Found 2 results
Open Access
Article
03 March 2025Harmony between Humanity and Nature in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration during Decadal Development
Building harmony between humanity and nature
(HHN) migrates the conflict between social-economic development and
eco-environmental conservation, promoting the coordination and balance between
economic development and ecological protection, and then achieving the state of harmonious coexistence
between humanity
and nature. Here, taking advantage of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban
agglomeration as the research region, this study aimed to evaluate the changes
in comprehensive level of economic, social, and ecological development, as well
as the coupling coordination degree of HHN from 2014 to 2021, and to identify
their spatio-temporal evolution patterns. The findings reveal that from 2014 to
2021, the comprehensive development level of HHN in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei
urban agglomeration exhibits a linearly increasing pattern, with significant
differences in time and space.
The comprehensive development level of HHN in the northern region of the
Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration has always been higher than that in
the southern region. By
2021, all the cities had basically reached a middle development level. And the
coordination degree of the comprehensive development of HHN showed a healthy
development trend. In 2021, the coordination degree of HHN in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration was at
transitional development, with an average annual increase of 3%. In the future, the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration should
prioritize coordinated development of HHN, enhance eco-environment protection
and management, promote industrial transformation and upgrading, explore new
development modes and ecological resource transformation strategies, and
establish a modern capital region characterized by high-level ecological
civilization development.

Open Access
Article
14 June 2023Spatio-temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Farmland Circulation Price at the County Level in China
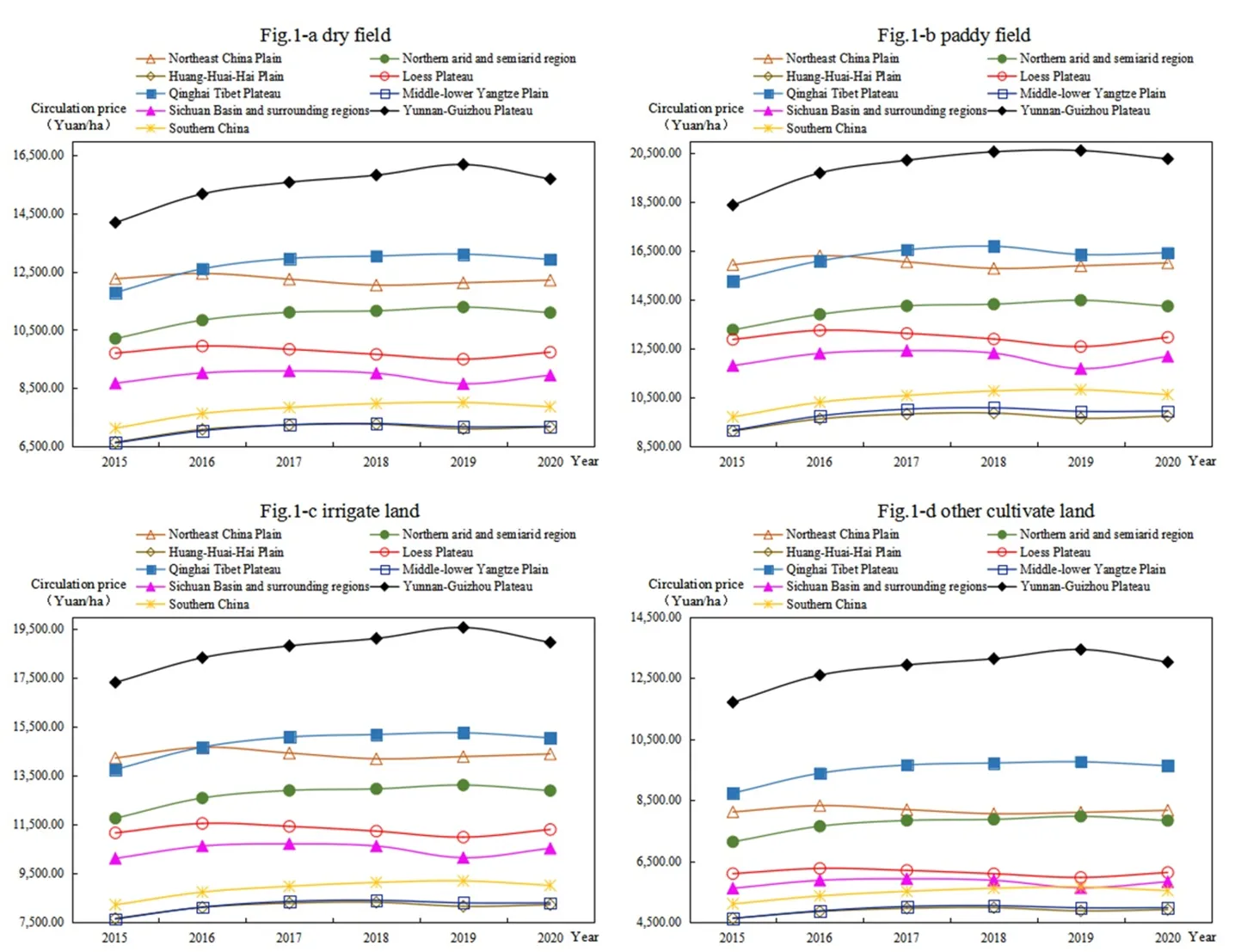
Farmland circulation is an important way to achieve moderate scale operation to ensure food security. Based on the spatial analysis and spatial econometric model, this paper studies the spatial-temporal evolution and influencing factors of cultivated land transfer price at the county level in China from 2015 to 2020. The results revealed the following: (1) the circulation price of farmland generally shows paddy field > irrigated land > dry land > other cultivated land. The farmland circulation price in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain is always the highest, whereas that in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau is always the lowest. (2) The spatial pattern of farmland circulation price is high in the south and low in the north, presenting an inverted U-shaped structure from east to west in 2015, and high in the east and low in the west, presenting an inverted U-shaped structure from north to south in 2020. Moreover, the spatial agglomeration was enhanced. (3) With the development of land market and urbanization, the restriction of natural factors of cultivated land on the farmland circulation price weakens, while the socio-economic attribute of cultivated land constantly strengthens. Based on the results, this paper puts forward some suggestions to prevent the overcapitalization of land.