Found 1 results
Open Access
Article
17 December 2024Upcycling of Waste Poly(ethylene terephthalate) into 2,4-Pyridine Dicarboxylic Acid by a Tandem Chemo-Microbial Process
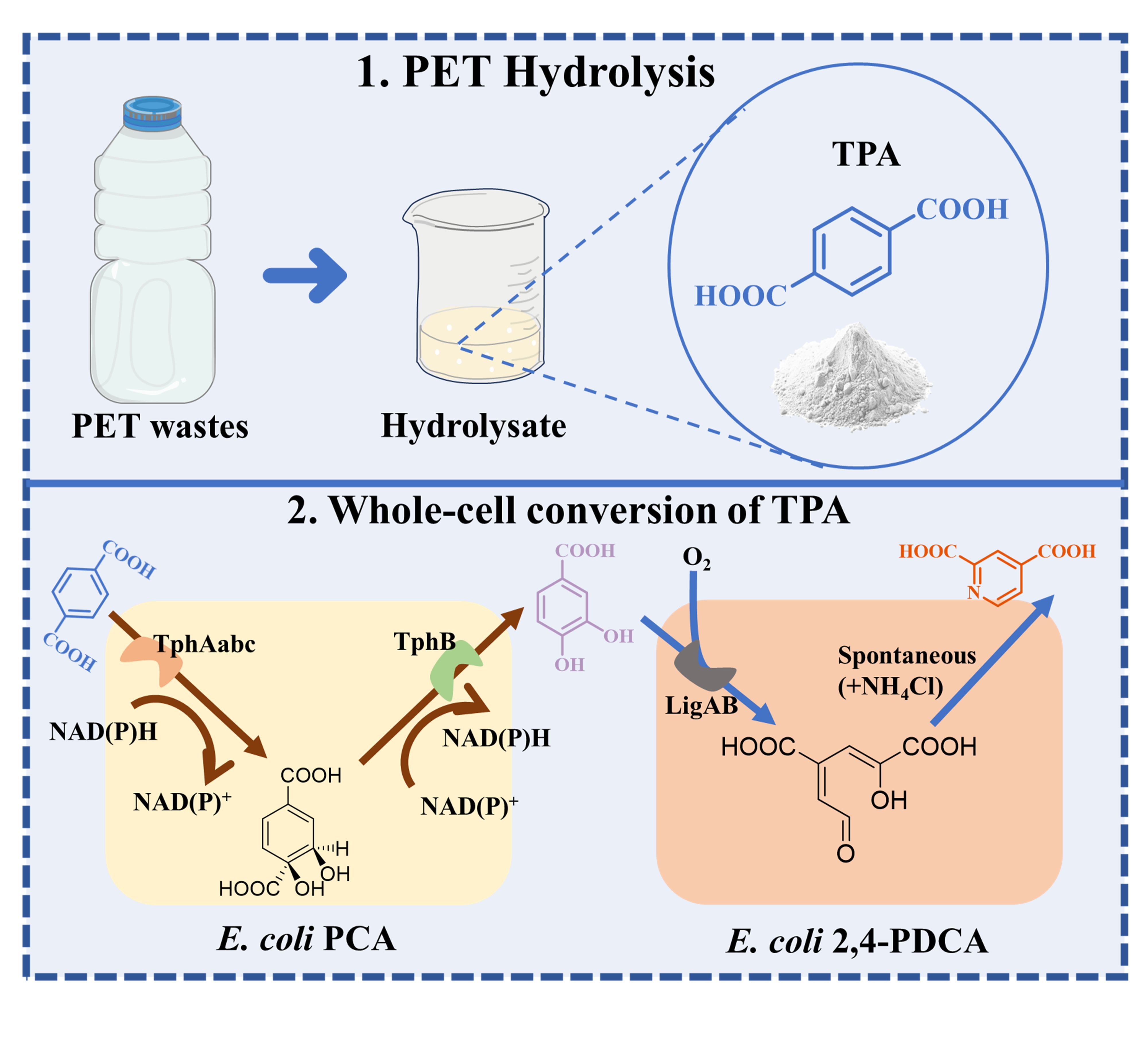
This study presents a chemo-microbial cascade process for the upcycling of waste poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) into valuable compound 2,4-pyridine dicarboxylic acid (2,4-PDCA). Initially, waste PET undergoes efficient hydrolysis to terephthalic acid (TPA) with a high yield of 92.36%, catalyzed by p-toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA). The acid catalyst exhibits excellent reusability, maintaining activity over five cycles. Subsequently, a one-pot, two-step whole-cell conversion system utilizing genetically modified Escherichia coli strains (E. coli PCA and E. coli 2,4-PDCA) converts the generated TPA into 2,4-PDCA. By integrating the PET hydrolysis module with the 2,4-PDCA biosynthesis module, the study achieves an impressive overall efficiency of 94.01% in converting challenging PET waste into valuable 2,4-PDCA. Our research presents a rational design strategy for PET upcycling and 2,4-PDCA synthesis methods. This research provides a systematic approach to PET upcycling, demonstrating its feasibility and potential for industrial application.