Found 2 results
Open Access
Article
05 June 2024An Architecture for Early Wildfire Detection and Spread Estimation Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, Base Stations, and Space Assets
This paper presents, an autonomous and scalable monitoring system for early detection and spread estimation of wildfires by leveraging low-cost UAVs, satellite data and ground sensors. An array of ground sensors, such as fixed towers equipped with infrared cameras and IoT sensors strategically placed in areas with a high probability of wildfire, will work in tandem with the space domain as well as the air domain to generate an accurate and comprehensive flow of information. This system-of-systems approach aims to take advantage of the key benefits across all systems while ensuring seamless cooperation. Having scalability and effectiveness in mind, the system is designed to work with low-cost COTS UAVs that leverage infrared and RGB sensors which will act as the primary situational awareness generator on demand. AI task allocation algorithms and swarming-oriented area coverage methods are at the heart of the system, effectively managing the aerial assets High-level mission planning takes place in the GCS, where information from all sensors is gathered and compiled into a user-understandable schema. In addition, the GCS issues warnings for events such as the detection of fire and hardware failures, live video feed and lower-level control of the swarm and IoT sensors when requested. By performing intelligent sensor fusion, this solution will offer unparalleled reaction times to wildfires while also being resilient and reconfigurable should any hardware failures arise by incorporating state of the art swarming capabilities.
Open Access
Article
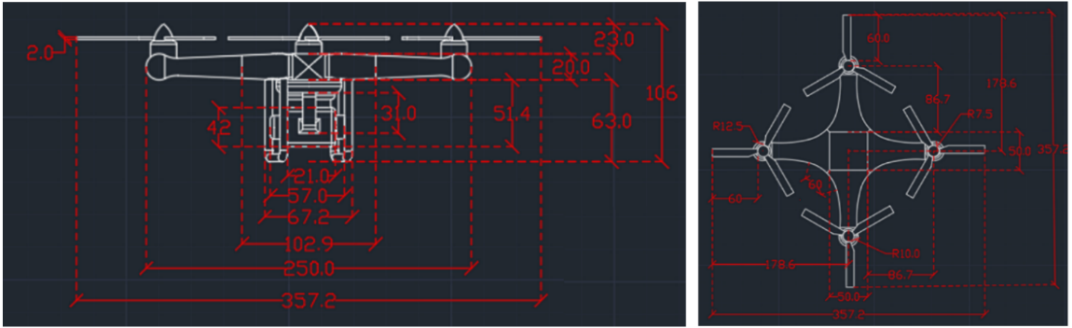
19 March 2024Designing a Quadcopter for Fire and Temperature Detection with an Infrared Camera and PIR Sensor
In agriculture, medicine, and engineering, sudden fire outbreaks are prevalent. During such events, the ensuing fire spread is extensive and unpredictable, necessitating crucial data for effective response and control. To address this need, the current initiative focuses on utilizing an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) with an Infrared (IR) sensor. This sensor detects and analyses temperature variations, accompanied by additional camera footage capturing thermal images to pinpoint the locations of the incidents precisely. The UAV’s programming is executed using Arduino-Nano and mission planner software, interfacing with the Pixhawk flight controller operating in a guided mode for autonomous navigation. The UAV configuration includes a radio module interfacing with Arduino-Nano, a flight controller, and remote-control functionality. The flight duration is approximately 10–15 min, contingent upon flight dynamics and environmental temperature. Throughout its airborne operation, the UAV transmits live telemetry and log feeds to the connected computer, displaying critical parameters such as altitude, temperature, battery status, vertical speed, and distance from the operator. The Pixhawk flight controller is specifically programmed to govern the UAV’s behavior, issuing warnings to the pilot in case of low voltage, prompting a timely landing to avert potential crashes. In case of in-flight instability or a crash, the mission planner can trace the UAV’s location, facilitating efficient recovery and minimizing costs and component availability losses. This integrated approach enhances situational awareness and mitigation strategies, offering a comprehensive solution for managing fire incidents in diverse fields.