Found 1 results
Article
10 May 2023Development of a New 1,2,4-butanetriol Biosynthesis Pathway in an Engineered Homoserine-producing Strain of Escherichia coli
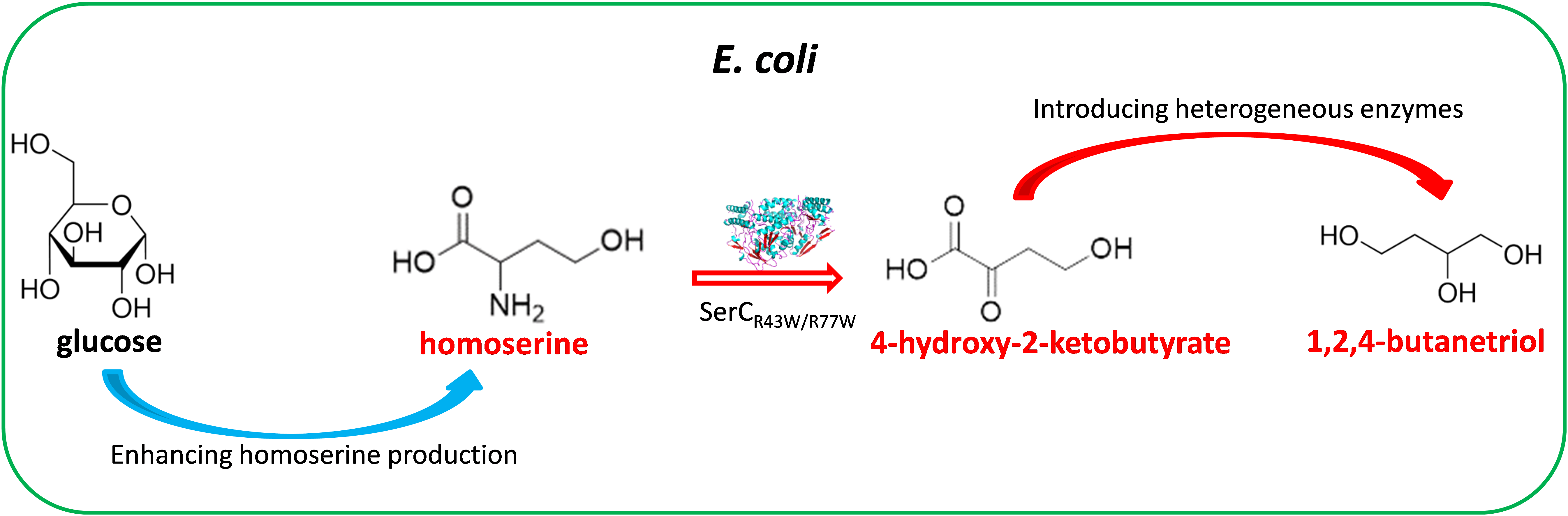
1,2,4-butanetriol (BT) is a compound of high interest with applications in pharmaceutical and materials. In this work, we designed a novel biosynthetic pathway for BT from glucose via a nonessential amino acid homoserine. This non-natural pathway used an engineered phosphoserine transaminase (SerCR42W/R77W) to achieve the deamination of homoserine to 4-hydroxy-2-oxobutanoic acid (HOBA). Three consecutive enzymes including a lactate dehydrogenase, a 4-hydroxybutyrate CoA-transferase and a bifunctional aldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase are used to catalyze HOBA to BT. To enhance the carbon flux to homoserine, a homoserine-producing Escherichia coli was developed by improving the overexpression of two relevant key genes metL and lysC (V339A). The simultaneous overexpression of the genes encoding these enzymes for the homoserine-derived BT pathway enabled production of 19.6 mg/L BT from glucose in the homoserine-producing E. coli.