response and antioxidant system of chili seeds, resulting in a gradient relief effect on the germination of chili seeds under salt stress. There is a significant negative correlation between MDA content and germination rate, indicating that soaking seeds in DA-6 can reduce MDA accumulation and effectively alleviate membrane lipid peroxidation damage. The significant positive correlation between POD and CAT and germination rate and root length reveals that the enhancement of antioxidant enzyme activity is the core mechanism for promoting seed germination and root extension. It is worth noting that there is a significant negative correlation between seed germination rate and antioxidant indicators. This phenomenon suggests that when DA-6 concentration is too high, it may trigger an excessive stress response in the plant’s antioxidant defense system. The excessive activation of the antioxidant system not only fails to promote seed germination but also interferes with its normal germination process, thereby inhibiting seed germination. This discovery reveals the inhibitory mechanism of high concentration DA-6 on seed germination, providing important dose-response data and a theoretical basis for scientifically determining the optimal concentration of DA-6 in promoting seed germination applications.
Table 6. Correlation between physiological and biochemical indices and other factors during pepper germination under different treatments.
|
Index |
M ± SD |
Germination Percentage |
Root Length |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Malondialdehyde content |
1.296 ± 0.010 |
−0.73 * |
−0.91 ** |
|
Peroxidase activity |
90.95 ± 1.56 |
0.82 * |
0.78 * |
|
Catalase activity |
86.83 ± 2.55 |
0.65 * |
0.85 ** |
Note: * indicates a significant correlation at the 0.05 level (two-tailed), ** indicates a significant correlation at the 0.01 level (two-tailed).
4. Discussion
The typical symptoms of plant salt stress damage include yellowing of leaves, imbalance of osmotic balance, and decreased yield. During seed germination, the harm of salt stress mainly manifests in reducing seed germination rate, germination vigor, increasing germination time, and inhibiting root and shoot growth. Research has shown that NaCl has a low promotion and high inhibition effect on the germination of Sichuan pepper seeds. When the NaCl concentration exceeds 150 mmol/L, the overall germination rate of Sichuan pepper decreases by about 16.33%, and root length is significantly inhibited [21]. This is generally consistent with the results of this experiment, that is, salt stress significantly inhibited the germination rate, germination vigor, and growth and development of chili seeds. Previous studies have shown that pre soaking seeds with certain chemicals is an effective method to alleviate the inhibitory effect of stress conditions on seed germination [22]. Studies by Dai et al. [23] have shown that DA-6 has a good promoting effect on the germination of crop seeds and the growth of roots. This study shows that soaking seeds in a 1.0 mmol/L plant growth regulator DA-6 solution can significantly improve the germination status of pepper seeds under salt stress, effectively increasing germination rate, germination potential, root length, and other indicators, and alleviating the inhibitory effect of salt stress on seed germination.
Non biological stresses, such as salt stress, can induce excessive accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in plants. These highly oxidative substances can directly attack the cell membrane system and organelles, leading to a series of oxidative damage, including lipid peroxidation, protein structural damage, and cellular dysfunction [9,19,24]. Under salt stress, the typical characteristic of oxidative damage in plant cells is the significant accumulation of membrane lipid peroxidation product MDA, which serves as an important indicator of the degree of membrane structure damage and changes in membrane permeability, intuitively reflecting the destructive effect of salt stress on cell integrity. The latest research shows that under salt stress, the content of MDA in tomatoes, corn, and smooth brome significantly increases, and the degree of membrane lipid oxidation increases [10,25,26]. This study showed that the MDA content of pepper seeds treated with salt stress was significantly higher than that of seeds treated with distilled water. DA-6 soaking pepper seeds can alleviate the effects of salt stress on pepper seed germination and growth. Compared with pepper seeds treated with distilled water, although the MDA content of pepper seeds under salt stress increased, it significantly decreased by 11.5% compared with those without DA-6 soaking. This indicates that DA-6 soaking pepper seeds can effectively reduce the degree of membrane lipid peroxidation, thereby alleviating the harm of salt stress on pepper seeds.
In addition, under salt stress, seeds pre treated with DA-6 soaking can maintain higher levels of antioxidant enzyme (CAT and POD) activity. Numerous studies have shown that under adverse conditions, plants produce a large amount of oxygen free radicals, which activate the body’s protective enzymes and enhance its vitality [4,7,27,28,29]. Therefore, the activities of CAT and POD in plants under salt stress are significantly increased compared to normal plants. This study showed that under salt stress, the activities of two enzymes in chili seeds increased by 25.6% and 70%, respectively. The pepper seeds treated with DA-6 soaking can effectively enhance the activity of two enzymes. Compared with distilled water treatment, POD activity increased by 21.0% and CAT activity increased by 72.2%. Therefore, the DA-6 soaking treatment significantly enhanced the antioxidant capacity of pepper seeds under salt stress conditions, enabling them to more effectively resist oxidative damage caused by salt stress during germination and growth.
In summary, DA-6, as a plant growth regulator, can effectively alleviate the inhibitory effect of salt stress on pepper seeds after seed soaking pretreatment. It should be noted that the concentration of DA-6 should not be too high or too low, and the promoting effect is most significant at a concentration of 1 mmol/L. Under salt stress conditions, exogenous DA-6 soaking treatment can significantly improve germination rate, germination vigor, and growth indicators, including root and stem length, in chili seeds. Salt stress conditions significantly induce the accumulation of MDA in seeds, and DA-6 pretreatment can reduce the MDA content in seeds, thereby alleviating the harm caused by salt stress. In addition, this treatment can enhance the antioxidant defense ability of seedlings by increasing the activity of CAT and POD, thereby effectively alleviating oxidative damage caused by salt stress, maintaining the stability of cell membrane structure, and creating favorable conditions for seed germination under a salt stress environment.
Statement of the Use of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
During the preparation of this manuscript, the author(s) used baidu translation software 2.21 AI tools. After using this tool/service, the author(s) reviewed and edited the content as needed and take(s) full responsibility for the content of the article.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Jie Liu (Huaibei Normal University, Department of School of life), Jiyuan Wang (Huaibei Normal university, Department of School of Life), Yupeng Fang (Huaibei Normal university, Department of School of Life) and Yanliang Guo (Huaibei Normal University, Department of School of Life), who were involved in the experiment.
Author Contribution
C.L. was responsible for experimental design and manuscript writing, M.F., J.L. and H.L. implemented the experimental content, and corrected and revised the paper.
Ethics Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The author confirms that all data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Funding
This work was supported by the Open Project of National Engineering Research Center of Tree breeding and Ecological restoration (LMYZKY2023001), supported by 2024 National College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project (202410373052), 2023 Anhui Province College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (S202310373010S), supported by 2019 Huaibei Normal University’s newly introduced doctoral teachers’ research startup fund (03106059), and supported by 2023 Anhui Province Watermelon and Melon Biological Breeding Engineering Center Open Project Fund (AHXTKF2023003), and Natural Science Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Anhui Province (2024AH051665).
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Salehi B, Zakaria ZA, Gyawali R, Ibrahim SA, Rajkovic J, Shinwari ZK, et al. Piper Species: A Comprehensive Review on Their Phytochemistry, Biological Activities and Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 1364. DOI:10.3390/molecules24071364 [Google Scholar]
- Ma J, Wang Y, Wang LY, Lin D, Yang Y. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the mechanism of the alleviation of salt stress by salicylic acid in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 50, 3593–3606. DOI:10.1007/s11033-022-08064-y [Google Scholar]
- Lu J, Guan P, Gu J, Yang X, Wang F, Qi M, et al. Exogenous DA-6 Improves the Low Night Temperature Tolerance of Tomato Through Regulating Cytokinin. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 599111. DOI:10.3389/fpls.2020.599111 [Google Scholar]
- Hassan MJ, Qi H, Cheng B, Hussain S, Peng Y, Liu W, et al. Enhanced adaptability to limited water supply regulated by diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate (DA-6) associated with lipidomic reprogramming in two white clover genotypes. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 879331. DOI:10.3389/fpls.2022.879331 [Google Scholar]
- Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Li X, Jiang Z, Dong S. Effects of DA-6 and MC on the growth, physiology, and yield characteristics of soybean. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 304. DOI:10.1186/s12870-025-06310-6 [Google Scholar]
- Huang X, Rao G, Peng X, Xue Y, Hu H, Feng N, et al. Effect of plant growth regulators DA-6 and COS on drought tolerance of pineapple through bromelain and oxidative stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 180. DOI:10.1186/s12870-023-04200-3 [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J, Li S, Cai Q, Wang Z, Cao J, Yu T, et al. Exogenous diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate ameliorates low temperature stress by improving nitrogen metabolism in maize seedlings. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232294. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0232294 [Google Scholar]
- Li XL, Su X, Liu YP, Yu MJ, Yang Q, Sun CL, et al. Effects of drought and salt stress on seed germination and seedling physiological index of Rumex patientia (polygonaceae). Pratacult. Sci. 2025, 43, 1–10. DOI: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2024-0547. [Google Scholar]
- Liu J, Wu Y, Dong G, Zhu G, Zhou G. Progress of Research on the Physiology and Molecular Regulation of Sorghum Growth under Salt Stress by Gibberellin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6777. DOI:10.3390/ijms24076777 [Google Scholar]
- Guo M, Wang XS, Guo HD, Bai SY, Khan A, Wang XM, et al. Tomato salt tolerance mechanisms and their potential applications for fighting salinity: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 949541. DOI:10.3389/fpls.2022.949541 [Google Scholar]
- Fu H, Yang Y. How Plants Tolerate Salt Stress. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 5914–5934. DOI:10.3390/cimb45070374 [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf M, Munns R. Evolution of approaches to increase the salt tolerance of crops. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2022, 41, 128–160. DOI:10.1080/07352689.2022.2065136 [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf M, Shahzad SM, Imtiaz M, Rizwan MS. Salinity effects on nitrogen metabolism in plants—Focusing on the activities of nitrogen metabolizing enzymes: A review. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 1065–1081. DOI:10.1080/01904167.2018.1431670 [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf M, Foolad MR, Tuberosa R. Crop breeding for salt tolerance in the era of molecular markers and marker-assisted selection. Plant Breed. 2012, 132, 10–20. DOI:10.1111/pbr.12000 [Google Scholar]
- Hua JS, Wang XJ, Chen LQ. The effect of soaking quinoa seeds in different concentrations of ammonium salt on germination. Tillage Cultiv. 2020, 40, 29–31. DOI:10.13605/j.cnki.52-1065/s.2020.01.009 [Google Scholar]
- Wang D, Tian YL, Zhang HJ, Zhang QQ, Chen KR, Li Z. Effects of diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate on seed germination characteristics of white clover under chromium stress. Pratacult. Sci. 2021, 38, 1986–1997. DOI:10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2021-0227 [Google Scholar]
- Yang Q. The Effect of DA-6 Treatment on the Vitality of Corn Seeds. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cao YQ, Cheng BZ, Li Z. Effects of the Seed Soaking with DA-6 on Germination Characteristics and Stress Tolerance of White Clover under Salt Stress. Acta Agrest. Sin. 2023, 31, 140–147. DOI:10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2023.01.016 [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Liu L, Kong X, Wang X, Si A, Zhao F, et al. Time-Course Transcriptomics Analysis Reveals Molecular Mechanisms of Salt-Tolerant and Salt-Sensitive Cotton Cultivars in Response to Salt Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 329. DOI:10.3390/ijms26010329 [Google Scholar]
- Zhou ZG, Deng C, Feng X. The effect of exogenous melatonin on physiological characteristics of eggplant seedlings under salt stress. Chin. J. Veg. 2025, 1, 126–133. DOI:10.19928/j.cnki.1000-6346.2025.5006 [Google Scholar]
- Qin J, Luo GX, Li T, Li Y, Hu T. Analysis of NaCl tolerance in seed germination and seedling growth of two types of Sichuan pepper. Seed 2016, 35, 24–28+31. DOI:10.16590/j.cnki.1001-4705.2016.09.024 [Google Scholar]
- Kang GZ, Li GZ, Liu GQ, Xu W, Peng XQ, Wang CY, et al. Exogenous salicylic acid enhanc-es wheat drought tolerance by influence on the expression of genes related to ascorbate-glutathione cycle. Biol. Plant. 2013, 57, 718–724. DOI:10.1007/s10535-013-0335-z [Google Scholar]
- Dai HY, Hua JS, Zhang RP, Cai GZ. The effect of DA-6 soaking on germination and seedling traits of colored red rice seeds. Seed 2018, 37, 38–44. DOI: 10.16590/j.cnki.1001-4705.2018.05.038. [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Zhou H, Feng N, Zheng D, Ma G, Feng S, et al. Physiological and transcriptome analysis reveals that prohexadione-calcium promotes rice seedling’s development under salt stress by regulating antioxidant processes and photosynthesis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286505. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0286505 [Google Scholar]
- Aydinoglu F, Kahriman TY, Balci H. Seed bio-priming enhanced salt stress tolerance of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings by regulating the antioxidant system and miRNA expression. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 378. DOI:10.1007/s13205-023-03802-w [Google Scholar]
- Wei L, Feng L, Liu Y, Liao W. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Is Involved in Salt Stress Response in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) Seedlings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7645. DOI:10.3390/ijms23147645 [Google Scholar]
- Hassan MJ, Zhou M, Ling Y, Li Z. Diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate ameliorates salt tolerance associated with ion transport, osmotic adjustment, and metabolite reprograming in white clover. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 950. DOI:10.1186/s12870-024-05657-6 [Google Scholar]
- Athar HU, Zulfiqar F, Moosa A, Ashraf M, Zafar ZU, Zhang L, et al. Salt stress proteins in plants: An overview. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 999058. DOI:10.3389/fpls.2022.999058 [Google Scholar]
- Zhang C, He P, Li Y, Li Y, Yao H, Duan J, et al. Exogenous diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate, a plant growth regulator, highly improved the salinity tolerance of important medicinal plant Cassia obtusifolia L. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 35, 330–344. DOI:10.1007/s00344-015-9536-3 [Google Scholar]