Found 5 results
Review
06 December 2024Recent Progress of High Safety Separator for Lithium-Ion Battery
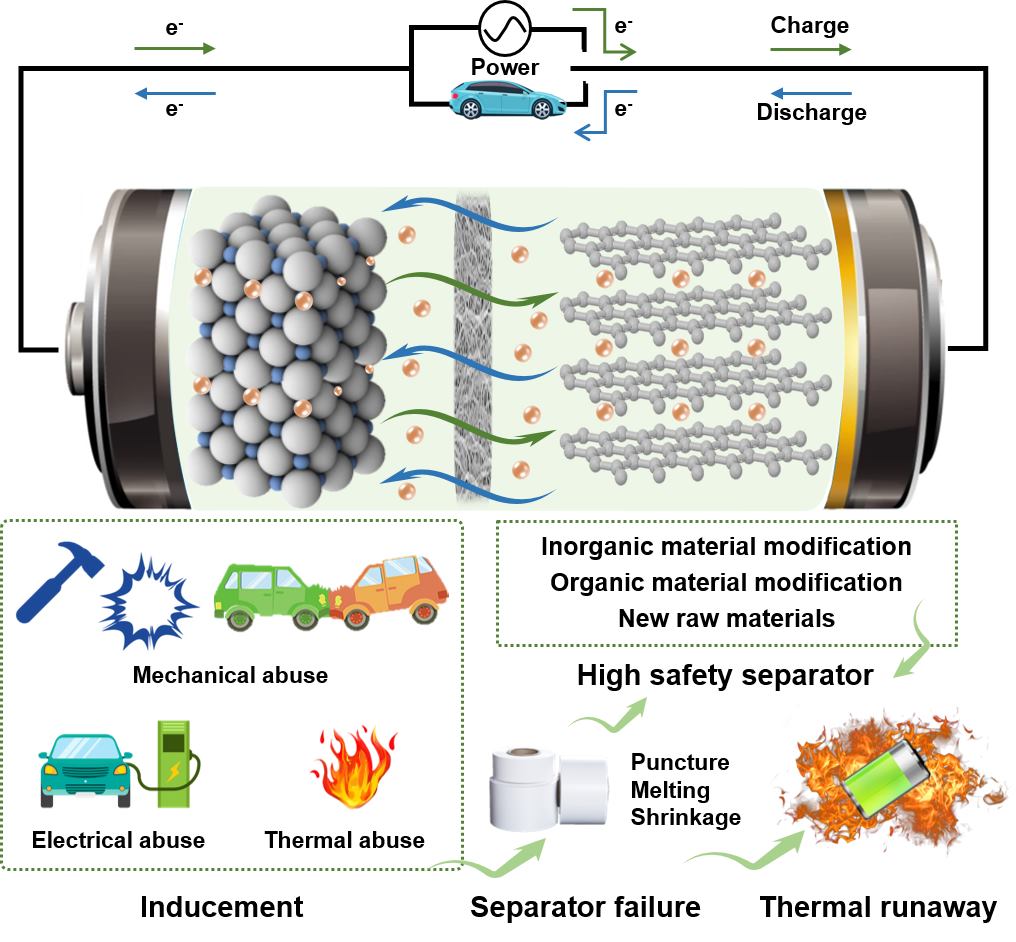
With the rapid increase in quantity and expanded application range of lithium-ion batteries, their safety problems are becoming much more prominent, and it is urgent to take corresponding safety measures to improve battery safety. Generally, the improved safety of lithium-ion battery materials will reduce the risk of thermal runaway explosion. The separator is a key component of lithium-ion batteries. It plays a crucial role in battery safety, serving as one of the most effective measures against internal short circuits.Separator failure is a direct cause of the thermal runaway and can be specifically divided into three categories: puncture, melting, and thermal shrinkage. The requirements for an ideal lithium-ion battery separator have a synergistic effect on the electrochemical performance, safety, and scalability of lithium-ion batteries. Focus on the separator, this review summaries the mechanism of separator in thermal runaway process, and reports the recent progress of high safety separator from the perspective of material preparation.
Article
02 September 2024Lithium-Rich Spinel Cathode with Higher Energy Density for Sustainable Li-Ion Batteries Operating in Extended Potential Range
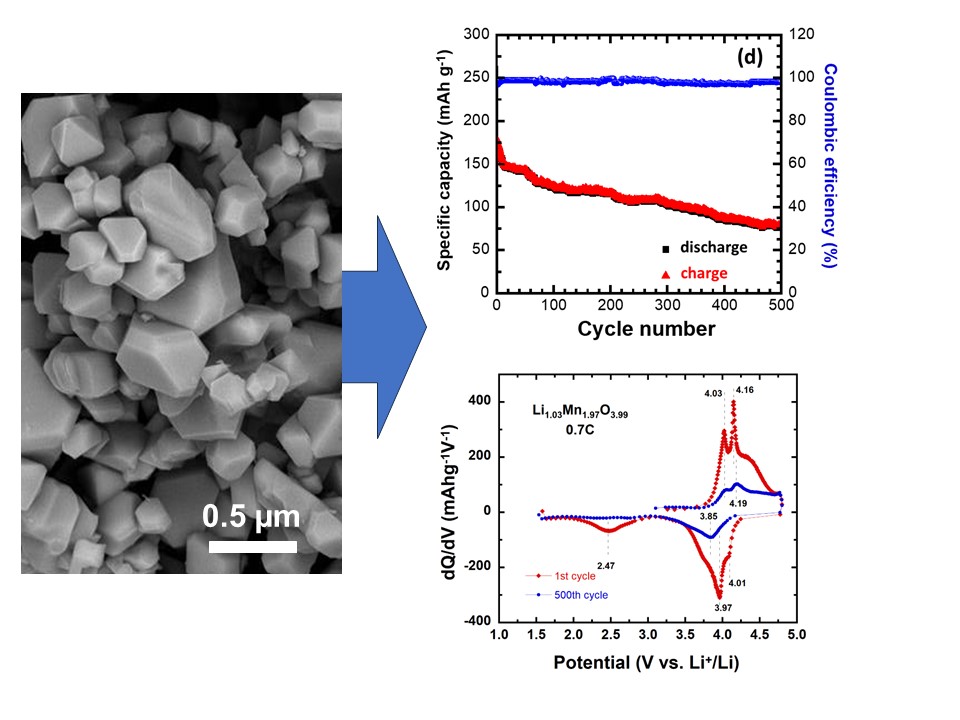
Lithium batteries pave way for rapidly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Still there are concerns associated with battery sustainability, such as the supply of key battery materials like cobalt, nickel and carbon emissions related to their manufacture. While LiMn2O4 spinel is a common cathode material for Li-ion batteries that remove Co and Ni, studies on over-stoichiometric variants and their behavior across a broad potential range may be limited. Research in this area could provide valuable insights into the performance, stability and electrochemical characteristics of such cathodes, offering potential benefits for the development and optimization of Li-ion battery technologies. This study investigates the electrochemical behavior of Li-rich Li1+yMn2−yO4−δ (LMO, y ≈ 0.03, δ ≈ 0.01) spinel as a cathode in Li-ion batteries, focusing on the phenomenon of extra capacity under the extended operating voltage 1.5–4.8 V vs. Li+/Li. The nanostructured LMO sample synthesized by sol-gel method and calcined at 900 °C is characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopy and surface area measurements. The Li-rich spinel electrode delivers a specific discharge capacity of 172 mAh g−1 at 1st cycle. It retains 123 mAh g−1 at the 100th cycle (71.5% capacity retention) at current density of 100 mA g−1 current density (i.e., ~0.7 C rate). An excellent stability is obtained in the 1.5–4.8 V potential window, with a discharge capacity of 77 mAh g−1 after 500 cycles at the same current density, owing to the reduction of the Jahn-Teller effect by Li doping. These results contrast with the specific capacity of 85 mAh g−1 (1st cycle) and the capacity retention of 54.3% after 100 cycles, obtained when the cell operates in the narrow potential range of 3.0–4.5 V.
Perspective
13 September 2023Estimate of Economic Impact of EVs Li-ion Batteries Recovery
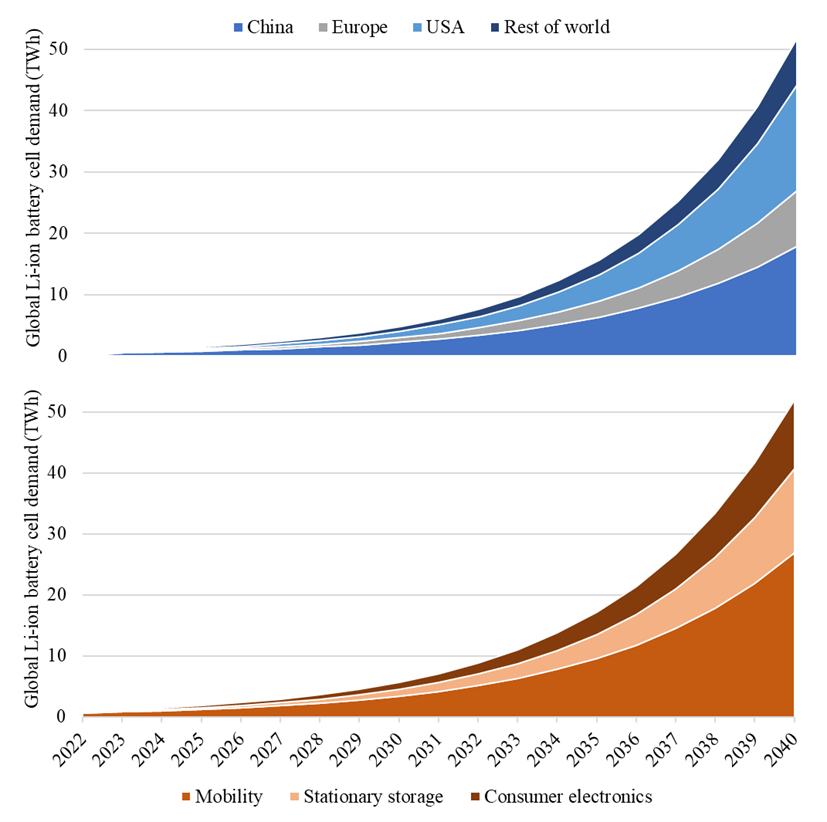
Nowadays, increasing attention is directed towards the sustainable use of raw materials. For a circular economy, recovery from spent devices represents a fundamental practice. With the transition to electric mobility, an increasing number of devices powered by lithium batteries are produced. Indeed, this is the fastest growing sector producing spent batteries, which are an important secondary source of critical raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, graphite, and nickel. Therefore, this work aims to quantify the economic impact of recovering raw materials from lithium batteries used in the electric vehicles sector. Based on the chemical composition of the various lithium batteries and their market diffusion, the intrinsic economic value of this waste has been estimated to be around 6500 €/ton. Starting from the literature data on the global energy demand from lithium batteries and deriving the trend of their specific energy over time, the mass of material introduced into the market annually is estimated to reach 60 Mton/year by 2040. The annual amount of end-of-life lithium batteries was calculated by applying the Weibull distribution to describe the probability of failure, yielding 10 Mton/year by 2040. Finally, based on these results, the economic impact of the recovery market was assessed for two different scenarios.
Article
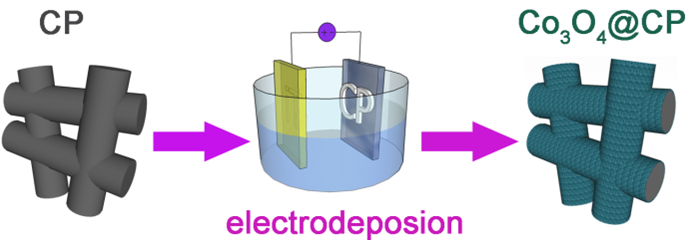
08 May 2023A High-efficiency Cathode Using Co3O4 and Carbon Paper by Electrodeposition for Rechargeable Lithium-oxygen Batteries
The conductivity, microstructure, low cost, eco-friendliness, simple and controllable preparation are key points of the preparation and application of cathode materials for lithium-oxygen batteries. Considering the above-mentioned important factors comprehensively, the Co3O4@CP electrode with a three-dimensional structure was prepared by directly growing Co3O4 on the surface of carbon paper (CP) using a simple and controllable electrodeposition method. The obtained Co3O4 depositing layer has a nanosheet microstructure and can provide abundant catalytic active sites for the oxygen evolution and reduction reactions. The network architecture of electronic transmission is constructed by CP in the cathode, promoting the efficiency of the electrode reaction. It’s worth noting that the binder-free and conductive additive-free cathode is beneficial to reduce side reactions. The lithium-oxygen battery assembled with the obtained Co3O4@CP electrode showed satisfactory electrochemical performance. The cell assembled with the obtained Co3O4@CP electrode provided a discharge specific capacity of 10954.7 mA·h·g−1 at a current density of 200 mA·g−1, and the voltage profiles of the cell were good under 100 mA·g−1 at a limited capacity of 500 mA·h g−1 based on the mass of Co3O4. Therefore, the Co3O4@CP composite material is a promising candidate with good application prospects as a cathode material for lithium-oxygen batteries.
Review
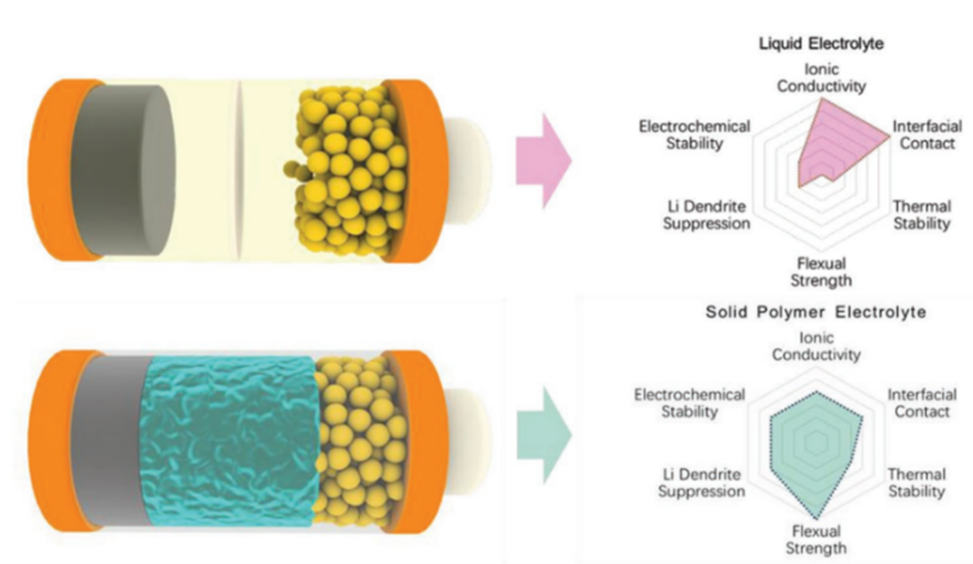
15 March 2023Ultra-Thin Solid Electrolyte in Lithium-Ion Batteries
Safety concern of lithium-ion battery, attributed to using volatile and flammable liquid electrolytes, could be addressed by using solid electrolytes. Solid electrolytes including inorganic solid electrolytes, polymer solid electrolytes and organic/inorganic composite electrolytes have the common drawbacks in low ion-conductivity. Much efforts have been devoted to increase the specific ion conductivity, especially for inorganic solid electrolyte whose intrinsic conductivity is close to liquid electrolyte. However, most solid-state electrolyte membranes in lithium-ion batteries are thick, resulting in long ion-conduction pathway, low energy density and high cost. In this review, the advantages and disadvantages of different kinds of solid electrolytes were analyzed, and the promising strategies of ultra-thin solid electrolyte preparation were summarized and prospected. Applied organic-inorganic composite, continuous phase enhancement and in situ integration have been devoted to reducing thickness of electrolyte membrane and improving battery performance. On the basis of the technical requirement of lithium-ion batteries, this review aims to provide a guidance in terms of rational design and synthesis of ultra-thin solid electrolytes for the further research that addresses the safety issues and improves cycling performance of batteries.