Found 2 results
Article
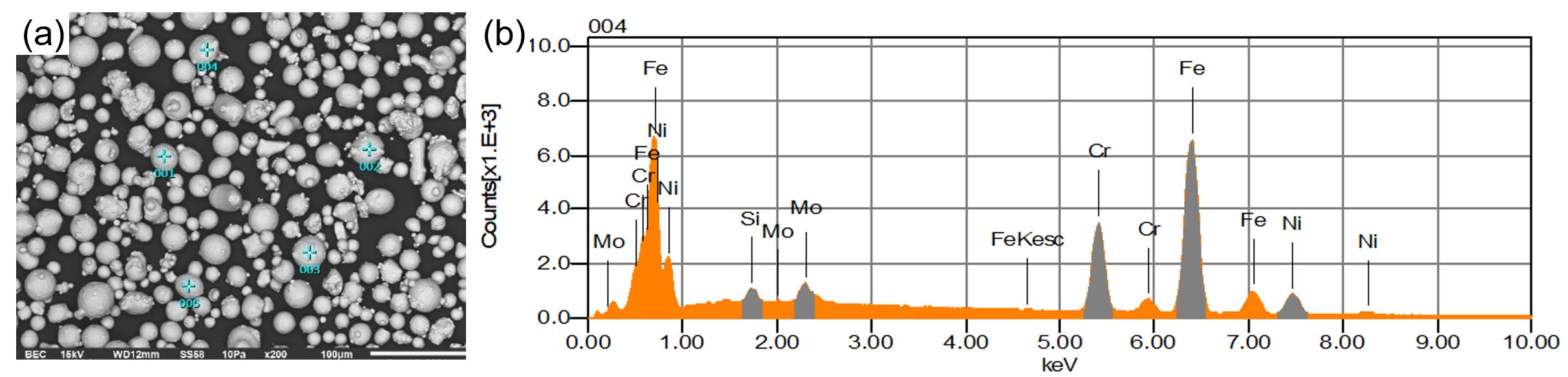
26 February 2025Life Cycle Assessment of Tensile Specimens of Stainless Steel Obtained by Additive Manufacturing versus Conventional Manufacturing
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of additive manufacturing (AM) evaluates the environmental impacts associated with each stage of the process, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. Unlike conventional manufacturing, AM offers significant advantages, such as reduced material waste, optimized designs for lightweight structures, and localized production, which can decrease transportation emissions. However, its environmental benefits are context-dependent, as energy-intensive processes like laser powder bed fusion or high reliance on specific materials can offset these gains. LCA provides a comprehensive framework to assess these trade-offs, guiding sustainable decision-making by identifying hotspots in energy use, material efficiency, and recyclability, ultimately driving innovation towards greener AM practices. This research conducted a cradle-to-gate study of a cylindrical dog-bone tensile specimen. The life-cycle inventory data were obtained from Ecoinvent for conventional manufacturing, while data from the literature review and our research were employed for laser-based powder bed fusion. The results obtained show that the additive manufacturing process is more environmentally friendly. Although the environmental impact is minor, this process consumes a large amount of energy, mainly due to the atomization process and the high laser power. Regarding the mechanical response, AM reduced the ductility but increased the yield strength and achieved the same fracture strength.
Perspective
29 January 2023Carbon Neutrality and Life Cycle Thinking
Climate change is one of the most critical sustainability challenges facing the humanity. International communities have joined forces to mitigate climate change impact and aim to achieve carbon neutrality in the coming decades. To achieve this ambitious goal, life cycle thinking can play critical roles. Specifically, life cycle thinking helps evaluate the true climate impacts to avoid shifting emissions across processes in a product life cycle. It can also help inform consumers with carbon footprint information to make climate-conscious choices. Finally, it can help identify key processes dominating the carbon footprint of a product so that future improvement can set priorities. High quality data is required for accurate and timely carbon footprint accounting and critical challenges exist to obtain and share such data.
