Found 2 results
Article
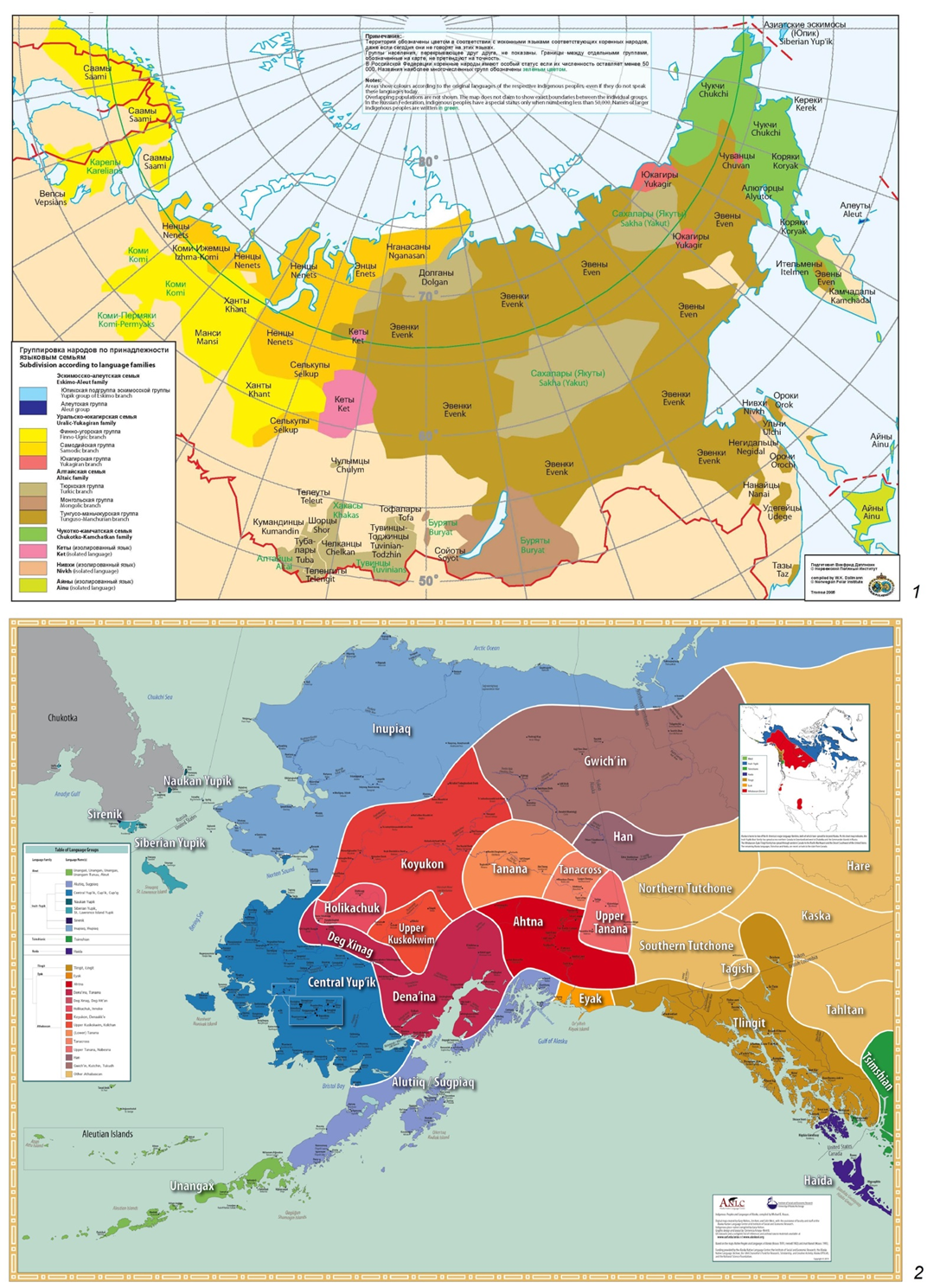
22 April 2024Paleo-Asian Cultural Phenomena of Ancient Beringia: Population Convergence and Solution of Ethnic Self-Identification
Authors offer for a discussion the materials from studies of archaic culture elements that include body modifications in ethnic groups in the context of population genetic data from native peoples of the Far North. The authors consider materials from the territory of ancient Beringia which include a part of Chukotka and Kamchatka in Russia, Alaska in the USA and several island groups in between. The working hypothesis of the study involves the identification of common and specific features of body modifications in ethnic groups having similar population genesis. This allows to clarify the specifics of the regional contacts. Body modifications (tattoos, piercings, etc.) are considered as a way of a person’s self-identification and a form of his group membership (in this case—ethnic group). The study used ethnographic, archaeological, paleo-history, folklore materials and up-to-date data that include genetic research of contemporary ethnic groups inhabiting the territory of ancient Beringia and maintaining their traditional way of life. The methodology base of the research is based on formalized approach and cross-cultural analysis evidence of the similarity/difference of the population in combination with the method of comparative analysis of DNA data and information about their genetic structure.
Article
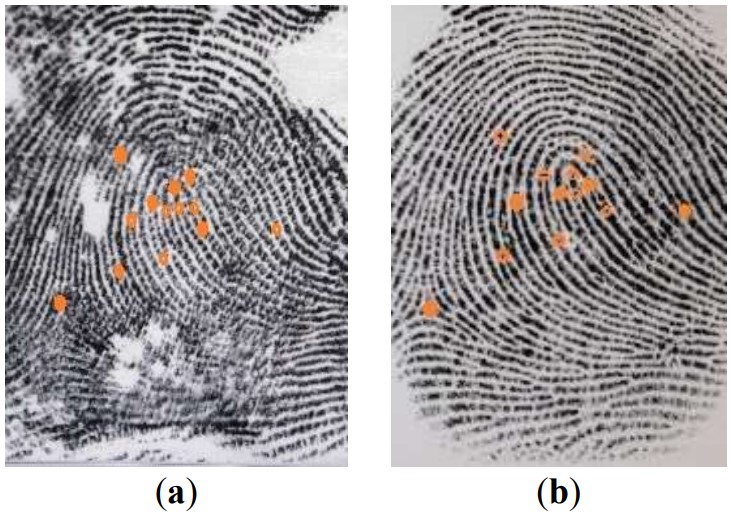
29 January 2024Determining the Identity of Corpses Using Fingerprints: Results from Practice and Analysis of Process Used in the Republic of Serbia
In today’s world, when there is a constant fight against organized crime and terrorism, when we have cases of mass accidents (plane crashes, train crashes, buses, etc.), the constant need for precise and quick identification of persons is evident in these cases. When we have situations with a large number of dead in various conditions, as well as complete or only parts of the body being on the spot, there is a need to use scientific and forensic methods in order to find out the reliable identity of these people. Furthermore, there is a need, in some cases, to identify persons who committed suicide, were killed, or died a natural death (accidental death) and who do not have documents according to which their identity can be determined. The aim of this paper will, however, be to identify a group of persons who need to be identified, known as unidentified corpses. Method. Describe and discuss the way of determining identity based on dactyloscopic data, which provides accurate and unambiguous identification, using fingerprints. Results. The identity was determined in 1271 cases of unidentified corpses by dactyloscopic comparison of fingerprints with a database containing fingerprints of about 8,000,000 indisputably identified persons. It was confirmed in 1139 cases. Conclusion. The high degree of identification in our research, as much as 89.6%, makes this method rightly represented as a standard method for confirming a person’s identity.
